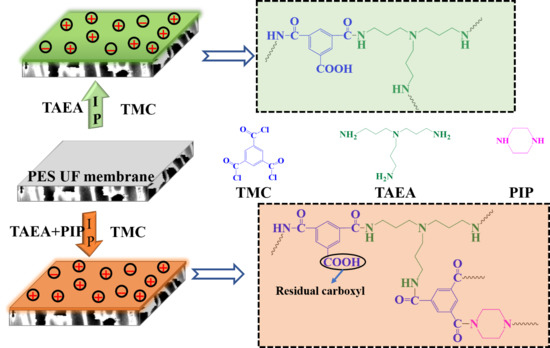
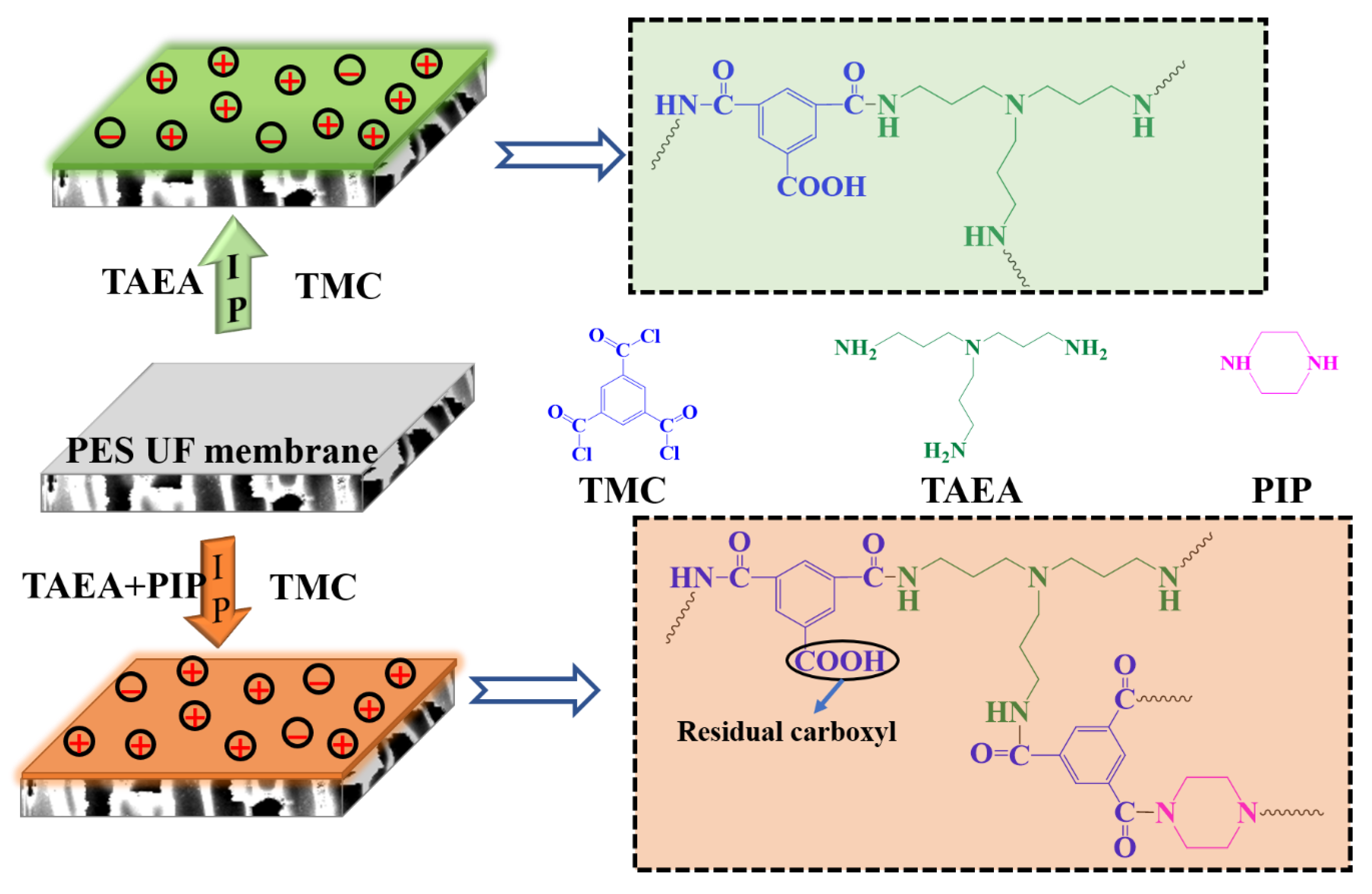
Tailoring Charged Nanofiltration Membrane Based on Non-Aromatic Tris(3-aminopropyl)amine for Effective Water Softening
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Fabrication of TFC NF Membranes
2.3. Characterization Methods
2.4. Membrane Performance Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
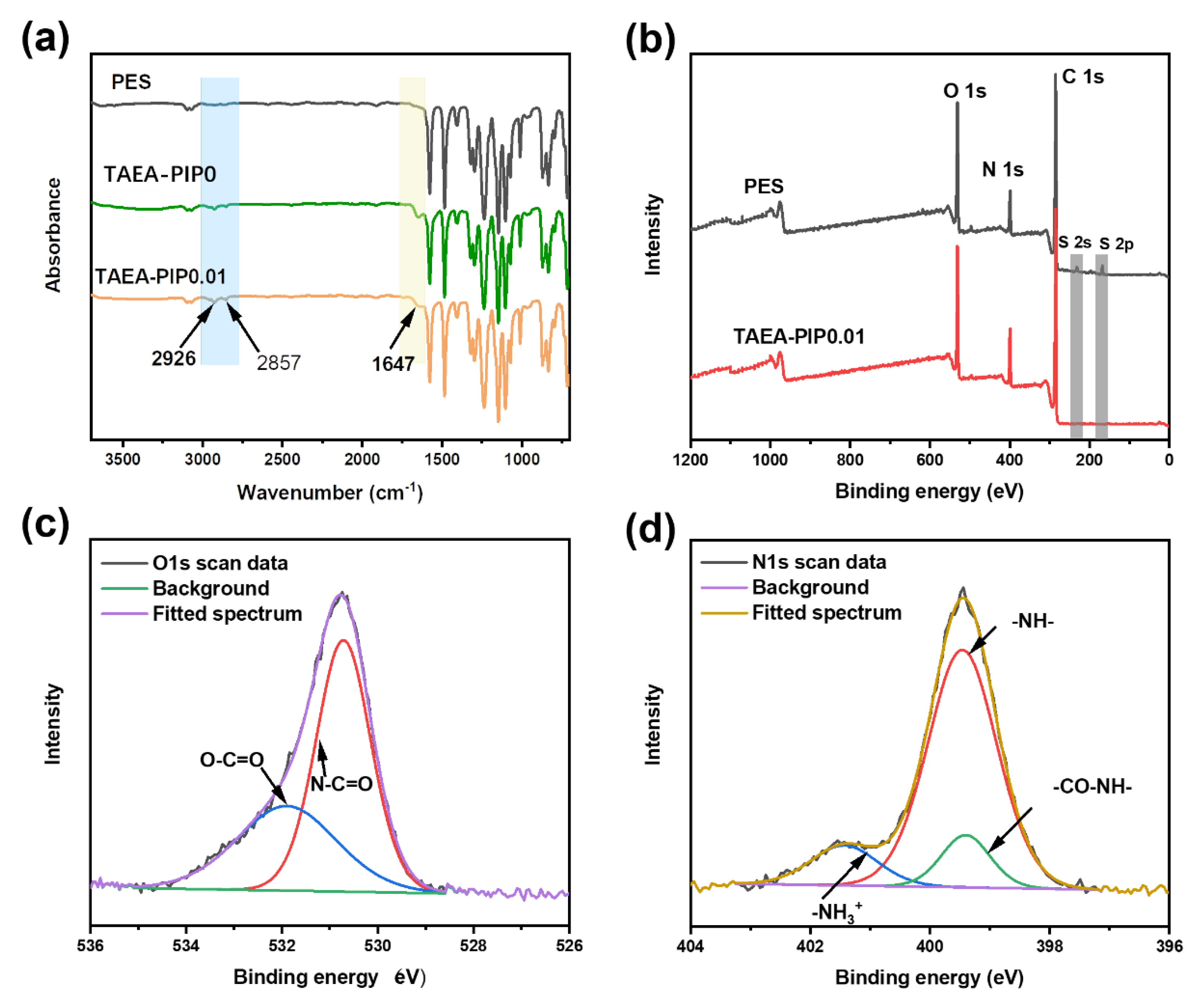
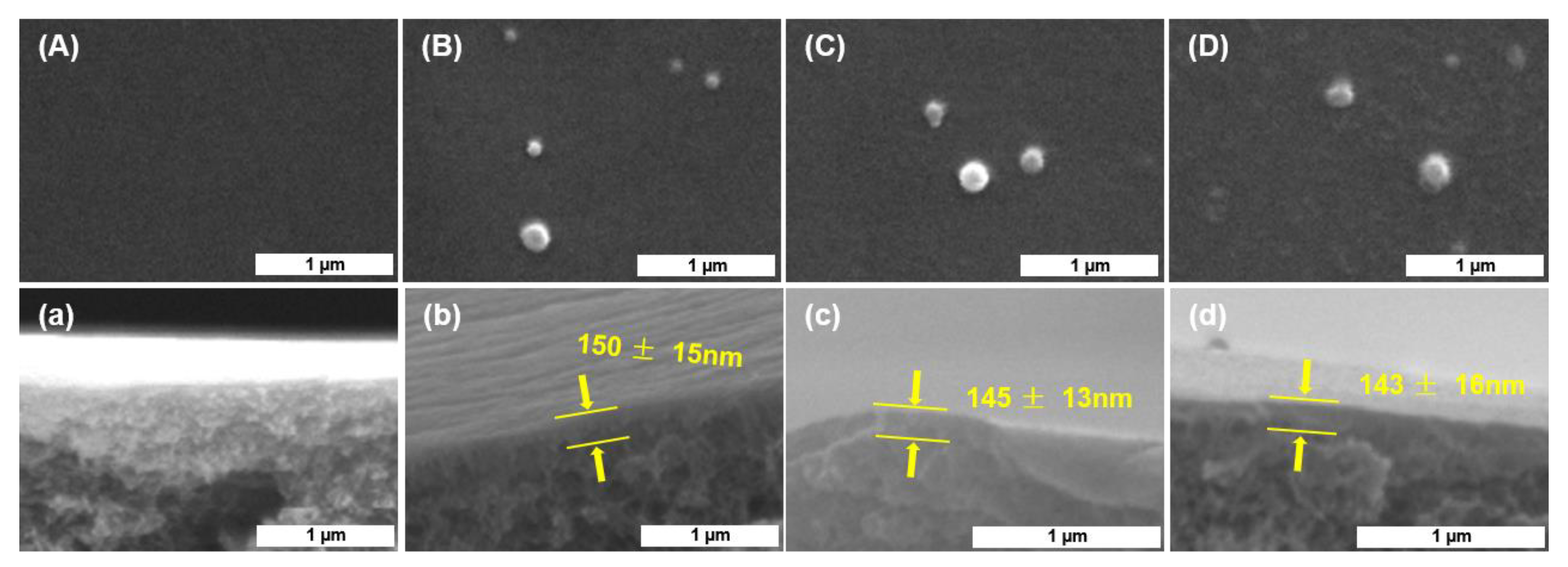
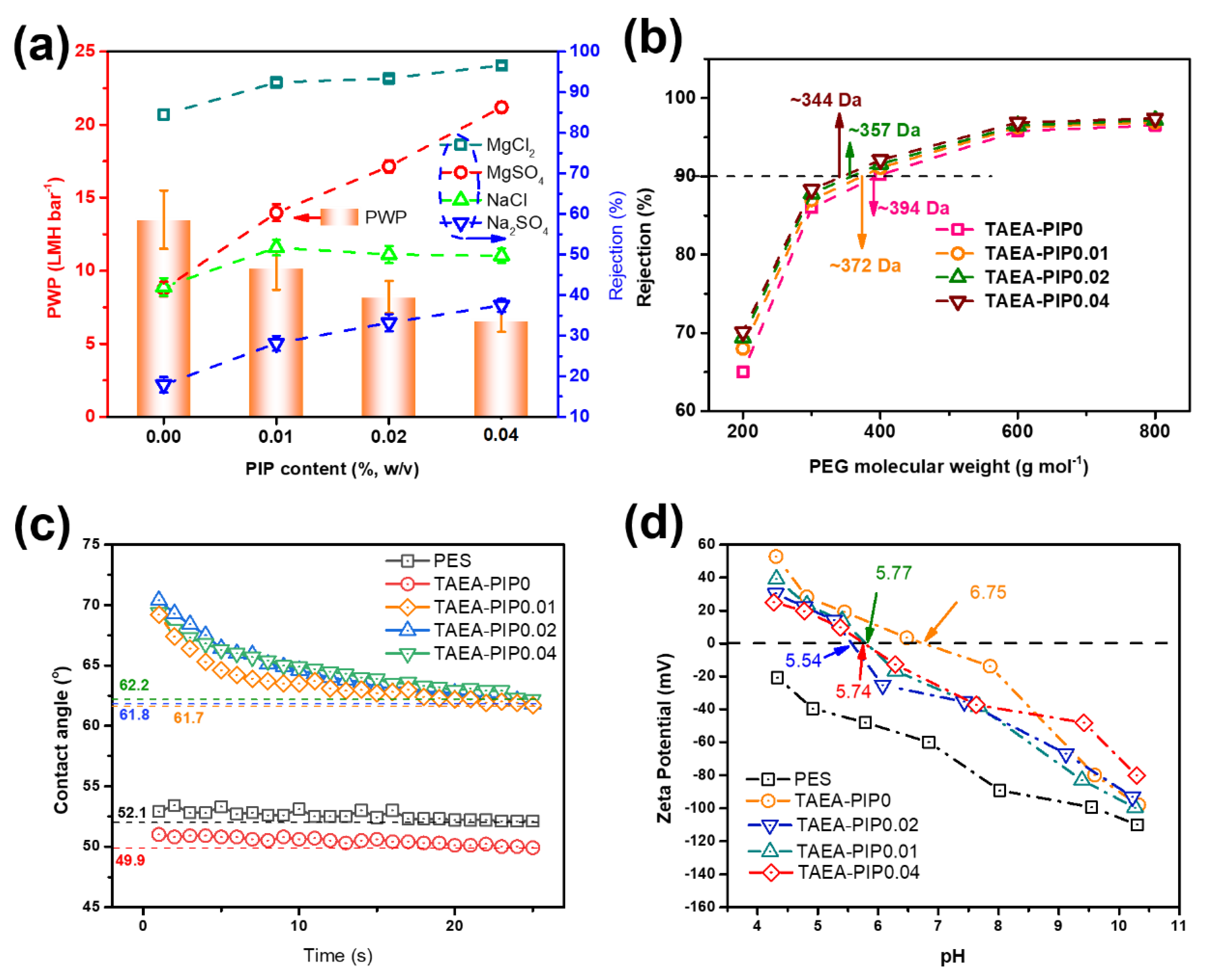
3.1. Characterizations of the Prepared Membranes
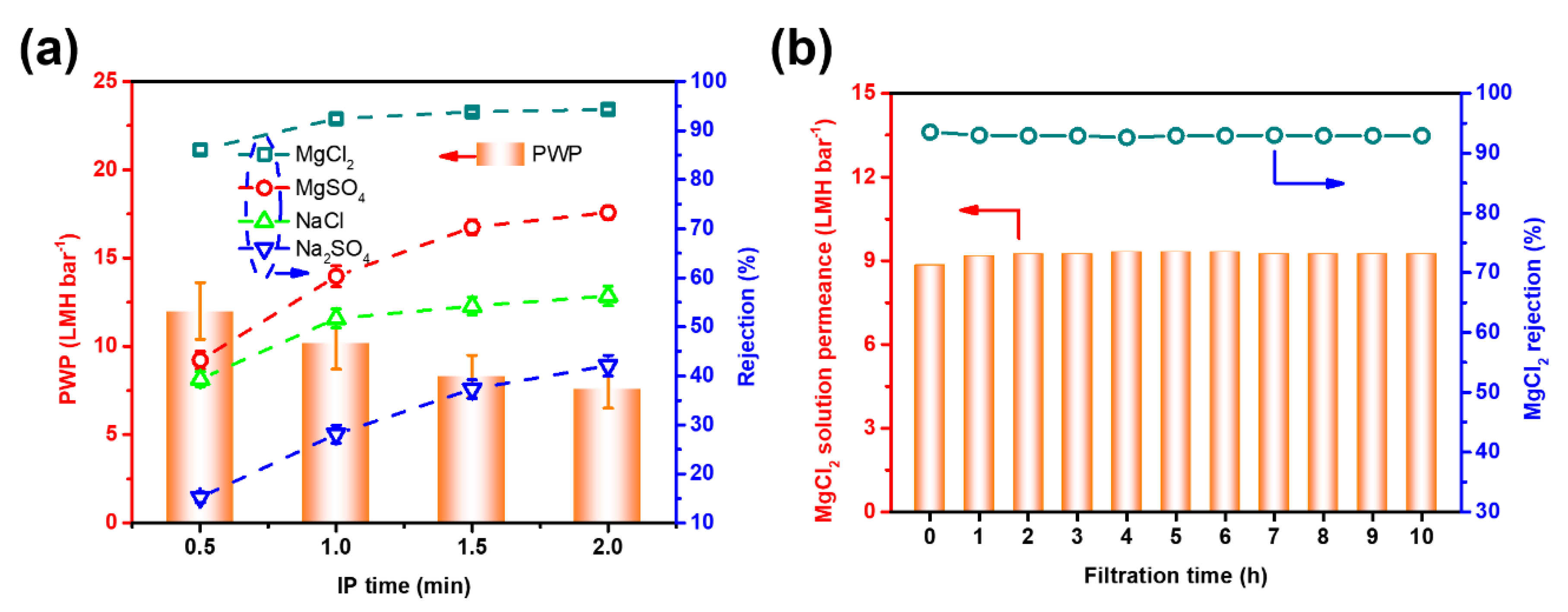
3.2. Optimization of Separation Performance
3.3. Stability of TAEA-PIP0.01 NF Membrane and Performance Comparison
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alvarez, P.J.; Chan, C.K.; Elimelech, M.; Halas, N.J.; Villagrán, D. Emerging opportunities for nanotechnology to enhance water security. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauter, M.S.; Zucker, I.; Perreault, F.; Werber, J.R.; Kim, J.-H.; Elimelech, M. The role of nanotechnology in tackling global water challenges. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M.; Phillip, W.A. The future of seawater desalination: Energy, technology, and the environment. Science 2011, 333, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Wang, H.; Shi, X.; Shen, B.; He, X.; Ghazi, Z.A.; Khan, N.A.; Sin, H.; Khattak, A.M.; Li, L. Microporous membranes comprising conjugated polymers with rigid backbones enable ultrafast organic-solvent nanofiltration. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, F.-Y.; An, Q.-F.; Ji, Y.-L.; Gao, C.-J. A novel type of polyelectrolyte complex/MWCNT hybrid nanofiltration membranes for water softening. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 492, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.-F.; Zhou, M.-Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhu, B.-K.; Matsuyama, H.; Zhao, S. Positively charged nanofiltration membrane based on cross-linked polyvinyl chloride copolymer. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, F.; Moattari, R.M.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Bagheri, M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Mohammadi, T.; Matsuyama, H. Preparation of thin film composite nano-filtration membranes for brackish water softening based on the reaction between functionalized UF membranes and polyethyleneimine. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 588, 117207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittbecker, E.L.; Morgan, P.W. Interfacial polycondensation. I. J. Polym. Sci. 1959, 40, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.W.; Kwolek, S.L. Interfacial polycondensation. II. Fundamentals of polymer formation at liquid interfaces. J. Polym. Sci. 1959, 40, 299–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Lee, K.-R.; Hung, W.-S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Elimelech, M.; Jin, J.; Lin, S. Polyamide nanofiltration membrane with highly uniform sub-nanometre pores for sub-1 Å precision separation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mo, Y.; Tiraferri, A.; Yip, N.Y.; Adout, A.; Huang, X.; Elimelech, M. Improved Antifouling Properties of Polyamide Nanofiltration Membranes by Reducing the Density of Surface Carboxyl Groups. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 13253–13261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.-L.; An, Q.-F.; Ji, Y.-L.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, X.-S.; Zhu, B.-K.; Gao, C.-J. Preparation and characterization of sulfated carboxymethyl cellulose nanofiltration membranes with improved water permeability. Desalination 2014, 338, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childress, A.E.; Elimelech, M. Relating nanofiltration membrane performance to membrane charge (electrokinetic) characteristics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3710–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.-Y.; Huang, Z.-H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.-L.; Ma, X.-H.; Xu, Z.