Onshore Wind Power Generation and Sustainability Challenges in Northeast Brazil: A Quick Scoping Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
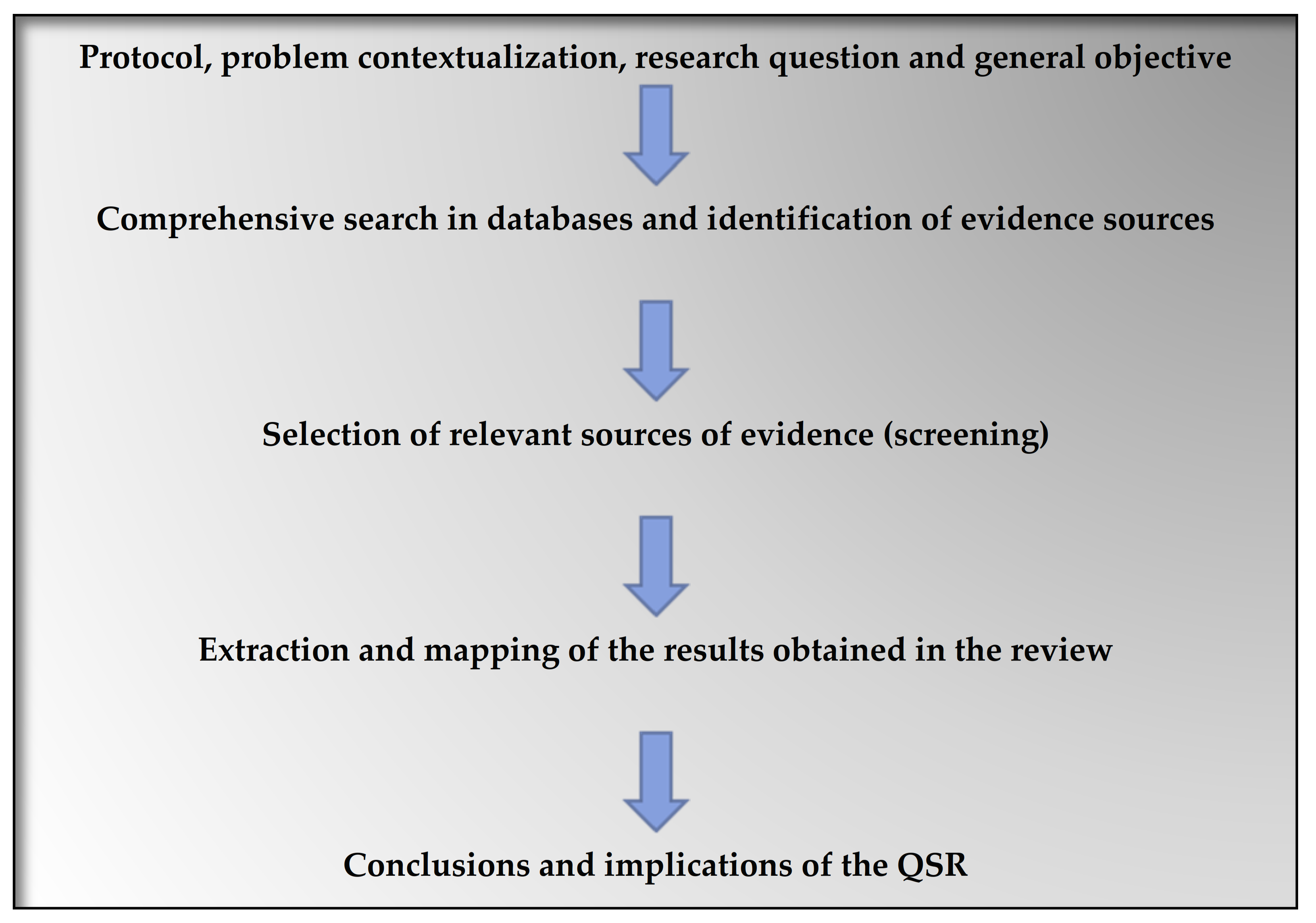
2. Materials and Methods
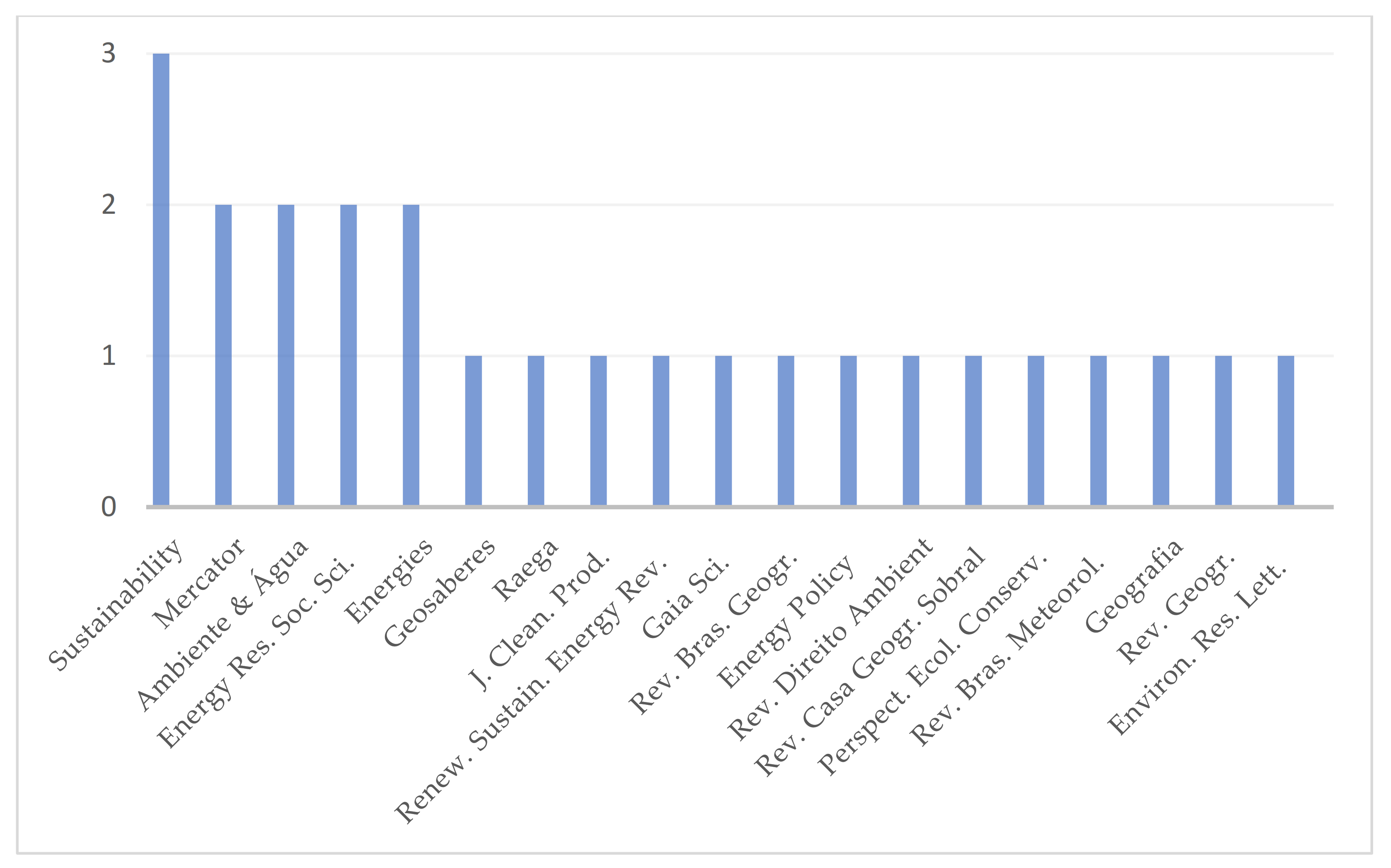
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Title | Authors | Year of Publication | Citations GS | General Purpose of the Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paths to participatory resource management of renewable energy sources (wind farms) in Northeast Brazil | Adryane Gorayeb; Christian Brannstrom | 2016 | 23 | Review deployment policies of the wind power matrix in Brazil, focusing on the Northeast region, with the aim of pointing out ways to a better planning of this activity, considering the problems linked to the implementation of enterprises in Ceará, responsible for a large part of the environmental and social impacts of traditional coastal communities today. |
| Participatory diagnosis and social cartography applied to impact studies of wind farms on the coast of Ceará: the case of Xavier beach, Camocim | Jocicléa de Sousa Mendes; Adryane Gorayeb; Christian Brannstrom | 2016 | 30 | To analyze, through participatory methodologies, the problems established with the implementation of one of the largest wind energy production centers in Ceará, in Xavier beach community, located in Camocim, Ceará, Brazil. |
| Comparative analysis of wind energy deployment policies and social outcomes in Ceará (Brazil) and Texas (USA) | Caroline Vitor Loureiro; Adryane Gorayeb; Christian Brannstrom | 2017 | 10 | To make a comparison between the region of Nolan County in West Texas (United States) and the west coast of Ceará (Brazil), as a way of qualifying the direct and indirect impacts on the social environment, resulting from the installation of this activity, and to reflect on its real degree of socio-political sustainability. |
| Sustainable development: case study in the implementation of renewable energy in Brazil | Mario Orestes Aguirre Gonzalez; Joeberson S. Gonçalves; Rafael M. Vasconcelos | 2017 | 65 | Propose a set of guidelines and best practices to public managers, public authorities and wind farm owners about the perspectives of communities’ sustainability. |
| Is Brazilian wind power development sustainable? Insights from a review of conflicts in Ceará state | Christian Brannstrom; Adryane Gorayeb; Jocicléa de Sousa Mendes; Caroline Loureiro; Antonio Jeovah de Andrade Meireles; Edson Vicente da Silva; Ana Larissa Ribeiro de Freitas; Rafael Fialho de Oliveira | 2017 | 82 | To analyze the development of Brazilian wind energy and its sustainability through a review of conflicts in the state of Ceará |
| The Brazilian wind energy market, social and environmental impacts | Lucía Iracema Chipponelli Pinto1; Fernando Ramos Martins; Enio Bueno Pereira | 2017 | 34 | Promote the dissemination of acquired knowledge and instigate curiosity for new issues that can provide sustainability for the expansion of electricity generation from wind energy in Brazil. |
