Design, Manufacturing, and Trial of a 3D Printed Customized Finger Splint for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
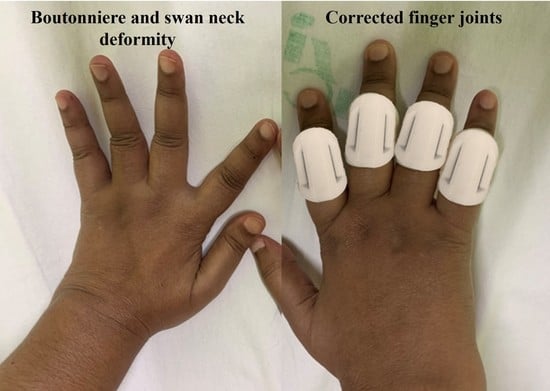
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Demographics
2.2. Geometrical Analysis of Splints
2.3. Fabrication of Splint
2.4. Testing of Splints
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Computational Analysis of Splints
3.2. Nine Hole Peg Test
3.3. QUEST
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scott, D.L.; Wolfe, F.; Huizinga, T.W.J. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2010, 376, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handa, R.; Rao, U.; Lewis, J.F.M.; Rambhad, G.; Shiff, S.; Ghia, C.J. Literature review of rheumatoid arthritis in India. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 19, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Giesen, F.J.; Nelissen, R.G.H.H.; van Lankveld, W.J.; Kremers-Selten, C.; Peeters, A.J.; Stern, E.B.; le Cessie, S.; Vlieland, T.P.M.V. Swan neck deformities in rheumatoid arthritis: A qualitative study on the patients’ perspectives on hand function problems and finger splints. Musculoskelet. Care 2010, 8, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, R.; Nallamothu, S.V. Swan-Neck Deformity. StatPearls, June. 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525970/ (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Nalebuff, E.A. The Rheumatoid Swan-Neck Deformity. Hand Clin. 1989, 5, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, P.; Watson, J.T. Boutonniere Deformity. J. Hand Surg. 2011, 36, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Giesen, F.J.; Van Lankveld, W.J.; Kremers-Selten, C.; Peeters, A.J.; Stern, E.B.; le Cessie, S.; Nelissen, R.; Vlieland, T.V. Effectiveness of two finger splints for swan neck deformity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized, crossover trial. Arthritis Care Res. 2009, 61, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijlstra, T.R.; Heijnsdijk-Rouwenhorst, L.; Rasker, J.J. Silver Ring Splints improve dexterity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2004, 51, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipping, A.; ter Schegget, M. A Study Comparing Use and Effects of Custom-Made versus Prefabricated Splints for Swan Neck Deformity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Br. J. Hand Ther. 2016, 5, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfagharian, A.; Gregory, T.M.; Bodaghi, M.; Gharaie, S.; Fay, P. Patient-specific 3D-Printed Splint for Mallet Finger Injury. Int. J. Bioprinting 2020, 6, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.H.; Kachooei, A.R.; Rivlin, M.; Beredjiklian, P. Comparison of Custom-made Versus Prefabricated Thumb Splinting for Carpometacarpal Arthrosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Arch. Bone Jt. Surg. 2018, 6, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, S.K.; Geigle, P.R. A comparison of prefabricated and custom made resting hand splints for individuals with cervical spinal cord injury: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2021, 35, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papavasiliou, T.; Shah, R.K.; Chatzimichail, S.; Uppal, L.; Chan, J.C. Three-dimensional Printed Customized Adjustable Mallet Finger Splint: A Cheap, Effective, and Comfortable Alternative. Plast. Reconstr. Surg.-Glob. Open 2021, 9, e3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Chaturvedi, S.; Bhat, A.K.; Samheel, M.; Saxena, A. Design and Manufacture of Customizable Finger Immobilizer and Mallet Finger Splints. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Biomedical Innovations and Applications, Varna, Bulgaria, 8–9 November 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzinga, K.; Chung, K.C. Managing Swan Neck and Boutonniere Deformities. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2019, 46, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldburger, L.; Schaller, R.; Furthmüller, C.; Schrepfer, L.; Schaefer, D.J.; Kaempfen, A. 3D-Printed Hand Splints versus Thermoplastic Splints: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Feasibility Trial. Int. J. Bioprinting 2022, 8, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tanaka, H. Rapid customization system for 3D-printed splint using programmable modeling technique–a practical approach. 3D Print. Med. 2018, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.Y. On-Site 3D Printing of Functional Custom Mallet Splints for Mars Analogue Crewmembers. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2015, 86, 911–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Gupta, V.; Chanda, A. Mechanical Characterization of Rotating Triangle Shaped Auxetic Skin Graft Simulants. Facta Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Gupta, V.; Chanda, A. Artificial skin with varying biomechanical properties. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 3162–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Chanda, A. Finite element analysis of a hybrid corrugated hip implant for stability and loading during gait phases. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2022, 8, 035028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Chanda, A. Expansion potential of skin grafts with alternating slit based auxetic incisions. Forces Mech. 2022, 7, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Singh, G.; Chanda, A. Prediction of diabetic foot ulcer progression: A computational study. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2021, 7, 065020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, V.; Chanda, A. Biomechanical modeling of novel high expansion auxetic skin grafts. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2022, 38, e3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Gupta, S.; Chanda, A. Expansion potential of skin grafts with novel rotating-triangle-shaped auxetic incisions. Emerg. Mater. Res. 2022, 11, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhikara, K.; Gupta, S.; Chanda, A. Development of a novel foot orthosis for plantar pain reduction. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 3532–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demers, L.; Monette, M.; Lapierre, Y.; Arnold, D.L.; Wolfson, C. Reliability, validity, and applicability of the Quebec User Evaluation of Satisfaction with assistive Technology (QUEST 2.0) for adults with multiple sclerosis. Disabil. Rehabil. 2002, 24, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, G.M.; Häger, C.K. A modified standardized nine hole peg test for valid and reliable kinematic assessment of dexterity post-stroke. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Gupta, S.; Chanda, A. Biomechanical modelling of diabetic foot ulcers: A computational study. J. Biomech. 2021, 127, 110699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizio, L.; Belsky, M.R. Finger Deformities in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Hand Clin. 1996, 12, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulmozhi, R.S.; Vaidya, M.; Poojalakshmi, M.G.; Kumar, A.; Anuraag, K. 3D Design and Printing of Custom-Fit Finger Splint. Biomed. Eng. Appl. Basis Commun. 2018, 30, 1850032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, M.; Brosseau, L.; Farmer, M.; Ouimet, M.-A.; Rees, S.; Tugwell, P.; A Wells, G. Splints and Orthosis for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2001, 2010, CD004018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Subject | Age (in Years) | Hands | Modifications and Follow-Up | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left Hand | Right Hand | |||||||||||
| L | R | M | I | T | T | I | M | R | L | |||
| 1 | 45 | P | PD | PD | PD | PD | PD | PD | P | Modified the dimensions | ||
| 2 | 41 | PD | P | PD | D | P | P | PD | PD | |||
| 3 | 38 | P | P | P | D | P | D | P | Uncomfortable in cooking | |||
| 4 | 60 | PD | P | P | P | P | P | P | ||||
| 5 | 45 | P | PD | P | PD | PD | D | P | ||||
| 6 | 56 | PD | P | P | D | P | PD | PD | D | |||
| 7 | 45 | PD | PD | D | PD | D | D | PD | P | |||
| 8 | 22 | P | D | P | P | D | ||||||
| 9 | 45 | P | PD | PD | PD | PD | P | Poor fit despite adjustments | ||||
| 10 | 46 | P | P | P | P | P | PD | P | D | |||
| 11 | 42 | P | PD | P | D | D | P | |||||
| 12 | 65 | P | PD | P | P | D | D | P | PD | PD | Unsatisfactory | |
| 13 | 56 | PD | PD | PD | P | PD | P | |||||
| 14 | 40 | PD | PD | D | P | D | D | |||||
| 15 | 55 | P | P | P | D | D | P | P | P | P | Splints reduced after 2 weeks due to discomfort | |
| 16 | 57 | P | P | PD | P | P | P | |||||
| 17 | 26 | P | PD | PD | P | PD | PD | PD | P | |||
| 18 | 34 | D | P | P | P | P | ||||||
| 19 | 50 | P | D | P | P | P | Splints added afterward | |||||
| 20 | 46 | PD | D | P | PD | D | PD | D | D | Arthritis increased | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chhikara, K.; Gupta, S.; Saharawat, S.; Sarkar, S.; Chanda, A. Design, Manufacturing, and Trial of a 3D Printed Customized Finger Splint for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumato 2023, 3, 51-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3010004
Chhikara K, Gupta S, Saharawat S, Sarkar S, Chanda A. Design, Manufacturing, and Trial of a 3D Printed Customized Finger Splint for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumato. 2023; 3(1):51-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleChhikara, Komal, Shubham Gupta, Sakshi Saharawat, Shruti Sarkar, and Arnab Chanda. 2023. "Design, Manufacturing, and Trial of a 3D Printed Customized Finger Splint for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis" Rheumato 3, no. 1: 51-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3010004
APA StyleChhikara, K., Gupta, S., Saharawat, S., Sarkar, S., & Chanda, A. (2023). Design, Manufacturing, and Trial of a 3D Printed Customized Finger Splint for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumato, 3(1), 51-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3010004