Electrospun Nanofibers of Natural and Synthetic Polymers as Artificial Extracellular Matrix for Tissue Engineering
Abstract
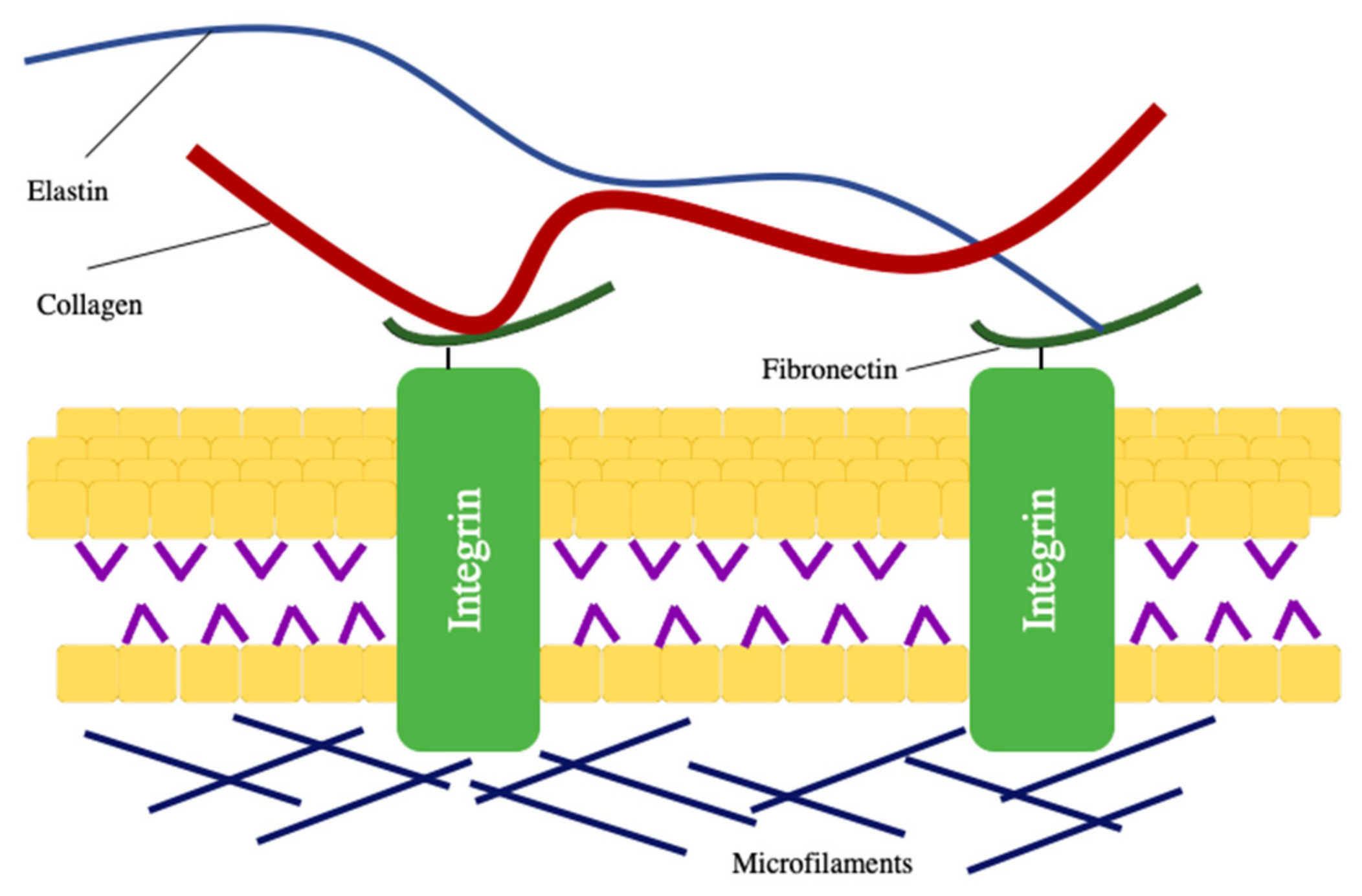
:1. Introduction
2. Application and Manufacture of Nanofibers
3. The Electrospinning Principle and Processing
4. Nanofibers as Scaffolds
4.1. Natural Polymer-Natural Polymer Composite Nanofibers
4.2. Natural Polymer-Synthetic Polymer Composite Nanofibers
4.3. Synthetic Polymer-Synthetic Polymer Composite Nanofibers
4.4. Nanofibers of Crosslinked Polymers
4.5. Nanofibers of Polymer–Inorganic Material Composites
5. Conclusions
6. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lutolf, M.; Hubbell, J. Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrucha, K. Physicochemical properties of 3D collagen-CS scaffolds for potential use in neural tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Tan, G.Z. Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) on the microstructure gradient T of biomimetic nanofiber scaffolds fabricated by cone electrospinning. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 44, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoa, C.; Niua, Y.; Zhangb, X.; Hea, X.; Zhanga, W.; Lua, C. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun cellulose/nano-hydroxyapatite nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, E.J.; Choi, S.M.; Singh, D.; Zo, S.M.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, J.H. Fabrication of cellulose-based scaffold with microarchitecture using a leaching technique for biomedical applications. Cellulose 2014, 21, 3515–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombini, S.; Mohammadnejad, J.; Bakhshandeh, B.; Narmani, A.; Nourmohammadi, J.; Sadaf Vahdat, S.Z. Chitosan-PVA-CNT nanofibers as electrically conductive scaffolds for cardiovascular tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliktar, D. Designing cell-compatible hydrogels for biomedical application. Science 2012, 336, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosoudi, N.; Holman, D.; Karamched, S.; Lei, Y.; Rodriguez-devora, J. Engineered Extracellular Matrix: Current Accomplishments and Future Trends. IJBES 2014, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Fan, Y.; Feng, Q.; Cui, F.-Z.; Watari, F. Nanostructured scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101, 2424–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaramurthi, D.; Krishnan, U.M.; Sethuraman, S. Electrospun Nanofibers as Scaffolds for Skin Tissue Engineering. Polym. Rev. 2014, 54, 348–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Bien, H.; Chung, C.; Yin, L.; Fang, D.; Hsiao, B.; Chu, B.; Entcheva, E. Electrospun fine-textured scaffolds for heart tissue constructs. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5330–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Klingner, A. A review on electrospun polymeric nanofibers: Production parameters and potential applications. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, H.M.; Ashraf, R.; Hanan Khan, A.; Beigh, M.A.; Majeed, S.; Sheikh, F.A. Reconstructing nanofibers from natural polymers using surface functionalization approaches for applications in tissue engineering, drug delivery and biosensing devices. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 1102–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Xiao, C.; Xiao, H.; Yang, H.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Electrospun polymer biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 90, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldana, A.A.; Abraham, G.A. Current advances in electrospun gelatin-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 25, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Qiu, L.; Ke, Q.; He, C.; Mo, X. Electrospinning Thermoplastic Polyurethane-Contained Collagen Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2009, 20, 1513–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, S.A.; McClure, M.J.; Garg, K.; Wolfe, P.S.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning of collagen/biopolymers for regenerative medicine and cardiovascular tissue engineering. Adv. Drug. Deliver. Rev. 2009, 61, 107–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hild, M.; Toskas, G.; Aibibu, D.; Wittenburg, G.; Meissner, H.; Cherif, C.; Hund, R.-D. Chitosan/gelatin micro/nanofiber 3D composite scaffolds for regenerative medicine. Compos. Interface 2014, 21, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.X. Scaffolds for tissue fabrication. Mater. Today 2004, 7, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.-F.; Zhang, K.H.; Chen, F.; Ke, Q.; Mo, X. Cross-Linking of gelatin and chitosan complex nanofibers for tissue-engineering scaffolds. J. Biomat. Sci. Polym. E. 2011, 22, 1099–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, W.; Markel, D.C.; Wang, S.; Shi, T.; Mao, G.; Ren, W. Electrospun polyvinyl alcohol–collagen–hydroxyapatite nanofibers: A biomimetic extracellular matrix for osteoblastic cells. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, B.P.; Leong, K.W. Scaffolding in tissue engineering: General approaches and tissue-specific considerations. Eur. Spine. J. 2008, 17, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karuppuswamy, P.; Venugopal, J.R.; Navaneethan, B.; Laiva, A.L.; Sridhar, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Functionalized hybrid nanofibers to mimic native ECM for tissue engineering applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 322, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, C.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Nanofibrous materials and their applications. Annu. Rev. 2006, 36, 333–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.E.; Yong, T.; Ma, Z.; Ramaseshan, R. Electrospun nanofibers: Solving global issues. Mater. Today 2006, 9, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, T.; Bhat, G.S.; Tock, R.W.; Pararneswaran, S.; Ramkumar, S.S. Electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 96, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lim, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S.; Huang, Z.M. Recent development of polymer nanofibers for biomedical and biotechnological applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2005, 16, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.; Hussain, T.; Raza, Z.A.; Nazir, A. Current applications of electrospun polymeric nanofibers in cancer therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 97, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, R.; Barhoum, A.; Bechelany, M.; Dufresne, A. Nanofibers for biomedical and healthcare applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, 1800256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y.N. Electrospinning of nanofibers: Reinventing the wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Feng, Y.; Huang, Z.M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lim, C.T. Fabrication of porous electrospun nanofibres. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.; Hussain, T.; Nazir, A.; Zahir, A.; Khenoussi, N. Acetaminophen loaded nanofibers as a potential contact layer for pain management in Burn wounds. Mater. Res. Express. 2018, 5, 085017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, T.J.; Waid, M.C.; McKenzie, J.L.; Price, R.L.; Ejiofor, J.U. Nano-biotechnology: Carbon nanofibres as improved neural and orthopaedic implants. Nanotechnology 2004, 15, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashammakhi, N.; Ndreu, A.; Nikkola, L.; Wimpenny, I.; Yang, Y. Advancing tissue engineering by using electrospun nanofibers. Regen. Med. 2008, 3, 547–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, W.; Chou, J.; Wen, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H. Electrospun nanosilicates-based organic/inorganic nanofibers for potential bone tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 172, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.Y.; Wen, Y.; Dzenis, Y.; Leong, K.W. The role of electrospinning in the emerging field of nanomedicine. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 4751–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, W.; Li, X.; Xie, C.; Zhuang, H.; Zhou, S.; Weng, J. Hydroxyapatite nucleation and growth mechanism on electrospun fibers functionalized with different chemical groups and their combinations. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4620–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneser, U.; Schaefer, D.J.; Polykandriotis, E.; Horch, R.E. Tissue engineering of bone: The reconstructive surgeon’s point of view. J. cell Mol. Med. 2006, 10, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshimotoa, H.; Shina, Y.M.; Teraia, H.; Vacanti, J.P. A biodegradable nanofiber scaffold by electrospinning and its potential for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2077–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppan, P.; Vasanthan, K.S.; Sundaramurthi, D.; Krishnan, U.M.; Sethuraman, S. Development of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) fibers for skin tissue engineering: Effects of topography, mechanical and chemical stimuli. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3156–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nune, S.K.; Rama, K.S.; Dirisala, V.R.; Chavali, M.Y. Electrospinning of Collagen Nanofiber Scaffolds for tissue Repair and Regeneration. In Nanostructures for Novel Therapy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, Y.; Unsworth, L.D.; Koutsopoulos, S.; Zhang, S. Slow release of molecules in self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffold. J. Control Release 2006, 115, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.S.S.; Nazeer, R.A. Wound healing properties of type I collagen from the bone of marine fishes. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2012, 18, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, A.; Maruyama, T.; Ohmukai, Y.; Sotani, T.; Matsuyama, H. Preparation of poly(lactic acid) hollow fiber membranes via phase separation methods. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 342, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, C.; Buriak, J.M. Template synthesis approach to nanomaterials: Charles Martin. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 4889–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, R.; Zhang, L.; Howe, J.; Hedin, N.; Zhang, Y.; Fong, H. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun titania nanofibers. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.P.; Sharma, U.; Mikos, A.G. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: A review. Tissue. Eng. 2006, 12, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sell, S.; Barnes, C.; Smith, M.; McClure, M. Extracellular matrix regenerated: Tissue engineering via electrospun biomimetic nanofibers. Polym. Int. 2007, 56, 1349–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, I.; Han, H.S.; Edwards, J.R.; Jeon, H. Electrospun fibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering: Viewpoints on architecture and fabrication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, S.I.; Krebs, M.D.; Bonino, C.A.; Khan, S.A.; Alsberg, E. Electrospun Alginate Nanofibers with Controlled Cell Adhesion for Tissue Engineering. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 10, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, J.D.; Schauer, C.L. A Review: Electrospinning of Biopolymer Nanofibers and their Applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 317–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Feng, Q.; Cui, F.; Watari, F. Biocomposites reinforced by fibers or tubes as scaffolds for tissue engineering or regenerative medicine. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 1580–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, W.; Xia, Y. Electrospun Nanofibers: New Concepts, Materials, and Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 1976–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L. Electrospinning jets and polymer nanofibers. Polymer 2008, 49, 2387–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taskin, M.B.; Xia, D.; Besenbacher, F.; Dong, M.; Chen, M. Nanotopography featured polycaprolactone/polyethyleneoxide microfibers modulate endothelial cell response. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 9218–9229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Yu, M.; Zong, X.; Chiu, J.; Fang, D.; Seo, Y.S.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B.; Hadjiargyrou, M. Control of degradation rate and hydrophilicity in electrospun non-woven poly (D, L-lactide) nanofiber scaffolds for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4977–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Gao, M.; Lin, J.; Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Chew, S.Y. Three-dimensional aligned nanofibers-hydrogel scaffold for controlled non-viral drug/gene delivery to direct axon regeneration in spinal cord injury treatment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norouzi, M.; Shabani, I.; Ahvaz, H.; Soleimani, M. PLGA/gelatin hybrid nano fibrous scaffolds encapsulating EGF for skin regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2015, 103, 2225–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Le, D.Q.S.; Li, H.; Lysdahl, H.; Chen, M.; Besenbacher, F.; Bünger, C. Engineered three-dimensional nanofibrous multi-lamellar structure for annulus fibrosus repair. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5462–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, J.V.; Uyar, T.; Chen, M.; Cloetens, P.; Kingshott, P.; Besenbacher, F. Characterisation of internal morphologies in electrospun fibers by X-ray tomographic microscopy. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3594–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ki, C.S.; Baek, D.H.; Gang, K.D.; Lee, K.H.; Um, I.C.; Park, Y.H. Characterization of gelatin nanofiber prepared from gelatin–formic acid solution. Polymer 2005, 46, 5094–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghi, A.K.; Akbari, M. Trends in electrospinning of natural nanofibers. Phys. Status. Solidi. A. 2007, 204, 1830–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, S.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. Influence of solvents on the formation of ultrathin uniform poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) nanofibers with electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 3721–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, M.G.; Layman, J.M.; Cashion, M.P.; Long, T.E. Phospholipid nonwoven electrospun membranes. Science 2006, 311, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koski, A.; Yim, K.; Shivkumar, S. Effect of molecular weight on fibrous PVA produced by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidi, S.S.; Slemming-Adamsen, P.; Hanif, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, M. Wet electrospun alginate/gelatin hydrogel nanofibers for 3D cell culture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 1648–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Lu, B.; Xie, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Duan, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; et al. Temperature effect on electrospinning of nanobelts: The case of hafnium oxide. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 285609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieze, S.D.; Camp, T.V.; Nelvig, A.; Hagstrom, B.; Westbroek, P.; Clerck, K.D. The effect of temperature and humidity on electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelipenko, J.; Kristl, J.; Jankovic, B.; Baumgartner, S.; Kocbek, P. The impact of relative humidity during electrospinning on the morphology and mechanical properties of nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Memic, A.; Annabi, N.; Hossain, M.; Paul, A.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Dehghani, F.; Khademhosseini, A. Electrospun scaffolds for tissue engineering of vascular grafts. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
