Abstract
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute febrile illness, principally affecting children under 5 years, due to a systemic vasculitis of obscure etiology. In 2017, the American Heart Association published the diagnostic criteria for KD in their scientific statement. Following the emergence of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), there has been an upsurge in the reports of KD as well as a novel multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). Clinical manifestations of MIS-C are similar to KD and toxic-shock syndrome, making the clinical diagnosis challenging. Studies have shown promising results to differentiate KD from MIS-C using epidemiological, clinical, hematological, and immunological characteristics. Serological evidence may be negative in these patients at presentation, as MIS-C is a late manifestation of SARS-CoV-2 exposure. However, diagnosis and management challenges currently exist due to a gap in knowledge of these conditions. Further research is warranted to identify diagnostic tools to differentiate KD and MIS-C and optimize the therapeutic strategy, reducing morbidity and mortality related to these phenotypically similar diseases. This review aims to highlight the best available evidence for managing children with KD and MIS-C in the background of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
1. Introduction
In 1967, Japanese pediatrician Tomisaku Kawasaki first published an article entitled “Infantile acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome: clinical observations of 50 cases”, and the clinical condition was later named Kawasaki disease (KD) [1]. Nearly 80% of children presenting with KD are younger than 5 years, with a median age of 2 years at onset. The disease more often occurs in the early spring and winter months and involves more boys than girls by a ratio of 1.5 to 1.7:1 [2]. KD has been reported worldwide, affecting children of different ethnicities; however, the higher incidence in Asian countries, particularly Japan, Korea, and Taiwan, has been documented in multiple studies. Japan’s annual incidence rates of KD were recorded as 264.8 per 100,000 children under 5 years of age, compared to an annual incidence of 20.8 per 100,000 children in a similar age group in the United States [3,4]. Of the untreated KD patients, 20% develop coronary artery aneurysms (CAA). Coronary artery aneurysms are the leading cause of acquired heart disease in children in the US and Japan, replacing rheumatic fever [5]. In <40-year-old adults, 5% of acute coronary syndromes follow KD-related CAA [6].
Classic KD is a clinical diagnosis based on set criteria. The diagnostic criteria include the presence of fever for at least a duration of 5 days and exclusion of other exanthematous febrile illnesses in children of this age group [1]. Atypical or incomplete KD (IKD) diagnoses are those who do not fulfill the diagnostic criteria [6]. While the etiology of KD remains poorly understood, there has been an increased awareness of the condition over the last decade, particularly regarding cardiac complications [7]. Timely recognition and appropriate management are crucial for a favorable long-term outcome. An upsurge in the incidence of KD, and the novel multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), following the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has raised new concerns among physicians. Diagnosis and management challenges currently exist due to a gap in knowledge of these conditions, notably how to differentiate KD and MIS-C. This review aims to highlight the best available evidence for diagnosing and treating children with KD and MIS-C in the background of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic due to the highly pathogenic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
2. Etiology and Pathogenesis
No clear causes or associations have been identified as potential underlying etiology in KD, despite various research and investigations into possible causes and explanations [8]. Epidemiological evidence indicates an immune basis for KD. Increased incidence in children 6 months to 5 years old suggests protection in the first 6 months of life by the transplacentally transferred maternal antibodies and beyond 6 years by the maturation of the immune system [9]. The possibility of an infectious trigger is supported by seasonal variability, with winter and spring peaks in temperate countries and summer peaks in Asian countries. The trigger is believed to be of viral origin (Corona, Retro, and Epstein-Barr viruses) and invades the body through the respiratory mucosa [10]. A superantigen response by bacterial strains streptococcus and staphylococcus spp. has also been considered as a trigger [11]. Intestinal dysbiosis has been considered in the pathogenesis of KD, suggested by the presence of increased secretory IgA in the serum and IgA(+) plasma cells in the coronary artery wall and respiratory epithelial cells [12].
However, the theory remains that widely distributed infectious agents trigger an inflammatory cascade. Consequently, activation of both the innate and adaptive arms of the immune system may occur in a genetically predisposed child [13]. In KD, innate and adaptive immune cells infiltrate the coronary artery wall. The release of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF cause coronary artery endothelial cell damage, thereby developing aneurysms [14]. Using mouse models, researchers have identified the role of IL-1β in the pathogenesis of vasculitis in KD. This has led to clinical trials of anakinra for blocking IL-1β as a second-line therapeutic option, especially in intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)-resistant patients [8].
3. Definition of Kawasaki Disease
3.1. Classic Kawasaki Disease
There is no diagnostic test for KD. The diagnosis of classic KD is made using recommended clinical criteria and excluding similar illnesses seen in this age group [6]. All clinical manifestations may not present together, making the diagnosis even more challenging. Sometimes, careful history and examination may reveal the presence of one or more of the clinical features that resolved before seeking medical attention [6,15]. A diagnosis of KD should be considered in any young child with persistent fever. The presence of fever for at least 5 days and ≥4 of the 5 principal clinical features as suggested by the American Heart Association (AHA, 2017) is diagnostic for classic KD (Table 1) [6]. If ≥4 of the clinical criteria is present, especially with redness and swelling of the extremities, a diagnosis of KD can be made with 4 days of fever. An experienced clinician may even diagnose KD in children with only 3 days of fever [6]. In 2018, AHA’s revised statement recommended checking C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocytic sedimentation rate in children less than 1 years of age with fever for ≥7 days in the absence of principal clinical features or children with only two or three of the clinical features, but with a duration of fever ≥ 5 days. In the presence of one or more abnormal laboratory tests, further laboratory evaluation and echocardiography are then recommended to evaluate the possibility of KD [15].