| Perception of the socio-environmental impacts resulting from the implementation of the Delta do Parnaíba wind farm | Maria Bernadete de Carvalho Bezerra; Dênis Barros de Carvalho; Wilza Gomes Reis Lopes; Teresinha de Jesus dos Santos Sousa; Francisco das Chagas Vieira Santos; Anderson Guzzi | 2017 | 4 | To analyze the perception of the community of Pedra do Sal on the socio-environmental impacts resulting from the implementation of the Delta do Parnaíba wind farm |
| Geographical perspectives in the transformations of the Brazilian coast by wind energy | Christian Brannstrom; Adryane Gorayeb; Wallason Farias de Souza; Nicolly Santos Leite; Leilane Oliveira Chaves; Rodrigo Guimarães; Dweynny Rodrigues Filgueira Gê | 2018 | 12 | Synthesize the socio-environmental impacts of wind energy on the Brazilian coast, identify the main causes for the negative and positive experiences and understand the main knowledge gaps to be deepened by future research. |
| Wind power gone bad: Critiquing wind power planning processes in northeastern Brazil | Adryane Gorayeb; Christian Brannstrom; Antonio Jeovah de Andrade Meireles; Jocicléa de Sousa Mendes | 2018 | 49 | To analyze wind energy planning processes in Northeast Brazil, emphasizing the negative impacts of a wind farm in the state of Ceará, Brazil. |
| Procedural and distributive justice inform subjectivity regarding wind power: a case from Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil | Cláudio Albuquerque Fratea; Christian Brannstromb; Marcus Vinícius Girão de Morais; Armando de Azevedo Caldeira-Piresc | 2019 | 19 | To analyze views on distributive and procedural justice of wind farms among community residents, municipal officials and wind energy investors in Brazil, focusing on the case of a controversial wind farm built next to a fishing and tourism park. dependent community, Galinhos, in Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil’s main wind power state. |
| The implementation of wind farms and the socio-environmental impacts on indigenous and traditional populations | Márcia Dieguez Leuzinger; Gabriel Leuzinger Coutinho | 2019 | – | Analyze the socio-environmental impacts related to the construction and operation of wind farms; evaluate the effects of installing these parks in areas occupied by indigenous or traditional populations or close to them; examine whether and how these groups are protected from these impacts by the regulations in force. |
| Analysis of coastal morphodynamics and socio-environmental impacts of large coastal developments: case study, Volta do Rio beach, Acaraú-CE | Otávio Augusto de Oliveira Lima Barra; Fábio Perdigão Vasconcelos; Danilo Vieira dos Santos; Adely Pereira Silveira | 2019 | – | Analyze coastal morphodynamics and socio-environmental impacts of large coastal developments: case study, Volta do Rio beach, Acaraú-CE |
| Analysis of the Levels of Alteration of Aquifers Caused by the Installation of Wind Farms on Dunes on the Coast of Ceará, Brazil | Maria da Conceição Rabelo Gomes; Adryane Gorayeb; Dimas de Brito Souza; Raquel Morais Silva | 2019 | 1 | Assess the levels of change in aquifers from the installation of wind farms on dunes on the coast of Ceará using the GOD and POSH vulnerability methods, groundwater flow and application of multivariate analysis to support the monitoring of groundwater quality in the area. |
