Anatomical Variations of Modiolus in Relation with Vestibular and Cranial Morphology on CT Scans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
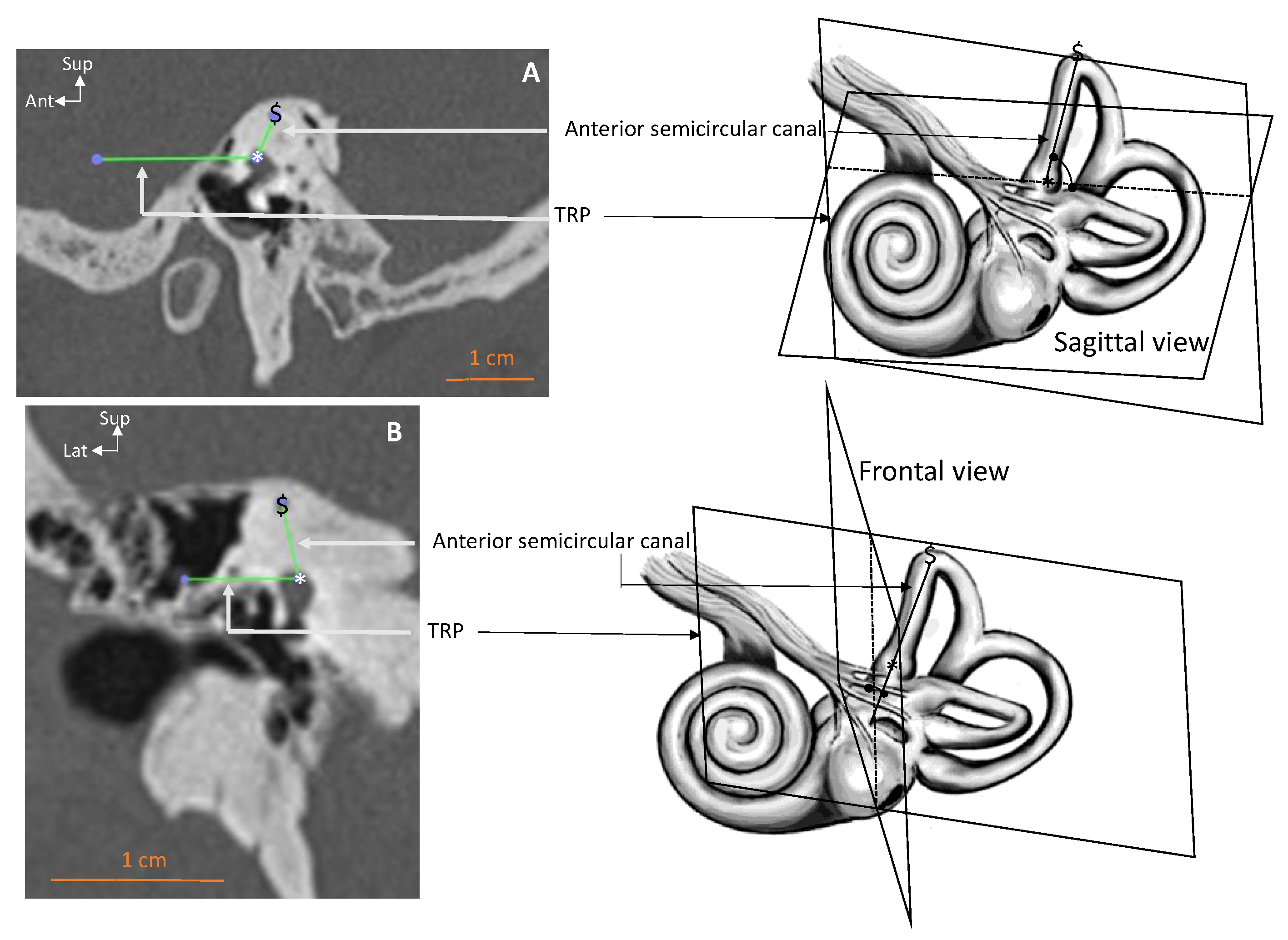
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson Chacko, L.; Schmidbauer, D.T.; Handschuh, S.; Reka, A.; Fritscher, K.D.; Raudaschl, P.; Saba, R.; Handler, M.; Schier, P.P.; Baumgarten, D.; et al. Analysis of Vestibular Labyrinthine Geometry and Variation in the Human Temporal Bone. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Della Santina, C.C.; Potyagaylo, V.; Migliaccio, A.A.; Minor, L.B.; Carey, J.P. Orientation of human semicircular canals measured by three-dimensional multiplanar CT reconstruction. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2005, 6, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanks, R.H.; Curthoys, I.S.; Markham, C.H. Planar relationships of the semicircular canals in man. Acta Otolaryngol. 1975, 8, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rask-Andersen, H.; Liu, W.; Erixon, E.; Kinnefors, A.; Pfaller, K.; Schrott-Fischer, A.; Glueckert, R. Human cochlea: Anatomical characteristics and their relevance for cochlear implantation. Anat. Rec. 2012, 295, 1791–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, B.; Suzuki, J.I.; Bender, M.B. Eye Movements from semicircular canal nerve stimulation in the cat. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1964, 73, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curthoys, I.S.; Blanks, R.H.; Markham, C.H. Semicircular canal functional anatomy in cat, guinea pig and man. Acta Otolaryngol. 1977, 83, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guigou, C.; Schein, A.; Trouilloud, P.; Lalande, A.; Hussain, R.; Grayeli, A.B. Curvilinear Multiplanar Reconstruction to Predict Useful Length and Diameter of Cochlear Lumen for Cochlear Implantation. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, e1207–e1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, M. The length of the organ of Corti in man. Am. J. Anat. 1938, 62, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, E.; Nauwelaers, T.; Lenarz, T.; Hamacher, V.; Kral, A. Variations in microanatomy of the human cochlea. J. Comp. Neurol. 2014, 522, 3245–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pietsch, M.; Schurzig, D.; Salcher, R.; Warnecke, A.; Erfurt, P.; Lenarz, T.; Kral, A. Variations in microanatomy of the human modiolus require individualized cochlear implantation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assenova, K.; Stoyanov, S.; Karchev, T. Anatomic considerations for electrode implantation into the modiolus. Mediterr. J. Otol. 2007, 3, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Guigou, C.; Hussain, R.; Lalande, A.; Bozorg Grayeli, A. Augmented Reality based Transmodiolar Cochlear Implantation. Otol. Neurotol. 2022, 43, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middlebrooks, J.C.; Snyder, R.L. Intraneural stimulation for auditory prosthesis: Modiolar trunk and intracranial stimulation sites. Hear. Res. 2008, 242, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhy Afifi, W.F.; Guigou, C.; Mazalaigue, S.; Camuset, J.P.; Ricolfi, F.; Grayeli, A.B. Navigation-guided transmodiolar approach for auditory nerve implantation via the middle ear in humans. Audiol. Neurotol. 2015, 20, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, M.D. The jugular bulb: Its anatomic and clinical considerations on contemporary otology. Laryngoscope 1977, 87, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao Trong, P.; Beynon, C.; Unterberg, A.; Schneider, T.; Jesser, J. Racial Differences in the Anatomy of the Posterior Fossa: Neurosurgical Considerations. World Neurosurg. 