Antibiotic Stewardship in Silkworms: Navigating the Pros and Cons
Abstract
1. Introduction
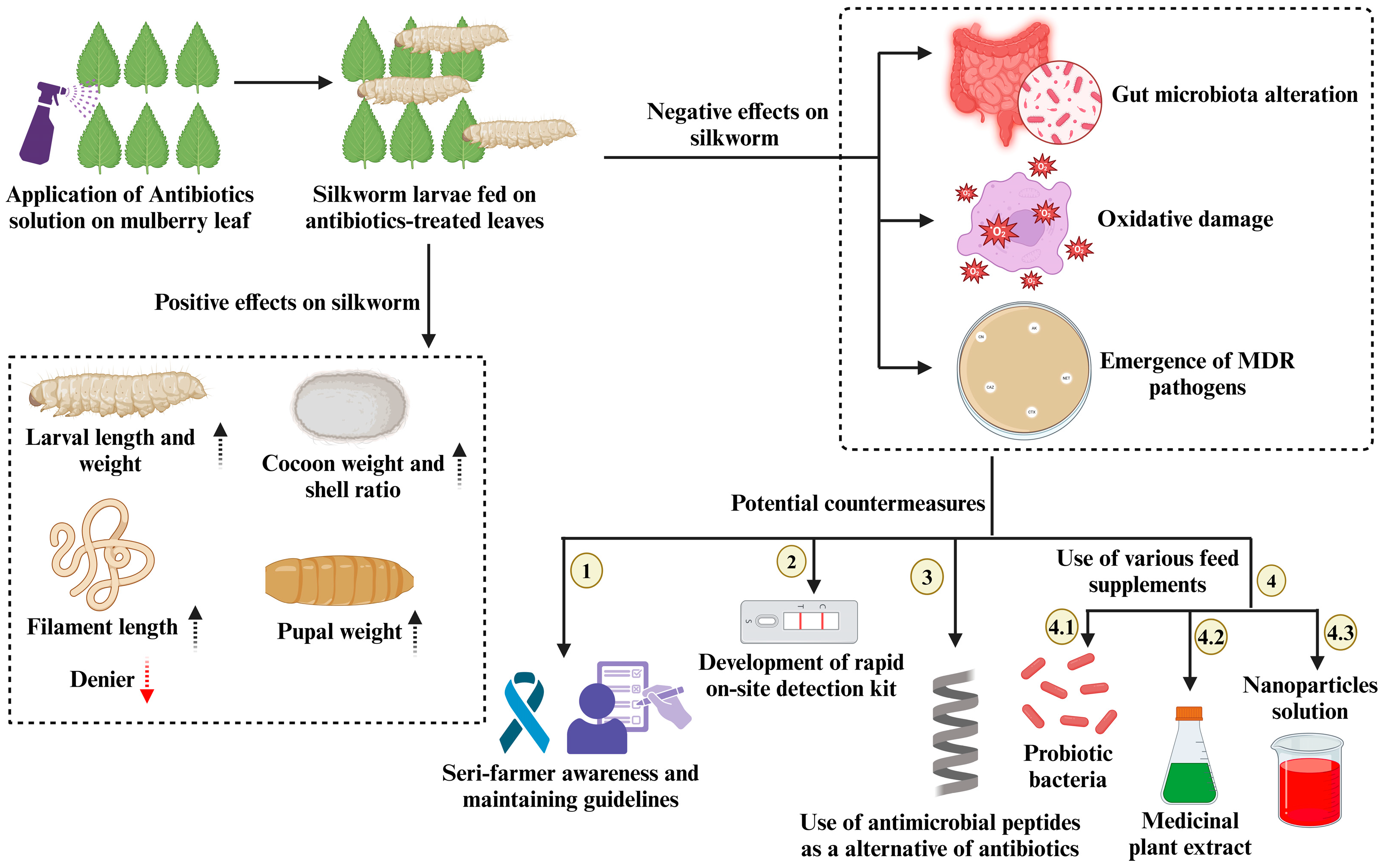
2. Positive Impact of Antibiotics on Silkworm
2.1. Growth Promotion
2.2. Disease Management
3. Negative Impact of Antibiotics in Sericulture
3.1. Oxidative Damage and Gut Microbiota Alterations
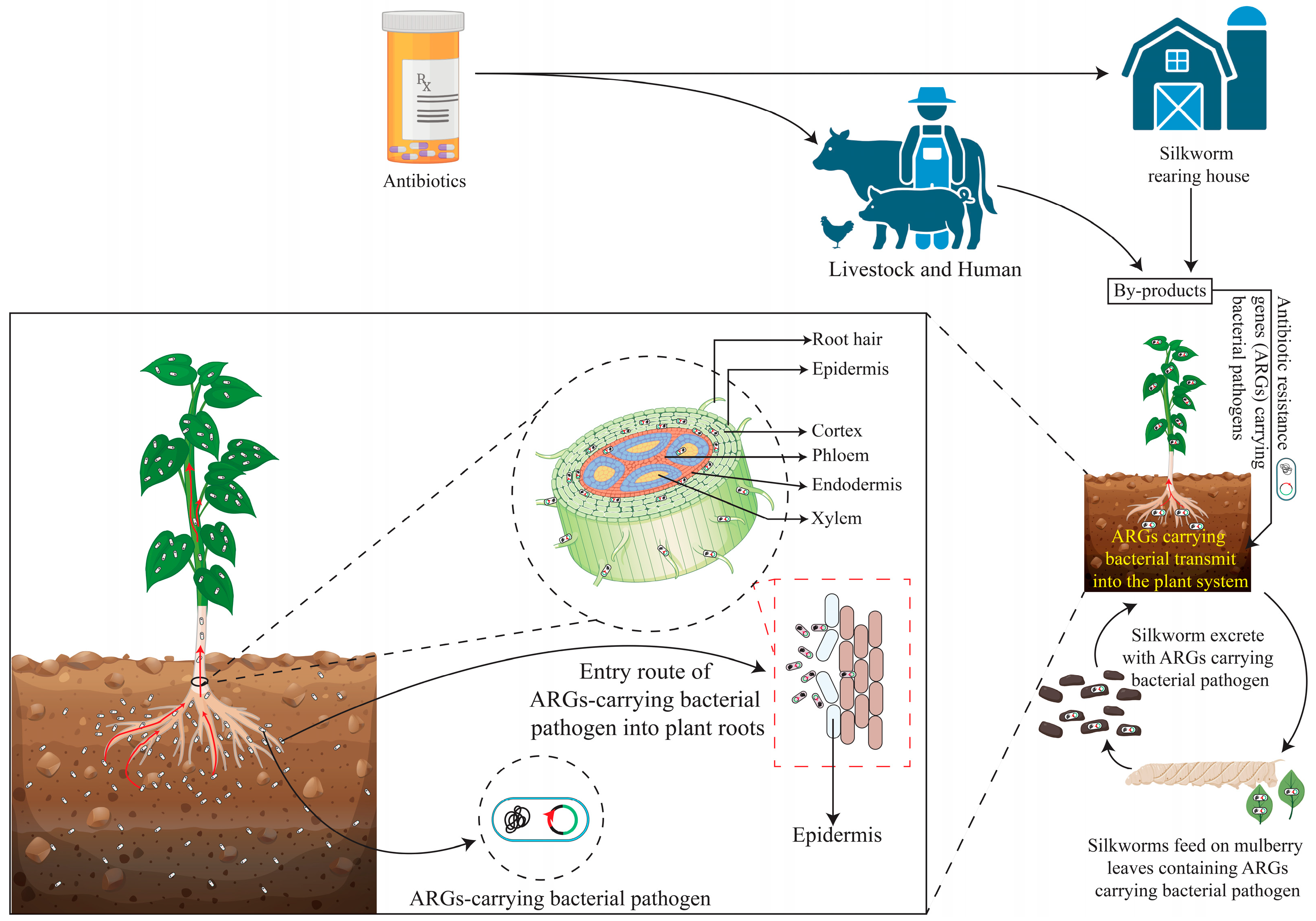
3.2. Emergence of Antibiotic-Resistant Microorganisms
4. Mitigation Strategies for Minimizing the Consequences of Antibiotic Overuse
4.1. Implementing Antibiotic Stewardship Programs (ASPs)
4.2. Enhancing Diagnostic and Waste Management Practices
4.3. Antimicrobial Peptides as an Alternative to Traditional Antibiotics
4.4. Introducing Various Feed Supplementation as Silkworm Growth Enhancer
4.4.1. Probiotic Bacteria as Feed Supplementation
4.4.2. Medicinal Plant Extract as Feed Supplementation
4.4.3. Nanoparticles (NPs) Solution as Feed Supplementation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashraf, H.; Qamar, A. Silkworm Bombyx mori as a Model Organism: A Review. Physiol. Entomol. 2023, 48, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Roy, S.S.; Mandal, P. Investigation of Protein Profile of Nano-Silver Preserved Mulberry Leaves and Silkworm Larvae Fed with the Same Leaves. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 2383–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingade, A.H.; Vijayan, K.; Somasundaram, P.; Srinivasababu, G.K.; Kamble, C.K. A Review of the Implications of Heterozygosity and Inbreeding on Germplasm Biodiversity and Its Conservation in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Insect Sci. 2011, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Deng, J.; Deng, X.; Liu, L.; Zha, X. Metabonomic Analysis of Silkworm Midgut Reveals Differences between the Physiological Effects of an Artificial and Mulberry Leaf Diet. Insects 2023, 14, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadharshini, P.; Mahalingam, C.A.; Shashidhar, K.R. Identification and Characterization of Bacterial Pathogens in Silkworm, Bombyx mori L. Curr. Biot. 2008, 2, 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Muzamil, A.; Tahir, H.M.; Ali, A.; Bhatti, M.F.; Munir, F.; Ijaz, F.; Adnan, M.; Khan, H.A.; Qayyum, K.A. Effect of Amino Acid Fortified Mulberry Leaves on Economic and Biological Traits of Bombyx mori L. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Shi, X.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Z. Nutritional and Functional Components of Mulberry Leaves from Different Varieties: Evaluation of Their Potential as Food Materials. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranya, M.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Murugesh, K. Fortification of Mulberry Leaves with Indigenous Probiotic Bacteria on Larval Growth and Economic Traits of Silkworm (Bombyx mori L.). J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2019, 7, 780–784. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiq, I.; Buhroo, Z.I.; Sahaf, K.A.; Ganie, N.A.; Baqual, M.F. Role of Antibiotics with Reference to Growth and Development of Silkworm (Bombyx mori L.). Pharma Innov. 