How Urban-Tolerant Are They? Testing Prey–Capture Behavior of Introduced Jorō Spiders (Trichonephila clavata) Next to Busy Roads
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Road Selection
2.2. Stimulus Procedure
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bradley, C.A.; Altizer, S. Urbanization and the ecology of wildlife diseases. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proppe, D.S.; Sturdy, C.B.; St Clair, C.C. Anthropogenic noise decreases urban songbird diversity and may contribute to homogenization. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahirel, M.; De Cock, M.; Vantieghem, P.; Bonte, D. Urbanization-driven changes in web building and body size in an orb web spider. J. Anim. Ecol. 2019, 88, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, H.; Lill, A.; Wong, B.B.M. Behavioural responses of wildlife to urban environments. Biol. Rev. 2013, 88, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquette, C.A.; Loss, S.R.; Hovick, T.J. A meta-analysis of the influence of anthropogenic noise on terrestrial wildlife communication strategies. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 58, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleist, N.J.; Guralnick, R.P.; Cruz, A.; Lowry, C.A.; Francis, C.D. Chronic anthropogenic noise disrupts glucocorticoid signaling and has multiple effects on fitness in an avian community. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E648–E657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, G.; McKenna, M.F.; Angeloni, L.M.; Crooks, K.R.; Fristrup, K.M.; Brown, E.; Warner, K.A.; Nelson, M.D.; White, C.; Briggs, J.; et al. A synthesis of two decades of research documenting the effects of noise on wildlife. Biol. Rev. 2016, 91, 982–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, B.X.M.; Carrera-Trevino, R.; Hobson, K.A. Mortality of monarch butterflies (Danaus plexippus) at two highway crossing “hotspots” during autumn migration in northeast Mexico. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keilsohn, W.; Narango, D.L.; Tallamy, D.W. Roadside habitat impacts insect traffic mortality. J. Insect Conserv. 