-L.; Tang, C.Y. Novel high-flux positively charged composite membrane incorporating titanium-based MOFs for heavy metal removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, S.; Behboudi, A.; Mohammadi, T.; Ulbricht, M. High-performance positively charged hollow fiber nanofiltration membranes fabricated via green approach towards polyethyleneimine layer assembly. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 251, 117313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peydayesh, M.; Mohammadi, T.; Nikouzad, S.K. A positively charged composite loose nanofiltration membrane for water purification from heavy metals. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, W. Hindered transport of large molecules in liquid-filled pores. AIChE J. 1987, 33, 1409–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnan, F.G. Theory of membrane equilibria and membrane potentials in the presence of non-dialysing electrolytes. A contribution to physical-chemical physiology. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 100, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, G.; Mai, Z.; Gu, Y. The effect of dielectric exclusion on the rejection performance of inhomogeneously charged polyamide nanofiltration membranes. J. Nanopart. Res. 2019, 21, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandini, S.; Vezzani, D. Nanofiltration modeling: The role of dielectric exclusion in membrane characterization. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 3303–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, M.B.M.Y.; Tang, C.-L.; De Guzman, M.R.; Maganto, H.L.C.; Caparanga, A.R.; Huang, S.-H.; Tsai, H.-A.; Hu, C.-C.; Lee, K.-R.; Lai, J.-Y. Improved performance of thin-film nanofiltration membranes fabricated with the intervention of surfactants having different structures for water treatment. Desalination 2020, 481, 114352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, K.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, C. A facile preparation of positively charged composite nanofiltration membrane with high selectivity and permeability. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 581, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wei, X.; Zhu, B. High flux positively charged nanofiltration membranes prepared by UV-initiated graft polymerization of methacrylatoethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (DMC) onto polysulfone membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 366, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhu, L.-P.; Zhang, P.-B.; Sun, J.; Zhu, B.-K.; Xu, Y.-Y. Molecular separation by poly (N-vinyl imidazole) gel-filled membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, L.; Wang, R. Crosslinked layer-by-layer polyelectrolyte nanofiltration hollow fiber membrane for low-pressure water softening with the presence of SO42− in feed water. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 486, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asatekin, A.; Menniti, A.; Kang, S.; Elimelech, M.; Morgenroth, E.; Mayes, A.M. Antifouling nanofiltration membranes for membrane bioreactors from self-assembling graft copolymers. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 285, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, Y. Efficient surface modification of thin-film composite membranes with self-catalyzed tris (2-aminoethyl) amine for forward osmosis separation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 178, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Zuo, J.; Wang, Y. Tris (2-aminoethyl) amine in-situ modified thin-film composite membranes for forward osmosis applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, J.; Luis, P.; Van der Bruggen, B. Polyarylene thioether sulfone/sulfonated sulfone nanofiltration membrane with enhancement of rejection and permeability via molecular design☆. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 6, 118241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, G.; Volodine, A.; Tian, M.; Wang, J.; Luis, P.; Van der Bruggen, B. Erythritol-based polyester loose nanofiltration membrane with fast water transport for efficient dye/salt separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 27, 126796. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Ye, W.; Zeng, H.; Yang, H.; Shen, J.; Darvishmanesh, S.; Luis, P.; Sotto, A.; Van der Bruggen, B. Fractionation of direct dyes and salts in aqueous solution using loose nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 477, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabde, A.D.; Trivedi, M.; Ramachandhran, V.; Hanra, M.; Misra, B. Casting and characterization of cellulose acetate butyrate based UF membranes. Desalination 1997, 114, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Yin, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhong, Y.; Wu, H. Covalent organic framework modified polyamide nanofiltration membrane with enhanced performance for desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.-W.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Xu, Z.-L.; Tang, Y.-J. Interfacial polymerization on PES hollow fiber membranes using mixed diamines for nanofiltration removal of salts containing oxyanions and ferric ions. Desalination 2016, 394, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, V.T.; Tang, C.Y.; Reinhard, M.; Leckie, J.O. Degradation of polyamide nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes by hypochlorite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Wang, Y.; Xia, W.; Muhler, M. Thermal stability and reducibility of oxygen-containing functional groups on multiwalled carbon nanotube surfaces: A quantitative high-resolution XPS and TPD/TPR study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 16869–16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.W.; Kwak, I.S.; Yun, Y.-S. The role of biomass in polyethylenimine-coated chitosan/bacterial biomass composite biosorbent fiber for removal of Ru from acetic acid waste solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza, M.; Benavente, J.; Rodriguez-Castellon, E.; Palacio, L. Effect of hydration of polyamide membranes on the surface electrokinetic parameters: Surface characterization by X-ray photoelectronic spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 247, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, J.