Table 1.
Diagnosis of Kawasaki Disease.
The AHA also proposed other clinical findings involving the cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal, musculoskeletal, genitourinary, and nervous systems, which could be considered as associated features in the diagnosis of KD [6].
3.2. Incomplete (Atypical) Kawasaki Disease
Incomplete KD refers to those patients who do not have the complete diagnostic criteria specified by AHA. Incomplete KD patients are at risk for CAA and long-term complications. Often, children with IKD present with vague symptoms, and recognizing and differentiating this from common febrile exanthematous illnesses, especially in infancy, is a challenge even for experienced clinicians [5].
Children with prolonged fever and <4 of the principal diagnostic criteria are considered as having IKD, especially with additional laboratory or echocardiographic findings, as shown in Figure 1. However, if cardiac imaging reports coronary artery abnormalities, the diagnosis is deemed confirmed [6,15,16].
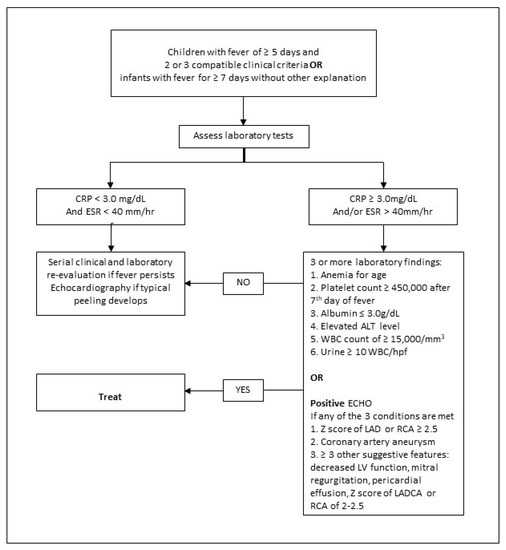
Figure 1.
Evaluation of suspected incomplete Kawasaki Disease based on the American Heart Association recommendations 2017. ALT: alanine aminotransferase; CRP: C-reactive protein; ECHO: echocardiogram; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; HPF: high power field; LAD: left anterior descending; LADCA: left anterior descending coronary artery; RCA: right coronary artery; LV: left ventricle; WBC: white blood count.
4. Kawasaki Disease and Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) Scar Reactivation
Incomplete KD in younger infants remains a challenging diagnosis. A higher prevalence of IKD was reported in infants (40%) compared to older children (10–12%) [17]. In children, the mean time to diagnose IKD was longer, 8 ± 4 days; however, diagnoses of some atypical cases were reported as early as 3 days of fever [17,18]. Coronary artery involvement was reported as high as 59% in IKD [18].
The coverage of the BCG vaccine is more than 80% in low- and middle-income countries [19]. Several case reports have highlighted the relevance of a BCG site reaction in young children with KD and IKD, suggesting its use as a marker of the disease [18,20,21]. Erythema and induration at BCG inoculation and Mantoux test site in infants with KD were first described by Kadowaki et al., adding another tool for suspicion of KD in febrile children [20]. Subsequently, changes in the BCG scar were reinforced as a sign of KD by Takayama et al. [22]. Pathophysiology of BCG scar reaction in KD continues to be an enigma and is hypothetically attributed to augmentation of immune response by heat shock proteins (HSPs) between mycobacterial HSP65 and human analog HSP63 [23]. Lai et al. found BCG scar reaction in 31.7% of 145 patients with KD, and all of them were <20 months, with 68% of the cohort being <6 months of age, suggesting declining reaction with time after BCG vaccination [24]. The authors also noted that the incidence of BCG scar reaction was higher than cervical adenopathy in children <2 years old with KD. In infants who had KD and BCG site reactions, the duration of fever before IVIG administration and the total duration of fever during the illness was shorter when compared to those who did not have a response. They also showed markedly significant inflammatory reactions with leukocytosis and thrombocytosis. The need for IVIG retreatment or development of CAA did not differ between children with positive and negative BCG reactions [24]. A severe form of BCG reaction pattern, “bull’s eye pattern,” was reported as a potential biomarker of KD by Tseng et al. [25]. In KD, the difference in BCG strains and method of administration may influence the reaction seen in BCG scars [26]. In AHA guidelines, erythema and induration at the BCG scar are not listed as cardinal signs of KD but are added as other clinical findings [6].
5. Recurrent Kawasaki Disease
A new episode of classic KD or IKD after the complete resolution of the preceding episode, known as recurrent KD (RKD), is uncommon. Generally, most recurrences occur within 2 years of the first attack. An interval of ≥2 months between the first and second episodes is considered RKD, as almost all affected children would have normalized the inflammatory markers after this time [27]. Compared to children with one episode of KD, those with RKD had longer durations of fever before IVIG treatment and lower hemoglobin levels with markedly raised alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels. However, no increased risk of CAA was reported with repeated episodes of vasculitis. Yan et al. also noted that 5 out of the 22 (22%) patients with RKD did not respond to IVIG initially, hypothesizing the tendency for these patients to develop recurrence more readily than those who responded to IVIG in the first instance. However, these results were not statistically significant [28].