2018, 22, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, D.D.; McKenna, K.M.; Malcolm, S.B.; Berenbaum, M.R. Mortality of lepidoptera along roadways in central Illinois. J. Lepid. Soc. 2001, 55, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel-Ferreira, J.; Berggren, A.; Bommarco, R.; Wissman, J.; Ockinger, E. Bumblebee queen mortality along roads increase with traffic. Biol. Conserv. 2022, 272, 109643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classen-Rodríguez, L.; Tinghitella, R.; Fowler-Finn, K. Anthropogenic noise affects insect and arachnid behavior, thus changing interactions within and between species. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2021, 47, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.K.; Schroeder, H.; Yeager, I.; Pearce, J. Effects of simulated highway noise on heart rates of larval monarch butterflies, Danaus plexippus: Implications for roadside habitat suitability. Biol. Lett. 2018, 14, 20180018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.S.; Agnew, L.; Meyer, R.; Sikkink, K.L.; Oberhauser, K.S.; Borer, E.T.; Snell-Rood, E.C. Traffic influences nutritional quality of roadside plants for monarch caterpillars. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orci, K.M.; Petróczki, K.; Barta, Z. Instantaneous song modification in response to fluctuating traffic noise in the tree cricket Oecanthus Pellucens. Anim. Behav. 2016, 112, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raboin, M.; Elias, D.O. Anthropogenic noise and the bioacoustics of terrestrial invertebrates. J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222, jeb178749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoebeke, E.R.; Huffmaster, W.; Freeman, B.J. Nephila clavata L Koch, the Jorō Spider of East Asia, newly recorded from North America (Araneae: Nephilidae). PeerJ 2015, 3, e763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, A.; Deitsch, J.F.; Nelsen, D.R.; Sitvarin, M.I.; Coyle, D.R. The Jorō spider (Trichonephila clavata) in the southeastern U.S.: An opportunity for research and a call for reasonable journalism. Biol. Invasions 2023, 25, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, A.K.; Frick, B.L. Physiological evaluation of newly invasive jorō spiders (Trichonephila clavata) in the southeastern USA compared to their naturalized cousin, Trichonephila Clavipes. Physiol. Entomol. 