Lyn Kinase Structure, Regulation, and Involvement in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Mini Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
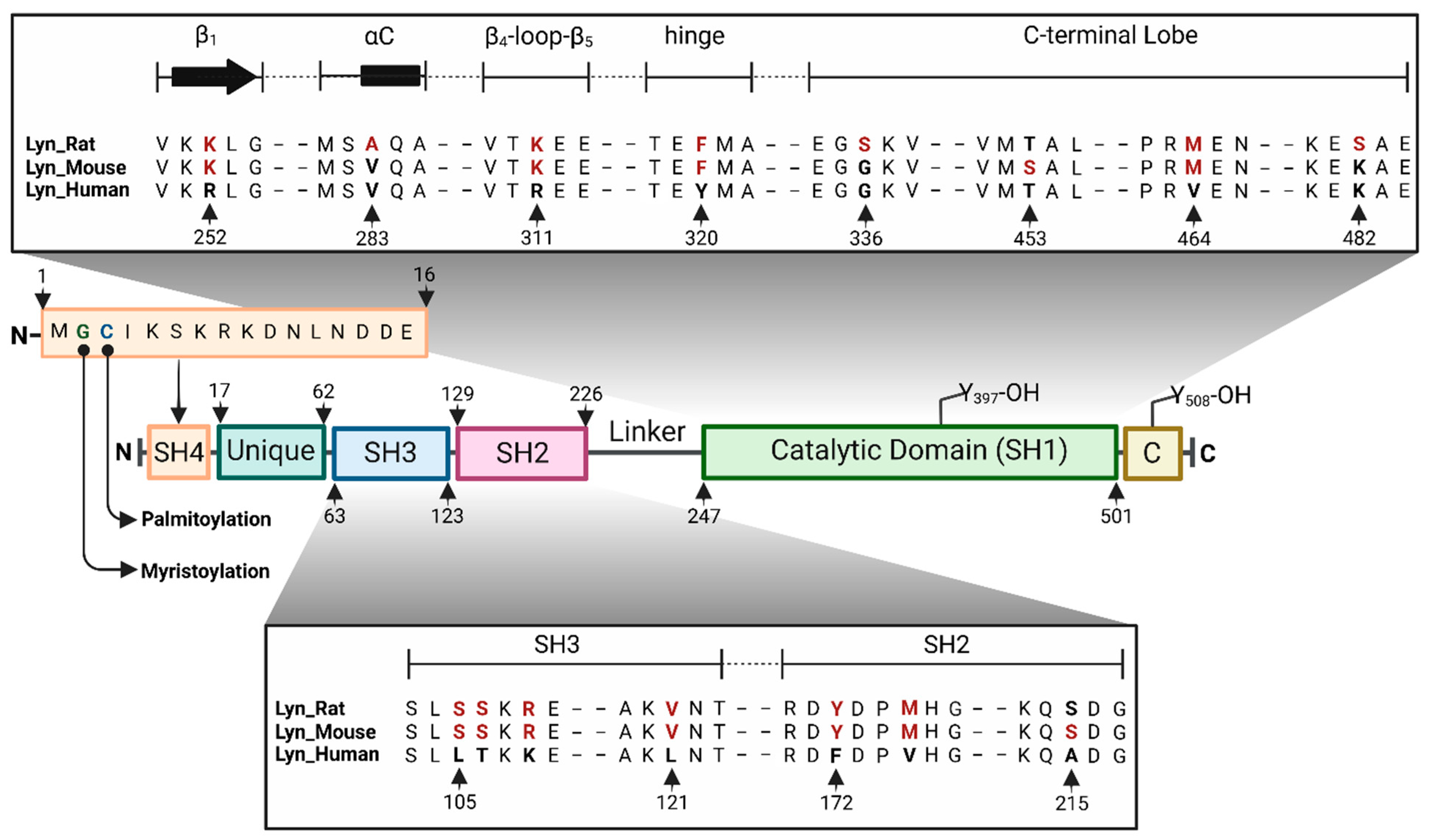
2. Lyn Kinase Structure
2.1. SH4 and Unique Domains
2.2. SH3 Domain
2.3. SH2 Domain
2.4. Catalytic (SH1) Domain
3. Regulation of the Lyn Kinase Activity
4. Lyn Kinase Function-Itim/Itam Phosphorylation
4.1. Phosphorylation of ITIM Motifs
4.2. Phosphorylation of ITAM Motifs
5. Lyn Kinase Binding Partners
6. Lyn Kinase in Neurodegenerative Diseases
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, M.T.; Cooper, J.A. Regulation, Substrates and Functions of Src. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 1996, 1287, 121–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, T.L.; Bolen, J.B.; Ihle, J.N. Hematopoietic Cells Express Two Forms of Lyn Kinase Differing by 21 Amino Acids in the Amino Terminus. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 2391–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanashi, Y.; Mori, S.; Yoshida, M.; Kishimoto, T.; Inoue, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Toyoshima, K. Selective Expression of a Protein-Tyrosine Kinase, P56lyn, in Hematopoietic Cells and Association with Production of Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus Type I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 6538–6542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umemori, H.; Wanaka, A.; Kato, H.; Takeuchi, M.; Tohyama, M.; Yamamoto, T. Specific Expressions of Fyn and Lyn, Lymphocyte Antigen Receptor-Associated Tyrosine Kinases, in the Central Nervous System. Mol. Brain Res. 1992, 16, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mkaddem, S.B.; Murua, A.; Flament, H.; Titeca-Beauport, D.; Bounaix, C.; Danelli, L.; Launay, P.; Benhamou, M.; Blank, U.; Daugas, E.; et al. Lyn and Fyn Function as Molecular Switches That Control Immunoreceptors to Direct Homeostasis or Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brodie, E.J.; Infantino, S.; Low, M.S.Y.; Tarlinton, D.M. Lyn, Lupus, and (B) Lymphocytes, a Lesson on the Critical Balance of Kinase Signaling in Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingley, E. Functions of the Lyn Tyrosine Kinase in Health and Disease. Cell Commun. Signal. 2012, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, R.; Zhang, J. Oncogenic Role of LYN in Human Gastric Cancer via the Wnt/Β-catenin and AKT/MTOR Pathways. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lowell, C. Src-Family Kinases: Rheostats of Immune Cell Signaling. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 41, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resh, M.D. Regulation of Cellular Signalling by Fatty Acid Acylation and Prenylation of Signal Transduction Proteins. Cell Signal. 1996, 8, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, A.; Harishchandran, A.; Nagaraj, R. Fatty Acyl Chain-Dependent but Charge-Independent Association of the SH4 Domain of Lck with Lipid Membranes. J. Biosci. 2013, 38, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnick, D.A.; McWherter, C.A.; Adams, S.P.; Ropson, I.J.; Duronio, R.J.; Gordon, J.I. Structural and Functional Studies of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Myristoyl-CoA:Protein N-Myristoyltransferase Produced in Escherichia Coli. Evidence for an Acyl-Enzyme Intermediate. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 13370–13378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthiaume, L.; Resh, M.D. Biochemical Characterization of a Palmitoyl Acyltransferase Activity That Palmitoylates Myristoylated Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 22399–22405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dunphy, J.T.; Greentree, W.K.; Manahan, C.L.; Linder, M.E. G-Protein Palmitoyltransferase Activity Is Enriched in Plasma Membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 7154–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovářová, M.; Tolar, P.; Arudchandran, R.; Dráberová, L.; Rivera, J.; Dráber, P. Structure-Function Analysis of Lyn Kinase Association with Lipid Rafts and Initiation of Early Signaling Events after Fcɛ Receptor I Aggregation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 8318–8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.