Researchers have attempted to elucidate the risk factors for RKD. The recurrence risk was highest in the Asian race, with the prevalence of RKD being highest in Japan at 3% [29,30]. The incidence of RKD has remained unchanged in Japan for the last 30 years, as reported in a national survey [31]. Male gender, age <3 years and resistance to IVIG in the first episode were also identified as risk factors for RKD [32]. Nakamura et al. reported higher cardiac morbidity attributable to RKD in patients with and without the sequelae at the first attack [33].
Similar to other infectious agents, coronaviruses can trigger a “final common pathway” of immune dysregulation, as evidenced by the marked rise in severe KD associated with the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic [34,35]. In a systematic review, Medaglia et al. found a clinical relationship between SARS-CoV-2 and KD in children, particularly highlighting concerns about RKD in the COVID-19 era and the need to be vigilant of the possible association between both illnesses [27]. This correlation is significant as the authors predicted that countries affected by the COVID-19 pandemic would see similar outbreaks of KD-like diseases and RKD. Further research is needed to evaluate the risk of RKD in IVIG non-responders and those exposed to COVID-19.
6. Kawasaki Disease and COVID-19
Since the emergence of COVID-19, first described in December 2019, the United States [36], United Kingdom [37], Italy [34], France [38], and Switzerland [38] have reported cases of children presenting with KD-like symptoms with co-existing COVID-19 infection or blood antibodies, suggesting recent recovery from COVID-19. Verdoni et al. described a monthly 30-fold increased incidence and severe form of KD-like illness in Italian children compared to 5 years before the COVID-19 pandemic. A significant number of cardiac complications and KD shock syndromes were reported in older children [34]. Esmaeilzadeh et al. reported COVID-19 positivity in 68% of KD patients in Iran, suggesting the role of ethnicity and genetics in this disease. Demographic, clinical, laboratory findings, and echocardiographic features of KD were similar to the pre-COVID-19 pandemic. The authors reported an increase in the incidence of skin rash in COVID-19 positive cases with KD [39]. Conversely, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the incidence of KD was lower in children <4 years in Singapore [40].
7. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children and Kawasaki Disease
In children, multisystem inflammatory syndrome is a newly reported inflammatory condition with KD-like features and a temporal association with COVID-19. Children with MIS-C present with persistent fever, conjunctivitis, mucositis, lymphadenopathy, rash, multisystem organ involvement, elevated inflammatory markers, and evidence of recent COVID-19 infection. Features of cardiac involvement and acute gastrointestinal problems have also been associated with MIS-C [41,42]. Since the first report of MIS-C in the UK in 2020, cases have been reported in Italy, France, Spain, and the USA, and further guidelines were published by the World Health Organization [41,42,43].
MIS-C presents 3–8 weeks following exposure to SARS-CoV-2 disease and is possibly related to immune activation during the recovery phase [43]. It remains unclear whether COVID-19 triggers KD, is a separate disease, a spectrum of diseases, or an overlap syndrome. Matucci-Cerinic et al. hypothesized that MIS-C is on the KD spectrum. The authors reiterated that KD is not a disease but a syndrome, as rightly described originally by Kawasaki as “mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome”. The severity of manifestations depends on the characteristics of the host, trigger, and the type of immune response [44]. Researchers attempting to differentiate between KD and MIS-C using clinical and laboratory findings, cellular phenotype, and antibody response have mixed results. An epidemiologic link of the COVID-19 outbreak can support MIS-C diagnosis, as RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 was not always positive. In laboratory findings, marked thrombocytosis after the initial febrile episode was characteristic of KD. The early hemodynamic shock developed in these patients was challenging to differentiate between KD shock or MIS-C shock [45].
The ethnicity of MIS-C shock patients was mostly African/American-Hispanic, whereas KD shock was more often of Asian descent in the UK. Researchers found a significant overlap between MIS-C and KD in immune response, a difference in targeted organ abnormalities, and signs of damage [44,45]. In the acute phase, lymphopenia, hypoalbuminemia, and thrombocytopenia were seen in MIS-C, whereas mild thrombocytopenia reversed to thrombocytosis in 10–14 days in patients with KD shock. Abdominal pain can be severe enough to mimic surgical emergency in MIS-C but is rare in KD [46]. The rise of ferritin and CRP was more striking in MIS-C than KD shock. Clinically, MIS-C predominantly affects the myocardium, versus coronary arteritis with secondary cardiac dysfunction in KD [45].
MIS-C and KD respond well to high-dose IVIG, corticosteroids, interleukin 1 (IL-1) inhibition, and aspirin. A recent retrospective propensity score-matched analysis using a combination of IVIG with methylprednisoslone in MIS-C patients showed a better course of fever [47]. MIS-C has claimed the title of the “most common cause of acquired heart disease in children” from KD [45]. Differentiating MIS-C from “look-alike” clinical conditions such as KD remains challenging, but a treatment response of MIS-C to IVIG and methylprednisolone looks promising.
8. Complications of Kawasaki Disease
The most pertinent cardiovascular risk for children who have KD is CAA. In 30–50% of cases from 10 days of onset of fever, mild diffuse coronary artery dilatation begins. Often, this coronary dilatation is transient and regresses within six to eight weeks of fever [6]. However, if not treated promptly with IVIG, true aneurysms can develop in up to 20% of cases. Giant aneurysms may develop in about 1% of KD cases and have a much poorer prognosis due to complications of stenosis, distal myocardial ischemia, or even rupture [3,6]. Myocarditis, pericarditis, valvular lesions, arrhythmias, and heart failure are complications described in KD patients [48].