2022, 2022, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelsen, D.R.; Corbit, A.G.; Chuang, A.; Deitsch, J.F.; Sitvarin, M.I.; Coyle, D.R. Veni, vidi, vici? Future spread and ecological impacts of a rapidly expanding invasive predator population. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, E.C.; Wilder, S.M.; Hochuli, D.F. Life history of an urban-tolerant spider shows resilience to anthropogenic habitat disturbance. J. Urban Ecol. 2017, 3, jux004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripp, J.; Eldakar, O.T.; Gallup, A.C.; Arena, P.T. The successful exploitation of urban environments by the golden silk spider, Nephila clavipes (Araneae, Nephilidae). J. Urban Ecol. 2018, 4, juy005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabanal, B.; Achondo, M.J.M.; Alviola, P.; Gamalo, L.E.; Responte, M. Diversity of spiders (Araneae) in the anthropic land covers of Davao City, Philippines. J. Anim. Divers. 2022, 4, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.K.; Anerao, A. Startle responses of jorō spiders (Trichonephila clavata) to artificial disturbance. Arthropoda 2023, 2023, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.S.; Hesselberg, T. The use of tuning forks for studying behavioural responses in orb web spiders. Insects 2022, 13, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, P.A.; Dyakonova, V.; Rillich, J.; Schildberger, K. Octopamine and experience-dependent modulation of aggression in crickets. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.E.; Pervin, E.; Graham, S.L.; Henry, M.; Fahrig, L. Abundance of aerially-dispersing spiders declines with increasing road traffic. Ecoscience 2019, 26, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessman, B.J.; Hays, M.; Agpawa, E.; Hebets, E.A. Urbanization affects web abundance and aggregation of a funnel-weaving spider, Agelenopsis pennsylvanica (Agelenidae). Urban Ecosyst. 2023, 26, 1275–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolfa, M.A.; Barth, F.G. Vibrations in the orb web of the spider Nephila clavipes: Cues for discrimination and orientation. J. Comp. Physiol. A-Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 1996, 179, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackledge, T.A. Prey capture in orb weaving spiders: Are we using the best metric? J. Arachnol. 