In Silico Study of Mangrove Triterpenoids as SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protein Preparation
2.2. Ligand Preparation
2.3. Molecular Docking
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Phytochemicals
3.2. Molecular Docking of Selected Compounds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malik, Y.S.; Sircar, S.; Bhat, S.; Sharun, K.; Dhama, K.; Dadar, M.; Tiwari, R.; Chaicumpa, W. Emerging novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV)—Current scenario, evolutionary perspective based on genome analysis and recent developments. Vet. Q. 2020, 40, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.I.; Hsueh, P.R. Emerging threats from zoonotic coronaviruses-from SARS and MERS to 2019-nCoV. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Morales, A.J.; MacGregor, K.; Kanagarajah, S.; Patel, D.; Schlagenhauf, P. Going global–Travel and the 2019 novel coronavirus. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 33, 101578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerriero, G.; Berni, R.; Muñoz-Sanchez, J.A.; Apone, F.; Abdel-Salam, E.M.; Qahtan, A.A.; Alatar, A.A.; Cantini, C.; Cai, G.; Hausman, J.F.; et al. Production of plant secondary metabolites: Examples, tips and suggestions for biotechnologists. Genes 2018, 9, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Wen, K.S.; Ruan, X.; Zhao, Y.X.; Wei, F.; Wang, Q. Response of plant secondary metabolites to environmental factors. Molecules 2018, 23, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thayil, S.M.; Thyagarajan, S.P. Pa-9: A flavonoid extracted from plectranthus amboinicus inhibits HIV-1 protease. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2016, 8, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Yan, Z.; You, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Lin, G. Mangroves: Obligate or facultative halophytes? A review. Trees 2011, 25, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishayee, A.; Ahmed, S.; Brankov, N.; Perloff, M. Triterpenoids as potential agents for the chemoprevention and therapy of breast cancer. Front. Biosci. A J. Virtual Libr. 2011, 16, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosidi, A.; Khomsan, A.; Setiawan, B.; Riyadi, H.; Briawan, D. Antioxidant potential of temulawak (Curcuma xanthorrhiza roxb). Pak. J. Nutr. 2016, 15, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, B.G.; Santos, M.S.; Ferrarini, M.; Fernandes, J.P.S. Evaluation of blockbuster drugs under the rule-of-five. Die Pharm. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 65, 148–152. [Google Scholar]
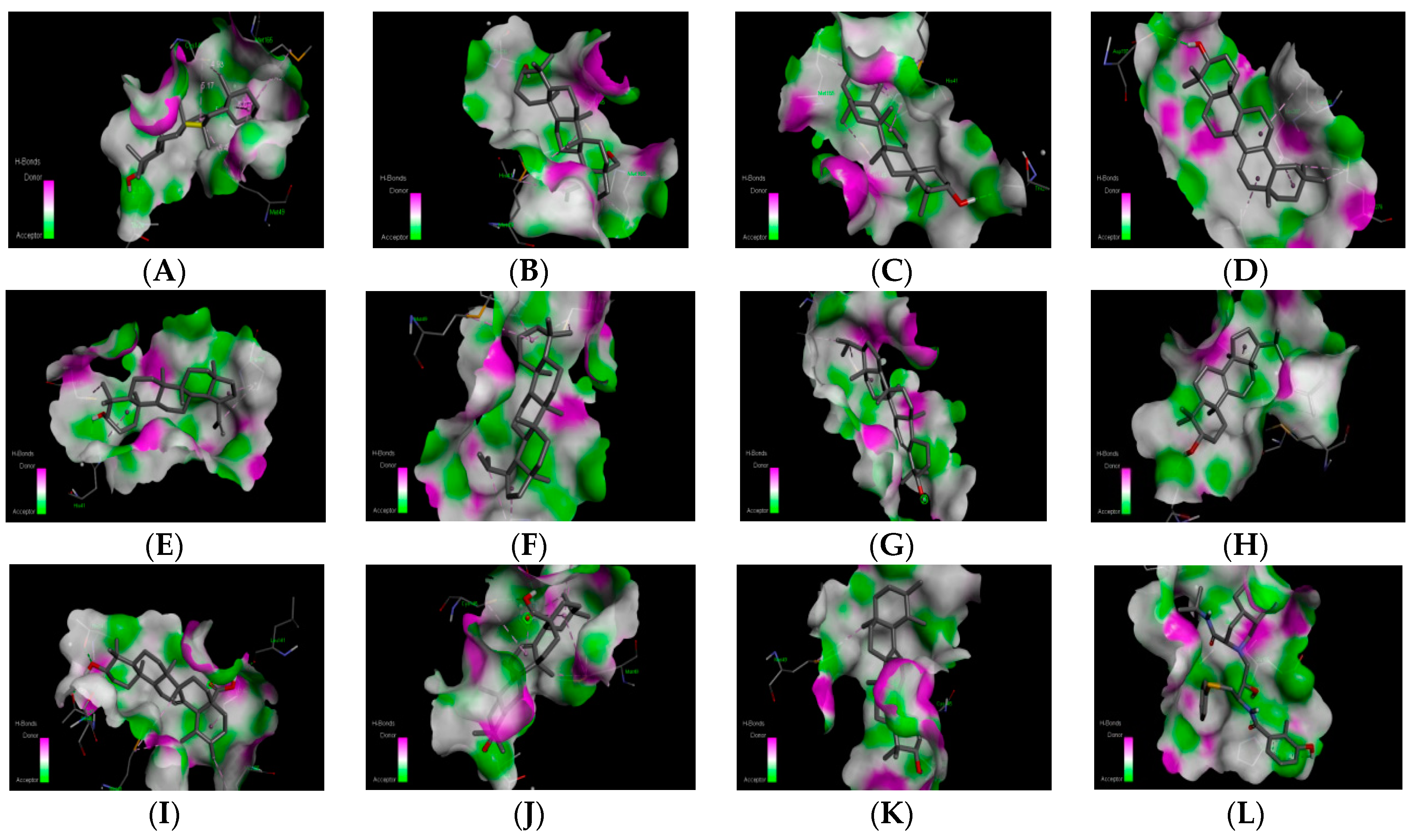
| S. No. | Compound Name | Molecular Formula | Molecular Structure and Interaction with 6LU7 | Lipinski’s Rule of Five | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Properties | Value | ||||
| 1. | Nelfinavir | C32H45N3O4S | 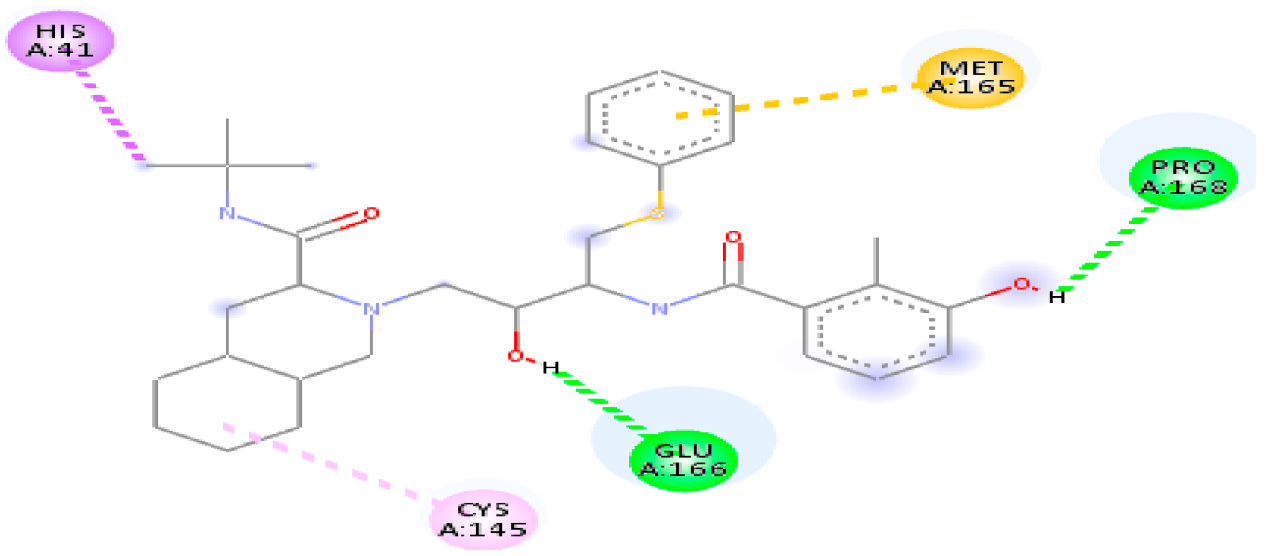 | Molecular weight (<500 Da) | 567.78 g/mol |
| LogP (<5) | 4.33 | ||||
| H-Bond donor (5) | 4 | ||||
| H-bond acceptor (<10) | 5 | ||||
| Violation | 1 | ||||
| 2. | beta-Amyrin | C30H50O |  | Molecular weight (<500 Da) | 426.72 g/mol |
| LogP (<5) | 4.63 | ||||
| H-Bond donor (5) | 1 | ||||
| H-bond acceptor (<10) | 1 | ||||
| Violation | 1 | ||||
| 3. | Betulin | C30H50O2 | 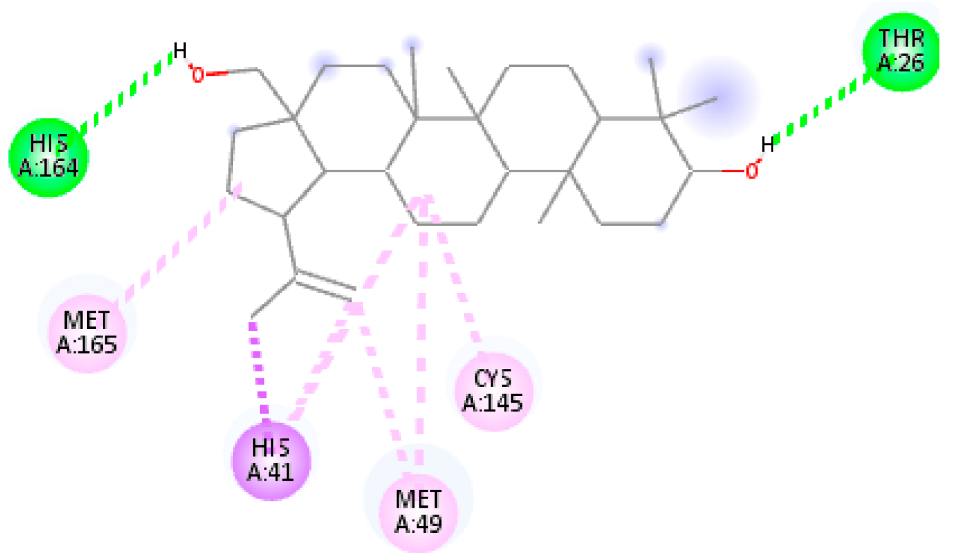 | Molecular weight (<500 Da) | 442.72 g/mol |
| LogP (<5) | 4.47 | ||||
| H-Bond donor (5) | 2 | ||||
| H-bond acceptor (<10) | 2 | ||||
| Violation | 1 | ||||
| 4. | Germanicol | C30H50O |  | Molecular weight (<500 Da) | 426.72 g/mol |
| LogP (<5) | 5.04 | ||||
| H-Bond donor (5) | 1 | ||||