Echocardiographic screening and cardiology follow-up are crucial in diagnosing and managing children with KD to promptly identify coronary artery involvement and other cardiovascular complications [6]. Echocardiography should be performed on suspicion of KD and then continued at 2, 4, and 8 weeks in uncomplicated cases. In patients with evolving CAA, this frequency should be increased to monitor the coronary artery dimensions and for the presence of thrombosis [49].
The AHA recommends low-dose aspirin (3–5 mg/kg/day) for 4–6 weeks from the onset of the illness in patients with no coronary artery dilatation. The addition of low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) or warfarin is recommended with low-dose aspirin in those with progressive CAA. “Triple therapy” using aspirin, a second antiplatelet agent, and warfarin or LMWH should be considered in patients with an increased risk of thrombosis, especially those having large or giant aneurysms, or a recent history of coronary artery thrombosis [6].
Other potential complications of KD include pneumonia, encephalitis, cholecystitis, anemia, hypoalbuminemia, dyselectrolytemia, gastroenteritis, and dehydration [48]. KD-related shock can occur with hypotension, platelet consumption, and CAA [50].
9. Treatment of Kawasaki Disease
9.1. Standard Treatment
9.1.1. Intravenous Immunoglobulin
Treatment of KD is divided into the acute phase of treatment and long-term management. The acute phase of therapy aims to suppress systemic inflammation and prevent thrombosis in coronary arteries. Intravenous immunoglobulin has been used to treat KD for the last 40 years. The administration of IVIG, together with aspirin, is accepted as the “first-line” treatment for KD, although the treatment dosage has since been refined over the years [51,52].
Since IVIG use, the risk of coronary arteritis and aneurysms has shown a downward trend from 30% to 5–7% [52]. The current recommendation from AHA is a single infusion of 2 g/kg of IVIG over 10 to 12 h, within the first 10 days of illness or as soon as possible after diagnosis, together with aspirin [6]. Furusho et al., in a randomized control trial (RCT), compared IVIG (400 mg/kg) plus aspirin and aspirin alone in the treatment of KD. Within 30 days, 15% of IVIG and 42% of the aspirin group developed coronary artery lesions. Of these, a persistent coronary artery lesion (30–60 days of treatment) was found only in 16% of IVIG and 58% of the aspirin group [53]. In 1986, Newburger et al. conducted a multicenter RCT to compare the efficacy of IVIG (400 mg/kg/day for 4 days) together with aspirin and high-dose aspirin alone in treating patients with KD. Both groups received aspirin in the dose of 100 mg/kg/day through the 14th day of illness and continued at 3 to 5 mg/kg/day. The prevalence of CAA at 2 and 7 weeks after treatment was approximately three- to five-fold lower among patients who received IVIG [54].
In cases with IVIG resistance, defined as persistent or recrudescent fever at least 36 h following IVIG infusion, the AHA recommended a second dose of IVIG at 2 g/kg. In contrast, patients with RKD should be given standard therapy with IVIG and aspirin [5]. Following high-dose IVIG therapy in young children, measles and varicella immunizations should be postponed for 11 months [6,55].
Prediction of IVIG Resistance in Kawasaki Disease—Kobayashi Score
Kobayashi et al. developed predictive models using demographic and laboratory variables to predict unresponsiveness to IVIG in KD [56]. In Japan, 7–23% of KD patients were reported to have IVIG resistance, increasing the risk of CAA [57]. The Kobayashi score showed high sensitivity and specificity in Japan, identifying IVIG non-responders to KD. However, the same scoring system failed to show a similar response in the North American, European, and Asian populations, possibly due to mixed ethnicity [58,59,60]. Unfortunately, attempts to use the Kobayashi scoring system to predict IVIG resistance in the Caucasian–Israeli population and to develop a specific scoring method in KD patients have been unsuccessful [61].
9.1.2. Aspirin
Aspirin has been used for many years in the acute management of KD to provide an additional anti-inflammatory effect together with IVIG. However, the optimal duration and dose remain uncertain. Treatment of the acute phase of KD using aspirin varied from a higher dose of 80 to 100 mg/kg/day in the US to 30 to 50 mg/kg/day in Japan and Western Europe [6]. There is currently no data to suggest which regimen is superior. A link between fever recrudescence or CAA with low-dose aspirin therapy was not observed in a study comparing low- and high-dose aspirin therapy in KD [62].
The dose of aspirin should be reduced to 3 to 5 mg/kg/day after the child has been afebrile for 48 to 72 h. This dose of aspirin is to be maintained until no coronary artery changes are observed in echocardiography, usually by 6 to 8 weeks of the onset of fever. Some centers prefer to continue high-dose aspirin until day 14 of illness, while afebrile [6,62]. Children who develop CAA may end up on aspirin treatment indefinitely [6].
Reye syndrome, a fatal illness, is strongly linked to active infection with chickenpox and influenza while on prolonged aspirin therapy [63]. Children on treatment with aspirin should be given varicella and the annual influenza vaccines [62]. The role of aspirin in the acute phase of KD needs to be further understood with future research to determine the optimum dose of this therapy, considering the risk of drug toxicity and the lack of evidence of its preventive role in the development of CAA.
