Pyrogallol-Phloroglucinol-6,6-Bieckol from Ecklonia cava Attenuates Tubular Epithelial Cell (TCMK-1) Death in Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
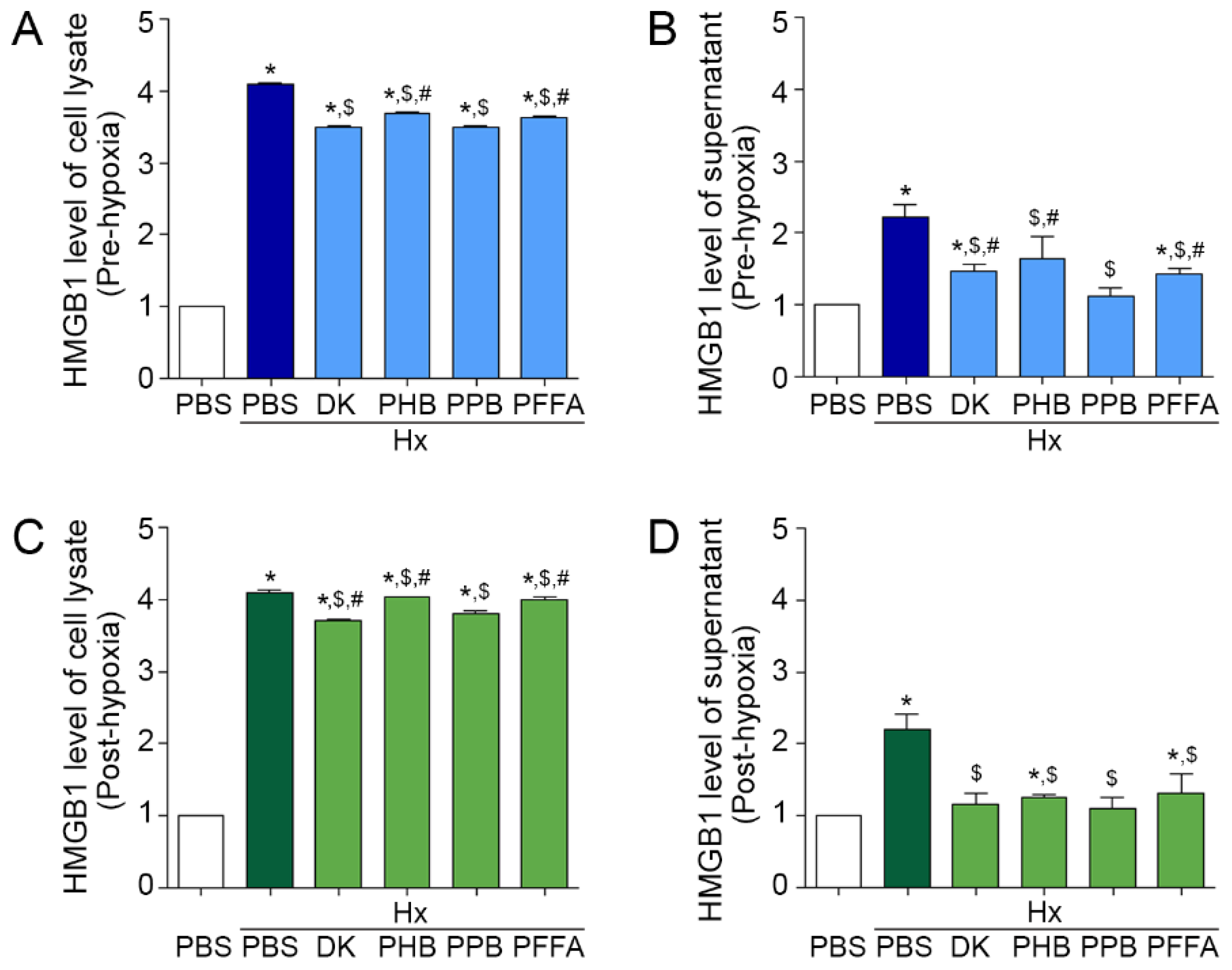
2.1. Attenuation of HMGB1 Release from TECs after H/R Injury by the Phlorotannins from E. cava Extracts
2.2. TLR4 and RAGE Expression Induced by H/R Injury Is Attenuated Most Efficiently by PPB
2.3. Expression of NF-kB and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines after H/R Injury Is Attenuated Efficiently by PPB
2.4. TEC Apoptosis Induced by H/R Injury Is Attenuated Efficiently by PPB
2.5. PPB Attenuated Cell Death Signals Induced by H/R Injury
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cell Culture
3.2. Hypoxia/Reoxygenation (H/R) Injury Cell Models
3.2.1. Pre-Hypoxia Treatment Model
3.2.2. Post-Hypoxia Treatment Model
3.3. Immunostaining
3.4. Immunoblotting
3.5. Detection of Apoptotic Cells by TUNEL Staining
3.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
3.7. Isolation of 4 Phlorotannins from E. cava
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Eltzschig, H.K.; Eckle, T. Ischemia and reperfusion—From mechanism to translation. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, F.; Romecín, P.; García-Guillén, A.I.; Wangesteen, R.; Vargas-Tendero, P.; Paredes, M.D.; Atucha, N.M.; García-Estañ, J. Flavonoids in Kidney Health and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2018, 24, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saat, T.C.; van den Akker, E.K.; IJzermans, J.N.; Dor, F.J.; de Bruin, R.W. Improving the outcome of kidney transplantation by ameliorating renal ischemia reperfusion injury: Lost in translation? J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; Han, N.J.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, M.J.; Park, S.K. TNF-alpha Activates High-Mobility Group Box 1—Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling Pathway in Human Aortic Endothelial Cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 2139–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, T.V.; Okun, E.; Tang, S.C.; Thundyil, J.; Taylor, S.M.; Woodruff, T.M. Toll-like receptors in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Shock 2009, 32, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonventre, J.V.; Yang, L. Cellular pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4210–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.B.; Liu, L.S.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.P.; Han, M.; Jiao, X.Y.; He, X.; Yuan, X.P. Up-Regulation of HMGB1 Exacerbates Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Stimulating Inflammatory and Immune Responses through the TLR4 Signaling Pathway in Mice. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 2447–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Chadban, S.J. Roles of Toll-like receptors in transplantation. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2014, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.F.; Hosgood, S.A.; Nicholson, M.L. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in renal transplantation: 3 key signaling pathways in tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, S.; Feirt, N.; Goldstein, M.; Guarrera, J.; Ippagunta, N.; Ekong, U.; Dun, H.; Lu, Y.; Qu, W.; Schmidt, A.M.; et al. Blockade of receptor for advanced glycation end product (RAGE) attenuates ischemia and reperfusion injury to the liver in mice. Hepatology 2004, 39, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrassy, M.; Volz, H.C.; Igwe, J.C.; Funke, B.; Eichberger, S.N.; Kaya, Z.; Buss, S.; Autschbach, F.; Pleger, S.T.; Lukic, I.K.; et al. High-mobility group box-1 in ischemia-reperfusion injury of the heart. Circulation 2008, 117, 3216–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.I.; Woo, J.H.; Seo, Y.J.; Lee, K.T.; Lim, Y.; Choi, J.H. Protective Effect of Brown Alga Phlorotannins against Hyperinflammatory Responses in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sepsis Models. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.I.; Shin, H.C.; Kim, S.H.; Park, W.Y.; Lee, K.T.; Choi, J.H. 6,6′-Bieckol, isolated from marine alga Ecklonia cava, suppressed LPS-induced nitric oxide and PGE production and inflammatory cytokine expression in macrophages: The inhibition of NFkappaB. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 12, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; Shin, T.; Utsuki, T.; Choi, J.S.; Byun, D.S.; Kim, H.R. Isolation and identification of phlorotannins from Ecklonia stolonifera with antioxidant and hepatoprotective properties in tacrine-treated HepG2 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5340–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eo, H.; Park, J.E.; Jeon, Y.J.; Lim, Y. Ameliorative Effect of Ecklonia cava Polyphenol Extract on Renal Inflammation Associated with Aberrant Energy Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in High Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3811–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, X.; Daofang, J.; Jing, X.; Chensheng, F.; Zhenxing, Z.; Zhibin, Y.; Xiaoli, Z. Ischemic preconditioning attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced kidney injury by activating autophagy via the SGK1 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 338. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Xun, L.; Jin, G.; Shi, L. Salidroside protects renal tubular epithelial cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in vitro. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 137, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraco, G.; Fossati, S.; Bianchi, M.E.; Patrone, M.; Pedrazzi, M.; Sparatore, B.; Moroni, F.; Chiarugi, A. High mobility group box 1 protein is released by neural cells upon different stresses and worsens ischemic neurodegeneration in vitro and in vivo. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadie, J.M.; Bae, H.B.; Jiang, S.; Park, D.W.; Bell, C.P.; Yang, H.; Pittet, J.F.; Tracey, K.; Thannickal, V.J.; Abraham, E.; et al. HMGB1 promotes neutrophil extracellular trap formation through interactions with Toll-like receptor 4. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2013, 304, L342–L349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hori, O.; Brett, J.; Slattery, T.; Cao, R.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.X.; Nagashima, M.; Lundh, E.R.; Vijay, S.; Nitecki, D.; et al. The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) is a cellular binding site for amphoterin. Mediation of neurite outgrowth and co-expression of rage and amphoterin in the developing nervous system. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 25752–25761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, B.D.; Ryan, S.; McNicholas, W.T. Obstructive sleep apnea and inflammation: Relationship to cardiovascular co-morbidity. Respir Physiol. Neurobiol. 2011, 178, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsu, A.; Shibutani, Y.; Seno, K.; Iwata, H.; Kuwayama, T.; Shirasuna, K. Advanced glycation end products and lipopolysaccharides stimulate interleukin-6 secretion via the RAGE/TLR4-NF-κB-ROS pathways and resveratrol attenuates these inflammatory responses in mouse macrophages. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 4363–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Zhao, J.; Cui, D.; Wang, F.; Song, Y.; Cheng, L.; Gao, K.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Li, S.; et al. Protective effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A against acute kidney injury via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.; Shi, J.; Shi, Q.; Xu, X.; Xia, Y.; He, X. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases and Hypoxic/Ischemic Nephropathy. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 1051–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ka, S.O.; Hwang, H.P.; Jang, J.H.; Hyuk Bang, I.; Bae, U.J.; Yu, H.C.; Cho, B.H.; Park, B.H. The protein kinase 2 inhibitor tetrabromobenzotriazole protects against renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alderliesten, M.; de Graauw, M.; Oldenampsen, J.; Qin, Y.; Pont, C.; van Buren, L.; van de Water, B. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation during renal ischemia/reperfusion mediates focal adhesion dissolution and renal injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Schnellmann, R.G. A death-promoting role for extracellular signal-regulated kinase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 319, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.C.; Ichimura, T.; Stevens, J.L.; Bonventre, J.V. Protection of renal epithelial cells against oxidative injury by endoplasmic reticulum stress preconditioning is mediated by ERK1/2 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 29317–29326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stambe, C.; Atkins, R.C.; Tesch, G.H.; Kapoun, A.M.; Hill, P.A.; Schreiner, G.F.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J. Blockade ofp38alpha MAPK ameliorates acute inflammatory renal injury in rat anti-GBM glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, N.S.; Jeong, Y.G.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, E.J.; Han, S.Y. Protective efficacy of an Ecklonia cava extract used to treat transient focal ischemia of the rat brain. Anat. Cell Biol. 2012, 45, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Yoo, S.Y.; Kwon, S.M. Cytoprotective effect of dieckol on human endothelial progenitor cells (hEPCs) from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. Free Radic. Res. 2013, 47, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Amarsanaa, K.; Lee, J.H.; Rhim, J.K.; Kwon, J.M.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.M.; Jung, S.C.; Eun, S.Y. Neuroprotective mechanisms of dieckol against glutamate toxicity through reactive oxygen species scavenging and nuclear factor-like 2/heme oxygenase-1 pathway. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 23, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Ko, J.Y.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.; Jeon, Y.J. Preparative isolation and purification of phlorotannins from Ecklonia cava using centrifugal partition chromatography by one-step. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, M.; Oh, S.; Choi, C.H.; Park, K.Y.; Son, K.H.; Byun, K. Pyrogallol-Phloroglucinol-6,6-Bieckol from Ecklonia cava Attenuates Tubular Epithelial Cell (TCMK-1) Death in Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110602
Son M, Oh S, Choi CH, Park KY, Son KH, Byun K. Pyrogallol-Phloroglucinol-6,6-Bieckol from Ecklonia cava Attenuates Tubular Epithelial Cell (TCMK-1) Death in Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(11):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110602
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Myeongjoo, Seyeon Oh, Chang Hu Choi, Kook Yang Park, Kuk Hui Son, and Kyunghee Byun. 2019. "Pyrogallol-Phloroglucinol-6,6-Bieckol from Ecklonia cava Attenuates Tubular Epithelial Cell (TCMK-1) Death in Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury" Marine Drugs 17, no. 11: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110602
APA StyleSon, M., Oh, S., Choi, C. H., Park, K. Y., Son, K. H., & Byun, K. (2019). Pyrogallol-Phloroglucinol-6,6-Bieckol from Ecklonia cava Attenuates Tubular Epithelial Cell (TCMK-1) Death in Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury. Marine Drugs, 17(11), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110602




