Al2O3 Disk Supported Si3N4 Hydrogen Purification Membrane for Low Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy

2.2. Gas Chromatography (GC)

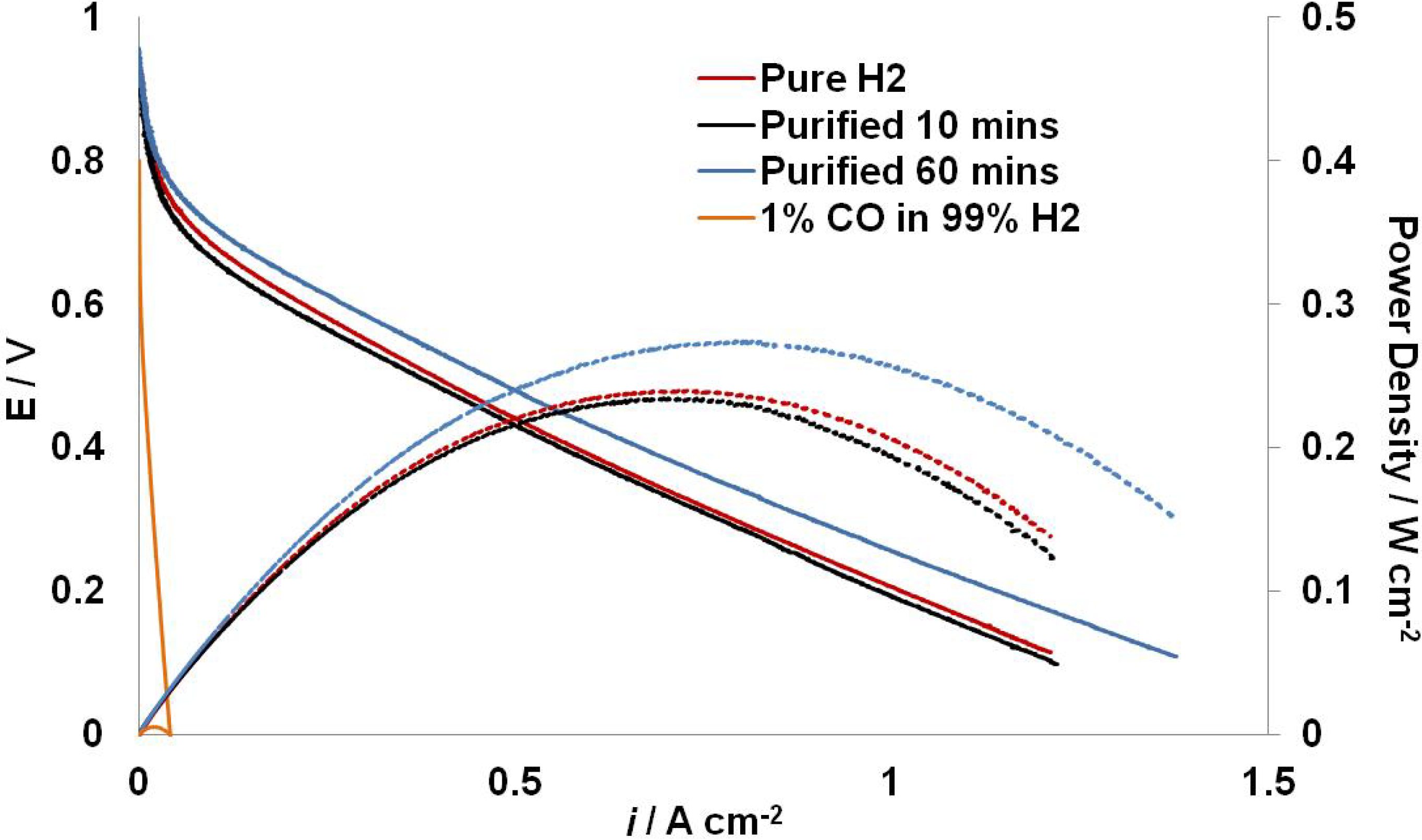
2.3. Fuel Cell Testing
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Si3N4 Membrane
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.3. The Membrane Holder