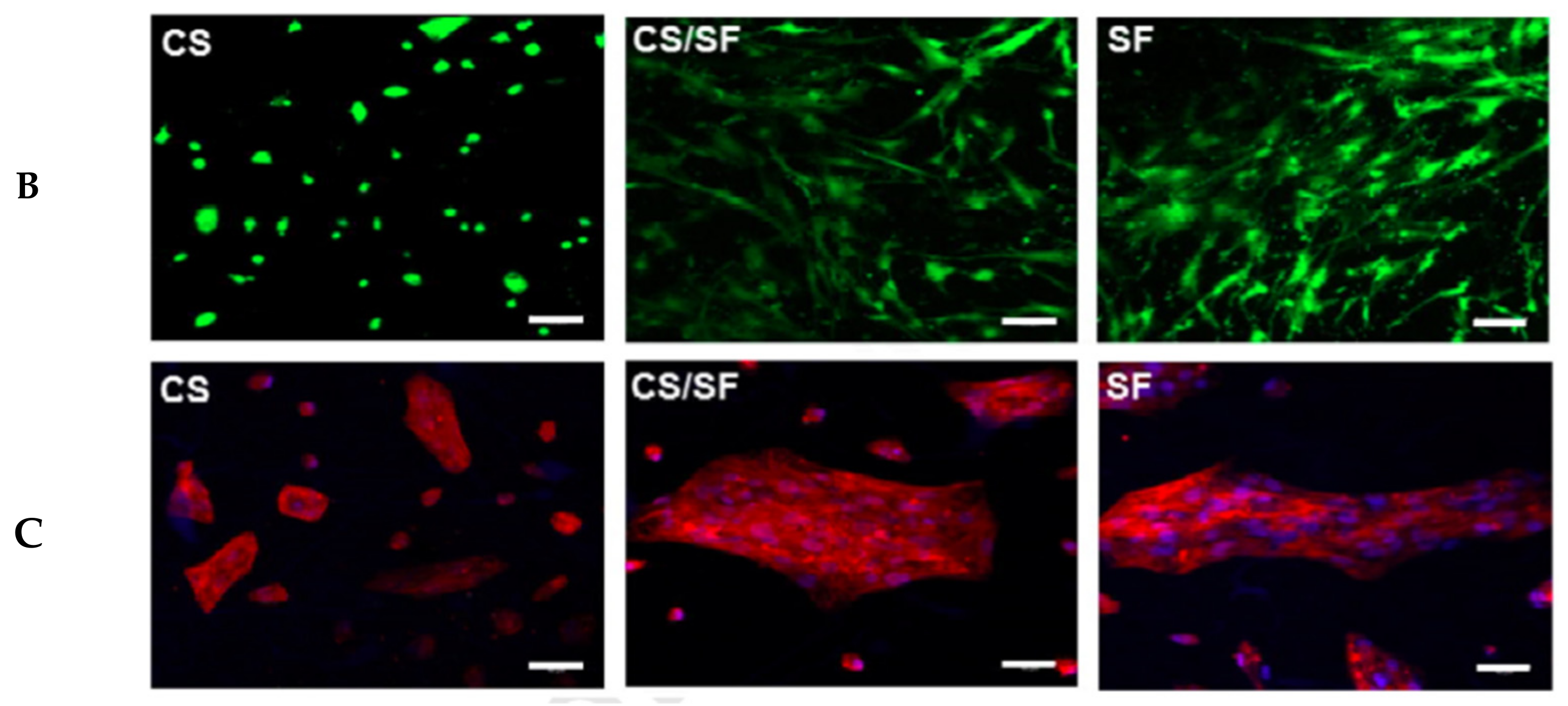
- Singh, B.N.; Pramanik, K. Generation of bioactive nano-composite scaffold of nanobioglass/silk fibroin/carboxymethyl cellulose for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 2011–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajavi, R.; Abbasipour, M.; Bahador, A. Electrospun biodegradable nanofibers scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegel, C.; Arrechi, A.; Kit, K.; McClements, D.J.; Weiss, J. Fabrication, Functionalization, and Application of Electrospun Biopolymer Nanofibers. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 775–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.-C.; Chang, J.-J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Wu, M.-H.; Yang, M.-C.; Chien, C.-T. Electrospun scaffolds composing of alginate, chitosan, collagen and hydroxyapatite for applying in bone tissue engineering. Mater. Lett. 2013, 93, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H. Novel chitin and chitosan nanofibers in biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhao, J.; Ou, Y.; Jiang, D. Biofunctionalized peptide nanofiber-based composite scaffolds for bone regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.G.; Wang, P.W.; Wei, B.; Mo, X.M.; Cui, F.Z. Electrospun collagen-chitosan nanofiber: A biomimetic extracellular matrix for endothelial cell and smooth muscle cell. Acta. Biomater. 2010, 6, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, V.; Dean, D.R.; Jose, M.V.; Mathew, B.; Chowdhury, S.; Vohra, Y.K. Nanostructured biocomposite scaffolds based on collagen coelectrospun with nanohydroxyapatite. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.; Hu, J.; Han, Y. Random and aligned electrospun gelatin nanofiber mats for human mesenchymal stem cells. Mater. Res. Innov. 2018, 23, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Song, J.H.; Kim, H.E. Nanofiber Generation of Gelatin–Hydroxyapatite Biomimetics for Guided Tissue Regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1988–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.E.; Jung, S.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Min, B.-M.; Park, W.H. Biomimetic nanofibrous scaffolds: Preparation and characterization of chitin/silk fibroin blend nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2006, 38, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, B.M.; Lee, G.; Kim, S.H.; Nam, Y.S.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. Electrospinning of silk fibroin nanofibers and its effect on the adhesion and spreading of normal human keratinocytes and fibroblasts in vitro. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Nam, Y.S.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. Silk Fibroin Nanofiber. Electrospinning, Properties, and Structure. Polymer 2003, 35, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-F.; Gregersen, H.; Nygaard, J.V.; Cheng, W.; Yu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Dong, M.; Besenbacher, F.; Chen, M. Ultraporous nanofeatured PCL–PEO microfibrous scaffolds enhance cell infiltration, colonization and myofibroblastic differentiation. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 14989–14995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Li, D.; Kong, D.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Gradient nanofibrous chitosan/poly-3 caprolactone scaffolds as extracellular microenvironments for vascular tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal-hay, A.; Taha, M.; Mousa, H.M.; Bartnikowski, M.; Hassan, M.L.; Dewidar, M.; Ivanovski, S. Engineering of electrically-conductive poly(ε-caprolactone)/ multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite nanofibers for tissue engineering applications. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 15736–15740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegal, S.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, T.-H.; Shin, U.S.; Kim, T.-I.; Kim, H.-W. Functional composite nanofibers of poly(lactide–co-caprolactone) containing gelatin–apatite bone mimetic precipitate for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.X.; Wang, Y.S.; Ma, C.; Zheng, W.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.F. Electrospinning of PLGA/gelatin randomly-oriented and aligned nanofibers as potential scaffold in tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibo, Y.; Youzhu, Z.; Weiwei, B.; Jialin, W.; De-bing, S.; Zhi-hui, D.; Wei-guo, F. Study on the Properties of the Electrospun Silk Fibroin/Gelatin Blend Nanofibers for Scaffolds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.