-H.; Huo, L.; Wang, Y.-N.; Xia, W.; Wei, Y.; Chang, S.-S.; Chang, W.-C.; Fang, Y.-F.; Chen, C.-T.; Lang, J.-Y.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Potentiates MCM7-Mediated DNA Replication through Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Lyn Kinase in Human Cancers. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toubiana, J.; Rossi, A.-L.; Belaidouni, N.; Grimaldi, D.; Pene, F.; Chafey, P.; Comba, B.; Camoin, L.; Bismuth, G.; Claessens, Y.-E.; et al. Src-Family-Tyrosine Kinase Lyn Is Critical for TLR2-Mediated NF-ΚB Activation through the PI 3-Kinase Signaling Pathway. Innate Immun. 2015, 21, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briggs, S.D.; Bryant, S.S.; Jove, R.; Sanderson, S.D.; Smithgall, T.E. The Ras GTPase-Activating Protein (GAP) Is an SH3 Domain-Binding Protein and Substrate for the Src-Related Tyrosine Kinase, Hck. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 14718–14724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Songyang, Z. Recognition and Regulation of Primary-Sequence Motifs by Signaling Modular Domains. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1999, 71, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.A.; Richards, F.M.; Fox, R.O. Structural Determinants of Peptide-Binding Orientation and of Sequence Specificity in SH3 Domains. Nature 1994, 372, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicheri, F.; Kuriyan, J. Structures of Src-Family Tyrosine Kinases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1997, 7, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.K. The Y’s That Bind: Negative Regulators of Src Family Kinase Activity in Platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, M.A.; Gonfloni, S.; Superti-Furga, G.; Roux, B.; Kuriyan, J. Dynamic Coupling between the SH2 and SH3 Domains of C-Src and Hck Underlies Their Inactivation by C-Terminal Tyrosine Phosphorylation. Cell 2001, 105, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, S.S.; Miller, W.T. Cooperative Activation of Src Family Kinases by SH3 and SH2 Ligands. Cancer Lett. 2007, 257, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, T.-J.; Shamsaddini, A.; Pan, Y.; Smith, K.; Crichton, D.J.; Simonyan, V.; Mazumder, R. A Framework for Organizing Cancer-Related Variations from Existing Databases, Publications and NGS Data Using a High-Performance Integrated Virtual Environment (HIVE). Database 2014, 2014, bau022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingerdissen, H.M.; Torcivia-Rodriguez, J.; Hu, Y.; Chang, T.-C.; Mazumder, R.; Kahsay, R. BioMuta and BioXpress: Mutation and Expression Knowledgebases for Cancer Biomarker Discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1128–D1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Karagiannis, K.; Zhang, H.; Dingerdissen, H.; Shamsaddini, A.; Wan, Q.; Simonyan, V.; Mazumder, R. Human Germline and Pan-Cancer Variomes and Their Distinct Functional Profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 11570–11588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malek, S.N.; Desiderio, S. SH2 Domains of the Protein-Tyrosine Kinases Blk, Lyn, and Fyn(T) Bind Distinct Sets of Phosphoproteins from B Lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 22557–22565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songyang, Z.; Shoelson, S.E.; McGlade, J.; Olivier, P.; Pawson, T.; Bustelo, X.R.; Barbacid, M.; Sabe, H.; Hanafusa, H.; Yi, T. Specific Motifs Recognized by the SH2 Domains of Csk, 3BP2, Fps/Fes, GRB-2, HCP, SHC, Syk, and Vav. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 2777–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksman, G.; Kominos, D.; Robertson, S.C.; Pant, N.; Baltimore, D.; Birge, R.B.; Cowburn, D.; Hanafusa, H.; Mayer, B.J.; Overduin, M.; et al. Crystal Structure of the Phosphotyrosine Recognition Domain SH2 of V-Src Complexed with Tyrosine-Phosphorylated Peptides. Nature 1992, 358, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber Chehayeb, R.; Boggon, T.J. SH2 Domain Binding: Diverse FLVRs of Partnership. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 575220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.L.; Wybenga-Groot, L.E.; Tong, J.; Taylor, P.; Minden, M.D.; Trudel, S.; McGlade, C.J.; Moran, M.F. Tyrosine Phosphorylation of the Lyn Src Homology 2 (SH2) Domain Modulates Its Binding Affinity and Specificity*[S]. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barouch-Bentov, R.; Che, J.; Lee, C.C.; Yang, Y.; Herman, A.; Jia, Y.; Velentza, A.; Watson, J.; Sternberg, L.; Kim, S.; et al. A Conserved Salt Bridge in the G Loop of Multiple Protein Kinases Is Important for Catalysis and for In Vivo Lyn Function. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Price, D.J.; Rivnay, B.; Avraham, H. CHK Down-Regulates SCF/KL-Activated Lyn Kinase Activity in Mo7e Megakaryocytic Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 259, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jesus, A.A.; Montealegre, G.; Liu, Y.; Marrero, B.; Kuehn, H.; Calvo, K.; Rosenzweig, S.; Fleisher, T.; Lee, R.C.-C.; Brundidge, A.; et al. A de Novo Nonsense Mutation in the Tyrosine Kinase Lyn in a Patient with an Early Onset Autoinflammatory Phenotype. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2014, 12, O25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, G.; Sharma, A.K.; Budde, R.J. Autophosphorylation of Src and Yes Blocks Their Inactivation by Csk Phosphorylation. Oncogene 1998, 17, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okada, M. Regulation of the Src Family Kinases by Csk. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanagi, S.; Sugawara, H.; Kurosaki, M.; Sabe, H.; Yamamura, H.; Kurosaki, T. CD45 Modulates Phosphorylation of Both Autophosphorylation and Negative Regulatory Tyrosines of Lyn in B Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 30487–30492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hochgräfe, F.; Zhang, L.; O’Toole, S.A.; Browne, B.C.; Pinese, M.; Porta Cubas, A.; Lehrbach, G.M.; Croucher, D.R.; Rickwood, D.; Boulghourjian, A.; et al. Tyrosine Phosphorylation Profiling Reveals the Signaling Network Characteristics of Basal Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9391–9401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umemori, H.; Ogura, H.; Tozawa, N.; Mikoshiba, K.; Nishizumi, H.; Yamamoto, T. Impairment of N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptor-Controlled Motor Activity in LYN-Deficient Mice. Neuroscience 2003, 118, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg-Furmanov, M.; Stein, I.; Pikarsky, E.; Rubin, H.; Kasem, S.; Wygoda, M.; Weinstein, I.; Reuveni, H.; Ben-Sasson, S.A. Lyn Is a Target Gene for Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingley, E.; McCarthy, D.J.; Pore, J.R.; Sarna, M.K.; Adenan, A.S.; Wright, M.J.; Erber, W.; Tilbrook, P.A.; Klinken, S.P. Lyn Deficiency Reduces GATA-1, EKLF and STAT5, and Induces Extramedullary Stress Erythropoiesis. Oncogene 2005, 24, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stettner, M.R.; Wang, W.; Nabors, L.B.; Bharara, S.; Flynn, D.C.; Grammer, J.R.; Gillespie, G.Y.; Gladson, C.L. Lyn Kinase Activity Is the Predominant Cellular Src Kinase Activity in Glioblastoma Tumor Cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 5535–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bates, R.C.; Edwards, N.S.; Burns, G.F.; Fisher, D.E. A CD44 Survival Pathway Triggers Chemoresistance via Lyn Kinase and Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Akt in Colon Carcinoma Cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5275–5283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berton, G.; Mócsai, A.; Lowell, C.A. Src and Syk Kinases: Key Regulators of Phagocytic Cell Activation. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, E.; Daëron, M. Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-Based Inhibition Motifs. Immunol. Today 1997, 18, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbec, O.; Fong, D.C.; Turner, M.; Tybulewicz, V.L.; Cambier, J.C.; Fridman, W.H.; Daëron, M. Fc Epsilon Receptor I-Associated Lyn-Dependent Phosphorylation of Fc Gamma Receptor IIB during Negative Regulation of Mast Cell Activation. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigorena, S.; Bonnerot, C.; Choquet, D.; Fridman, W.H.; Teillaud, J.L. Fc Gamma RII Expression in Resting and Activated B Lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 1989, 19, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, V.W.F.; Meng, F.; Soriano, P.; DeFranco, A.L.; Lowell, C.A. Characterization of the B Lymphocyte Populations in Lyn-Deficient Mice and the Role of Lyn in Signal Initiation and Down-Regulation. Immunity 1997, 7, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daëron, M.; Jaeger, S.; Du Pasquier, L.; Vivier, E. Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-Based Inhibition Motifs: A Quest in the Past and Future. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 224, 11–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damen, J.E.; Liu, L.; Rosten, P.; Humphries, R.K.; Jefferson, A.B.; Majerus, P.W.; Krystal, G. The 145-KDa Protein Induced to Associate with Shc by Multiple Cytokines Is an Inositol Tetraphosphate and Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-Triphosphate 5-Phosphatase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 1689–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jellusova, J.; Nitschke, L. Regulation of B Cell Functions by the Sialic Acid-Binding Receptors Siglec-G and CD22. Front. Immunol. 2012, 2, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tedder, T.F.; Tuscano, J.; Sato, S.; Kehrl, J.H. CD22, A B Lymphocyte–Specific Adhesion Molecule That Regulates Antigen Receptor Signaling. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambier, J.C. Inhibitory Receptors Abound? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5993–5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nitschke, L. The Role of CD22 and Other Inhibitory Co-Receptors in B-Cell Activation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2005, 17, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doody, G.M.; Justement, L.B.; Delibrias, C.C.; Matthews, R.J.; Lin, J.; Thomas, M.L.; Fearon, D.T. A Role in B Cell Activation for CD22 and the Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP. Science 1995, 269, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubagawa, H.; Burrows, P.D.; Cooper, M.D. A Novel Pair of Immunoglobulin-like Receptors Expressed by B Cells and Myeloid Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5261–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayami, K.; Fukuta, D.; Nishikawa, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; Inui, M.; Ohyama, Y.; Hikida, M.; Ohmori, H.; Takai, T. Molecular Cloning of a Novel Murine Cell-Surface Glycoprotein Homologous to Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 7320–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maeda, A.; Kurosaki, M.; Ono, M.; Takai, T.; Kurosaki, T. Requirement of SH2-Containing Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2 for Paired Immunoglobulin-like Receptor B (PIR-B)–Mediated Inhibitory Signal. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Touw, W.; Chen, H.-M.; Pan, P.-Y.; Chen, S.-H. LILRB Receptor-Mediated Regulation of Myeloid Cell Maturation and Function. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.; van der Laan, L.J.; Vernon-Wilson, E.; Renardel de Lavalette, C.; Döpp, E.A.; Dijkstra, C.D.; Simmons, D.L.; van den Berg, T.K. Signal-Regulatory Protein Is Selectively Expressed by Myeloid and Neuronal Cells. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harder, K.W.; Parsons, L.M.; Armes, J.; Evans, N.; Kountouri, N.; Clark, R.; Quilici, C.; Grail, D.; Hodgson, G.S.; Dunn, A.R.; et al. Gain- and Loss-of-Function Lyn Mutant Mice Define a Critical Inhibitory Role for Lyn in the Myeloid Lineage. Immunity 2001, 15, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, X.-N.; Yan, H.-X.; Chen, L.; Dong, L.-W.; Yang, W.; Liu, Q.; Yu, L.-X.; Huang, D.-D.; Liu, S.-Q.; Liu, H.; et al. LPS-Induced Down-Regulation of Signal Regulatory Protein {alpha} Contributes to Innate Immune Activation in Macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2719–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezbradica, J.S.; Medzhitov, R. Role of ITAM Signaling Module in Signal Integration. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogarth, P.M. Fc Receptors Are Major Mediators of Antibody Based Inflammation in Autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2002, 14, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, M.B.; Lanier, L.L.; Nakamura, M.C. Role of ITAM-Containing Adapter Proteins and Their Receptors in the Immune System and Bone. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 208, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, M.; Sabe, H.; Hata, A.; Inazu, T.; Homma, Y.; Nukada, T.; Yamamura, H.; Kurosaki, T. Tyrosine Kinases Lyn and Syk Regulate B Cell Receptor-Coupled Ca2+ Mobilization through Distinct Pathways. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullen, N.A.; Falanga, Y.T.; Morales, J.K.; Ryan, J.J. The Fyn-STAT5 Pathway: A New Frontier in IgE- and IgG-Mediated Mast Cell Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben Mkaddem, S.; Hayem, G.; Jönsson, F.; Rossato, E.; Boedec, E.; Boussetta, T.; El Benna, J.; Launay, P.; Goujon, J.-M.; Benhamou, M.; et al. Shifting FcγRIIA-ITAM from Activation to Inhibitory Configuration Ameliorates Arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3945–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanamaru, Y.; Pfirsch, S.; Aloulou, M.; Vrtovsnik, F.; Essig, M.; Loirat, C.; Deschênes, G.; Guérin-Marchand, C.; Blank, U.; Monteiro, R.C. Inhibitory ITAM Signaling by FcαRI-FcRγ Chain Controls Multiple Activating Responses and Prevents Renal Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 2669–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquier, B.; Launay, P.; Kanamaru, Y.; Moura, I.C.; Pfirsch, S.; Ruffié, C.; Hénin, D.; Benhamou, M.; Pretolani, M.; Blank, U.; et al. Identification of FcαRI as an Inhibitory Receptor That Controls Inflammation. Immunity 2005, 22, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Štefanová, I.; Hemmer, B.; Vergelli, M.; Martin, R.; Biddison, W.E.; Germain, R.N. TCR Ligand Discrimination Is Enforced by Competing ERK Positive and SHP-1 Negative Feedback Pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getahun, A.; Beavers, N.A.; Larson, S.R.; Shlomchik, M.J.; Cambier, J.C. Continuous Inhibitory Signaling by Both SHP-1 and SHIP-1 Pathways Is Required to Maintain Unresponsiveness of Anergic B Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 751–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.B.M.; Prigent, S.A. Insights into the Shc Family of Adaptor Proteins. J. Mol. Signal. 