Lung Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis—From Pathogenesis to Prediction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
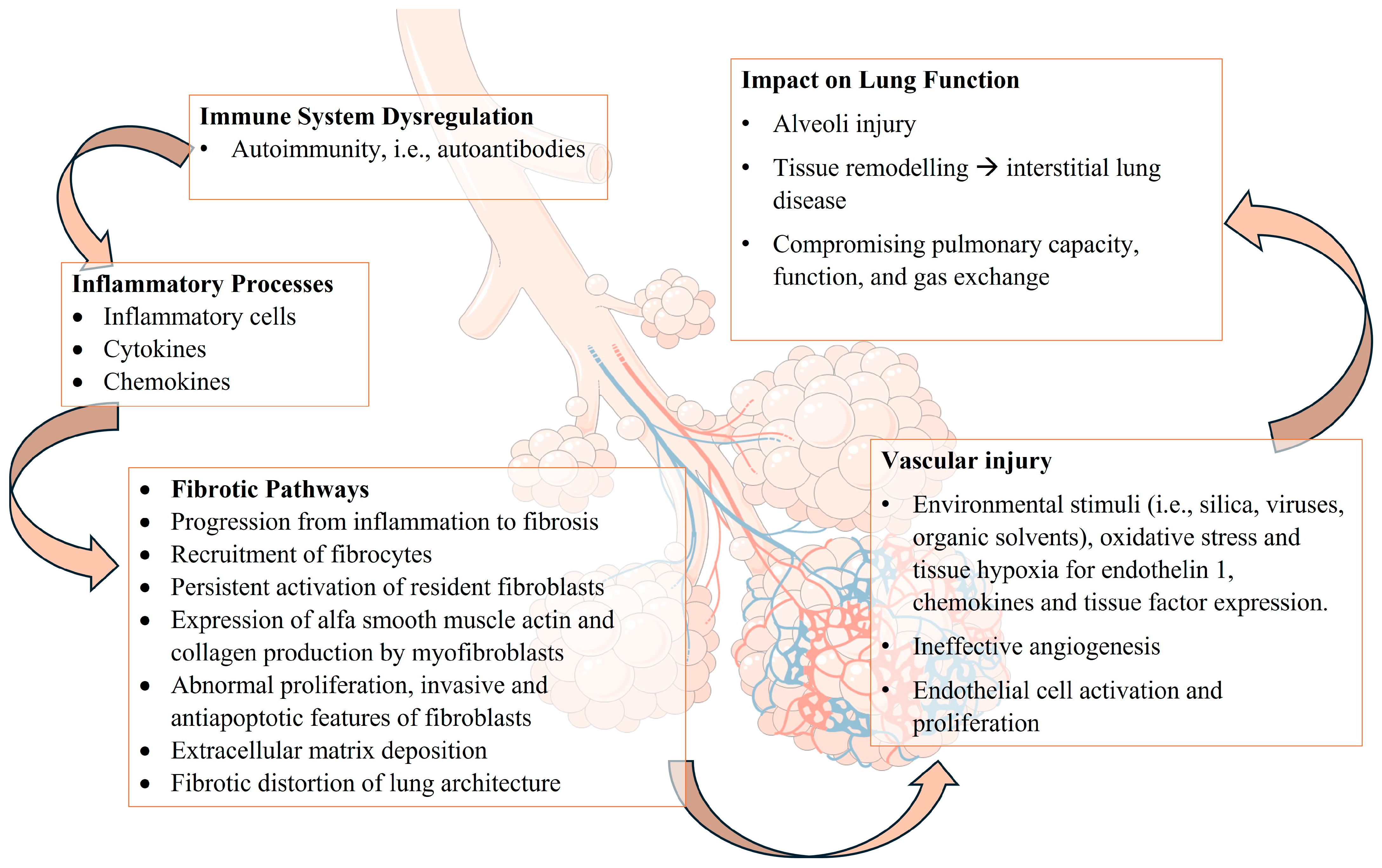
2. Pathogenesis of Lung Involvement in SSc
2.1. Interstitial Lung Involvement
2.2. Mechanisms of Fibrosis in SSc
2.3. Vascular Abnormalities in SSc: Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Hypertension, Endothelial Cell Dysfunction, and Vascular Remodeling
2.4. Immunological and Inflammatory Processes: Autoantibodies, Immune System Dysregulation, Cytokines, and Inflammatory Mediators
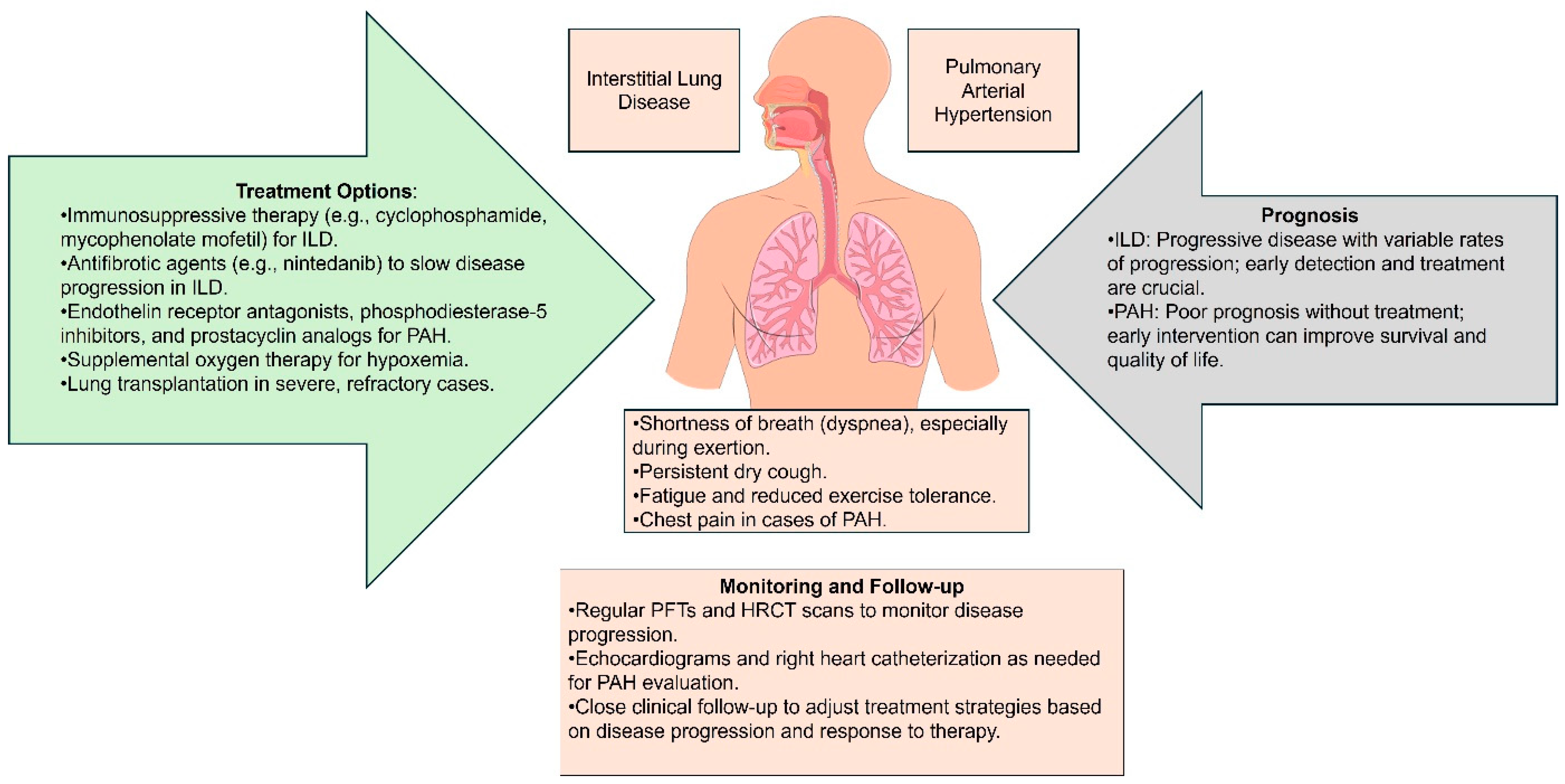
3. Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis
3.1. Symptoms of Lung Involvement in SSc
3.2. Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
3.3. Differential Diagnosis
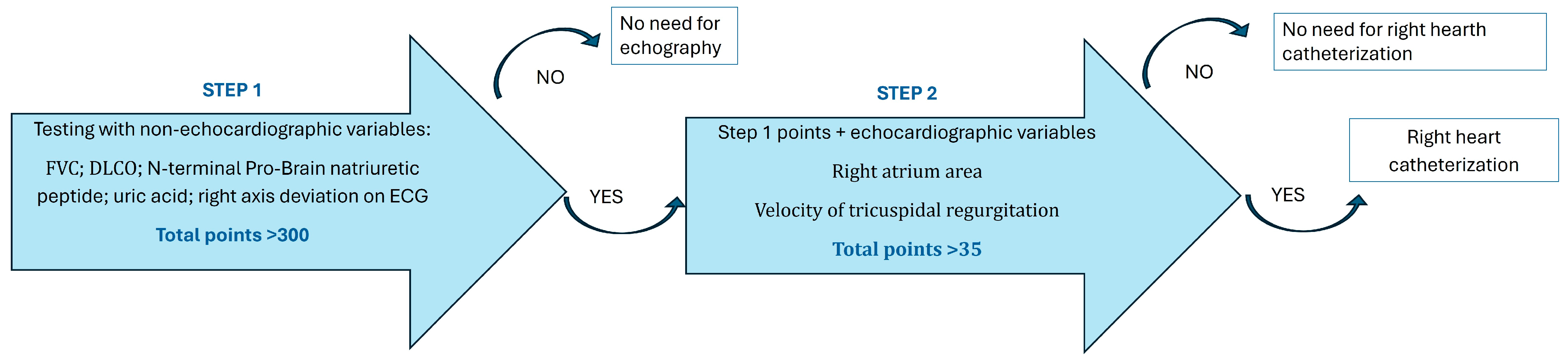
4. Prediction and Monitoring of Lung Involvement
4.1. Risk Factors and Predictive Models: Genetic Predisposition and Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
4.2. Biomarkers for Early Detection: Emerging Biomarkers and Role of Autoantibodies in Prediction
4.3. Monitoring Disease Progression
5. Current and Emerging Therapies for SSc
5.1. Pharmacological Treatment
5.2. Non-Pharmacological Approaches
5.3. Future Directions and Research for SSc Lung Complications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Kang, S.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Gui, X.; Yao, X.; Lu, Q. Global, regional, and national incidence and prevalence of systemic sclerosis. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 248, 109267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perelas, A.; Silver, R.M.; Arrossi, A.V.; Highland, K.B. Systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 304–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, D.; Tashkin, D.P.; Denton, C.P.; Renzoni, E.A.; Desai, S.R.; Varga, J. Etiology, Risk Factors, and Biomarkers in Systemic Sclerosis with Interstitial Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hoffmann-Vold, A.-M.; Allanore, Y.; Alves, M.; Brunborg, C.; Airó, P.; Ananieva, L.P.; Czirják, L.; Guiducci, S.; Hachulla, E.; Li, M.; et al. Progressive interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease in the EUSTAR database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gladue, H.; Altorok, N.; Townsend, W.; McLaughlin, V.; Khanna, D. Screening and diagnostic modalities for connective tissue disease-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension: A systematic review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 43, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Distler, O.; Highland, K.B.; Gahlemann, M.; Azuma, A.; Fischer, A.; Mayes, M.D.; Raghu, G.; Sauter, W.; Girard, M.; Alves, M.; et al. Nintedanib for Systemic Sclerosis–Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, R.; Konstantinidis, I.; O’Sullivan, D.M.; Farber, H.W. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with interstitial lung disease: A tool for early detection. Pulm. Circ. 2022, 12, e12141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacprzak, A.; Tomkowski, W.; Szturmowicz, M. Pulmonary Hypertension in the Course of Interstitial Lung Diseases—A Personalised Approach Is Needed to Identify a Dominant Cause and Provide an Effective Therapy. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.S.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dhont, S.; Zwaenepoel, B.; Vandecasteele, E.; Brusselle, G.; De Pauw, M. Pulmonary hypertension in interstitial lung disease: An area of unmet clinical need. ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8, 00272-2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, A.; Smith, J.; Qureshi, M.R.; Uysal, A.; Patel, K.K.; Herazo-Maya, J.D.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Evolution of pulmonary hypertension in interstitial lung disease: A journey through past, present, and future. Front. Med. 2024, 10, 1306032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, Z.A.; Chandel, A.; King, C.S. Pulmonary Hypertension in Interstitial Lung Disease: Updates in Disease, Diagnosis, and Therapeutics. Cells 2023, 12, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, C.P.; Wells, A.U.; Coghlan, J.G. Major lung complications of systemic sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 511–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafyatis, R. Transforming growth factor β—At the centre of systemic sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumnalieva, R.; Kachakova, D.; Kaneva, R.; Kolarov, Z.; Monov, S. Serum miR-21 and miR-29a expression in systemic sclerosis patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2023, 41, 1688–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Wei, J.; Varga, J. Understanding fibrosis in systemic sclerosis: Shifting paradigms, emerging opportunities. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 8, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nihtyanova, S.I.; Denton, C.P. Scleroderma Lung Involvement, Autoantibodies, and Outcome Prediction: The Confounding Effect of Time. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 404–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassoun, P.M. Lung involvement in systemic sclerosis. Presse Med. 2011, 40, e25–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Muruganandam, M.; Ariza-Hutchinson, A.; Patel, R.A.; Sibbitt, W.L., Jr. Biomarkers in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, ume 16, 4633–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mulkoju, R.; Saka, V.K.; Rajaram, M.; Kumari, R.; Negi, V.S.; Mohapatra, M.M.; Govindaraj, V.; Dwivedi, D.P.; Babu, V.M. Pulmonary Manifestations in Systemic Sclerosis: Hospital-Based Descriptive Study. Cureus 2020, 12, e8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cavazzana, I.; Vojinovic, T.; Airo’, P.; Fredi, M.; Ceribelli, A.; Pedretti, E.; Lazzaroni, M.G.; Garrafa, E.; Franceschini, F. Systemic Sclerosis-Specific Antibodies: Novel and Classical Biomarkers. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 412–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doskaliuk, B.; Zaiats, L.; Yatsyshyn, R.; Gerych, P.; Cherniuk, N.; Zimba, O. Pulmonary involvement in systemic sclerosis: Exploring cellular, genetic and epigenetic mechanisms. Rheumatol. Int. 2020, 40, 1555–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stochmal, A.; Czuwara, J.; Trojanowska, M.; Rudnicka, L. Antinuclear Antibodies in Systemic Sclerosis: An Update. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 58, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedoe, P.; Marges, E.; Hiemstra, P.; Ninaber, M.; Geelhoed, M. Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: Toward Personalized-Medicine-Based Prediction and Drug Screening Models of Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease (SSc-ILD). Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepa, A.; Rachel, R.P.; Ramchandran, P.; Devaraj, U.; Arnold, S.A.; Shobha, V.; D’Souza, G. Pulmonary involvement in systemic sclerosis: A clinical profile. Lung India 2016, 33, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Perelas, A.; Arrossi, A.V.; Highland, K.B. Pulmonary Manifestations of Systemic Sclerosis and Mixed Connective Tissue Disease. Clin. Chest Med. 2019, 40, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, J.J.; Olson, A.L.; Fischer, A.; Bull, T.; Brown, K.K.; Raghu, G. Scleroderma lung disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2013, 22, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Khanna, D.; Distler, O.; Cottin, V.; Brown, K.K.; Chung, L.; Goldin, J.G.; Matteson, E.L.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Walsh, S.L.; McNitt-Gray, M.; et al. Diagnosis and monitoring of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease using high-resolution computed tomography. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2022, 7, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Di Maggio, G.; Confalonieri, P.; Salton, F.; Trotta, L.; Ruggero, L.; Kodric, M.; Geri, P.; Hughes, M.; Bellan, M.; Gilio, M.; et al. Biomarkers in Systemic Sclerosis: An Overview. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 7775–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wijsenbeek, M.; Suzuki, A.; Maher, T.M. Interstitial lung diseases. Lancet 2022, 400, 769–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, Y.; Kuwana, M. Updates on genetics in systemic sclerosis. Inflamm. Regen. 