A New Approach for Motor Imagery Classification Based on Sorted Blind Source Separation, Continuous Wavelet Transform, and Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Blind Source Separation
2.2. Wavelet Transform
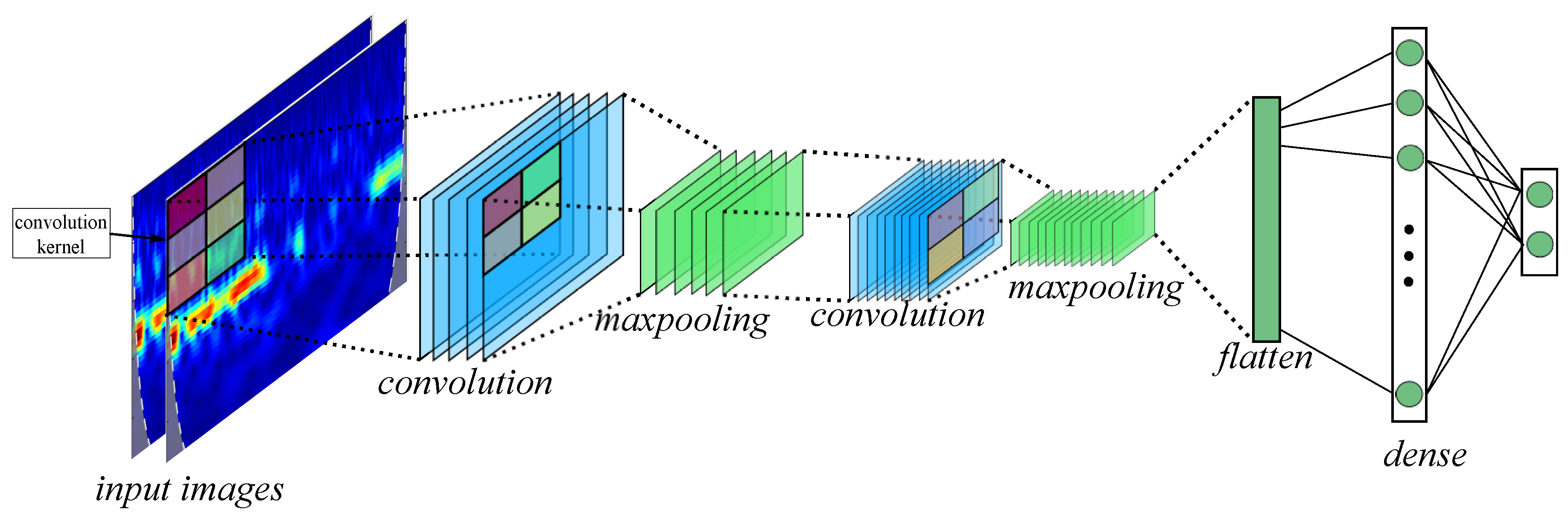
2.3. Convolutional Neural Network
- Filters: The number of output filters in the convolution.
- kernel size: The height and width of the 2D convolution window.
- Strides: The strides of the convolution along the height and width.
3. Methodology
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Proposed Approach
3.3. Experiment Setup
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Validation of Proposed Method
4.2. Comparison with Other Methods
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gandhi, V.; Prasad, G.; Coyle, D.; Behera, L.; McGinnity, T.M. Evaluating Quantum Neural Network filtered motor imagery brain-computer interface using multiple classification techniques. Neurocomputing 2015, 170, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanei, S.; Chambers, J.A. EEG Signal Processing; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Niedermeyer, E.; da Silva, F.L. Electroencephalography: Basic Principles, Clinical Applications, and Related Fields; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wolpaw, J.R.; McFarland, D.J. Control of a two-dimensional movement signal by a noninvasive brain-computer interface in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17849–17854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineda, J.A. The functional significance of mu rhythms: Translating “seeing” and “hearing” into “doing”. Brain Res. Rev. 2005, 50, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, D.J.; Miner, L.A.; Vaughan, T.M.; Wolpaw, J.R. Mu and beta rhythm topographies during motor imagery and actual movements. Brain Topogr. 2000, 12, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Tanaka, T.; Molla, M.K.I. Multiband tangent space mapping and feature selection for classification of EEG during motor imagery. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 046021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Aranibar, A. Evaluation of event-related desynchronization (ERD) preceding and following voluntary self-paced movement. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1979, 46, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfurtscheller, G. Central beta rhythm during sensorimotor activities in man. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1981, 51, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Neuper, C. Event-related synchronization of mu rhythm in the EEG over the cortical hand area in man. Neurosci. Lett. 1994, 174, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Da Silva, F.L. Event-related EEG/MEG synchronization and desynchronization: Basic principles. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1999, 110, 1842–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Brunner, C.; Schlögl, A.; Da Silva, F.L. Mu rhythm (de) synchronization and EEG single-trial classification of different motor imagery tasks. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koles, Z.; Lind, J.; Soong, A. Spatio-temporal decomposition of the EEG: A general approach to the isolation and localization of sources. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1995, 95, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Chen, K.; Liu, Q.; Ai, Q.; Xie, Y.; Chen, A. Feature selection for motor imagery EEG classification based on firefly algorithm and learning automata. Sensors 2017, 17, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeem, M.; Brunner, C.; Leeb, R.; Graimann, B.; Pfurtscheller, G. Seperability of four-class motor imagery data using independent components analysis. J. Neural Eng. 2006, 3, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez, R.R.; Velez-Perez, H.; Ranta, R.; Dorr, V.L.; Maquin, D.; Maillard, L. Blind source separation, wavelet denoising and discriminant analysis for EEG artefacts and noise cancelling. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2012, 7, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.P.; Makeig, S.; Westerfield, M.; Townsend, J.; Courchesne, E.; Sejnowski, T.J. Removal of eye activity artifacts from visual event-related potentials in normal and clinical subjects. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000, 111, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mur, A.; Dormido, R.; Duro, N. An Unsupervised Method for Artefact Removal in EEG Signals. Sensors 2019, 19, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Jung, T.P. Translation of EEG spatial filters from resting to motor imagery using independent component analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wu, X.; Ruan, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, L. How many channels are suitable for independent component analysis in motor imagery brain-computer interface. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2019, 50, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chen, S.A.; Lin, C.T. Using a novel LDA-ensemble framework to classification of motor imagery tasks for brain-computer interface applications. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Systems and Applications: Proceedings of the International Computer Symposium (ICS), Taichung, Taiwan, 12–14 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.B.; Bhuiyan, M.I.H.; Alam, S.S. Classification of EEG signals using normal inverse Gaussian parameters in the dual-tree complex wavelet transform domain for seizure detection. Signal Image Video Process. 2016, 10, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, R.; Bandyopadhyay, T. EEG based Motor Imagery Classification using SVM and MLP. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Networks (CINE), Bhubaneswar, India, 11 January 2016; pp. 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Hu, D.; Wan, M.; Wen, Y.; Von Deneen, K.M.; Zhou, M. Common Bayesian network for classification of EEG-based multiclass motor imagery BCI. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2015, 46, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Dai, Z.; He, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Learning traffic as images: A deep convolutional neural network for large-scale transportation network speed prediction. Sensors 2017, 17, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Zheng, D.; Na, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S. EEG Classification of Motor Imagery Using a Novel Deep Learning Framework. Sensors 2019, 19, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, N.; Li, T.; Ren, X.; Miao, H. A deep learning scheme for motor imagery classification based on restricted boltzmann machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 25, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirrmeister, R.T.; Springenberg, J.T.; Fiederer, L.D.J.; Glasstetter, M.; Eggensperger, K.; Tangermann, M.; Hutter, F.; Burgard, W.; Ball, T. Deep learning with convolutional neural networks for EEG decoding and visualization. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 5391–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Li, C.; Sun, S. Single-trial EEG classification of motor imagery using deep convolutional neural networks. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 2017, 130, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeb, Z.; Fedjaev, J.; Ghaboosi, N.; Richter, C.; Everding, L.; Qu, X.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, G.; Conradt, J. Validating deep neural networks for online decoding of motor imagery movements from EEG signals. Sensors 2019, 19, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Duan, F.; Solé-Casals, J.; Dinarès-Ferran, J.; Cichocki, A.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Z. A novel deep learning approach with data augmentation to classify motor imagery signals. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 15945–15954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, L.; Wang, X.; Monaghan, J.; Mcalpine, D. A Survey on Deep Learning based Brain Computer Interface: Recent Advances and New Frontiers. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.04149. [Google Scholar]
- Tabar, Y.R.; Halici, U. A novel deep learning approach for classification of EEG motor imagery signals. J. Neural Eng. 2016, 14, 016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, Y.; Banville, H.; Albuquerque, I.; Gramfort, A.; Falk, T.H.; Faubert, J. Deep learning-based electroencephalography analysis: A systematic review. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belouchrani, A.; Abed-Meraim, K.; Cardoso, J.; Moulines, E. Second-order blind separation of temporally correlated sources. Proc. Int. Conf. Digit. Signal Process. 1993, 346–351. [Google Scholar]
- Comon, P.; Jutten, C. Handbook of Blind Source Separation: Independent Component Analysis and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hyvärinen, A.; Oja, E. Independent component analysis: Algorithms and applications. Neural Netw. 2000, 13, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S. A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Itoh, K.; Tanida, J.; Ichioka, Y. Parallel distributed processing model with local space-invariant interconnections and its optical architecture. Appl. Opt. 1990, 29, 4790–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Comprehensive Guide to Convolutional Neural Networks—The ELI5 Way. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/a-comprehensive-guide-to-convolutional-neural-networks-the-eli5-way-3bd2b1164a53 (accessed on 9 September 2019).
- Data Set IVa. Available online: http://www.bbci.de/competition/iii/desc_IVa.html (accessed on 9 September 2019).