2011, 39, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabarczyk, E.E.; Querejeta, M.; Tillman, P.G.; Wallace, R.D.; Barnes, B.F.; Meinecke, C.D.; Villari, C.; Gandhi, K.J.K.; LaForest, J.; Elliott, M.; et al. DNA metabarcoding analysis of three material types to reveal Jorō spider (Trichonephila clavata) trophic interactions and web capture. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1177446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
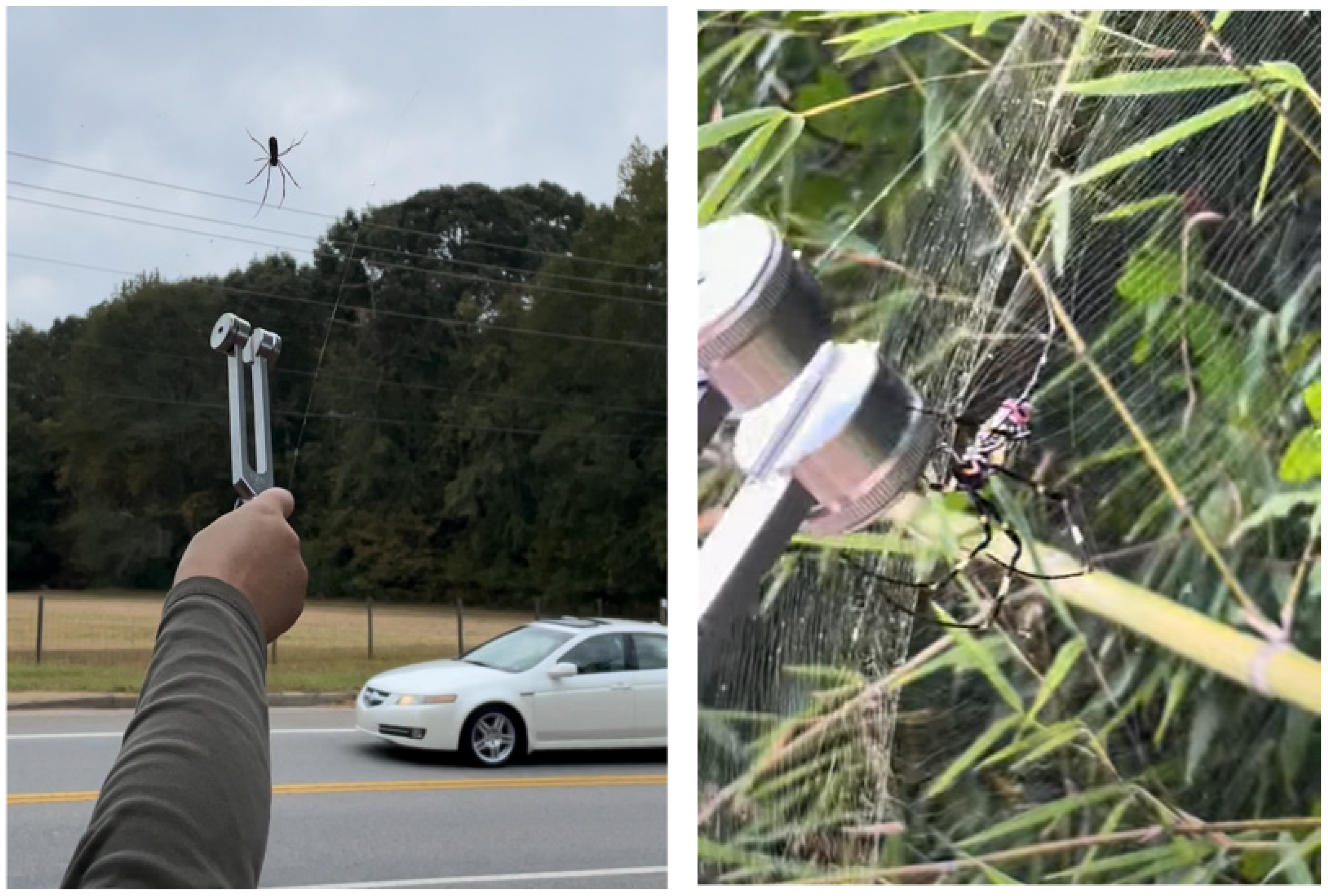



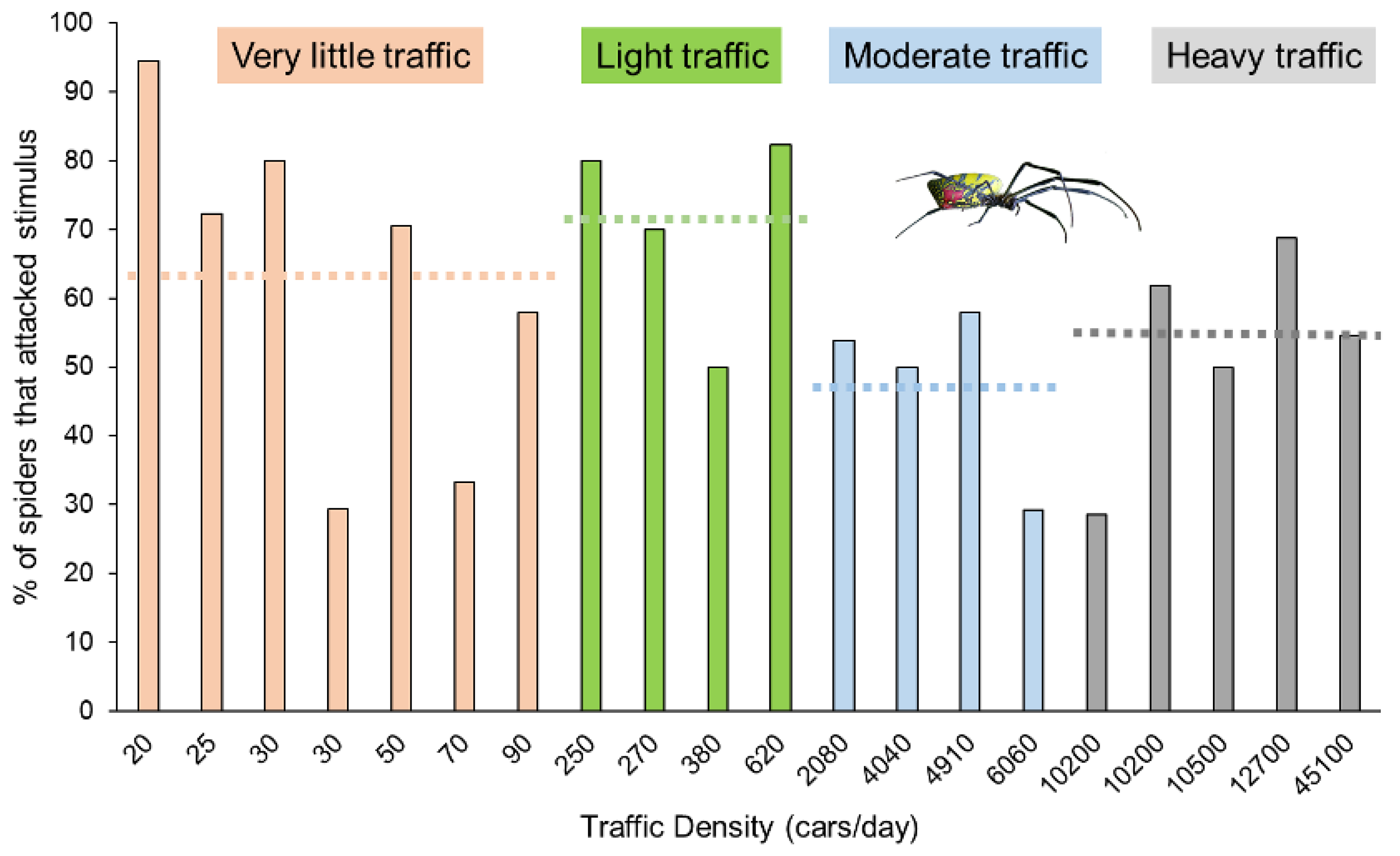
| Road Name | County | Traffic Density | Density Category | # Attack | # Nothing | # Retreat | Total Trials | % Attack | Ave. Spider Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marshall Store Rd. | Oconee | 20 | 1 | 17 | 1 | 0 | 18 | 94.4 | 0.33 |
| Rose Creek Dr. | Oconee | 25 | 1 | 13 | 5 | 0 | 18 | 72.2 | 0.55 |
| Freeman Creek Rd. | Oconee | 30 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 2 | 15 | 80.0 | 0.37 |
| JT Elder Rd. | Oconee | 30 | 1 | 5 | 11 | 1 | 17 | 29.4 | 0.34 |
| Hardigree Bell Rd. | Oconee | 50 | 1 | 12 | 4 | 1 | 17 | 70.6 | 0.23 |
| Old Farmington Rd. | Oconee | 70 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 3 | 15 | 33.3 | 0.66 |
| Old Ila Rd. | Madison | 90 | 1 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 19 | 57.9 | 0.40 |
| Antioch Church Rd. | Oconee | 250 | 2 | 16 | 3 | 1 | 20 | 80.0 | 0.42 |
| Mayne Mill Rd. | Oconee | 270 | 2 | 14 | 4 | 2 | 20 | 70.0 | 0.40 |
| Oliver Bridge Rd. | Oconee | 380 | 2 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 18 | 50.0 | 0.53 |
| Wesley Chapel Rd. | Madison | 620 | 2 | 14 | 1 | 2 | 17 | 82.4 | 0.36 |
| Colham Ferry Rd. | Oconee | 2080 | 3 | 14 | 11 | 1 | 26 | 53.8 | 0.64 |
| South Main St. Watkinsville | Oconee | 4040 | 3 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 18 | 50.0 | 0.35 |
| Greensboro Hwy. | Oconee | 4910 | 3 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 19 | 57.9 | 0.58 |
| E Whitehall Rd. | Clarke | 6060 | 3 | 7 | 11 | 6 | 24 | 29.2 | 0.38 |
| S. Milledge Rd. | Clarke | 10,200 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 28.6 | 0.22 |
| US 441 | Oconee | 10,200 | 4 | 13 | 7 | 1 | 21 | 61.9 | 0.52 |