2021, 41, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, C.J.W.; Renzoni, E.A. Genetic predictors of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: A review of recent literature. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 26, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dieudé, P.; Guedj, M.; Wipff, J.; Ruiz, B.; Riemekasten, G.; Airo, P.; Melchers, I.; Hachulla, E.; Cerinic, M.M.; Diot, E.; et al. NLRP1 influences the systemic sclerosis phenotype: A new clue for the contribution of innate immunity in systemic sclerosis-related fibrosing alveolitis pathogenesis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Nagaoka, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Tamatani, T.; Nakanishi, T.; Takigawa, M.; Takehara, K. Serum levels of connective tissue growth factor are elevated in patients with systemic sclerosis: Association with extent of skin sclerosis and severity of pulmonary fibrosis. J. Rheumatol. 2000, 27, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Dieudé, P.; Boileau, C.; Guedj, M.; Avouac, J.; Ruiz, B.; Hachulla, E.; Diot, E.; Cracowski, J.L.; Tiev, K.; Sibilia, J.; et al. Independent replication establishes the CD247 gene as a genetic systemic sclerosis susceptibility factor. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1695–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajda, A.; Walczyk, M.; Dudek, E.; Stypińska, B.; Lewandowska, A.; Romanowska-Próchnicka, K.; Chojnowski, M.; Olesińska, M.; Paradowska-Gorycka, A. Serum microRNAs in Systemic Sclerosis, Associations with Digital Vasculopathy and Lung Involvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Hu, C.; Zhou, J.; Xu, D.; Hou, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, M.; Zeng, X.; et al. MicroRNA-320a: An important regulator in the fibrotic process in interstitial lung disease of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, G.F. Systemic Sclerosis: Environmental Factors. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 2383–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria, A.T.J.; Partouche, L.; Goulabchand, R.; Rivière, S.; Rozier, P.; Bourgier, C.; Le Quellec, A.; Morel, J.; Noël, D.; Guilpain, P. Intriguing Relationships Between Cancer and Systemic Sclerosis: Role of the Immune System and Other Contributors. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9, 3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Truchetet, M.E.; Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. Current Concepts on the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 262–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Coghlan, J.G.; Denton, C.P.; Grünig, E.; Bonderman, D.; Distler, O.; Khanna, D.