Changes in Air Quality, Meteorology and Energy Consumption during the COVID-19 Lockdown and Unlock Periods in India
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
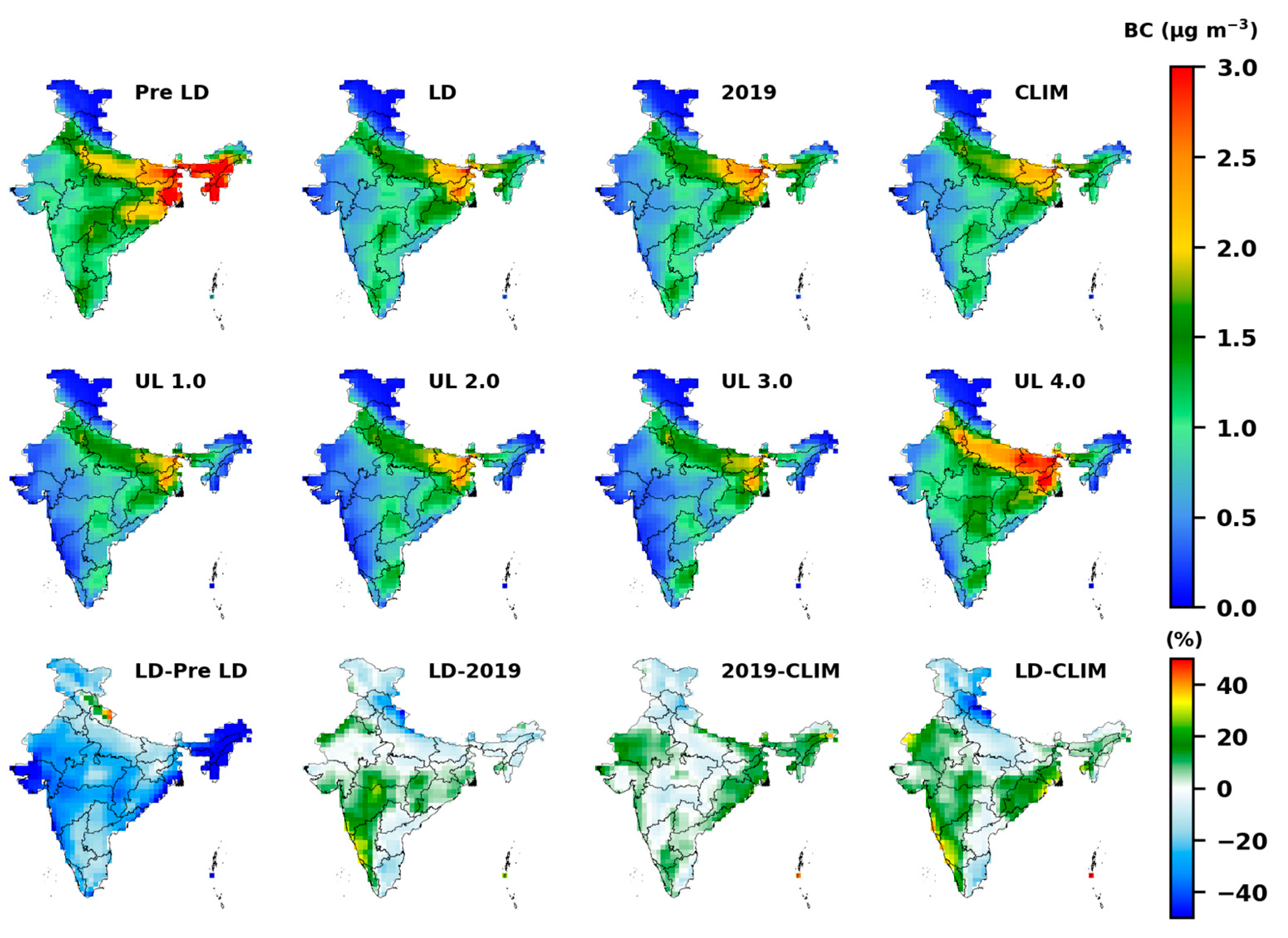
3.1. Changes in Air Quality: SO2, AOD, BC and Dust
3.2. Changes and Impact on Meteorology: T, RH, P, UV, TCC and Winds
3.3. Implications for Energy Consumption
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, S.; Joshi, L. Socioeconomic and Environmental Implications of Agricultural Residue Burning: A Case Study of Punjab, India; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 9788132220145. [Google Scholar]
- Guttikunda, S.K.; Nishadh, K.A.; Gota, S.; Singh, P.; Chanda, A.; Jawahar, P.; Asundi, J. Air quality, emissions, and source contributions analysis for the Greater Bengaluru region of India. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, S.; Jahangir, S.; Haque, M.S.; Chen, R.; Kumar, P. Spatio-temporal changes of green spaces and their impact on urban environment of Mumbai, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 6481–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO|Air Pollution; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, S.; Dey, S.; Guttikunda, S.; Pillarisetti, A.; Smith, K.R.; Girolamo, L.D. Indian annual ambient air quality standard is achievable by completely mitigating emissions from household sources. PNAS Sci. 2019, 116, 10711–10716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Ambient Air Pollution: A Global Assessment of Exposure and Burden of Disease. 2016. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/250141/9789241511353-eng.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Mishra, M. Poison in the air: Declining air quality in India. Lung India 2019, 36, 160–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, J.; Ohara, T. Long-term historical trends in air pollutant emissions in Asia: Regional Emission inventory in ASia (REAS) version 3.1. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12761–12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Hama, S.; Omidvarborna, H.; Sharma, A.; Sahani, J.; Abhijith, K.V.; Debele, S.E.; Zavala-Reyes, J.C.; Barwise, Y.; Tiwari, A. Temporary reduction in fine particulate matter due to ‘anthropogenic emissions switch-off’ during COVID19 lockdown in Indian cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 62, 102382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Kumar, A.; Bauddh, K.; Gautam, A.S.; Kumar, S. 21-Day Lockdown in India Dramatically Reduced Air Pollution Indices in Lucknow and New Delhi, India. Bull. Environ. Contam. Tox. 2020, 105, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Zhang, M.; Anshika Gao, J.; Zhang, H.; Kota, S.H. Effect of restricted emissions during COVID19 on air quality in India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, S. A full-scale analysis of chemical characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 during haze and non-haze episodes in Cixi city, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Chauhan, A. Impact of lockdown on air quality in India during COVID-19 pandemic. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, D. How are the two most polluted metro-cities of India combating air pollution? Way forward after lifting of COVID-19 lockdown. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopikrishnan, G.S.; Kuttippurath, J.; Raj, S.; Singh, A.; Abbhishek, K. Air Quality during the COVID-19 Lockdown and Unlock Periods in India Analyzed Using Satellite and Ground-based Measurements. Environ. Proc. 2022, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, S.; Pal, S.; Ghosh, K.P. Effect of lockdown amid COVID-19 pandemic on air quality of the megacity Delhi, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, P.; Toshniwal, D. Impact of lockdown measures during COVID-19 on air quality—A case study of India. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2020, 32, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S. The Influence of COVID-19 on Air Quality in India: A Boon or Inutile. Bull. Environ. Contam. Tox. 2020, 104, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabiraj, S.; Gavli, N.V. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic Lockdown on Air Quality Using Satellite Imagery with Ground Station Monitoring Data in Most Polluted City Kolkata, India. Aerosol Sci. Eng. 2020, 4, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, S. The influence of pollution on the shortwave albedo of clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, M.G.; Devara, P.C.S.; Safai, P.D.; Goswami, B.N. Absorbing aerosols facilitate transition of Indian monsoon breaks to active spells. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 37, 2181–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, I.; Vanderlei Martins, J.; Remer, L.A.; Afargan, H. Smoke invigoration versus inhibition of clouds over the amazon. Science 2008, 321, 946–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latha, R.; Murthy, B.S.; Sandeepan, B.S.; Bhanage, V.; Rathod, A.; Tiwari, A.; Beig, G.; Singh, S. Propagation of cloud base to higher levels during COVID-19-lockdown. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 144299. [Google Scholar]
- Staffell, I.; Pfenninger, S. The increasing impact of weather on electricity supply and demand. Energy 2018, 145, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Chang, W.K.; Lin, H.W. A fresh look at weather impact on peak electricity demand and energy use of buildings using 30-year actual weather data. Appl. Energy 2013, 111, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Considine, T.J. The impacts of weather variations on energy demand and carbon emissions. Resour. Energy Econ. 2000, 22, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. The Impact of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Crisis on Development Finance. 2020. Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/development/the-impact-of-the-coronavirus-covid-19-crisis-on-development-finance_9de00b3b-en (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Aggarwal, M. Within 10 Days of the Lockdown, India Was Consuming 20% Less Power than Usual. 2020. Available online: https://epic.uchicago.edu/news/indias-power-consumption-falls-by-19-percent-during-covid-19-lockdown/ (accessed on 24 December 2020).
- Livemint. Electricity Demand Improves as India Unlocks Gradually. 2020. Available online: https://www.livemint.com/industry/energy/electricity-demand-improves-as-india-unlocks-gradually-11596112487139.html (accessed on 28 October 2020).