2021, 10, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiq, I.; Buhroo, Z.I.; Sahaf, K.A.; Ganie, N.A.; Mir, S.A. Impact of Antibiotic Administration on the Growth and Development of Silkworm Bombyx mori L. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 18, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmathulla, V.K.; Nayak, P. Effect of Antibiotic Administration on Growth and Development of Silk Gland in Mulberry Silkworm (Bombyx mori L.). Mun. Ent. Zool. 2017, 12, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanta, M.K.; Saha, A.K.; Saleh, D.K.M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Mannan, K.S.B.; Fakruddin, M. Characterization of Klebsiella Granulomatis Pathogenic to Silkworm, Bombyx mori L. 3 Biotech 2015, 5, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Xu, S.; Xiang, C.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J. The Gut Microbiota of Silkworm Are Altered by Antibiotic Exposure. FEBS Open Bio 2022, 12, 2203–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyamala, M.B.; Bhat, J.V. On the Relationship between Panthothenate Levels and the Growth Response of the Silkworm to Chloromycetin. J. Sci. Industr. Res. 1961, 20, 333–335. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmathulla, V.K.; Nayak, P.; Vindya, G.S.; Himantharaj, M.T.; Rajan, R.K. Effect of Antibiotic (Norfloxacin) Administration on Commercial Characters of New Bivoltine and Cross Breed Hybrid Silkworm (Bombyx mori L.). Int. J. Indust. Entomol. 2003, 7, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdi, S.H.; Rokonuzzaman, M.; Uddin, M.A.; Kamrul, M. The Effects of Amoxicillin, Oxytetracyclin and Doxycyclin on the Growth and Development of Silkworm, Bombyx mori L. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 1316–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Javaid, A.; Hussain, M.; Aftab, K.; Malik, M.F.; Umar, M.; Iqbal, T. Isolation and Characterization of Bacteria Associated with Silkworm Gut under Antibiotic-Treated Larval Feeding. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 84, e249664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, T.O.; Samson, M.V.; Govindaiah, D.R. Effect of Antibiotics on Streptococcus faecalis Infection in the Silkworm Bombyx mori L. Bull. Seric 1995, 6, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Dechu, P.S.; Govindan, R.; Devaiah, M.C.; Swamy, T.K.N. Effect of Antibiotics on Growth and Cocoon Parameters of Silkworm, Bombyx mori L. Mysore J. Agric. Sci. 1997, 31, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, A.N.; Atwal, A.S. Effect of Chloromycetin, Glycine and Molasses on the Growth and Production of Silk by Bombyx mori L. Indian J. Seric 1963, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiq, I.; Buhroo, Z.I.; Sahaf, K.A.; Padder, B.A.; Ganie, N.A.; Mir, A.; Baqual, M.F.; Nagoo, S.A.; Ashraf, S. Effect of Antibiotics on the Rearing Performance of Silkworm Bombyx mori L. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2021, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab Ahamed, C.A.; Chandrakala, M.V.; Maribashetty, V.G.; Raghuraman, R. Impact of Chloramphenicol Administration on Nutritional Efficiency in a Multibivoltine Race of Silkworm Bombyx mori. Entomon 2001, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Thilagavathi, G.; Sabhanayakam, S.; Ganesh Prabu, P. Studies on the Impact of Amoxicillin on Growth Rate and Economic Parameters of Silkworm Bombyx mori (L.) (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae) in Relation to Silk Production. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2013, 5, 3232–3237. [Google Scholar]