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Pope, J.E.; Vonk, M.C.; Doelberg, M.; et al. Evidence-based detection of pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis: The DETECT study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Williams, M.H.; Handler, C.E.; Akram, R.; Smith, C.J.; Das, C.; Smee, J.; Nair, D.; Denton, C.P.; Black, C.M.; Coghlan, J.G. Role of N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide (N-TproBNP) in scleroderma-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaya, N.; Nishikimi, T.; Uematsu, M.; Satoh, T.; Kyotani, S.; Sakamaki, F.; Kakishita, M.; Fukushima, K.; Okano, Y.; Nakanishi, N.; et al. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide as a prognostic indicator in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 2000, 102, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, A.I.; Zakynthinos, E.; Kostikas, K.; Kiropoulos, T.; Koutsokera, A.; Ziogas, A.; Koutroumpas, A.; Sakkas, L.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Daniil, Z.D. Serum VEGF levels are related to the presence of pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2009, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, C.A.; Risbano, M.G.; Zhang, L.; Geraci, M.W.; Tuder, R.M.; Collier, D.H.; Bull, T.M. Increased expression of growth differentiation factor-15 in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest 2011, 139, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, P.M.; Oliver, E.; Dorfmuller, P.; Dubois, O.D.; Reed, D.M.; Kirkby, N.S.; Mohamed, N.A.; Perros, F.; Antigny, F.; Fadel, E.; et al. Evidence for the involvement of type I interferon in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eloranta, M.-L.; Franck-Larsson, K.; Lövgren, T.; Kalamajski, S.; Rönnblom, A.; Rubin, K.; Alm, G.V.; Rönnblom, L. Type I interferon system activation and association with disease manifestations in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, M.; Mahler, M.; Pope, J.; You, D.; Tatibouet, S.; Steele, R.; Baron, M.; Canadian Scleroderma Research Group; Fritzler, M. Clinical correlates of CENP-A and CENP-B antibodies in a large cohort of patients with systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitri, G.M.; Lucas, M.; Fertig, N.; Steen, V.D.; Medsger, T.A. A comparison between anti-Th/To–and anticentromere antibody–positive systemic sclerosis patients with limited cutaneous involvement. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.O.; Kill, A.; Kutsche, M.; Guenther, J.; Rose, A.; Tabeling, C.; Witzenrath, M.; Kühl, A.A.; Heidecke, H.; Ghofrani, H.A.; et al. Vascular receptor autoantibodies in pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with systemic sclerosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Launay, D.; Sitbon, O.; Cordier, J.-F.; Hachulla, E.; Mouthon, L.; Gressin, V.; Rottat, L.; Clerson, P.; Simonneau, G.; Humbert, M. Survival and prognostic factors in patients with incident systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension from the french registry. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Ma, L.L.; Wang, L.X. Relationship between serum uric acid levels and ventricular function in patients with idiopathic pulmonary hypertension. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2013, 18, e37–e39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galiè, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Hoeper, M. 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 67–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal-Bielecka, O.; Fransen, J.; Avouac, J.; Becker, M.; Kulak, A.; Allanore, Y.; Distler, O.; Clements, P.; Cutolo, M.; Czirjak, L.; et al. Update of EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, J.K.; Quah, E.; Earnshaw, B.; Amoasii, C.; Mudawi, T.; Spencer, L.G. Does methotrexate cause progressive fibrotic interstitial lung disease? A systematic review. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashkin, D.P.; Elashoff, R.; Clements, P.J.; Goldin, J.; Roth, M.D.; Furst, D.E.; Arriola, E.; Silver, R.; Strange, C.; Bolster, M.; et al. Cyclophosphamide versus Placebo in Scleroderma Lung Disease. New Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2655–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashkin, D.P.; Roth, M.D.; Clements, P.J.; Furst, D.E.; Khanna, D.; Kleerup, E.C.; Goldin, J.; Arriola, E.; Volkmann, E.R.; Kafaja, S.; et al. Mycophenolate mofetil versus oral cyclophosphamide in scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease (SLS II): A randomised controlled, double-blind, parallel group trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funatogawa, T.; Narita, Y.; Tamura, A.; Mii, K.; Sugitani, Y.; Uchida, T. Use of mycophenolate mofetil for systemic sclerosis and systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: Information from a Japanese hospital claims database. Mod. Rheumatol. 2022, 32, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyles, R.K.; Ellis, R.W.; Wellsbury, J.; Lees, B.; Newlands, P.; Goh, N.S.L.; Roberts, C.; Desai, S.; Herrick, A.L.; McHugh, N.J.; et al. A multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of corticosteroids and intravenous cyclophosphamide followed by oral azathioprine for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 3962–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, R.P.; Ray, A.; Chatterjee, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Sircar, G.; Ghosh, P. Rituximab in the treatment of systemic sclerosis–related interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, T.M.; Tudor, V.A.; Saunders, P.; Gibbons, M.A.; Fletcher, S.V.; Denton, C.P.; Hoyles, R.K.; Parfrey, H.; Renzoni, E.A.; Kokosi, M.; et al. Rituximab versus intravenous cyclophosphamide in patients with connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease in the UK (RECITAL): A double-blind, double-dummy, randomised, controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, Y. Review of tocilizumab in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Biol. Targets Ther. 2008, 2, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Roofeh, D.; Lin, C.J.F.; Goldin, J.; Kim, G.H.; Furst, D.E.; Denton, C.P.; Huang, S.; Khanna, D.; focuSSced Investigators. Tocilizumab Prevents Progression of Early Systemic Sclerosis–Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Khanna, D.; Denton, C.P.; Jahreis, A.; van Laar, J.M.; Frech, T.M.; Anderson, M.E.; Baron, M.; Chung, L.; Fierlbeck, G.; Lakshminarayanan, S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of subcutaneous tocilizumab in adults with systemic sclerosis (faSScinate): A phase 2, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 2630–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, D.; Lin, C.J.F.; Furst, D.E.; Goldin, J.; Kim, G.; Kuwana, M.; Allanore, Y.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Distler, O.; Shima, Y.; et al. Tocilizumab in systemic sclerosis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuster, S.; Jordan, S.; Elhai, M.; Held, U.; Steigmiller, K.; Bruni, C.; Cacciapaglia, F.; Vettori, S.; Siegert, E.; Rednic, S.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of tocilizumab in patients with systemic sclerosis: A propensity score matched controlled observational study of the EUSTAR cohort. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boleto, G.; Avouac, J.; Allanore, Y. The role of antifibrotic therapies in the treatment of systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2022, 14, 1759720X211066686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pope, J.E.; Denton, C.P.; Johnson, S.R.; Fernandez-Codina, A.; Hudson, M.; Nevskaya, T. State-of-the-art evidence in the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maron, B.A. Revised Definition of Pulmonary Hypertension and Approach to Management: A Clinical Primer. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e029024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardinge, M.; Annandale, J.; Bourne, S.; Cooper, B.; Evans, A.; Freeman, D.; Green, A.; Hippolyte, S.; Knowles, V.; MacNee, W.; et al. British Thoracic Society guidelines for home oxygen use in adults: Accredited by NICE. Thorax 2015, 70, i1–i43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutrition and Pulmonary Fibrosis. American Lung Association. Available online: https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/pulmonary-fibrosis/patients/living-well-with-pulmonary-fibrosis/nutrition#:~:text=Eating%20a%20bland%20diet%2C%20made,BRAT%20diet)%2C%20can%20help (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Biney, I.; Dudney, T.; Goldman, M.; Carder, L.; Schriver, E. Successful Use of Hyperbaric Oxygen as Adjunctive Therapy for a Nonhealing Venous Ulcer in a Patient with Systemic Sclerosis and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Pulmonol. 