-J.; Shalumon, K.T.; Chen, S.-H.; Chen, J.-P. Composite Chitosan/Silk Fibroin Nanofibers for Modulation of Osteogenic Differentiation and Proliferation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorani, B.; Tabandeh, F.; Yazdian, F.; Soheili, Z.-S.; Shakibaie, M.; Rahmani, S. Thin natural Gelatin/Chitosan nanofibrous scaffolds for Retinal Pigment Epithelium cells. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Po. 2018, 67, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatankhah, E.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Semnani, D.; Razavi, S.; Morshed, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun tecophilic/gelatin nanofibers with potential for small diameter blood vessel tissue engineering. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 1165–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, F.; Atyabi, S.M.; Norouzian, D.; Zandi, M.; Irani, S.; Bakhshi, H. Polycaprolactone/Carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering Application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Xu, J.; Ding, S.; Li, H.; Zhou, C.; Li, L. In vitro evaluation of random and aligned polycaprolactone/gelatin fibers via eletrospinning for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2015, 26, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.K.; Park, S.J.; Kim, C.-H. Beneficial effect of aligned nanofiber scaffolds with electrical conductivity for the directional guide of cells. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Hu, J.; Chen, M.; Besenbacher, F.; Ramakrishna, S. Synergistic effect of topography, surface chemistry and conductivity of the electrospun nanofibrous scaffold on cellular response of PC12 cells. Colloids. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Zhang, H.; Yan, J.; Gong, X. Effect of Nanofiber Orientation of Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffolds on Cell Growth and Elastin Expression of Muscle Cells. Colloids. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tian, L.; Luo, B.; Ramakrishna, S.; Kai, D.; Loh, X.J.; Yang, I.H.; Deen, G.R.; Mo, X. Engineering PCL/Lignin Nanofibers as an Antioxidant Scaffold for the Growth of Neuron and Schwann cell. Colloids. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 169, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agheb, M.; Dinari, M.; Rafienia, M.; Salehi, H. Novel electrospun nanofibers of modified gelatin-tyrosine in cartilage tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomes, S.R.; Rodrigues, G.; Martins, G.G.; Roberto, M.A.; Mafra, M.; Henriques, C.M.R.; Silva, J.C. Cross-link polymer provides insolubility, rigidity, and stiffness to the polymer which offer potential applications in solid-phase synthesis, solid-phase extraction, and biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 46, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Scharnweber, D.; Koul, V. Co-cultivation of keratinocyte-human mesenchymal stem cell (hMSC) on sericin loaded electrospun nanofibrous composite scaffold (cationic gelatin/hyaluronan/chondroitin sulfate) stimulates epithelial differentiation in hMSCs: In vitro study. Biomaterials 2016, 88, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.-H.; Yu, J.; Chen, G.; Tsai, W.-B. Fabrication of multi-biofunctional gelatin-based electrospun fibrous scaffolds for enhancement of osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Colloids. Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2016, 138, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pati, F.; Adhikari, B.; Dhara, S. Development of chitosan-tripolyphosphate non-woven fibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering application. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vozzi, G.; Corallo, C.; Carta, S.; Fortina, M.; Gattazzo, F.; Galletti, M.; Giordano, N. Collagen-gelatin-genipin-hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds colonized by human primary osteoblasts are suitable for bone tissue engineering applications: In vitro evidences. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj, J.; Khalil, T.H.; Falah, M.; Zussman, E.; Srouji, S. An ECM-Mimicking, Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Embedded Hybrid Scaffold for Bone Regeneration. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadisi, Z.; Nourmohammadi, J.; Mohammadi, J. Composite of porous starch-silk fibroin nanofiber-calcium phosphate for bone regeneration. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 10745–10754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadke, P.; Chhabra, R.; Jain, R.; Dandekar, P. Silver-embedded starch-based nanofibrous mats for soft tissue engineering. Surf. Interfaces 2017, 8, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.C.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.E.; Song, S.-J.; Hong, S.W.; Oh, J.-W.; Lee, J.; Park, J.-C.; Hyon, S.-H.; Han, D.-W. RGD peptide and graphene oxide co-functionalized PLGA nanofiber scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. Regener. Biomater. 2017, 4, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, E.; Azami, M.; Kajbafzadeh, A.-M.