9.2. Second-Line Treatments
The efficacy of steroids in the initial treatment of KD is still unclear. In 1979, Kato et al. suggested a detrimental effect when steroids were used as first-line treatment [64]. Since then, further studies have been published, but they report conflicting evidence [7,65]. Sundel et al. conducted a small RCT investigating whether adding 30 mg/kg of intravenous methylprednisolone to conventional therapy with IVIG (2 g/kg) and aspirin improved outcomes. Patients who received steroids had a shorter duration of fever, reduced hospital stay, and lower acute phase reactants 6 weeks after the onset of illness. However, there were no differences in coronary artery outcomes between treatment groups [66]. An RCT comparing IVIG alone and IVIG with steroids found no significant difference in coronary artery Z scores [67]. Routine use of corticosteroids is not recommended in AHA guidelines but is considered for high-risk patients [6].
In 2006, Inoue et al. conducted an RCT with one arm receiving IVIG and the other arm combining IVIG and prednisolone. The outcome was an improved clinical course with a shorter duration of fever, rapid drop in CRP, less frequent treatment failure, and a statistically significant reduction in CAA in the corticosteroid group [68]. SHARE (The European Single Hub and Access point for Rheumatology in Europe) guidelines recommend adjunctive primary corticosteroid therapy in children with IVIG-resistant KD if the Kobayashi score >4 or if they developed hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis or shock [69].
More recent therapies, particularly for patients with IVIG resistance, include monoclonal antibodies (infliximab), IL-1 inhibitor (Anakinra), cyclosporin A, cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, ulinastatin, and plasma exchange [49,70]. The AHA 2017 guidelines, as well as recommendations from SHARE and the Italian Society of Pediatrics, suggested considering infliximab (5 mg/kg) in IVIG-resistant patients as an alternative to the second infusion of IVIG or corticosteroids [70]. However, these societies cannot agree on the other alternative therapies recommendations. More research is required to understand the safety and efficacy of these newer therapies in managing KD.
10. Prognosis
Timely diagnosis and adequate treatment with IVIG and aspirin have reduced the incidence of CAA to approximately 5% and mortality by 0.1% [33]. In Japanese children, the risk of relapse of KD has been reported to be 2.9% [68]. Management of IVIG resistance in 10–20% of KD cases using various other therapeutic agents in several clinical trials has not yielded conclusive results [6].
Cardiovascular pathology in KD remains the most critical contributor to long-term morbidity and mortality. A minority of KD patients may have noncoronary arterial pathology, adding to the overall morbidity depending on the organs affected [6]. Coronary arteries affected in KD are at risk of stenosis or occlusion over time due to abnormal function, although the internal luminal dimension remains normal [71]. Patients with KD who had necrotizing arteritis and later coronary aneurysms are at increased risk of thrombosis. Hence, thromboprophylaxis and close echo monitoring for coronary artery stenosis or obstruction is recommended to prevent myocardial ischemia [6]. In a long-term follow-up study of 546 patients who had treatment for KD in infancy, three of them subsequently developed acute coronary syndrome at 14, 19, and 32 years of age. Two more in the same cohort developed sudden cardiac death at 5 and 11 years of age, although one of them did not show coronary artery thrombosis or infarct in autopsy [72]. The use of IVIG and aspirin has been shown to improve long-term prognosis; however, despite this, in a minority of KD cases, cardiac morbidity occurs.
11. Conclusions
Kawasaki disease is an acute systemic vasculitis of unknown etiology that primarily affects medium-sized arteries presenting with high-grade fever and increased risk of coronary artery disease. Early clinical features of KD mimic more common self-limiting exanthematous febrile illnesses, especially in infants. With increasing reports of KD in children since the emergence of COVID-19, early diagnosis and treatment are paramount. Treatment response of KD to IVIG and aspirin remains the gold standard recommendation. Favorable reports on the treatment of MIS-C with IVIG and methylprednisolone are propitious. Evidence is lacking regarding the choice of optimal therapy in RKD. For the Asian population, risk assessment scores are available to estimate the risk for CAA but not for other ethnicities. Close monitoring after treatment resolution can reduce long-term morbidities related to KD. Further research is required to aid early diagnosis and optimize treatment of KD, especially with the number of cases increasing with emerging new mutant strains of COVID-19 and MIS-C.