| Green versus green? Adverting potential conflicts between wind power generation and biodiversity conservation in Brazil | Marlon Neri; Davi Jameli; Enrico Bernard; Felipe P.L. Melo | 2019 | 18 | Alert on potential conflicts between wind power generation and biodiversity conservation in Brazil. |
| Socioeconomic, environmental and technological impacts caused by the installation of wind farms in Ceará | Mônica Antonizia de Sales Costa; Monilson de Sales Costa; Maria Monizia de Sales Costa; Marcos Antônio Tavares Lira | 2019 | 3 | Present the environmental, social, economic and technological impacts originated with the implementation and operation of the Wind Power Plants in the coast of Ceará through the comparative analysis between the Beberibe and Fleixeiras I wind farms. |
| Wind power on the Brazilian Northeast Coast, from the whiff of hope to turbulent convergence: the case of the Galinhos Wind Farms | Eduardo Janser de Azevedo Dantas; Luiz Pinguelli Rosa; Neilton Fidelis da Silva; Marcio Giannini Pereira | 2019 | 8 | To assess how the arrival of wind power dialogues with the demands of the communities living in the projects’ vicinities, as well as repercussions on institutional, socioeconomic and environmental developments. |
| Chapada do Piauí I wind farm: social benefits and environmental impacts in the municipality of Marcolândia, State of Piauí | Jaerle Rodrigues Câmpelo; Emanuel Lindemberg Silva Albuquerque; José Maria Marques de Melo Filho | 2020 | – | To analyze, in an integrated way, the socio-environmental impacts arising from the implementation of the Chapada do Piauí I Wind Complex, in communities located in the municipality of Marcolândia, with a view to correlating the advantages of wind energy generation with the environmental and social conflicts that are identified and materialized in loco. |
| Connections between wind energy, poverty and social sustainability in Brazil’s Semiarid | Maria Luiza de Medeiros Galvão; Marco Aurélio dos Santos; Neilton Fidelis da Silva; Valdenildo Pedro da Silva | 2020 | 6 | To understand the connections between the implementation of wind farms as sustainability promoters and the permanence of poverty levels. |
| Environmental licensing and social opposition to energy wind power: a case study focusing on the social gap in Coastal community of Ceará, Brazil | Adryane Gorayeb; Christian Brannstrom | 2020 | – | To analyze the flaws in the environmental licensing process that allowed the installation of the wind farm in Praia de Xavier, as well as the consequences of the mitigation efforts, which resulted in wear and internal conflicts that affected the community at various levels. |