| Mitchell Bridge Rd. | Clarke | 10,500 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 12 | 50.0 | 0.45 |
| Experiment Stn Rd. | Oconee | 12,700 | 4 | 11 | 5 | 0 | 16 | 68.8 | 0.50 |
| Athens Perimeter/10 Loop | Clarke | 45,100 | 4 | 12 | 6 | 4 | 22 | 54.5 | 0.28 |
| Grand Total | 213 | 109 | 37 | 359 | 59.3 | 0.43 |
| Traffic Density | Attack | Nothing | Retreat | No Attack | Grand Total | % Attack |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1—Very little a | 75 | 35 | 9 | 44 | 119 | 63.0 |
| 2—Light a | 53 | 15 | 7 | 22 | 75 | 70.7 |
| 3—Moderate b | 41 | 35 | 11 | 46 | 87 | 47.1 |
| 4—Heavy b | 44 | 24 | 10 | 34 | 78 | 56.4 |
| Grand Total | 213 | 109 | 37 | 146 | 359 |
| Predictor | Estimate | SE | Wald | Lower 95% CL | Upper 95% CL | p |
| Spider Mass | 0.688 | 0.442 | 2.429 | −1.177 | 1.554 | 0.1191 |
| Traffic Volume | −0.106 | 0.044 | 5.592 | −0.193 | −0.018 | 0.0180 |
| Predictor | Estimate | SE | Wald | Lower 95% CL | Upper 95% CL | p |
| Spider Mass | −0.828 | 0.450 | 3.391 | −1.709 | 0.053 | 0.0656 |
| Volume Category | −0.498 | 0.212 | 5.534 | −0.914 | −0.083 | 0.0187 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davis, A.K.; Stewart, K.; Phelan, C.; Schultz, A. How Urban-Tolerant Are They? Testing Prey–Capture Behavior of Introduced Jorō Spiders (Trichonephila clavata) Next to Busy Roads. Arthropoda 2024, 2, 55-65. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda2010004
Davis AK, Stewart K, Phelan C, Schultz A. How Urban-Tolerant Are They? Testing Prey–Capture Behavior of Introduced Jorō Spiders (Trichonephila clavata) Next to Busy Roads. Arthropoda. 2024; 2(1):55-65. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda2010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavis, Andrew K., Kade Stewart, Caitlin Phelan, and Alexa Schultz. 2024. "How Urban-Tolerant Are They? Testing Prey–Capture Behavior of Introduced Jorō Spiders (Trichonephila clavata) Next to Busy Roads" Arthropoda 2, no. 1: 55-65. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda2010004
APA StyleDavis, A. K., Stewart, K., Phelan, C., & Schultz, A. (2024). How Urban-Tolerant Are They? Testing Prey–Capture Behavior of Introduced Jorō Spiders (Trichonephila clavata) Next to Busy Roads. Arthropoda, 2(1), 55-65. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda2010004