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.F.; Huang, X.; Van der Bruggen, B. A Facile and Scalable Fabrication Procedure for Thin-Film Composite Membranes: Integration of Phase Inversion and Interfacial Polymerization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.-Q.; Tang, Y.-J.; Zeng, Z.-X.; Xu, Z.-L. Microwave heating assistant preparation of high permselectivity polypiperazine-amide nanofiltration membrane during the interfacial polymerization process with low monomer concentration. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 596, 117718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yu, S.; Shi, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, B.; Bao, X. A novel polyesteramide thin film composite nanofiltration membrane prepared by interfacial polymerization of serinol and trimesoyl chloride (TMC) catalyzed by 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP). J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 68–80. [Google Scholar]
- Misdan, N.; Lau, W.; Ismail, A.; Matsuura, T.; Rana, D. Study on the thin film composite poly (piperazine-amide) nanofiltration membrane: Impacts of physicochemical properties of substrate on interfacial polymerization formation. Desalination 2014, 344, 198–205. [Google Scholar]
- Schaep, J.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Vandecasteele, C.; Wilms, D. Influence of ion size and charge in nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 1998, 14, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.-S.; Ji, Y.-L.; Wu, B.; Wang, N.-X.; Yin, M.-J.; An, Q.-F.; Gao, C.-J. High-flux zwitterionic nanofiltration membrane constructed by in-situ introduction method for monovalent salt/antibiotics separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 593, 117441. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, K.; Wang, X.