| H-bond acceptor (<10) | 1 | ||||
| Violation | 1 | ||||
| 5. | Taraxerol | C30H50O | 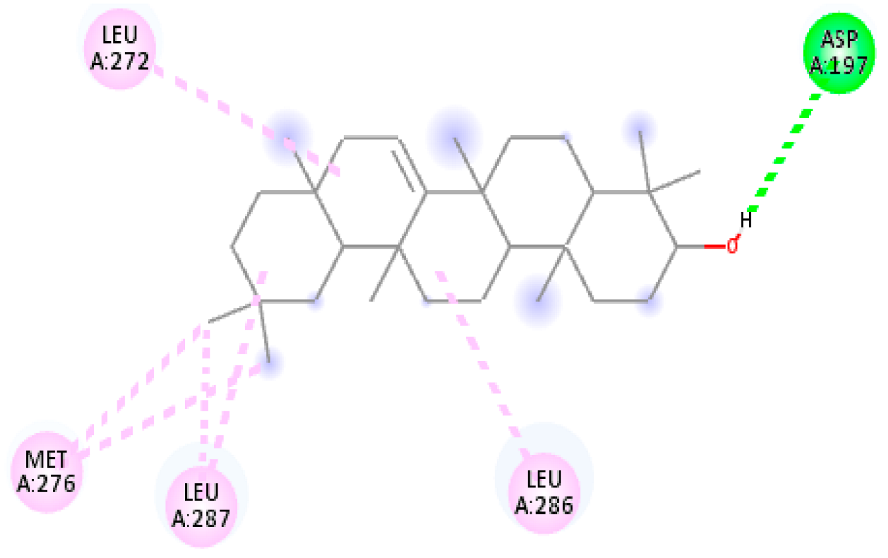 | Molecular weight (<500 Da) | 426.72 g/mol |
| LogP (<5) | 4.73 | ||||
| H-Bond donor (5) | 1 | ||||
| H-bond acceptor (<10) | 1 | ||||
| Violation | 1 | ||||
| 6. | Lupeol | C30H50O | 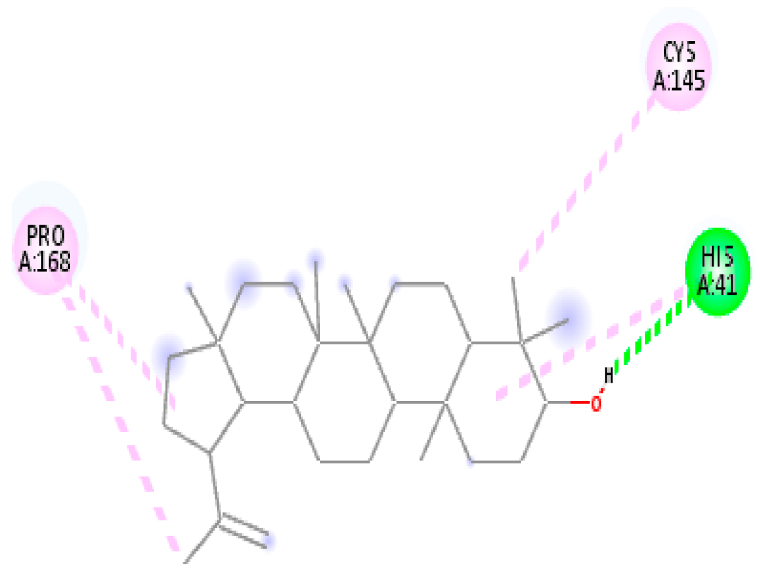 | Molecular weight (<500 Da) | 426.72 g/mol |
| LogP (<5) | 4.63 | ||||
| H-Bond donor (5) | 1 | ||||
| H-bond acceptor (<10) | 1 | ||||
| Violation | 1 | ||||
| 7. | Lupane | C30H52 | 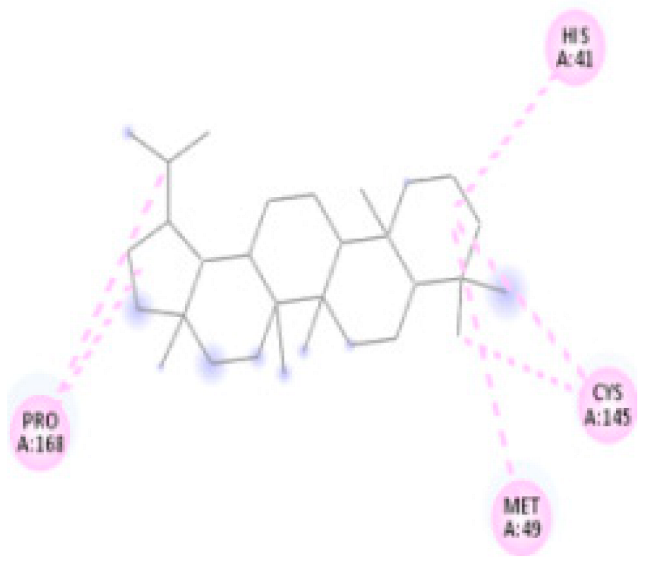 | Molecular weight (<500 Da) | 426.72 g/mol |
| LogP (<5) | 4.63 | ||||
| H-Bond donor (5) | 1 | ||||
| H-bond acceptor (<10) | 1 | ||||
| Violation | 1 | ||||
| 8. | Simiarenol | C30H50O |  | Molecular weight (<500 Da) | 426.72 g/mol |
| LogP (<5) | 4.63 | ||||
| H-Bond donor (5) | 1 | ||||
| H-bond acceptor (<10) | 1 | ||||
| Violation | 1 | ||||
| 9. | Tirucallol | C30H50O | 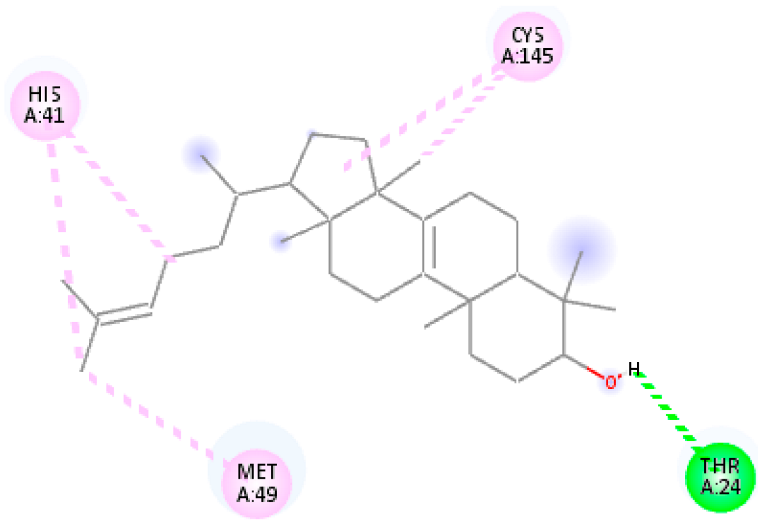 | Molecular weight (<500 Da) | 426.72 g/mol |
| LogP (<5) | 5.14 | ||||
| H-Bond donor (5) | 1 | ||||
| H-bond acceptor (<10) | 1 | ||||
| Violation | 1 | ||||