Author Contributions
G.H. conceptualized and wrote the first draft of the manuscript and searched extensively to find articles relevant to this review article. S.C. contributed substantially to the conception and design of the review article and editing of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kawasaki, T. Acute febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of the fingers and toes in children. Arerugi 1967, 16, 178–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holman, R.C.; Curns, A.T.; Belay, E.D.; Steiner, C.A.; Schonberger, L.B. Kawasaki syndrome hospitalizations in the United States, 1997 and 2000. Pediatrics 2003, 112, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnden, A.; Tulloh, R.; Burgner, D. Kawasaki disease. BMJ 2014, 349, g5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.T.; Wu, M.H. The global epidemiology of Kawasaki disease: Review and future perspectives. Glob. Cardiol. Sci. Pract. 2017, 31, e201720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rowley, A.H.; Shulman, S.T. Kawasaki disease. In Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 19th ed.; Behrman, R.E., Kliegman, R.M., Jenson, H.B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 823–826. [Google Scholar]
- McCrindle, B.W.; Rowley, A.H.; Newburger, J.W.; Burns, J.C.; Bolger, A.F.; Gewitz, M.; Baker, A.L.; Jackson, M.A.; Takahashi, M.; Shah, P.B.; et al. Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term Management of Kawasaki Disease: A Scientific Statement for Health Professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e927–e999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newburger, J.W.; Takahashi, M.; Gerber, M.A.; Gewitz, M.H.; Tani, L.Y.; Burns, J.C.; Shulman, S.T.; Bolger, A.F.; Ferrieri, P.; Baltimore, R.S.; et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: A statement for health professionals from the committee on rheumatic fever, endocarditis, and Kawasaki disease, council on cardiovascular disease in the young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 1708–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noval Rivas, M.; Arditi, M. Kawasaki disease: Pathophysiology and insights from mouse models. Nat. Rev. Rheu. Matol. 2020, 16, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, A.H. Is Kawasaki disease an infectious disorder? Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.Y.; Lu, C.Y.; Shao, P.L.; Lee, P.I.; Lin, M.T.; Fan, T.Y.; Cheng, A.L.; Lee, W.L.; Hu, J.J.; Yeh, S.J.; et al. Viral infections associated with Kawasaki disease. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, M.; Hoyt, L.; Ferrieri, P.; Schlievert, P.M.; Jenson, H.B. Kawasaki syndrome-like illness associated with infection caused by entero toxin B-secreting Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 29, 586–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowley, A.H.; Shulman, S.T.; Mask, C.A.; Finn, L.S.; Terai, M.; Baker, S.C.; Galliani, C.A.; Takahashi, K.; Naoe, S.; Kalelkar, M.B.; et al. IgA plasma cell infiltration of proximal respiratory tract, pancreas, kidney, and coronary artery in acute Kawasaki disease. J. Infect Dis. 2000, 182, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rife, E.; Gedalia, A. Kawasaki Disease: An Update. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, Y.; Takano, N.; Kanegane, H.; Yokoi, T.; Yachie, A.; Miyawaki, T.; Taniguchi, N. The acute phase nature of inter leukin 6: Studies in Kawasaki disease and other febrile illnesses. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1989, 76, 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Rowley, A.H. Kawasaki disease: AHA statement and recommendations. Contemp. Pediatr. 2018, 35, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Sundel, R.P.; Petty, R.E. Kawasaki disease. In Textbook of Pediatric Rheumatology, 6th ed.; Cassidy, J.T., Petty, R.E., Laxer, R.M., Lindsley, C.B., Eds.; Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 505–520. [Google Scholar]
- Mastrangelo, G.; Cimaz, R.; Calabri, G.B.; Simonini, G.; Lasagni, D.; Resti, M.; Trapani, S. Kawasaki disease in infants less than one year of age: An Italian cohort from a single center. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, K.Y.Y.; Chua, M.C.; Tan, N.W.H.; Chandran, S. Reactivation of BCG inoculation site in a child with febrile exanthema of 3 days duration: An early indicator of incomplete Kawasaki disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e239648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trollfors, B.; Sigurdsson, V.; Dahlgren-Aronsson, A. Prevalence of Latent TB and Effectiveness of BCG Vaccination against Latent Tuberculosis: An Observational Study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 109, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, J.; Yamaguchi, M.; Sato, S. Three cases suspected as acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome: Emphasis on cutaneous changes at the BCG and tuberculin inoculated site in one case. Jpn. J. Pediatr. 1972, 25, 901–905. [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers, D.; Corban, J.G.; Moore, P.P. BCG site inflammation: A useful diagnostic sign in incomplete Kawasaki disease. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2008, 44, 525–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, J.; Yanase, Y.; Kawasaki, T. A study on erythematous change at the site of the BCG inoculation. Acta Paediatr. Jpn. 1982, 86, 567–572. [Google Scholar]