- IEA. Global Energy Review; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Veefkind, J.P.; Aben, I.; McMullan, K.; Förster, H.; de Vries, J.; Otter, G.; Claas, J.; Eskes, H.J.; De Haan, J.F.; Kleipool, Q.; et al. TROPOMI on the ESA Sentinel-5 Precursor: A GMES mission for global observations of the atmospheric composition for climate, air quality and ozone layer applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queißer, M.; Burton, M.; Theys, N.; Pardini, F.; Salerno, G.; Caltabiano, T.; Varnam, M.; Esse, B.; Kazahaya, R. TROPOMI enables high resolution SO2 flux observations from Mt. Etna, Italy, and beyond. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garane, K.; Koukouli, M.E.; Verhoelst, T.; Fioletov, V.; Lerot, C.; Heue, K.P.; Fioletov, V.; Balis, D.; Bais, A.; Bazureau, A.; et al. TROPOMI/S5ptotal ozone column data: Global ground-based validation & consistency with other satellite missions. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 5263–5287. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, C.; Cai, Z.; Liu, X.; Bak, J.; Kim, J.; Hu, Q.; Xia, C.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; et al. Ozone profile retrievals from TROPOMI: Implication for the variation of tropospheric ozone during the outbreak of COVID-19 in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 764, 142886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelaro, R.; McCarty, W.; Suárez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.A.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R.; et al. The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, C.A.; da Silva, A.M.; Buchard, V.; Colarco, P.R.; Darmenov, A.; Govindaraju, R.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; et al. The MERRA-2 aerosol reanalysis, 1980 onward. Part I: System description and data assimilation evaluation. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6823–6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanniah, K.D.; Kamarul Zaman, N.A.F.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Latif, M.T. COVID-19′s impact on the atmospheric environment in the Southeast Asia region. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navinya, C.; Patidar, G.; Phuleria, H.C. Examining effects of the COVID-19 national lockdown on ambient air quality across urban India. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathakoti, M.; Muppalla, A.; Hazra, S.; Dangeti, M.; Shekhar, R.; Jella, S.; Mullapudi, S.S.; Andugulapati, P.; Vijayasundaram, U. An assessment of the impact of a nation-wide lockdown on air pollution—A remote sensing perspective over India. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheesh, S.; Srinivasan, J. Enhanced aerosol loading over Arabian Sea during the pre-monsoon season: Natural or anthropogenic? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 21-1–21-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttippurath, J.; Raj, S. Two decades of aerosol observations by AATSR, MISR, MODIS and MERRA-2 over India and Indian Ocean. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 257, 112363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Kota, S.H.; Sahu, S.K.; Hu, J.; Ying, Q.; Gao, A.; Zhang, H. Source apportionment of PM2.5 in North India using source-oriented air quality models. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Kota, S.H.; Sahu, S.K.; Zhang, H. Contributions of local and regional sources to PM2.5 and its health effects in north India. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Singh, R.P. Decline in PM2.5 concentrations over major cities around the world associated with COVID-19. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, P.; Hayasaka, T.; Holben, B.; Tripathi, S.N.; Misra, P.; Patra, P.K.; Hayashida, S.; Dumka, U.C. Aerosol Loading and Radiation Budget Perturbations in Densely Populated and Highly Polluted Indo-Gangetic Plain by COVID-19: Influences on Cloud Properties and Air Temperature. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Y.; Loeb, N.G.; Lin, P.; Shen, Z.; Naik, V.; Singer, C.E.; Ward, R.X.; Paulot, F.; Zhang, Z.; Bellouin, N.; et al. Assessing the Influence of COVID-19 on the shortwave radiative fluxes over the east asian marginal seas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL091699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuttippurath, J.; Patel, V.K.; Gopikrishnan, G.P.; Varikoden, H. Changes in Air Quality, Meteorology and Energy Consumption during the COVID-19 Lockdown and Unlock Periods in India. Air 2023, 1, 125-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/air1020010
Kuttippurath J, Patel VK, Gopikrishnan GP, Varikoden H. Changes in Air Quality, Meteorology and Energy Consumption during the COVID-19 Lockdown and Unlock Periods in India. Air. 2023; 1(2):125-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/air1020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuttippurath, Jayanarayanan, Vikas Kumar Patel, Gopalakrishna Pillai Gopikrishnan, and Hamza Varikoden. 2023. "Changes in Air Quality, Meteorology and Energy Consumption during the COVID-19 Lockdown and Unlock Periods in India" Air 1, no. 2: 125-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/air1020010
APA StyleKuttippurath, J., Patel, V. K., Gopikrishnan, G. P., & Varikoden, H. (2023). Changes in Air Quality, Meteorology and Energy Consumption during the COVID-19 Lockdown and Unlock Periods in India. Air, 1(2), 125-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/air1020010