| 10. | Ursolic acid | C30H48O3 | 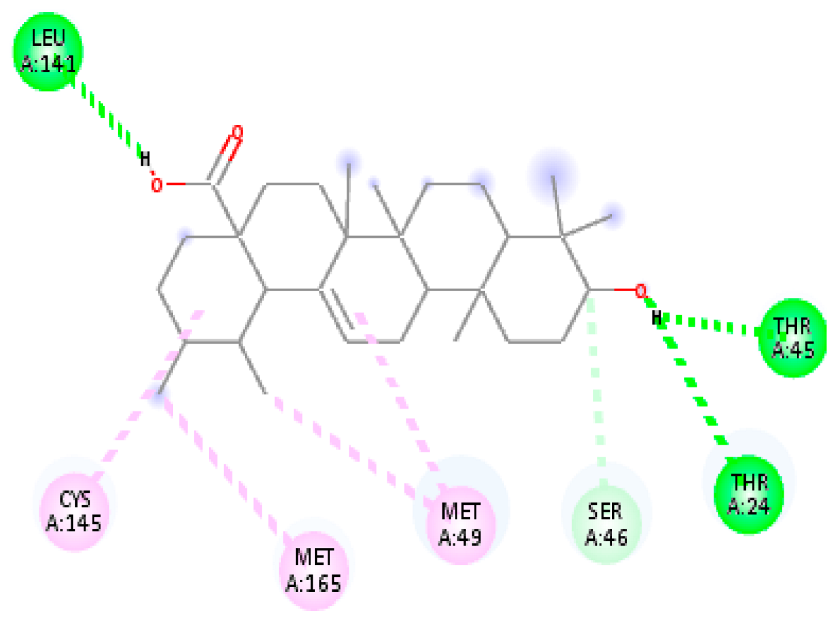 | Molecular weight (<500 Da) | 456.70 g/mol |
| LogP (<5) | 5.82 | ||||
| H-Bond donor (5) | 1 | ||||
| H-bond acceptor (<10) | 1 | ||||
| Violation | 1 | ||||
| 11. | Oleanolic acid | C30H48O3 | 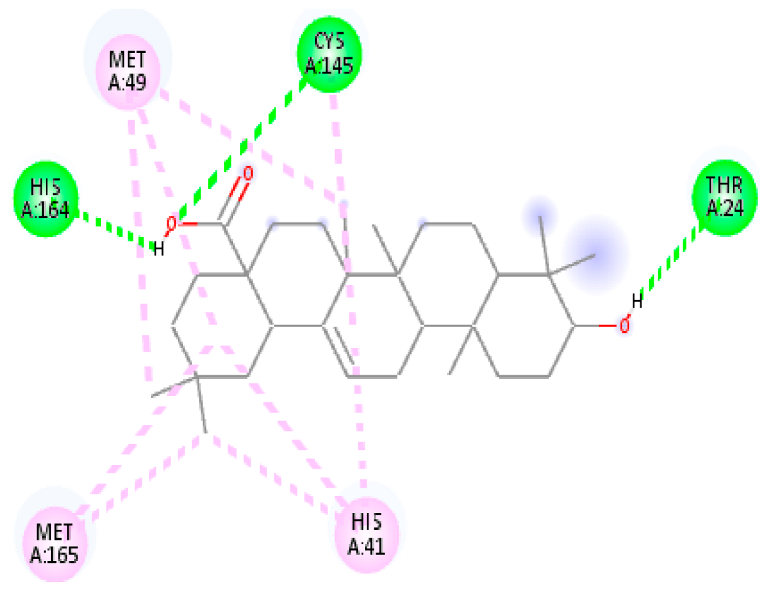 | Molecular weight (<500 Da) | 456.70 g/mol |
| LogP (<5) | 5.82 | ||||
| H-Bond donor (5) | 1 | ||||
| H-bond acceptor (<10) | 1 | ||||
| Violation | 1 | ||||
| 12. | alpha-Amyrin | C30H50O | 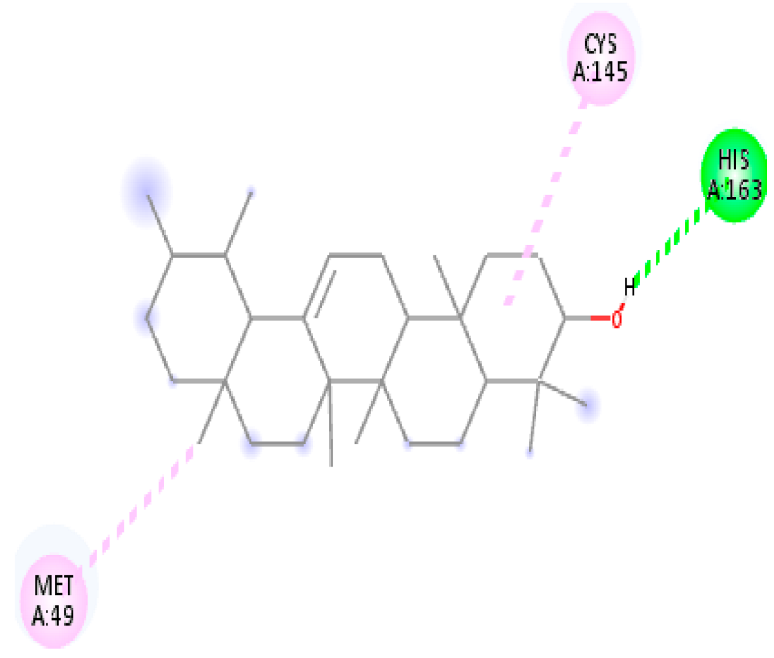 | Molecular weight (<500 Da) | 426.72 g/mol |
| LogP (<5) | 6.92 | ||||
| H-Bond donor (5) | 1 | ||||
| H-bond acceptor (<10) | 1 | ||||
| Violation | 1 | ||||
| Protein | Ligand | Lowest Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Ligand Efficiency | Inhibition Constant | Intermolecular Energy (kcal/mol) | VDW-H Bond Desolvation Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6lu7 | Nelfinavir | −6.21 | −9.709 | 27.83 uM | −9.79 | −9.77 |
| beta-Amyrin | −8.08 | −4.445 | 1.20 µM | −8.37 | −8.33 | |
| Betulin | −7.54 | −6.161 | 2.96 µM | −8.73 | −8.70 | |
| Germanicol | −7.76 | −4.229 | 2.04 µM | −8.06 | −8.02 | |
| Taraxerol | −7.41 | −25.601 | 3.68 µM | −7.71 | −7.43 | |