- Sireci, G.; Dieli, F.; Salerno, A. T cells recognize an immunodominant epitope of heat shock protein 65 in Kawasaki disease. Mol. Med. 2000, 6, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.C.; Lee, P.C.; Wang, C.C.; Hwang, B.T.; Meng, C.C.; Tsai, M.C. Reaction at the bacillus Calmette–Guérin inoculation site in patients with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2013, 54, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tseng, H.C.; Ho, J.C.; Guo, M.M.; Lo, M.H.; Hsieh, K.S.; Tsai, W.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Lee, C.H. Bull’s eye dermatoscopy pattern at bacillus Calmette-Guérin inoculation site correlates with systemic involvements in patients with Kawasaki disease. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollmann, T.R.; Klein, E.J.; Stefanelli, C.B.; Marcuse, E.K. Purified protein derivative anergy in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2001, 20, 81–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medaglia, A.A.; Siracusa, L.; Gioè, C.; Giordano, S.; Cascio, A.; Colomba, C. Kawasaki disease recurrence in the COVID-19 era: A systematic review of the literature. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.M.; Du, Z.D.; Fu, P.P. Clinical features of recurrent Kawasaki disease and its risk factors. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2013, 172, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddox, R.A.; Belay, E.D.; Holman, R.C. Recurrent Kawasaki syndrome in the United States. In Proceedings of the Abstracts of the Ninth International Kawasaki Symposium, Taipei, Taiwan, 10–12 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, Y.; Hirose, K.; Yanagawa, H.; Kato, H.; Kawasaki, T. Incidence rate of recurrent Kawasaki disease in Japan. Acta Paediatr. 1994, 83, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, D.; Nakamura, Y. Nationwide surveys show that the incidence of recurrent Kawasaki disease in Japan has hardly changed over the last 30 years. Acta Paediatr. 2017, 106, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Yanagawa, H. Incidence rate of recurrent Kawasaki disease and related risk factors: From the results of nationwide surveys of Kawasaki disease in Japan. Acta Paediatr. 2001, 90, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Oki, I.; Tanihara, S.; Ojima, T.; Yanagawa, H. Cardiac sequelae in recurrent cases of Kawasaki disease: A comparison between the initial episode of the disease and a recurrence in the same patients. Pediatrics 1998, 102, E66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verdoni, L.; Mazza, A.; Gervasoni, A.; Martelli, L.; Ruggeri, M.; Ciuffreda, M.; Bonanomi, E.; D’Antiga, L. An outbreak of severe Kawasaki-like disease at the Italian epicentre of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic: An observational cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toubiana, J.; Poirault, C.; Corsia, A.; Bajolle, F.; Fourgeaud, J.; Angoulvant, F.; Debray, A.; Basmaci, R.; Salvador, E.; Biscardi, S.; et al. Kawasaki-like multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children during the COVID-19 pandemic in Paris, France: Prospective observational study. BMJ 2020, 369, m2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, V.G.; Mills, M.; Suarez, D.; Hogan, C.A.; Yeh, D.; Segal, J.B.; Nguyen, E.L.; Barsh, G.R.; Maskatia, S.; Mathew, R. COVID-19 and Kawasaki disease: Novel virus and novel case. Hosp. Pediatr. 2020, 10, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riphagen, S.; Gomez, X.; Gonzalez-Martinez, C.; Wilkinson, N.; Theocharis, P. Hyperinflammatory shock in children during COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2020, 395, 1607–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadjer, Z.; Méot, M.; Bajolle, F.; Khraiche, D.; Legendre, A.; Abakka, S.; Auriau, J.; Grimaud, M.; Oualha, M.; Beghetti, M.; et al. Acute heart failure in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children in the context of global SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Circulation 2020, 142, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeilzadeh, H.; Mortazavi, N.; Salehi, A.; Fatemian, H.; Dehghani, S.M.; Vali, M.; Vardanjani, H.M. Effect of COVID-19 on Kawasaki Disease: Decrease Age of Onset and Increase Skin Manifestation. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, C.F.; Nadua, K.D.; Oh, B.K.; Thoon, K.C. Epidemiologic trends in Kawasaki disease during coronavirus disease-19 in Singapore. J. Pediatr. 2020, 226, 314–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, E.; Bamford, A.; Kenny, J.; Kaforou, M.; Jones, C.E.; Shah, P.; Ramnarayan, P.; Fraisse, A.; Miller, O.; Davies, P.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 58 Children with a Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2. JAMA 2020, 324, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Rapid Risk Assessment: Paediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome and SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children. Published 15 May 2020. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/paediatric-inflammatory-multisystem-syndrome-and-sars-cov-2-rapid-risk-assessment (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- World Health Organization. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children and Adolescents with COVID-19. Published 15 May 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail/multisystem-inflammatory-syndrome-in-children-and-adolescents-with-covid-19 (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- Matucci-Cerinic, C.; Caorsi, R.; Consolaro, A.; Rosina, S.; Civino, A.; Ravelli, A. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: Unique Disease or Part of the Kawasaki Disease Spectrum? Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 680813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukulmez, H. Current Understanding of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome (MIS-C) Following COVID-19 and Its Distinction from Kawasaki Disease. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2021, 23, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomba, C.; La Placa, S.; Saporito, L.; Corsello, G.; Ciccia, F.; Medaglia, A.; Romanin, B.; Serra, N.; Di Carlo, P.; Cascio, A. Intestinal Involvement in Kawasaki Disease. J. Pediatr. 2018, 202, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ouldali, N.; Toubiana, J.; Antona, D.; Javouhey, E.; Madhi, F.; Lorrot, M.; Léger, P.L.; Galeotti, C.; Claude, C.; Wiedemann, A.; et al. Association of intravenous immunoglobulins plus methylprednisolone vs immunoglobulins alone with course of fever in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. JAMA 2021, 325, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.C. Kawasaki disease. Adv. Pediatr. Infect Dis. 2001, 48, 157–177. [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi, A.; Rigante, D.; Cimaz, R.; Ravelli, A.; de Jacobis, I.T.; Rimini, A.; Cardinale, F.; Cattalini, M.; De Zorzi, A.; Dellepiane, R.M.; et al. Revised recommendations of the Italian Society of Pediatrics about the general management of Kawasaki disease. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanegaye, J.T.; Wilder, M.S.; Molkara, D.; Frazer, J.R.; Pancheri, J.; Tremoulet, A.H.; Watson, V.E.; Best, B.M.; Burns, J.C. Recognition of a Kawasaki disease shock syndrome. Pediatrics 2009, 123, e783–e789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burns, J.C.; Capparelli, E.V.; Brown, J.A.; Newburger, J.W.; Glode, M.P.; US/Canadian Kawasaki Syndrome Study Group. Intravenous gamma-globulin treatment and retreatment in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1998, 17, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates-Whitehead, R.M.; Baumer, J.H.; Haines, L.; Love, S.; Maconochie, I.K.; Gupta, A.; Roman, K.; Dua, J.S.; Flynn, I. Intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment of Kawasaki disease in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2003, 4, CD004000. [Google Scholar]