| Sustainability challenges of wind power deployment in Coastal Ceará State, Brazil | Júlio César Holanda Araújo; Wallason Farias de Souza; Antonio Jeovah de Andrade Meireles; Christian Brannstrom | 2020 | 3 | To better understand the licensing materials for wind farms and the content of the host communities’ concerns about wind farms. We analyzed 18 “simplified” environmental impact reports, which created a legal path for wind farm construction, and conducted qualitative interviews in host communities in coastal Ceará state in northeastern Brazil. |
| Land use and occupation of agricultural areas with wind energy | Manoel Fortunato Sobrinho Júnior; Elis Regina Costa de Morais; Paulo César Moura da Silva | 2020 | 1 | Analyze changes in land use and occupation of agricultural areas exploited by wind energy, identify the potential of these agricultural areas for the construction of wind farms and verify the conciliation between wind and agricultural activity. |
| Bigger is not always better: review of small wind in Brazil | Fábio Ricardo Procópio de Araújo; Marcio Giannini Pereira; Marcos Aurélio Vasconcelos Freitas; Neilton Fidelis da Silva; Eduardo Janser de Azevedo Dantas | 2021 | 2 | At evaluating the current situation of the wind energy market for SmallWind Turbines in Brazil (SWT) and its future perspectives, identifying the main characteristics of the sector, its challenges, and opportunities |
| Land-use impacts of Brazilian wind power expansion | Olga Turkovska; Gabriel Castro, Michael Klingler; Felix Nitsch, Peter Regner; Aline Cristina Soterroni; Johannes Schmidt | 2021 | 12 | To analyze the land use impacts of the expansion of Brazilian wind energy in four federal states: Bahia, Ceará, Rio Grande do Norte and Rio Grande do Sul, which cover 80% of the total installed capacity. |
| Perception of environmental impacts ofwind farms in agricultural areas of Northeast Brazil | Manoel Fortunato Sobrinho Junior; Maria Carolina Ramirez Hernandez; Sthenia Santos Albano Amora; Elis Regina Costa de Morais | 2022 | – | To analyze, through the perception of the inhabitants of the agricultural areas of Serra do Mel-RN, which basically had their economy and customs linked to subsistence agriculture, the environmental impacts caused by the installation and operation of wind farms. |
| What explains the community acceptance of wind energy? Exploring benefits, consultation, and livelihoods in coastal Brazil | Christian Brannstrom; Nicolly Santos Leite; Anna Lavoie; Adryane Gorayeb | 2022 | - | To analyze the levels of acceptance of wind energy by host communities, exploring benefits, consultations and livelihoods on the coast of Ceará, Brazil. |
References
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). 10 Years, Progress to Action. Available online: https://irena.org/publications/2020/Jan/ (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Renewable Capacity Statistics 2019. Available online: https://www.irena.org/publications/2019/Mar/Renewable-Capacity-Statistics-2019 (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- Associação Brasileira de Energia Eólica (ABEEólica). Energia Eólica Ultrapassa 20 GW de Capacidade Instalada No Brasil. Available online: http://abeeolica.org.br/noticias/energia-eolica-ultrapassa-20-gw-de-capacidade-instalada-no-brasil/ (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- Agência Nacional de