- Blankertz, B.; Muller, K.R.; Krusienski, D.J.; Schalk, G.; Wolpaw, J.R.; Schlogl, A.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Millan, J.R.; Schroder, M.; Birbaumer, N. The BCI competition III: Validating alternative approaches to actual BCI problems. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2006, 14, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse Wavelets. Available online: https://la.mathworks.com/help/wavelet/ug/morse-wavelets.html (accessed on 10 August 2019).
- Oosugi, N.; Kitajo, K.; Hasegawa, N.; Nagasaka, Y.; Okanoya, K.; Fujii, N. A new method for quantifying the performance of EEG blind source separation algorithms by referencing a simultaneously recorded ECoG signal. Neural Netw. 2017, 93, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, M.; Haueisen, J.; Ivanova, G. Independent component analysis: Comparison of algorithms for the investigation of surface electrical brain activity. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2009, 47, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albera, L.; Kachenoura, A.; Comon, P.; Karfoul, A.; Wendling, F.; Senhadji, L.; Merlet, I. ICA-based EEG denoising: A comparative analysis of fifteen methods. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2012, 60, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuly, S.; Li, Y. Improving the separability of motor imagery EEG signals using a cross correlation-based least square support vector machine for brain–computer interface. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2012, 20, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Detection of motor imagery EEG signals employing Naïve Bayes based learning process. Measurement 2016, 86, 148–158. [Google Scholar]
- Kevric, J.; Subasi, A. Comparison of signal decomposition methods in classification of EEG signals for motor-imagery BCI system. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 31, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taran, S.; Bajaj, V. Motor imagery tasks-based EEG signals classification using tunable-Q wavelet transform. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Layer | Operation | Kernel | Stride | Output Shape |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Conv2D | (63,256,250) | ||
| Activation | (63,256,250) | |||
| Max-pooling | (15,64,250) | |||
| 2 | Conv2D | (15,63,150) | ||
| Activation | (15,63,150) | |||
| Max-pooling | (5,21,150) | |||
| 3 | Flatten | (15750) | ||
| Dense | (2048) | |||
| Activation | (2048) | |||
| Dropout | (2048) | |||
| 4 | Dense | (2) | ||
| Activation | (2) |
| Subject | Accuracy | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k = 1 | k = 2 | k = 3 | k = 4 | k = 5 | k = 6 | k = 7 | k = 8 | k = 9 | k = 10 | Average | Std | |
| subject aa | 94.79 | 100.00 | 96.87 | 89.58 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 98.95 | 98.95 | 98.95 | 97.81 | 3.34 |
| subject al | 91.66 | 94.79 | 94.79 | 98.95 | 85.41 | 87.50 | 97.91 | 100.00 | 98.95 | 94.79 | 94.47 | 4.96 |
| subject av | 95.83 | 97.91 | 100.00 | 98.95 | 97.91 | 88.54 | 68.75 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 94.78 | 9.79 |
| subject aw | 98.75 | 92.50 | 95.00 | 99.37 | 99.37 | 91.87 | 100.00 | 98.75 | 76.87 | 88.12 | 94.06 | 7.26 |
| subject ay | 85.41 | 97.91 | 85.41 | 79.16 | 96.87 | 95.83 | 95.83 | 100.00 | 96.87 | 88.54 | 92.18 | 6.98 |
| Average | 94.66 | 6.46 | ||||||||||
| Author | Method | Classifier | Accuracy (%) | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lu et al. | R-CSP with aggregation | R-CSP | 83.90 | 2010 |
| Siuly et al. | CT | LS-SVM | 88.32 | 2011 |
| Zhang et al. | Z-score | LDA | 81.10 | 2013 |
| Siuly et al. | OA | NB | 96.36 | 2016 |
| Kevric et al. | MSPCA, WPD, HOS | k-NN | 92.80 | 2017 |
| Taran et al. | TQWT | LS-SVM | 96.89 | 2018 |
| Proposed | sorted-fastICA-CWT | CNN | 94.66 | 2019 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz-Echeverri, C.J.; Salazar-Colores, S.; Rodríguez-Reséndiz, J.; Gómez-Loenzo, R.A. A New Approach for Motor Imagery Classification Based on Sorted Blind Source Separation, Continuous Wavelet Transform, and Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2019, 19, 4541. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204541
Ortiz-Echeverri CJ, Salazar-Colores S, Rodríguez-Reséndiz J, Gómez-Loenzo RA. A New Approach for Motor Imagery Classification Based on Sorted Blind Source Separation, Continuous Wavelet Transform, and Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors. 2019; 19(20):4541. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204541
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz-Echeverri, César J., Sebastián Salazar-Colores, Juvenal Rodríguez-Reséndiz, and Roberto A. Gómez-Loenzo. 2019. "A New Approach for Motor Imagery Classification Based on Sorted Blind Source Separation, Continuous Wavelet Transform, and Convolutional Neural Network" Sensors 19, no. 20: 4541. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204541
APA StyleOrtiz-Echeverri, C. J., Salazar-Colores, S., Rodríguez-Reséndiz, J., & Gómez-Loenzo, R. A. (2019). A New Approach for Motor Imagery Classification Based on Sorted Blind Source Separation, Continuous Wavelet Transform, and Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors, 19(20), 4541. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204541