- Furusho, K.; Kamiya, T.; Nakano, H.; Kiyosawa, N.; Shinomiya, K.; Hayashidera, T.; Tamura, T.; Hirose, O.; Manabe, Y.; Yokoyama, T. High-dose intravenous gammaglobulin for Kawasaki disease. Lancet 1984, 2, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newburger, J.W.; Takahashi, M.; Burns, J.C.; Beiser, A.; Chung, K.J.; Duffy, C.E.; Glode, M.P.; Mason, W.H.; Reddy, V.; Sanders, S.; et al. The treatment of Kawasaki syndrome with intravenous gamma globulin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerding, R. Kawasaki disease: A review. J. Pediatr. Health Care 2011, 25, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Inoue, Y.; Takeuchi, K.; Okada, Y.; Tamura, K.; Tomomasa, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Morikawa, A. Prediction of intravenous immunoglobulin unresponsiveness in patients with Kawasaki disease. Circulation 2006, 113, 2606–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibata, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Hasegawa, S.; Matsushige, T.; Kusuda, T.; Hoshide, M.; Takahashi, K.; Okada, S.; Wakiguchi, H.; Moriwake, T. Coronary artery lesions and the increasing incidence of Kawasaki disease resistant to initial immune globulin. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 214, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleeper, L.A.; Minich, L.L.; McCrindle, B.M.; Li, J.S.; Mason, W.; Colan, S.D.; Atz, A.M.; Printz, B.F.; Baker, A.; Vetter, V.L.; et al. Pediatric Heart Network Investigators. Evaluation of Kawasaki disease risk-scoring systems for intravenous immunoglobulin resistance. J. Pediatr. 2011, 158, 831–835.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, S.; Sutton, N.; Blackstock, S.; Gormley, S.; Hoggart, C.J.; Levin, M.; Herberg, J.A. Predicting IVIG resistance in UK Kawasaki disease. Arch. Dis. Child. 2015, 100, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Lee, H.; Eun, L. Verification of Current Risk Scores for Kawasaki Disease in Korean Children. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 1991–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arane, K.; Mendelsohn, K.; Mimouni, M.; Mimouni, F.; Koren, Y.; Simon, D.B.; Bahat, H.; Helou, M.H.; Mendelson, A.; Hezkelo, N. Japanese scoring systems to predict resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin in Kawasaki disease were unreliable for Caucasian Israeli children. Acta Paediatr. 2018, 107, 2179–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, B.; Belarski, E.; Manaloor, J.; Ofner, S.; Carroll, A.E.; John, C.C.; Wood, J.B. Comparison of Risk of Recrudescent Fever in Children with Kawasaki Disease Treated with Intravenous Immunoglobulin and Low-Dose vs High-Dose Aspirin. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e1918565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freeman, A.F.; Shulman, S.T. Kawasaki disease: Summary of the American Heart Association guidelines. Am. Fam. Physician 2006, 74, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, H.; Koike, S.; Yokoyama, T. Kawasaki disease: Effect of treatment on coronary artery involvement. Pediatrics 1979, 63, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijima, Y.; Kamiya, T.; Suzuki, A.; Hirose, O.; Manabe, H. A trial procedure to prevent aneurysm formation of the coronary arteries by steroid pulse therapy in Kawasaki disease. Jpn. Circ. J. 1982, 46, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundel, R.P.; Baker, A.L.; Fulton, D.R.; Newburger, J.W. Corticosteroids in the initial treatment of Kawasaki disease: Report of a randomized trial. J. Pediatr. 2003, 142, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newburger, J.W.; Sleeper, L.A.; McCrindle, B.W.; Minich, L.L.; Gersony, W.; Vetter, V.L.; Atz, A.M.; Li, J.S.; Takahashi, M.; Baker, A.L.; et al. Randomized trial of pulsed corticosteroid therapy for primary treatment of Kawasaki disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Okada, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Tomomasa, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Morikawa, A. A multicenter prospective randomized trial of corticosteroids in primary therapy for Kawasaki disease: Clinical course and coronary artery outcome. J. Pediatr. 2006, 149, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Graeff, N.; Groot, N.; Ozen, S.; Eleftheriou, D.; Avcin, T.; Bader-Meunier, B.; Dolezalova, P.; Feldman, B.M.; Kone-Paut, I.; Lahdenne, P.; et al. European consensus-based recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of Kawasaki disease-the SHARE initiative. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buda, P.; Friedman-Gruszczyńska, J.; Książyk, J. Anti-inflammatory Treatment of Kawasaki Disease: Comparison of Current Guidelines and Perspectives. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 738850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orenstein, J.M.; Shulman, S.T.; Fox, L.M.; Baker, S.C.; Takahashi, M.; Bhatti, T.R.; Russo, P.A.; Mierau, G.W.; de Chadarévian, J.P.; Perlman, E.J.; et al. Three linked vasculopathic processes characterize Kawasaki disease: A light and transmission electron microscopic study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holve, T.J.; Patel, A.; Chau, Q.; Marks, A.R.; Meadows, A.; Zaroff, J.G. Long-Term cardiovascular outcomes in survivors of Kawasaki disease. Pediatrics 2014, 133, e305–e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).