- Santha, P.C.; Bhargava, S.K.; Sindagi, S.S.; Kamble, C.K. Bacterial Flacherie of Silkworm, Bombyx mori and It’s Control by the Application of Antibiotics. J. Exp. Zool. 2007, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, J.; Krishnan, N.; Chandra, A.K.; Das, N.K.; Sen, S.K. Reduction of Mortality by Some Antibiotics in Nuclear Polyhedrosis of Silkworm, Bombyx mori L. Sericologia 1998, 38, 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, S.M.; Taha, R.H. Antibiotic (Gentamicin) Impact on Bacterial Flacherrie Disease of Silkworm, Bombyx mori L. Egypt. Acad. J. Biolog. Sci. 2012, 5, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montali, A.; Berini, F.; Brivio, M.F.; Mastore, M.; Saviane, A.; Cappellozza, S.; Marinelli, F.; Tettamanti, G. A Silkworm Infection Model for in Vivo Study of Glycopeptide Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamoto, H.; Kurokawa, K.; Kaito, C.; Kamura, K.; Manitra Razanajatovo, I.; Kusuhara, H.; Santa, T.; Sekimizu, K. Quantitative Evaluation of the Therapeutic Effects of Antibiotics Using Silkworms Infected with Human Pathogenic Microorganisms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xia, X.; Zhao, S.; Shi, M.; Liu, F.; Zhu, Y. The Physiological and Toxicological Effects of Antibiotics on an Interspecies Insect Model. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Lou, M.-M.; Xie, G.-L.; Zhang, G.-Q.; Zhou, X.-P.; Li, B.; Jin, G.-L. Horizontal Gene Transfer in Silkworm, Bombyx mori. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Wei, M.; Li, F.; Wu, C.; Yi, S.; Tian, J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, H. Diffusion and Enrichment of High-Risk Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs) via the Transmission Chain (Mulberry Leave, Guts and Feces of Silkworm, and Soil) in an Ecological Restoration Area of Manganese Mining, China: Role of Heavy Metals. Environ. Res. 2023, 225, 115616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, K.; Nath, U.; Nataraja, K.N.; Chakravortty, D. Root Mediated Uptake of Salmonella Is Different from Phyto-Pathogen and Associated with the Colonization of Edible Organs. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panthee, S.; Paudel, A.; Hamamoto, H.; Sekimizu, K. Advantages of the Silkworm as an Animal Model for Developing Novel Antimicrobial Agents. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryuno, H.; Nigo, F.; Naguro, I.; Sekimizu, K.; Kaito, C. Staphylococcus aureus Aggregation in the Plasma Fraction of Silkworm Hemolymph. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, R.; Chakraborty, J.; Dam, P.; Shaw, S.; Gangopadhyay, D.; Ertas, Y.N.; Mandal, A.K. Development of Aptamer-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles as Probes in Point-of-Care Diagnostic Device for Rapid Detection of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in Bombyx mori L. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 5740–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Some, S.; Sarkar, B.; Biswas, K.; Jana, T.K.; Bhattacharjya, D.; Dam, P.; Mondal, R.; Kumar, A.; Deb, A.K.; Sadat, A. Bio-Molecule Functionalized Rapid One-Pot Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Efficacy toward the Multidrug Resistant (MDR) Gut Bacteria of Silkworms (Bombyx mori). RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 22742–22757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, R.; Dam, P.; Chakraborty, J.; Shaw, S.; Pradhan, S.; Das, S.; Nesa, J.; Meena, K.; Ghati, A.; Chaudhuri, S.D. Genomic Dataset of a Multiple-Drug Resistant Pseudomonas Sp. Strain RAC1 Isolated from a Flacherie Infected Nistari Race of Bombyx mori L. Data Brief 2024, 54, 110293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshwar, J.S.; Ahire, R.D.; Patange, N.R. Sericulturist’s Knowledge Regarding Improved Practices of Sericulture. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 8, 2061–2064. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayakumar, G.; George, P.R.; Jiji, R.S.; Senthilkumar, R.; Mini, M.; Gleeja, V.L. A Scale to Measure the Perception of Veterinarians towards Antimicrobial Use and Resistance. J. Vet. Med. Anim. Sci. 2022, 53, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, R.; Qadiri, B.; Lone, F.A.; Raja, T.A.; Singh, H.; Ahmed, P.; Sharma, R. Role of Sericulture in Achieving Sustainable Development Goals. Probl. Ekorozwoju 2023, 18, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, B.V.; Sudhakar, P.; Kumar, K.K.; Tewary, P. Impact of Bivoltine Sericulture in Improving Socio Economic Conditions of Sericulture Farmers of Madakasira Cluster Through Cluster Promotion Programme (CPP). Res. Bio 2019, 1, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umber, J.K.; Moore, K.A. Assessment of Antibiotic Stewardship Components of Certification Programs in US Animal Agriculture Using the Antibiotic Stewardship Assessment Tool. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 724097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speksnijder, D.C.; Wagenaar, J.A. Reducing Antimicrobial Use in Farm Animals: How to Support Behavioral Change of Veterinarians and Farmers. Anim. Front. 2018, 8, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, R.; Shaw, S.; Mandal, P.; Dam, P.; Mandal, A.K. Recent Advances in the Biosensors Application for Reviving Infectious Disease Management in Silkworm Model: A New Way to Combat Microbial Pathogens. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajam, O.A.; Rafiqui, A.R.; Ayoub, O.B.; Rufaie, Z.H. Boosting Silkworm Health: Enhancing Mulberry Leaves with Plant Extracts for Superior Silk Production. Vigyan Varta 2024, 5, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Ni, Q.; Song, Y.; Wang, R.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Bao, J.; Chen, J.; Long, M. Development of a Nucleic Acid Lateral Flow Strip for Rapid, Visual Detection of Nosema bombycis in Silkworm Eggs. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2019, 164, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Lin, F.; Chen, N.; Yuan, S.; Ding, L.; Gao, L.; Hang, B. Rapid Detection of Bombyx mori Nucleopolyhedrovirus (BmNPV) by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay Combined with a Lateral Flow Dipstick Method. Mol. Cell. Probes. 