-M. Role of coexistence of negative and positive membrane surface charges in electrostatic effect for salt rejection by nanofiltration. Desalination 2018, 444, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.-L.; Yan, Y.-N.; Zhou, F.-Y.; Sun, S.-P. Tailoring nanofiltration membranes for effective removing dye intermediates in complex dye-wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117476. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.-J.; Yang, H.-C.; Wu, M.-B.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanofiltration membranes with cellulose nanocrystals as an interlayer for unprecedented performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16289–16295. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Jiao, Z.; Bi, R.; Zhang, R.; You, X.; Wang, F.; Zhou, L.; Su, Y.; Jiang, Z. Chlorine-resistant polyester thin film composite nanofiltration membranes prepared with β-cyclodextrin. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 584, 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, W.Z.; Du, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yang, H.C.; Xu, Z.K. Codeposition of catechol–polyethyleneimine followed by interfacial polymerization for nanofiltration membranes with enhanced stability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45422. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Du, Y.; Qiu, W.-Z.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanocomposite membranes via the codeposition of polydopamine/polyethylenimine with silica nanoparticles for enhanced mechanical strength and high water permeability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2966–2972. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Hou, S.; Mao, H.; Zhang, S. Green fabrication of a positively charged nanofiltration membrane by grafting poly (ethylene imine) onto a poly (arylene ether sulfone) membrane containing tertiary amine groups. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 517, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Tang, C.Y. Novel polyethyleneimine/TMC-based nanofiltration membrane prepared on a polydopamine coated substrate. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Membrane | PWP (LMH bar−1) | Conditions | MgCl2 Rejection (%) | NaCl Rejection (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAEA-PIP0.01 | 10.2 | 1000 ppm, 4 bar | 92.4 | 51.3 | This work |
| PVC-g-PDMA | 9.3 | 950 ppm, 4 bar | 93.1 | ≈67.0 | [6] |
| PEI-(C-PES)/PES | 10.1 | 1000 ppm, 2 bar | 90.0 | [7] | |
| TFC-SDS | 7.5 | 1000 ppm, 6 bar | 94.1 | 47.1 | [21] |
| CCh/PEI-TFC | 4.4 | 1000 ppm, 7 bar | 93.0 | 38.2 | [49] |
| SiO2-PDA/PEI-TFN | 5.3 | 1000 ppm, 6 bar | 91.0 | ≈23.0 | [50] |
| PEI-PEGDGE-PES | 3.9 | 1000 ppm, 4 bar | 94.9 | 46.2 | [51] |
| PDA-PEI/TMC | 2.15 | 1000 ppm, 8 bar | 92.4 | 27.8 | [52] |
| Commercial NF90 | 10.2 | 1000 ppm, 6 bar | 50.83 | 60.1 | [21] |
| Commercial NF270 | 10.9 | 1000 ppm, 6 bar | 50.03 | 47.8 | [21] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, P.; Robeyn, M.; Zheng, J.; Yuan, S.; Van der Bruggen, B. Tailoring Charged Nanofiltration Membrane Based on Non-Aromatic Tris(3-aminopropyl)amine for Effective Water Softening. Membranes 2020, 10, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100251
Jin P, Robeyn M, Zheng J, Yuan S, Van der Bruggen B. Tailoring Charged Nanofiltration Membrane Based on Non-Aromatic Tris(3-aminopropyl)amine for Effective Water Softening. Membranes. 2020; 10(10):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100251
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Pengrui, Michiel Robeyn, Junfeng Zheng, Shushan Yuan, and Bart Van der Bruggen. 2020. "Tailoring Charged Nanofiltration Membrane Based on Non-Aromatic Tris(3-aminopropyl)amine for Effective Water Softening" Membranes 10, no. 10: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100251
APA StyleJin, P., Robeyn, M., Zheng, J., Yuan, S., & Van der Bruggen, B. (2020). Tailoring Charged Nanofiltration Membrane Based on Non-Aromatic Tris(3-aminopropyl)amine for Effective Water Softening. Membranes, 10(10), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100251