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Faridi-Majidi, R.; Shamousi, A.; Karimi, R.; Ai, J. Preparation of a biomimetic composite scaffold from gelatin/collagen and bioactive glass fibers for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Padera, R.; Sanders, G.H.W.; Cannizzaro, S.M.; Davies, M.C.; Langer, R.; Roberts, C.J.; Tendler, S.J.B.; Williams, P.M.; Shakesheff, K.M. Spatially controlled cell engineering on biodegradable polymer surfaces. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooten, T.G.V.; Whitesides, J.F.; Recum, A.F.V. Influence of silicone (PDMS) surface texture on human skin fibroblast proliferation as determined by cell cycle analysis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, A.D.; Sittinger, M.; Risbud, M.V. Chitosan: A versatile biopolymer for orthopaedic tissue-engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5983–5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.P.; Chen, S.H.; Lai, G.J. Preparation and characterization of biomimetic silk fibroin/chitosan composite nanofibers by electrospinning for osteoblasts culture. Nanoscale. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.-l.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P. Composite electrospun nanomembranes of fish scale collagen peptides/chito-oligosaccharides: Antibacterial properties and potential for wound dressing. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 667–676. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, Y.K.; Costa, A.D.S.D.; Park, Y.S.; Du, P.; Kim, I.-H.; Park, K. Fabrication of bacterial cellulose-collagen composite scaffolds and their osteogenic effect on human mesenchymal stem cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 219, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sell, S.A.; Wolfe, P.S.; Garg, K.; McCool, J.M.; Rodriguez, I.A.; Bowlin, G.L. The use of natural polymers in tissue engineering: A focus on electrospun extracellular matrix analogues. Polymers 2010, 2, 522–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, C.; Talukdar, S.; Novoyatleva, T.; Velagala, S.R.; Mühlfeld, C.; Kundu, B.; Kundu, S.C.; Engel, F.B. Silk protein fibroin from Antheraea mylitta for cardiac tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2673–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbasipour, M.; Khajavi, R. Nanofiber Bundles and Yarns Production by Electrospinning: A Review. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2013, 32, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal-hay, A.; Vanegas, P.; Lim, J.K. Air jet spray of nylon 6 membrane structures for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Lett. 2014, 125, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalumon, K.T.; Deepthi, S.; Anupama, M.S.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R.; Chennazhi, K.P. Fabrication of poly (l-lactic acid)/gelatin composite tubular scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atyabi, S.M.; Sharifi, F.; Irani, S.; Zandi, M.; Mivehchi, H.; Nagheh, Z. Cell attachment and viability study of PCL nano-fiber modified by cold atmospheric plasma. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 74, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.F.; Vaquette, C.; Zhang, Q.; Reis, R.L.; Ivanovski, S.; Hutmacher, D.W. Advanced tissue engineering scaffold design for regeneration of the complex hierarchical periodontal structure. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2014, 41, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.H.; Chang, M.C.; Hung, S.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Lin, Y.M. Bioactive surface modification of polycaprolactone using MG63-conditioned medium can induce osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 3967–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, F.; Agabalyan, N.A.; Sparks, H.D.; Rosin, N.L.; Kallos, M.S.; Biernaskie, J. Biocomposite nanofiber matrices to support ECM remodeling by human dermal progenitors and enhanced wound closure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Xu, R.; Li, D.; Bortolini, C.; He, J.; Dong, M.; Besenbacher, F.; Huang, Y.; Chen, M. Artificial Extracellular Matrix Deliver TGFb1 Regulating Myofibroblasts Differentiation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 21922–21928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molas, J.A.; Chen, M. Injectable PLCL/gelatin core-shell nanofibers support noninvasive 3D delivery of stem cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 568, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Abdal-hay, A.; Hamdy, A.S.; Khalil, K.A. Fabrication of durable high performance hybrid nanofiber scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration using a novel, simple in situ deposition approach of polyvinyl alcohol on electrospun nylon 6 nanofibers. Mater. Lett. 2015, 147, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, L.; Cheng, R.; Cui, W. ECM Decorated Electrospun Nanofiber for Improving Bone Tissue Regeneration. Polymers 2018, 10, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, R.; Zhao, H.; Muhammad, H.; Dong, M.; Chen, M. Dual-delivery of FGF-2/CTGF from Silk Fibroin/PLCL-PEO Coaxial Fibers Enhances MSC Proliferation and Fibrogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Taskin, M.B.; Zhang, Z.; Su, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, M. Bioadhesive anisotropic nanogrooved microfibers directing three-dimensional neurite extension. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2165–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Guo, W.; Chen, M.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Xi, T.; Guo, Q. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun nanofibers composed of decellularized meniscus extracellular matrix and polycaprolactone for meniscus tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2273–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinlapabodin, S.; Amornsudthiwat, P.; Damrongsakkul, S.; Kanokpanont, S. An axial distribution of seeding, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells and rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells across a 3D Thai silk fibroin/gelatin/hydroxyapatite scaffold in a perfusion bioreactor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, S.-M.; Ko, L.-Y.; Huang, T.-J. Effect of crosslinking temperature on compression strength of gelatin scaffold for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Progress in the Field of Electrospinning for Tissue Engineering Applications. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3343–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barhoum, A.; Pal, K.; Rahier, H.; Uludag, H.; Soo Kim, I.; Bechelany, M. Nanofibers as new-generation materials: From spinning and nano-spinningfabrication techniques to emerging applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 17, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Deng, C.; Cheng, R.; Meng, F.; Zhong, Z. In situ forming hydrogels via catalyst-free and bioorthogonal “tetrazole–alkene” photo-click chemistry. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 2814–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mane, S.; Ponrathnam, S.; Chavan, N. Effect of Chemical Cross-linking on Properties of Polymer Microbeads: A Review. Can. Chem. Trans. 2015, 3, 473–485. [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman, J.D.; Schauer, C.L. One-Step Electrospinning of Cross-Linked Chitosan Fibers. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2665–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzavolta, S.; Gioffrè, M.; Focarete, M.L.; Gualandi, C.; Foroni, L.; Bigi, A. Electrospun gelatin nanofibers: Optimization of GEN cross-linking to preserve fiber morphology after exposure to water. Acta. Biomater. 2011, 7, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisson, K.; Zhang, C.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Evaluation of Cross- Linking Methods for Electrospun Gelatin on Cell Growth and Viability. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiguera, S.; Gaudio, C.D.; Lucatelli, E.; Kuevda, E.; Boieri, M.; Mazzanti, B.; Bianco, A.; Macchiarini, P. Electrospun gelatin scaffolds incorporating rat decellularized brain extracellular matrix for neural tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angarano, M.; Schulz, S.; Fabritius, M.; Vogt, R.; Steinberg, T.; Tomakidi, P.; Friedrich, C.; Mulhaupt, R. Layered Gradient Nonwovens of In Situ Crosslinked Electrospun Collagenous Nanofibers Used as Modular Scaffold Systems for Soft Tissue Regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3277–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.; Soussan, L.; Bechelany, M.; Teyssier, C.; Cavaillès, V.; Pochat-Bohatier, C.; Miele, P.; Kalkura, N.; Janot, J.; Balme, S. Novel biocompatible electrospun gelatin fibers mat with antibiotic drug delivery properties. J. Materi. Chem. B 2016, 4, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonsomboon, K.; Oyen, M.L. Composite electrospun gelatin fiber-alginate gel scaffolds for mechanically robust tissue engineered cornea. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2013, 21, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, A.R.; Lopes, L.C.; Caleare, A.O.; Britta, E.A.; Nakamura, C.V.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Silver sulfadiazine loaded chitosan/chondroitin sulfate films for a potential wound dressing application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.H.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Zhang, G.R.; Jin, H.M.; Hieu, N.T.M.; Ouyang, H.W. Specific interactions between human fibroblasts and particular chondroitin sulfate molecules for wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1588–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshki-Modaress, M.; Mirzadeh, H.; Zandi, M. Gelatin-GAG electrospun nanofibrous scaffold for skin tissue engineering: Fabrication and modeling of process parameters. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 48, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagiah, N.; Madhavi, L.; Anitha, R.; Anandan, C.; Srinivasan, N.T.; Sivagnanam, U.T. Development and characterization of coaxially electrospun gelatin coated poly (3-hydroxybutyric acid) thin films as potential scaffolds for skin regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 4444–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