| Lupeol | −7.73 | −10.786 | 2.17 µM | −8.32 | −8.31 | |
| Lupane | −8.19 | −9.698 | 996.23 nM | −8.49 | −8.48 | |
| Simiarenol | −7.56 | −10.006 | 2.87 µM | −8.16 | −8.15 | |
| Tirucallol | −8.99 | −4.998 | 255.21 nM | −10.49 | −10.46 | |
| Ursolic acid | −9.24 | −3.784 | 168.90 nM | −10.13 | −10.05 | |
| Oleanolic acid | −8.87 | −5.134 | 314.36 nM | −9.77 | −9.69 | |
| alpha-Amyrin | −8.89 | −11.721 | 306.52 nM | −9.18 | −9.14 |
| Compounds | Species Name | Parts | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| beta-Amyrin | Rhizophora mucronata | Bark | Rohini, R.M et al., 2009 |
| Betulin | Rhizophora mucronata | Leaf | Ghosh A et al., 1985 |
| Germanicol | Rhizophora sp. | Leaf | Koch, B.P et al., 2003 |
| Taraxerol | Avicennia marina | Root | Mahera, S.A et al., 2011 |
| Lupeol | Rhizophora mucronata | Bark | Rohini, R.M et al., 2009 |
| Lupane | Ceriops decandra | Leaf | Ponglimanont, C. and Thongdeeying, P., 2005 |
| Simiarenol | Rhizophora mucronata | Bark | Rohini, R.M et al., 2009 |
| Tirucallol | Excoecaria agallocha | Leaf | Zou, J.H et al., 2006 |
| Ursolic acid | Brugurera gymnorhiza | Leaf | Ghosh, A et al., 1985 |
| Oleanolic acid | Acanthus ilicifolius | Leaf | Ghosh, A et al., 1985 |
| alpha-Amyrin | Ceriops decandra | Leaf | Ghosh, A et al., 1985 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Purushothaman, R.; Vishnuram, G.; Ramanathan, T. In Silico Study of Mangrove Triterpenoids as SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors. Med. Sci. Forum 2023, 21, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECB2023-14332
Purushothaman R, Vishnuram G, Ramanathan T. In Silico Study of Mangrove Triterpenoids as SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors. Medical Sciences Forum. 2023; 21(1):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECB2023-14332
Chicago/Turabian StylePurushothaman, Ramamoorthy, Ganapathy Vishnuram, and Thirugnanasambandam Ramanathan. 2023. "In Silico Study of Mangrove Triterpenoids as SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors" Medical Sciences Forum 21, no. 1: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECB2023-14332
APA StylePurushothaman, R., Vishnuram, G., & Ramanathan, T. (2023). In Silico Study of Mangrove Triterpenoids as SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors. Medical Sciences Forum, 21(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECB2023-14332






