Effects of Electrolyte Solvent Composition on Solid Electrolyte Interphase Properties in Lithium Metal Batteries: Focusing on Ethylene Carbonate to Ethyl Methyl Carbonate Ratios
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electrode and Electrolyte Materials
2.2. Electrolyte Formulations
2.3. Material Characterizations
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results
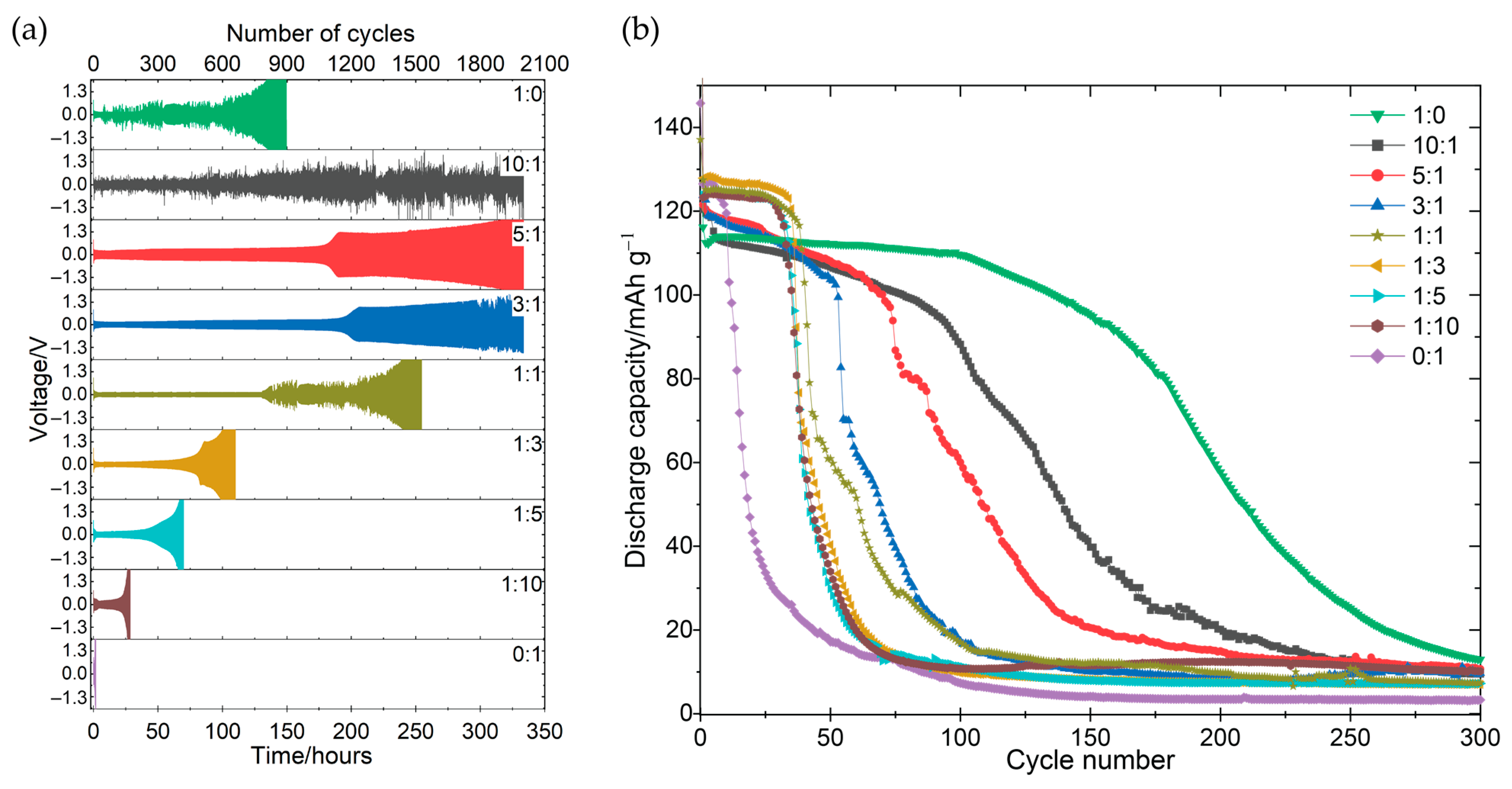
3.1. Electrochemical Performance and Stability
3.2. Ionic Conductivity in EC:EMC Mixtures
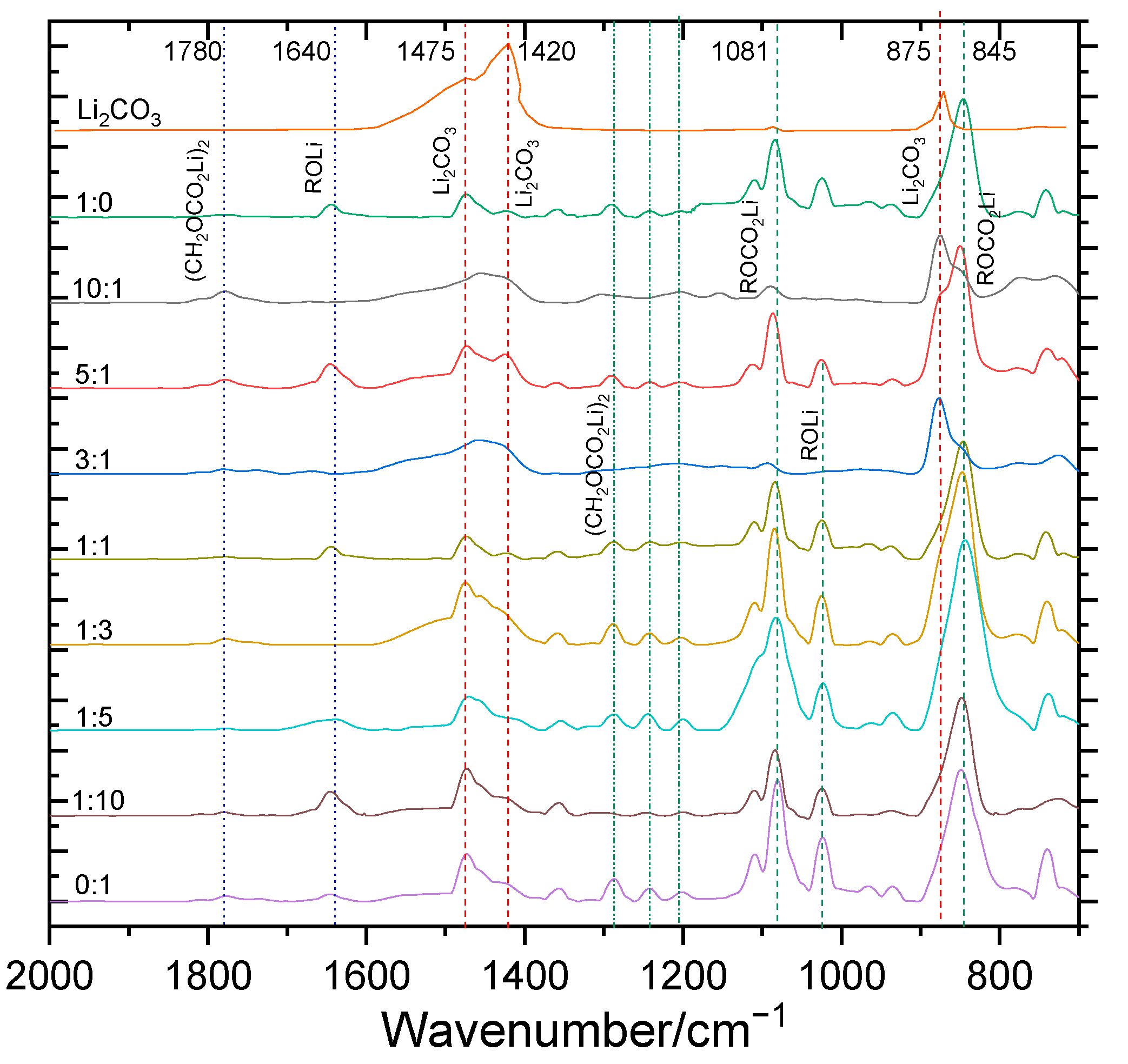
3.3. Composition and Structural Analysis of SEI
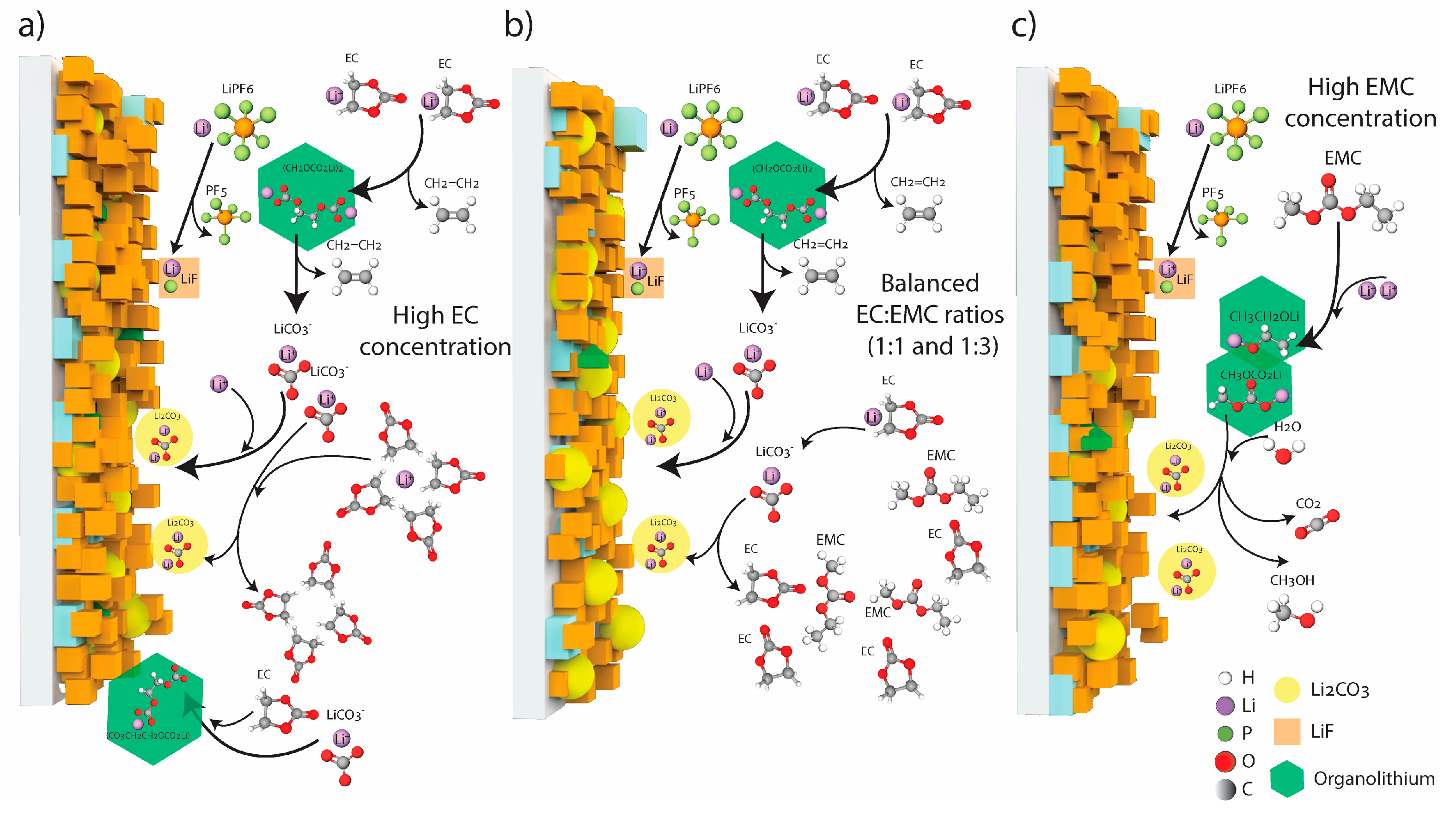
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, K. Electrolytes and Interphases in Li-Ion Batteries and Beyond. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11503–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varzi, A.; Thanner, K.; Scipioni, R.; Di Lecce, D.; Hassoun, J.; Dörfler, S.; Altheus, H.; Kaskel, S.; Prehal, C.; Freunberger, S.A. Current Status and Future Perspectives of Lithium Metal Batteries. J. Power Sources 2020, 480, 228803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Ding, F.; Huang, J.-Q.; Xu, R.; Chen, X.; Yan, C.; Su, F.-Y.; Chen, C.-M.; Liu, X.; et al. Advanced Electrode Materials in Lithium Batteries: Retrospect and Prospect. Energy Mater. Adv. 2021, 2021, 1205324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, P.; Cao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yan, C.; Qian, T. Advances and Prospects in Improving the Utilization Efficiency of Lithium for High Energy Density Lithium Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2302055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.S.; Xu, K.; Zhang, S.; Jow, T.R. Liquid/Solid Phase Diagrams of Binary Carbonates for Lithium Batteries Part II. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, A299–A304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurbach, D.; Levi, M.D.; Levi, E.; Schechter, A. Failure and Stabilization Mechanisms of Graphite Electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 2195–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ein-Eli, Y.; McDevitt, S.F.; Laura, R. The Superiority of Asymmetric Alkyl Methyl Carbonates. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, L1–L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peled, E. The Electrochemical Behavior of Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals in Nonaqueous Battery Systems—The Solid Electrolyte Interphase Model. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1979, 126, 2047–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peled, E.; Golodnitsky, D.; Menachem, C.; Bartow, D. An Advanced Tool for the Selection of Electrolyte Components for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 3482–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurbach, D.; Ein-Eli, Y.; Markovsky, B.; Zaban, A.; Luski, S.; Carmeli, Y.; Yamin, H. The Study of Electrolyte Solutions Based on Ethylene and Diethyl Carbonates for Rechargeable Li Batteries: II. Graphite Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 2882–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ding, M.S.; Xu, K.; Allen, J.; Jow, T.R. Understanding Solid Electrolyte Interface Film Formation on Graphite Electrodes. ECS Electrochem. Lett. 2001, 4, A206–A208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, R.; von Sacken, U.; Dahn, J.R. Studies of Lithium Intercalation into Carbons Using Nonaqueous Electrochemical Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 2009–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyomard, D.; Tarascon, J.M. Rechargeable Li1 + xMn2O4/Carbon Cells with a New Electrolyte Composition: Potentiostatic Studies and Application to Practical Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, 3071–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarascon, J.; Guyomard, D. New Electrolyte Compositions Stable over the 0 to 5 V Voltage Range and Compatible with the Li1+xMn2O4/Carbon Li-Ion Cells. Solid State Ion. 1994, 69, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilken, S.; Treskow, M.; Scheers, J.; Johansson, P.; Jacobsson, P. Initial Stages of Thermal Decomposition of LiPF6-Based Lithium Ion Battery Electrolytes by Detailed Raman and NMR Spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 16359–16364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurbach, D.; Gofer, Y.; Ben-Zion, M.; Aped, P. The Behaviour of Lithium Electrodes in Propylene and Ethylene Carbonate: Te Major Factors That Influence Li Cycling Efficiency. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1992, 339, 451–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurbach, D.; Markovsky, B.; Weissman, I.; Levi, E.; Ein-Eli, Y. On the Correlation between Surface Chemistry and Performance of Graphite Negative Electrodes for Li Ion Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 1999, 45, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Ue, M.; Balbuena, P.B. Theoretical Studies to Understand Surface Chemistry on Carbon Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries: Reduction Mechanisms of Ethylene Carbonate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 11708–11718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurbach, D.; Markovsky, B.; Shechter, A.; Ein-Eli, Y.; Cohen, H. A Comparative Study of Synthetic Graphite and Li Electrodes in Electrolyte Solutions Based on Ethylene Carbonate-Dimethyl Carbonate Mixtures. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 3809–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Balbuena, P.B. Theoretical Studies on Cosolvation of Li Ion and Solvent Reductive Decomposition in Binary Mixtures of Aliphatic Carbonates. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2005, 102, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K. Two-Electron Reduction of Ethylene Carbonate: A Quantum Chemistry Re-Examination of Mechanisms. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2013, 568–569, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Balbuena, P.B.; Budzien, J.; Leung, K. Hybrid DFT Functional-Based Static and Molecular Dynamics Studies of Excess Electron in Liquid Ethylene Carbonate. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, A400–A410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Van Duin, A.C.T. Reductive Decomposition Reactions of Ethylene Carbonate by Explicit Electron Transfer from Lithium: An EReaxFF Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 27128–27134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez De La Hoz, J.M.; Leung, K.; Balbuena, P.B. Reduction Mechanisms of Ethylene Carbonate on Si Anodes of Lithium-Ion Batteries: Effects of Degree of Lithiation and Nature of Exposed Surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 13457–13465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, K.; Budzien, J.L. Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Initial Stages of Solid-Electrolyte Interphase Formation on Lithium Ion Battery Graphitic Anodes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 6583–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kominato, A.; Yasukawa, E.; Sato, N.; Ijuuin, T.; Asahina, H.; Mori, S. Analysis of surface films on lithium in various organic electrolytes. J. Power Sources 1997, 68, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Morita, M.; Yamada, K.; Hirai, K. Characteristics of Sulfolane-Based Electrolytes for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1985, 132, 2538–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Gao, J.; Qi, L.; Wang, H. Hexafluorophosphate Anion Intercalation into Graphite Electrode from Sulfolane/Ethylmethyl Carbonate Solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 189, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K. Nonaqueous Liquid Electrolytes for Lithium-Based Rechargeable Batteries. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4303–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borodin, O.; Smith, G.D. Quantum Chemistry and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of Dimethyl Carbonate: Ethylene Carbonate Electrolytes Doped with LiPF6. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 1763–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.S. A Review on Electrolyte Additives for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 1379–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.; Zou, Y.; Liu, C.; Yan, P.; Wu, D.Y.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, J. Synergistical Stabilization of Li Metal Anodes and LiCoO2 Cathodes in High-Voltage Li||LiCoO2 Batteries by Potassium Selenocyanate (KSeCN) Additive. ACS Energy. Lett. 2022, 7, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Guo, R.; Hobold, G.M.; Gao, H.; Gallant, B.M. The Intrinsic Behavior of Lithium Fluoride in Solid Electrolyte Interphases on Lithium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.H.; Lu, G.X.; Zheng, J.H.; Zhou, F.; Chen, M.; Ma, T.; Lu, L.L.; Song, Y.H.; Guan, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Lithium Fluoride in Electrolyte for Stable and Safe Lithium-Metal Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Duan, X.; Liu, X.; Zhan, R.; Wang, X.; Du, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Shen, Y.; et al. Locking Active Li Metal through Localized Redistribution of Fluoride Enabling Stable Li-Metal Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Peng, Z. The Salt Matters: Enhanced Reversibility of Li–O2 Batteries with a Li[(CF3SO2)(n-C4F9SO2)N]-Based Electrolyte. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, W.W.; Li, Y.J.; Wu, Q.H.; Tang, S.; Yan, J.W.; Zheng, M.S.; Wu, D.Y.; Fan, C.H.; Hu, W.Q.; et al. Designable Ultra-Smooth Ultra-Thin Solid-Electrolyte Interphases of Three Alkali Metal Anodes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, P.; Duan, J.; Lin, X.; Sun, J.; Shi, W.; Xu, H.; Dou, W.; Zheng, Q.; Yuan, R.; et al. A Dicarbonate Solvent Electrolyte for High Performance 5 V-Class Lithium-Based Batteries. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ji, X.; Yue, J.; Hou, S.; Wang, P.; Cui, C.; Chen, J.; Shao, B.; Li, J.; Han, F.; et al. High Interfacial-Energy Interphase Promoting Safe Lithium Metal Batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2438–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nogales, P.M.; Lee, S.; Yang, S.; Jeong, S.-K. Effects of Electrolyte Solvent Composition on Solid Electrolyte Interphase Properties in Lithium Metal Batteries: Focusing on Ethylene Carbonate to Ethyl Methyl Carbonate Ratios. Batteries 2024, 10, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10060210
Nogales PM, Lee S, Yang S, Jeong S-K. Effects of Electrolyte Solvent Composition on Solid Electrolyte Interphase Properties in Lithium Metal Batteries: Focusing on Ethylene Carbonate to Ethyl Methyl Carbonate Ratios. Batteries. 2024; 10(6):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10060210
Chicago/Turabian StyleNogales, Paul Maldonado, Sangyup Lee, Seunga Yang, and Soon-Ki Jeong. 2024. "Effects of Electrolyte Solvent Composition on Solid Electrolyte Interphase Properties in Lithium Metal Batteries: Focusing on Ethylene Carbonate to Ethyl Methyl Carbonate Ratios" Batteries 10, no. 6: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10060210
APA StyleNogales, P. M., Lee, S., Yang, S., & Jeong, S.-K. (2024). Effects of Electrolyte Solvent Composition on Solid Electrolyte Interphase Properties in Lithium Metal Batteries: Focusing on Ethylene Carbonate to Ethyl Methyl Carbonate Ratios. Batteries, 10(6), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10060210