Energia Elétrica (ANEEL). Brasil Termina 2021 com Maior Acréscimo em Potência Instalada Desde 2016. Available online: https://www.aneel.gov.br/ (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- Associação Brasileira de Energia Eólica (ABEEólica). Eólica: Energia Para um Futuro Inovador. Available online: http://abeeolica.org.br/energia-eolica-o-setor/ (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- Lang, D.J.; Wiek, A. Structuring and advancing solution-oriented research for sustainability. Ambio 2022, 51, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wals, A.E.J.; Benavot, A. Can we meet the sustainability challenges? The role of education and lifelong learning. Eur. J. Educ. 2017, 52, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibson, K.; Bird Rose, D.; Fincher, R. Manifesto for Living in the Anthropocene; Livros Punctum: Brooklyn, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, A.; Coughlin, D.; Miller, J.; Kirk, S. The Production of Quick Scoping Reviews and Rapid Evidence Assessments, a How to Guide; JWEG: London, UK, 2015. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/560521/Production_of_quick_scoping_reviews_and_rapid_evidence_assessments.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Pham, M.T.; Rajić, A.; Greig, J.D.; Sargeant, J.M.; Papadopoulos, A.; McEwen, S.A. A scoping review of scoping reviews: Advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency. Res. Synth. Methods 2014, 5, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorayeb, A.; Brannstrom, C. Caminhos para uma gestão participativa dos recursos energéticos de matriz renovável (parques eólicos) no Nordeste do Brasil. Mercator 2016, 15, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, J.S.; Gorayeb, A.; Brannstrom, C. Diagnóstico participativo e cartografia social aplicados aos estudos de impactos das usinas eólicas no litoral do Ceará: O caso da praia de Xavier, Camocim. Geosaberes 2015, 6, 243–245. Available online: http://www.geosaberes.ufc.br/geosaberes/article/view/510. (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- Loureiro, C.V.; Adryane Gorayeb, A.; Christian Brannstrom, C. Análise comparativa de políticas de implantação e resultados sociais da energia eólica no Ceará (Brasil) e no Texas (EUA). Raega-O Espaç. Geogr. Anál. 2017, 40, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, M.O.A.; Gonçalves, J.S.; Vasconcelos, R.M. Sustainable development: Case study in the implementation of renewable energy in Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannstrom, C.; Gorayeb, A.; Mendes, J.S.; Loureiro, C.; Meireles, A.J.A.; Silva, E.V.; Freitas, A.L.R.; Oliveira, R.F. Is Brazilian wind power development sustainable? Insights from a review of conflicts in Ceará state. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L.I.C.; Martins, F.R.; Pereira, E.B. O mercado brasileiro da energia eólica, impactos sociais e ambientais. Ambiente Água 2017, 12, 1083–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.B.C.; Carvalho, D.B.; Lopes, W.G.R.; Sousa, T.J.S.; Santos, F.C.V.; Guzzi, A. Percepção dos impactos socioambientais decorrentes da implantação do complexo eólico Delta do Parnaíba. Gaia Sci. 2017, 11, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannstrom, C.; Gorayeb, A.; Souza, W.F.; Leite, N.S.; Chaves, L.O.; Guimarães, R.; Gê, D.R.F. Perspectivas geográficas nas transformações do litoral brasileiro pela energia eólica. Rev. Bras. Geogr. 