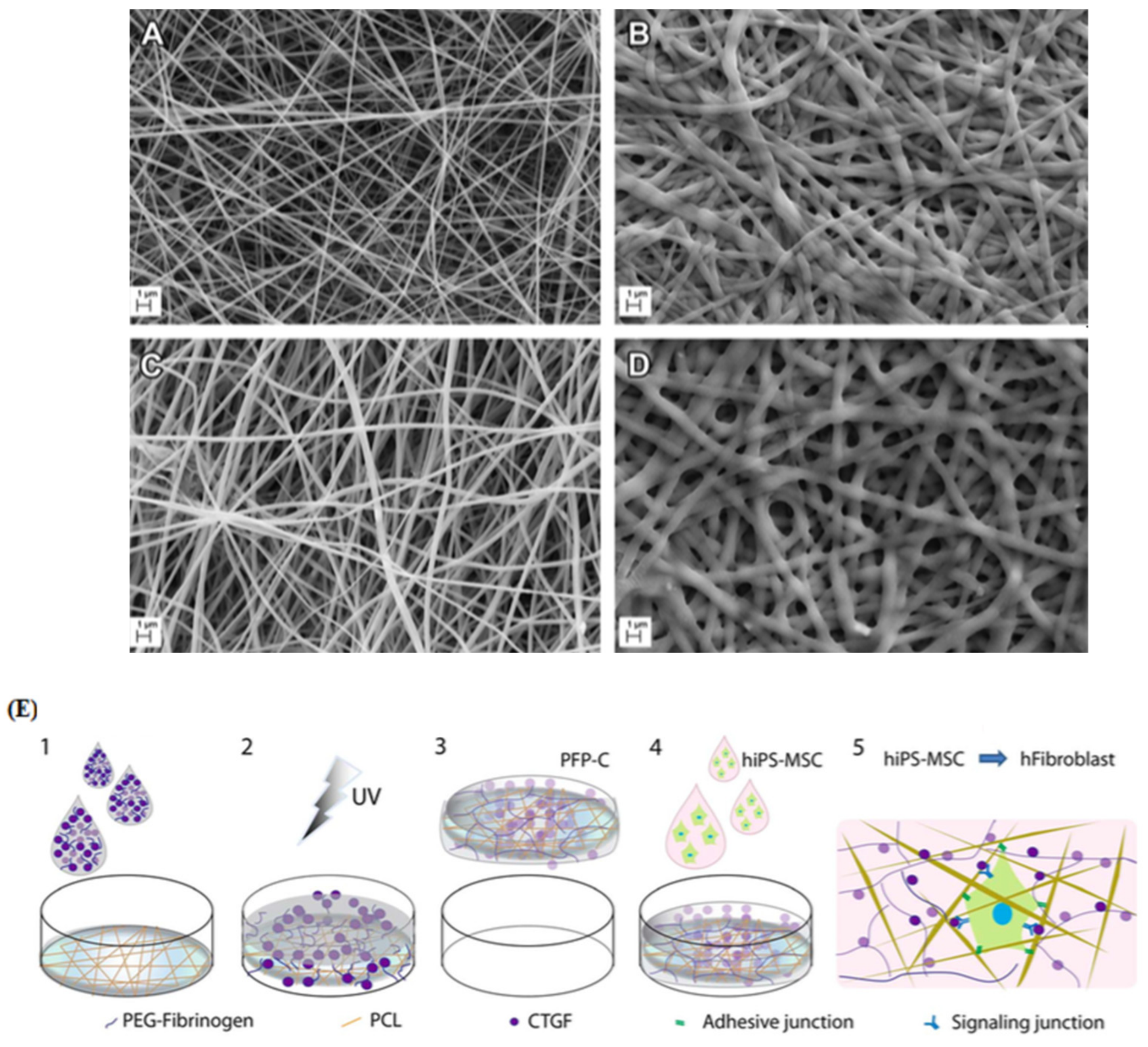
- Xu, R.; Taskin, M.B.; Rubert, M.; Seliktar, D.; Besenbacher, F.; Chen, M. hiPS-MSCs differentiation towards fibroblasts on a 3D ECM mimicking scaffold. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagarajan, S.; Belaid, H.; Pochat-Bohatier, C.; Teyssier, C.; Iatsunskyi, I.; Coy, E.; Balme, S.; Cornu, D.; Miele, P.; Kalkura, N.S.; et al. Design of boron nitride/gelatin electrospun nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 33695–33706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, F.; Adhikari, B.; Dhara, S. Collagen Intermingled Chitosan-Tripolyphosphate Nano/Micro Fibrous Scaffolds for Tissue-Engineering Application. Biomater. Sci. 2012, 23, 1923–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, H.; Irani, M.; Ahmad, Z. Starch-based hydrogels: Present status and applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Po. 2013, 62, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourmohammadi, J.; Ghaee, A.; Liavali, S.H. Preparation and characterization of bioactive composite scaffolds from polycaprolactone nanofibers-chitosan-oxidized starch for bone regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 138, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Hu, J.; Huang, H.; Han, J.; Hu, H. Study of multi-functional electrospun composite nanofibrous mats for smart wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Klausen, L.H.; Chen, M.; Dong, M. Electroactive Scaffolds for Neurogenesis and Myogenesis: Graphene-Based Nanomaterials. Small 2019, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, R.; Wang, Z.; Dong, M.; Cui, B.; Chen, M. Visible Light Neural Stimulation on graphitic-Carbon Nitride/Graphene Photocatalytic Fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2017, 9, 34736–34743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Polymer | Reinforced by | Mean Diameter (nm) | Cell Proliferation | Tissue | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | Day | Number of Cells | |||||
| Gelatin | Silk | 83.9 | OD450 | 1 | 1.5 | Vessel | [90] |
| 2 | 1.6 | ||||||
| Chitosan | Silk | 446.9 ± 167 | OD492 | 7 | 1.7 | Bone | [91] |
| 28 | 2.6 | ||||||
| Chitosan | Gelatin | 180 | OD490 | 5 | 0.8 | Retina | [92] |
| 7 | 1.1 | ||||||
| Gelatin | Tecophilic | 409 ± 150 | OD490 | 7 | 0.5 | Vessel | [93] |
| 10 | 0.9 | ||||||
| Carboxymethyl chitosan | PCL | 356 | OD570 | 2 | 0.42 | Bone | [94] |
| 3 | 0.3 | ||||||
| Gelatin | PCL | 330–370 | OD490 | 3 | 0.8 | Bone | [95] |
| 5 | 1.7 | ||||||
| Chitin | Polyaniline | 88.7 ± 19.1 | OD450 | 4 | 1.2 | Nerve cardiac muscle | [96] |
| 7 | 2.4 | ||||||
| Poly (lactic acid) | Poly (pyrrole) | 128.8 ± 27.9 | FI | 6 | 290 | [97] | |
| 8 | 380 | Nerve | |||||
| PLGA | PCL | 554 | OD450 | 4 | 0.7 | Muscle | [98] |
| 8 | 2.2 | ||||||
| PCL | Lignin | 259 ± 42 | FI | 5 | 460 | Nerve | [99] |
| 10 | 590 | ||||||
| Gelatin | Tyrosine, glutaraldehyde, 1, 2, 3-triazole ring | 350–500 | OD570 | 4 | 0.6 | Cartilage | [100] |
| 7 | 0.8 | ||||||
| Gelatin | Glutaraldehyde | - | Cell Number (104) | 6 | 3.8 | Skin | [101] |
| 13 | 7 | ||||||
| Cationic gelatin | Sericin, hyaluronan, chondroitin sulfate, glutaraldehyde | 206 ± 45 | Cell Number (104) | 1 | 3.7 | Skin | [102] |
| 3 | 7 | ||||||
| Gelatin | Hydroxyapatite, peptides, UV crosslinking, bone morphogenetic protein-2 | - | Cell Number (104) | 4 | 3.3 | Bone | [103] |
| 7 | 5.5 | ||||||
| Chitosan | Tripolyphosphate | - | Cell Number (105) | 5 | 15 | TE | [104] |
| 7 | 17 | ||||||
| Gelatin | Collagen, genipin, hydroxyapatite | - | % | 7 | 150 | Bone | [105] |
| 21 | 300 | ||||||
| PCL | Ceramic | - | FU | 7 | 11,000 | Bone | [106] |
| 21 | 46,000 | ||||||
| Silk fibroin | Starch, calcium phosphate, glutaraldehyde | - | % | 3 | 125 | Bone | [107] |
| 7 | 118 | ||||||
| Starch | Polyvinyl alcohol, Ag nanoparticles, glutaraldehyde | 110–300 | % | 7 | 130 | Skin | [108] |
| 21 | 190 | ||||||
| PLGA | Graphene oxide, arginylglycylaspartic acid | 558 | % | 5 | 350 | Muscle | [109] |
| 7 | 420 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keshvardoostchokami, M.; Majidi, S.S.; Huo, P.; Ramachandran, R.; Chen, M.; Liu, B. Electrospun Nanofibers of Natural and Synthetic Polymers as Artificial Extracellular Matrix for Tissue Engineering. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010021
Keshvardoostchokami M, Majidi SS, Huo P, Ramachandran R, Chen M, Liu B. Electrospun Nanofibers of Natural and Synthetic Polymers as Artificial Extracellular Matrix for Tissue Engineering. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeshvardoostchokami, Mina, Sara Seidelin Majidi, Peipei Huo, Rajan Ramachandran, Menglin Chen, and Bo Liu. 2021. "Electrospun Nanofibers of Natural and Synthetic Polymers as Artificial Extracellular Matrix for Tissue Engineering" Nanomaterials 11, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010021
APA StyleKeshvardoostchokami, M., Majidi, S. S., Huo, P., Ramachandran, R., Chen, M., & Liu, B. (2021). Electrospun Nanofibers of Natural and Synthetic Polymers as Artificial Extracellular Matrix for Tissue Engineering. Nanomaterials, 11(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010021