2017, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ptasznik, A.; Traynor-Kaplan, A.; Bokoch, G.M. G Protein-Coupled Chemoattractant Receptors Regulate Lyn Tyrosine Kinase·Shc Adapter Protein Signaling Complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 19969–19973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kyo, S.; Sada, K.; Qu, X.; Maeno, K.; Miah, S.M.S.; Kawauchi-Kamata, K.; Yamamura, H. Negative Regulation of Lyn Protein-Tyrosine Kinase by c-Cbl Ubiquitin-Protein Ligase in FcɛRI-Mediated Mast Cell Activation. Genes Cells 2003, 8, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrosky-Ferlan, P.; Grishin, A.; Botelho, R.J.; Sampson, M.; Wang, L.; Rudert, W.A.; Grinstein, S.; Corey, S.J. Felic (CIP4b), a Novel Binding Partner with the Src Kinase Lyn and Cdc42, Localizes to the Phagocytic Cup. Blood 2003, 101, 2804–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, R.; Malik, M.; Ravyn, V.; Tomkowicz, B.; Ptasznik, A.; Collman, R.G. An Arrestin-Dependent Multi-Kinase Signaling Complex Mediates MIP-1β/CCL4 Signaling and Chemotaxis of Primary Human Macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houslay, K.F.; Christian, F.; MacLeod, R.; Adams, D.R.; Houslay, M.D.; Baillie, G.S. Identification of a Multifunctional Docking Site on the Catalytic Unit of Phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) That Is Utilised by Multiple Interaction Partners. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, K.; Kharbanda, S.; Kufe, D. Functional Interaction between SHPTP1 and the Lyn Tyrosine Kinase in the Apoptotic Response to DNA Damage. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 34663–34668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Q.; Yu, S.P. Novel Regulation of Na+, K+-ATPase by Src Tyrosine Kinases in Cortical Neurons. J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Umemori, H.; Mishina, M.; Yamamoto, T. The AMPA Receptor Interacts with and Signals through the Protein Tyrosine Kinase Lyn. Nature 1999, 397, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roseweir, A.K.; Qayyum, T.; Lim, Z.; Hammond, R.; MacDonald, A.I.; Fraser, S.; Oades, G.M.; Aitchison, M.; Jones, R.J.; Edwards, J. Nuclear Expression of Lyn, a Src Family Kinase Member, Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Renal Cancer Patients. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elsberger, B.; Fullerton, R.; Zino, S.; Jordan, F.; Mitchell, T.J.; Brunton, V.G.; Mallon, E.A.; Shiels, P.G.; Edwards, J. Breast Cancer Patients’ Clinical Outcome Measures Are Associated with Src Kinase Family Member Expression. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croucher, D.R.; Hochgräfe, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Lyons, R.J.; Rickwood, D.; Tactacan, C.M.; Browne, B.C.; Ali, N.; Chan, H.; et al. Involvement of Lyn and the Atypical Kinase SgK269/PEAK1 in a Basal Breast Cancer Signaling Pathway. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1969–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, G.; Breen, E.J.; Ranganathan, S. Identification of Ovarian Cancer Associated Genes Using an Integrated Approach in a Boolean Framework. BMC Syst. Biol. 2013, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dos Santos, C.; Demur, C.; Bardet, V.; Prade-Houdellier, N.; Payrastre, B.; Récher, C. A Critical Role for Lyn in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 2269–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michell-Robinson, M.A.; Touil, H.; Healy, L.M.; Owen, D.R.; Durafourt, B.A.; Bar-Or, A.; Antel, J.P.; Moore, C.S. Roles of Microglia in Brain Development, Tissue Maintenance and Repair. Brain 2015, 138, 1138–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, M.; Parikh, I.; Vasquez, J.B.; Smith, C.; Tai, L.; Bu, G.; LaDu, M.J.; Fardo, D.W.; Rebeck, G.W.; Estus, S. Genetics Ignite Focus on Microglial Inflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keren-Shaul, H.; Spinrad, A.; Weiner, A.; Matcovitch-Natan, O.; Dvir-Szternfeld, R.; Ulland, T.K.; David, E.; Baruch, K.; Lara-Astaiso, D.; Toth, B.; et al. A Unique Microglia Type Associated with Restricting Development of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell 2017, 169, 1276–1290.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierksma, A.; Lu, A.; Mancuso, R.; Fattorelli, N.; Thrupp, N.; Salta, E.; Zoco, J.; Blum, D.; Buée, L.; De Strooper, B.; et al. Novel Alzheimer Risk Genes Determine the Microglia Response to Amyloid-β but Not to TAU Pathology. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e10606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, A.; Ekavali. A Review on Alzheimer’s Disease Pathophysiology and Its Management: An Update. Pharmacol. Reports 2015, 67, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J. Alzheimer’s Disease: The Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis: An Update and Reappraisal. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2006, 9, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Portugal, C.C.; Almeida, T.O.; Socodato, R.; Relvas, J.B. Src Family Kinases (SFKs): Critical Regulators of Microglial Homeostatic Functions and Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Diseases. FEBS J. 2021, 289, 7760–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, C.K.; Johnson, D.E.; Cannady, S.B.; Lehman, T.M.; Landreth, G.E. Identification of Microglial Signal Transduction Pathways Mediating a Neurotoxic Response to Amyloidogenic Fragments of β-Amyloid and Prion Proteins. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanke, J.H.; Gardner, J.P.; Dow, R.L.; Changelian, P.S.; Brissette, W.H.; Weringer, E.J.; Pollok, B.A.; Connelly, P.A. Discovery of a Novel, Potent, and Src Family-Selective Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sondag, C.M.; Dhawan, G.; Combs, C.K. Beta Amyloid Oligomers and Fibrils Stimulate Differential Activation of Primary Microglia. J. Neuroinflamm. 2009, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhawan, G.; Floden, A.M.; Combs, C.K. Amyloid-β Oligomers Stimulate Microglia through a Tyrosine Kinase Dependent Mechanism. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 2247–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manocha, G.D.; Puig, K.L.; Austin, S.A.; Seyb, K.; Glicksman, M.A.; Combs, C.K. Characterization of Novel Src Family Kinase Inhibitors to Attenuate Microgliosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, H.T.; Kam, T.-I.; Park, J.; Lim, B.; Cha, H.; Chang, H.-J.; Hong, Y.R.; Jung, Y.-K. Amelioration of Amyloid Β-FcγRIIb Neurotoxicity and Tau Pathologies by Targeting LYN. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 4300–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, Y.; Kam, T.-I.; Kim, S.-H.; Song, S.; Park, H.; Lim, B.; Lee, H.; Lee, W.; Jo, D.-G.; Jung, Y.-K. TOM1 Regulates Neuronal Accumulation of Amyloid-β Oligomers by FcγRIIb2 Variant in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 9001–9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peikert, K.; Federti, E.; Matte, A.; Constantin, G.; Pietronigro, E.C.; Fabene, P.F.; Defilippi, P.; Turco, E.; Del Gallo, F.; Pucci, P.; et al. Therapeutic Targeting of Lyn Kinase to Treat Chorea-Acanthocytosis. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weerawarna, P.M.; Richardson, T.I. Lyn Kinase Structure, Regulation, and Involvement in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Mini Review. Kinases Phosphatases 2023, 1, 23-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases1010004
Weerawarna PM, Richardson TI. Lyn Kinase Structure, Regulation, and Involvement in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Mini Review. Kinases and Phosphatases. 2023; 1(1):23-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases1010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeerawarna, Pathum M., and Timothy I. Richardson. 2023. "Lyn Kinase Structure, Regulation, and Involvement in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Mini Review" Kinases and Phosphatases 1, no. 1: 23-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases1010004
APA StyleWeerawarna, P. M., & Richardson, T. I. (2023). Lyn Kinase Structure, Regulation, and Involvement in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Mini Review. Kinases and Phosphatases, 1(1), 23-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases1010004