2018, 63, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorayeb, A.; Brannstrom, C.; Meireles, A.J.A.; Mendes, J.S. Wind power gone bad: Critiquing wind power planning processes in northeastern Brazil. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2018, 40, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frate, C.A.; Brannstrom, C.; Morais, M.V.G.; Caldeira-Pires, A.A. Procedural and distributive justice inform subjectivity regarding wind power: A case from Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil. Energy Policy 2019, 132, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuzinger, M.D.; Coutinho, G.L. A implantação de parques eólicos e os impactos socioambientais em populações indígenas e tradicionais. Rev. Direito Ambient. Soc. 2019, 9, 91–114. Available online: http://www.ucs.br/etc/revistas/index.php/direitoambiental/article/view/7882 (accessed on 13 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Barra, O.A.O.L.; Vasconcelos, F.P.; Santos, D.V.; Silveira, A.P. Análise da morfodinâmica costeira e dos impactos socioambientais de grandes empreendimentos litorâneos: Estudo de caso, praia de Volta do Rio, Acaraú-CE. Rev. Casa Geogr. Sobral Sobral/CE 2019, 21, 45–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.C.R.; Gorayeb, A.; Souza, D.B.; Silva, R.M. Analysis of the levels of alteration of aquifers caused by the installation of wind farms on dunes on the coast of Ceará, Brazil. Ambiente Água 2019, 14, e2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, M.; Jamelia, D.; Bernard, E.; Melo, F.P.L. Green versus green? Adverting potential conflicts between wind power generation and biodiversity conservation in Brazil. Perspect. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 17, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.A.S.; Costa, M.S.; Costa, M.M.S.; Lira, M.A.T. Impactos socioeconômicos, ambientais e tecnológicos causados pela instalação dos parques eólicos no Ceará. Rev. Bras. Meteorol. 2019, 34, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, E.J.A.; Rosa, L.P.; Silva, N.F.; Pereira, M.G. Wind power on the Brazilian Northeast Coast, from the whiff of hope to turbulent convergence: The case of the Galinhos wind farms. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Câmpelo, J.R.; Albuquerque, E.L.S.; Melo Filho, J.M.M. Complexo eólico Chapada do Piauí I: Benefícios sociais e impactos ambientais no município de Marcolândia, Estado do Piauí. Geografia 2020, 29, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galvão, M.L.M.; Santos, M.A.; Silva, N.F.; Silva, V.P. Connections between wind energy, poverty and social sustainability in Brazil’s Semiarid. Sustainability 2020, 12, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorayeb, A.; Brannstrom, C. Licenciamento ambiental e oposição social à energia Eólica: Estudo de caso com foco no social gap em comunidade litorânea do Ceará, Brasil. Rev. Geogr. 