3.4. The Fuel Cell Test Rig

3.5. GC
3.6. Fuel Cell and Membrane Electrolyte Assembly (MEA)

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lemons, R.A. Fuel cells for transportation. J. Power Sources 1990, 29, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulianelli, A.; Longo, T.; Basile, A. Methanol steam reforming reaction in a Pd–Ag membrane reactor for CO-free hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 5583–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgouropoulos, G.; Ioannides, T. CO tolerance of Pt and Rh catalysts: Effect of CO in the gas-phase oxidation of H2 over Pt and Rh supported catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2005, 56, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.G.S.; Paganin, V.A.; Ticianelli, E.A. Investigation of the CO tolerance mechanism at several Pt-based bimetallic anode electrocatalysts in a PEM fuel cell. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 1992–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, H.; Xu, Z. In-situ investigation on the CO tolerance of carbon supported Pd–Pt electrocatalysts with low Pt content by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 2129–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, H.; Ozuka, H.; Watanabe, M. Electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance analysis of CO-tolerance at Pt–Fe alloy electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 3629–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-Q.; Shao, Z.-G.; Scott, K. A high conductivity Cs2.5H0.5PMo12O40/polybenzimidazole (PBI)/H3PO4 composite membrane for proton-exchange membrane fuel cells operating at high temperature. J. Power Sources 2008, 183, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K. The effect of electrode parameters on performance of a phosphoric acid-doped PBI membrane fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K. An investigation of Pt alloy oxygen reduction catalysts in phosphoric acid doped PBI fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, T.; Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K. A dynamic non-isothermal model of a laboratory intermediate temperature fuel cell using PBI doped phosphoric acid membranes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 12065–12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, T.; Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K. An isothermal model of a laboratory intermediate temperature fuel cell using PBI doped phosphoric acid membranes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 2513–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.; Düsterwald, H.G.; Höhlein, B. Investigation of a methanol reformer concept considering the particular impact of dynamics and long-term stability for use in a fuel-cell-powered passenger car. J. Power Sources 2000, 86, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, L.J.; Westerholm, R. State of the art of multi-fuel reformers for fuel cell vehicles: Problem identification and research needs. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2001, 26, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Clark, S.; Kelly, S.M.; Bradley, J.S.; Lefebvre, F. Preparation of mesoporous silicon nitride via a nonaqueous sol–gel route. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 87, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Kelly, S.M.; Clark, S.; Bradley, J.S.; Baumbach, M.; Schütze, A. Preparation and characterization of a supported Si3N4 membrane via a non-aqueous sol–gel process. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraoka, K.; Kubo, N.; Yazawa, T. Microporous silica xerogel membrane with high selectivity and high permeance for carbon dioxide separation. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2000, 19, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Mase, S.; Yoshimura, N.; Hotta, T.; Ayama, K.; Tsubaki, J.I. Fabrication of supported Si3N4 membranes using the pyrolysis of liquid polysilazane precursor. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 147, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.D.; Jansen, H.V.; Gadgil, V.J.; Bostan, C.G.; Berenschot, E.; van Rijn, C.J.M.; Elwenspoek, M. Silicon nitride nanosieve membrane. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovai, R.; Lehmann, C.W.; Bradley, J.S. Non-oxide sol–gel chemistry: Preparation from tris(dialkylamino)silazanes of a carbon-free, porous, silicon diimide gel. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 2036–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K. Analysis of high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell electrodes using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 5493–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Christensen, P.A.; Kelly, S.M.; Rocher, V.; Scott, K. Al2O3 Disk Supported Si3N4 Hydrogen Purification Membrane for Low Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Membranes 2013, 3, 406-414. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3040406
Liu X, Christensen PA, Kelly SM, Rocher V, Scott K. Al2O3 Disk Supported Si3N4 Hydrogen Purification Membrane for Low Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Membranes. 2013; 3(4):406-414. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3040406
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoteng, Paul A. Christensen, Stephen M. Kelly, Vincent Rocher, and Keith Scott. 2013. "Al2O3 Disk Supported Si3N4 Hydrogen Purification Membrane for Low Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells" Membranes 3, no. 4: 406-414. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3040406
APA StyleLiu, X., Christensen, P. A., Kelly, S. M., Rocher, V., & Scott, K. (2013). Al2O3 Disk Supported Si3N4 Hydrogen Purification Membrane for Low Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Membranes, 3(4), 406-414. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3040406