2015, 29, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, P.; He, Y.; Lin, F.; Pan, Y.; Yu, Q.; Guo, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Yao, Q.; Fu, Y. Rapid Detection of Bombyx mori Bidensovirus by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Based Lateral Flow Dipstick Assay for Field Applications. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2019, 163, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastore, M.; Quadroni, S.; Caramella, S.; Brivio, M.F. The Silkworm as a Source of Natural Antimicrobial Preparations: Efficacy on Various Bacterial Strains. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mba, I.E.; Nweze, E.I. Antimicrobial Peptides Therapy: An Emerging Alternative for Treating Drug-Resistant Bacteria. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2022, 95, 445–463. [Google Scholar]
- Nesa, J.; Jana, S.K.; Sadat, A.; Biswas, K.; Kati, A.; Kaya, O.; Mondal, R.; Dam, P.; Thakur, M.; Kumar, A. Antimicrobial Potential of a Ponericin-like Peptide Isolated from Bombyx mori L. Hemolymph in Response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makwana, P.; Rahul, K.; Ito, K.; Subhadra, B. Diversity of Antimicrobial Peptides in Silkworm. Life 2023, 13, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Lu, Z. Immune Responses to Bacterial and Fungal Infections in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 83, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesa, J.; Sadat, A.; Buccini, D.F.; Kati, A.; Mandal, A.K.; Franco, O.L. Antimicrobial Peptides from Bombyx mori: A Splendid Immune Defense Response in Silkworms. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri-Araghi, S. Synergistic Action of Antimicrobial Peptides and Antibiotics: Current Understanding and Future Directions. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1390765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzolato-Cezar, L.R.; Okuda-Shinagawa, N.M.; Machini, M.T. Combinatory Therapy Antimicrobial Peptide-Antibiotic to Minimize the Ongoing Rise of Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Li, J.; Sun, Z. The Combination of Antibiotic and Non-Antibiotic Compounds Improves Antibiotic Efficacy against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Liu, L.; Deng, J.; Zha, X. Specific Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides from the Black Soldier Fly in the Midgut of Silkworms (Bombyx mori) Regulates Silkworm Immunity. Insects 2023, 14, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.R.; Park, S.W.; Choi, K.H.; Goo, T.W. Production of the BmCecB1 Antimicrobial Peptide in Transgenic Silkworm. Int. J. Indust. Entomol. 2015, 31, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nishida, S.; Ishii, M.; Nishiyama, Y.; Abe, S.; Ono, Y.; Sekimizu, K. Lactobacillus paraplantarum 11-1 Isolated from Rice Bran Pickles Activated Innate Immunity and Improved Survival in a Silkworm Bacterial Infection Model. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Tong, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, S.; Zhang, G.; Dai, F. Pediococcus pentosaceus ZZ61 Enhances Growth Performance and Pathogenic Resistance of Silkworm Bombyx mori by Regulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 402, 130821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suraporn, S.; Sangsuk, W.; Chanhan, P.; Promma, S. Effects of Probiotic Bacteria on the Growth Parameters of the Thai Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Thai J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 48, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Pachiappan, P.; Swathiga, G.; Alagesan, T.; Umapathy, G.; Chozhan, K. Impact of Probiotics on Enzymatic Activity and Economic Traits of Double Hybrid Silkworm, Bombyx mori L. Pharma Innov. 2021, SP-10, 1022–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Bhalchandra, P.M.; Pathade, G.R. Antibacterial and Cholesterol Reducing Lactic Acid Bacteria from Silk Worm(Bombyx mori) Gut Environment—A Review. Nat. Environ. Poll. Technol. 2011, 10, 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, P.S.V.; Bai, R.M. Effect of Ocimum sanctum L. Plant Extract on the Economic Parameters of Silkworm, Bombyx mori L. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2015, 3, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Hajam, O.A.; Rufaie, Z.-H.; Khan, I.L.; Mir, S.A.; Gul, S.; Buhroo, Z.I.; Baqual, M.F. Influence of Plant Extract Fortified Mulberry Leaf on Some Reeling Parameters of Silkworm, Bombyx mori L. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Anim. Husb. 2024, 9, 429–433. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, E.M.; Morsy, G.M.A.; Hashish, M.E. Influence of Some Natural Products of Moringa oleifera (L.) on Some Biochemical and Economical Characters of Infected Mulberry Silkworm, Bombyx mori L. (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). J. Phytopathol. Pest. Manag. 2018, 5, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Shao, H.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y. Reinforced and Ultraviolet Resistant Silks from Silkworms Fed with Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2551–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Jian, M.; Zhang, Y. Feeding Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes or Graphene to Silkworms for Reinforced Silk Fibers. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6695–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Huang, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Dai, F.; Zhao, H. Characterization of Silkworm Larvae Growth and Properties of Silk Fibres after Direct Feeding of Copper or Silver Nanoparticles. Mater. Des. 2017, 129, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, P.G.; Sabhanayakam, S.; Mathivanan, V.; Balasundaram, D. Studies on the Growth Rate of Silkworm Bombyx mori (L.) (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae) Fed with Control and Silver Nanoparticles (AgNps) Treated MR 2 Mulberry Leaves. Int. J. Indust. Entomol. Biomater. 2011, 22, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.; Mondal, R.; Dam, P.; Mandal, A.; Acharya, R.; Manna, S.; Gangopadhyay, D.; Mandal, A.K. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Silk Sericin-Based Silver Nanocomposites for Antibacterial and Food Coating Solutions. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 33068–33079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Some, S.; Bulut, O.; Biswas, K.; Kumar, A.; Roy, A.; Sen, I.K.; Mandal, A.; Franco, O.L.; İnce, İ.A.; Neog, K. Effect of Feed Supplementation with Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Morus indica L. V1 on Bombyx mori L. (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Li, F.; Ma, L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Ni, M.; Hong, F.; Shen, W.; Li, B. Mechanism of Enhanced Bombyx mori Nucleopolyhedrovirus-Resistance by Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Silkworm. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antibiotic | Dosage | Effect on Silkworm | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceftiofur sodium | 0.05%, 0.10%, and 0.15% | The weight of the larvae, silk gland, cocoon, and shell increased, along with filament length, cocoon yield, shell ratio, effective rearing rate (ERR), and raw silk percentage, while the denier decreased. | [21] |
| Oxytetracycline | |||
| Enroflaxcin | |||
| Oxytetracycline | 1%, 2%, and 5% | The weight of the larvae and pupae increased while the mortality rate decreased. | [16] |
| Amoxicillin | |||
| Doxycycline | |||
| Norfloxacin | 50 ppm, and 100 ppm | The weight of the silk gland, larval, shell, and cocoon increased. | [11] |
| Chloramphenicol | 25 ppm, and 50 ppm | Enhanced shell content and silk production. | [22] |
| Amoxicillin | 1%, 3%, and 5% | Enhanced cocoon weight, shell content, filament length, and raw silk percentage. | [23] |
| Antibiotics | MIC (µg/mL) | Targeted Pathogens | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vancomycin | 1 | Staphylococcus aureus | [27] |
| Dalbavancin | 0.5 | ||
| Teicoplanin | 1 | ||
| Kanamycin | 8 | Staphylococcus aureus | [28] |
| Arbekacin | 8 | ||
| Teicoplanin | 0.5 | ||
| Vancomycin | 1 | ||
| Tetracycline | 0.5 | ||
| Minocycline | 0.4 | ||
| 1 | Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | ||
| Chloramphenicol | 16 | Staphylococcus aureus | |
| Flomoxef | 0.4 | ||
| Linezolid | 4 | ||
| Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (ST) | 256 | Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | |
| Imipenem-cilastatin (IPM/CS) | 256 | ||
| Amphotericin B | 3.2 | Candida tropicalis | |
| 1.6 | Candida albicans | ||
| Fluconazole | 1.6 | Candida tropicalis | |
| 0.4 | Candida albicans |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mondal, R.; Das, D.; Mandal, A.K. Antibiotic Stewardship in Silkworms: Navigating the Pros and Cons. Bacteria 2025, 4, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria4010002
Mondal R, Das D, Mandal AK. Antibiotic Stewardship in Silkworms: Navigating the Pros and Cons. Bacteria. 2025; 4(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria4010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleMondal, Rittick, Dipanjan Das, and Amit Kumar Mandal. 2025. "Antibiotic Stewardship in Silkworms: Navigating the Pros and Cons" Bacteria 4, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria4010002
APA StyleMondal, R., Das, D., & Mandal, A. K. (2025). Antibiotic Stewardship in Silkworms: Navigating the Pros and Cons. Bacteria, 4(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria4010002