2020, 2020, 4750375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugii, N.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Maddali-Bongi, S. Clinical significance and usefulness of rehabilitation for systemic sclerosis. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2018, 3, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.L.; Poole, J.L.; Chen, Y.T.; Lescoat, A.; Khanna, D. Rehabilitation Interventions in Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Future Directions. Arthritis Care Res. 2022, 74, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohdziewicz, A.; Pawlik, K.K.; Maciejewska, M.; Sikora, M.; Alda-Malicka, R.; Czuwara, J.; Rudnicka, L. Future Treatment Options in Systemic Sclerosis—Potential Targets and Ongoing Clinical Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
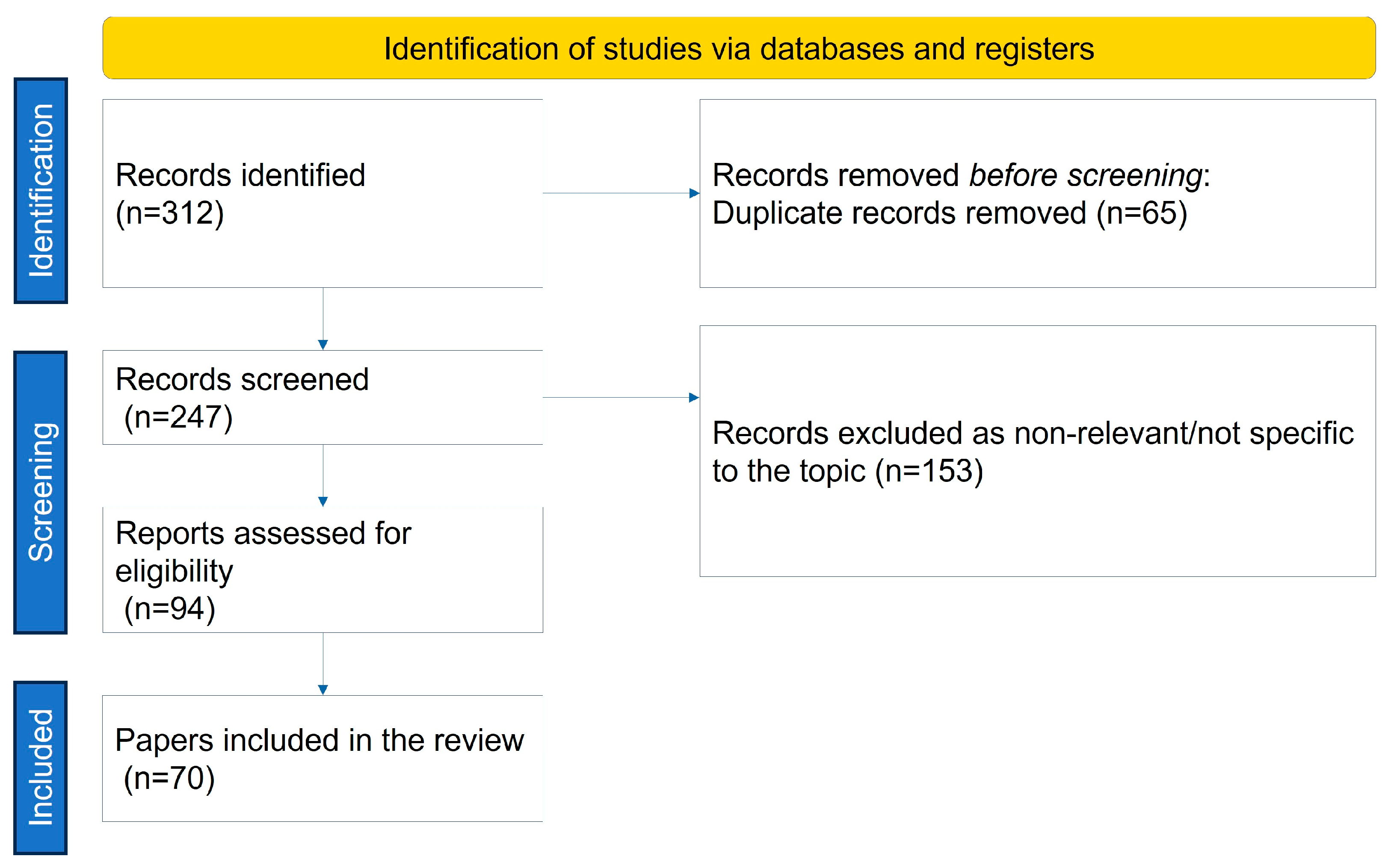
| Group of Factors | Examples |
|---|---|
| Genetic | IRF5, STAT4, CD247, CD226, NLRP1, IRAK1, CTGF, HLA DRB1, HLA-DQB1 |
| Environmental and lifestyle | Silica, silicone breast implants Vinyl chloride, trichloroethylene, benzene, toluene Bleomycin, L-5-hydroxytryptophan Rapeseed oil Epoxy resins Infectious: CMV, EBV, parvovirus B19, retroviruses Neoplastic: lung cancer, breast cancer, esophageal cancer, hematological malignancies |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaouri, I.E.; Bakopoulou, K.; Padjen, I.; Lazarov, V.; Sdralis, P.P.; Velikova, T.; Shumnalieva, R. Lung Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis—From Pathogenesis to Prediction. Sclerosis 2024, 2, 199-216. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis2030014
Kaouri IE, Bakopoulou K, Padjen I, Lazarov V, Sdralis PP, Velikova T, Shumnalieva R. Lung Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis—From Pathogenesis to Prediction. Sclerosis. 2024; 2(3):199-216. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis2030014
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaouri, Issa El, Konstantina Bakopoulou, Ivan Padjen, Velik Lazarov, Paraskevas Panagiotis Sdralis, Tsvetelina Velikova, and Russka Shumnalieva. 2024. "Lung Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis—From Pathogenesis to Prediction" Sclerosis 2, no. 3: 199-216. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis2030014
APA StyleKaouri, I. E., Bakopoulou, K., Padjen, I., Lazarov, V., Sdralis, P. P., Velikova, T., & Shumnalieva, R. (2024). Lung Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis—From Pathogenesis to Prediction. Sclerosis, 2(3), 199-216. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis2030014