2018, 117, e571–e574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roller, L.A.; Bruce, B.B.; Saindane, A.M. Demographic confounders in volumetric MRI analysis: Is the posterior fossa really small in the adult Chiari 1 malformation? AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhide, A. Study of interpetrous angle in chronic otitis media cases. Indian J. Otolaryngol. 1983, 35, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, H. Topography of the human labyrinth in the temporal bone. Acra Anat. 1965, 60, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, M. Dimensional study of the vestibular apparatus. Laryngoscope 1967, 77, 1806–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Parameter–View | All Ears | Right Ears | Left Ears | RSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervestibular distance (cm) | 7.8 ± 0.38 [6.9–8.7] | - | - | 5 |
| Interpetrous angle (deg.) | 107 ± 3.7 [94–123] | - | - | 3 |
| Modiolus–transverse (deg.) | 52.5 ± 9.74 [30.8–70.3] | 54.7 ± 6.75 * | 50.3 ± 5.56 | 19 |
| Modiolus–sagittal (deg.) | 17.1 ± 8.09 [1–50.5] | 17.4 ± 5.77 | 16.8 ± 5.27 | 47 |
| Lateral SCC–transverse (deg.) | 62.3 ± 7.31 [43.1–75.6] | 63.9 ± 7.39 * | 60.8 ± 9.15 | 11.7 |
| Lateral SCC–frontal (deg.) | 6.8 ± 3.86 [1–17] | 7.1 ± 5.21 | 6.5 ± 2.01 | 57 |
| Posterior SCC–sagittal (deg.) | 142.6 ± 11.3 [118.2–169.4] | 142.2 ± 16.79 | 142.9 ± 10.25 | 8 |
| Posterior SCC–frontal (deg.) | 16.9 ± 7.34 [5–43.5] | 18.4 ± 14.93 * | 15.3 ± 8.64 | 43 |
| Superior SCC–frontal (deg.) | 75.3 ± 9.81 [53.7–107.2] | 76.7 ± 9.61 | 73.9 ± 6.79 | 13 |
| Superior SCC–sagittal (deg.) | 111.4 ± 12.53 [73.7–135.1] | 114.5 ± 7.74 * | 108.4 ± 17.88 | 11 |
| Parameter–Plane | Pearson’s r | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value (Fisher’s r to z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modiolus–Sagittal | 0.686 | 0.432–0.839 | <0.0001 |
| Modiolus–Transverse | 0.580 | 0.277–0.778 | 0.0006 |
| Lateral SCC–Frontal | 0.344 | −0.190–0.627 | 0.0625 |
| Lateral SCC–Transverse | 0.602 | 0.309–0.791 | 0.0003 |
| Posterior SCC–Frontal | 0.622 | 0.377–0.803 | 0.0002 |
| Posterior SCC–Sagittal | 0.694 | 0.446–0.844 | p < 0.0001 |
| Superior SCC–Frontal | 0.239 | −0.133–0.552 | 0.2 |
| Superior SCC–Sagittal | 0.536 | 0.218–0.751 | 0.0019 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guigou, C.; Hussain, R.; Lalande, A.; Bozorg Grayeli, A. Anatomical Variations of Modiolus in Relation with Vestibular and Cranial Morphology on CT Scans. Anatomia 2023, 2, 99-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/anatomia2010009
Guigou C, Hussain R, Lalande A, Bozorg Grayeli A. Anatomical Variations of Modiolus in Relation with Vestibular and Cranial Morphology on CT Scans. Anatomia. 2023; 2(1):99-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/anatomia2010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuigou, Caroline, Raabid Hussain, Alain Lalande, and Alexis Bozorg Grayeli. 2023. "Anatomical Variations of Modiolus in Relation with Vestibular and Cranial Morphology on CT Scans" Anatomia 2, no. 1: 99-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/anatomia2010009
APA StyleGuigou, C., Hussain, R., Lalande, A., & Bozorg Grayeli, A. (2023). Anatomical Variations of Modiolus in Relation with Vestibular and Cranial Morphology on CT Scans. Anatomia, 2(1), 99-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/anatomia2010009