2020, 37, 65–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.C.H.; Souza, W.F.D.; Meireles, A.J.D.A.; Brannstrom, C. Sustainability Challenges of Wind Power Deployment in Coastal Ceará State, Brazil. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrinho Júnior, M.F.; Morais, E.R.C.; Silva, P.C.M. Uso e ocupação do solo de áreas agrícolas com energia eólica. Mercator 2020, 19, e19030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, F.R.P.D.; Pereira, M.G.; Freitas, M.A.V.; da Silva, N.F.; Dantas, E.J.D.A. Bigger Is Not Always Better: Review of Small Wind in Brazil. Energies 2021, 14, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkovska, O.; Castro, G.; Klingler, M.; Nitsch, F.; Regner, P.; Soterroni, A.C.; Schmidt, J. Land-use impacts of Brazilian wind power expansion. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 024010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrinho Junior, M.F.; Ramirez Hernandez, M.C.; Albano Amora, S.S.; Costa de Morais, E.R. Perception of Environmental Impacts of Wind Farms in Agricultural Areas of Northeast Brazil. Energies 2022, 15, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannstrom, C.; Leite, N.S.; Lavoie, A.; Gorayeb, A. What explains the community acceptance of wind energy? Exploring benefits, consultation, and livelihoods in coastal Brazil. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2022, 83, 102344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Brazilian States/Region | Power (MW) | Wind Farms | Wind Turbines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rio Grande do Norte/NE | 6,082,825 | 201 | 2.571 |
| Bahia/NE | 5,395,545 | 204 | 2.287 |
| Ceará/NE | 2438.14 | 94 | 1.107 |
| Piauí/NE | 2354.65 | 81 | 1.007 |
| Rio Grande do Sul/S | 1835.89 | 80 | 830 |
| Pernambuco/NE | 798,365 | 34 | 417 |
| Maranhão/NE | 426 | 15 | 172 |
| Paraíba/NE | 469.05 | 25 | 211 |
| Santa Catarina/S | 238,499 | 14 | 173 |
| Sergipe/NE | 34.5 | 1 | 23 |
| Rio de Janeiro/SE | 28.05 | 1 | 17 |
| Paraná/S | 2.5 | 1 | 5 |
| Total | 20,104.01 | 751 | 8.820 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Silva, V.P.; Galvão, M.L.d.M. Onshore Wind Power Generation and Sustainability Challenges in Northeast Brazil: A Quick Scoping Review. Wind 2022, 2, 192-209. https://doi.org/10.3390/wind2020011
da Silva VP, Galvão MLdM. Onshore Wind Power Generation and Sustainability Challenges in Northeast Brazil: A Quick Scoping Review. Wind. 2022; 2(2):192-209. https://doi.org/10.3390/wind2020011
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Silva, Valdenildo Pedro, and Maria Luiza de Medeiros Galvão. 2022. "Onshore Wind Power Generation and Sustainability Challenges in Northeast Brazil: A Quick Scoping Review" Wind 2, no. 2: 192-209. https://doi.org/10.3390/wind2020011
APA Styleda Silva, V. P., & Galvão, M. L. d. M. (2022). Onshore Wind Power Generation and Sustainability Challenges in Northeast Brazil: A Quick Scoping Review. Wind, 2(2), 192-209. https://doi.org/10.3390/wind2020011







