Molecular Interactions Driving Intermediate Filament Assembly
Abstract
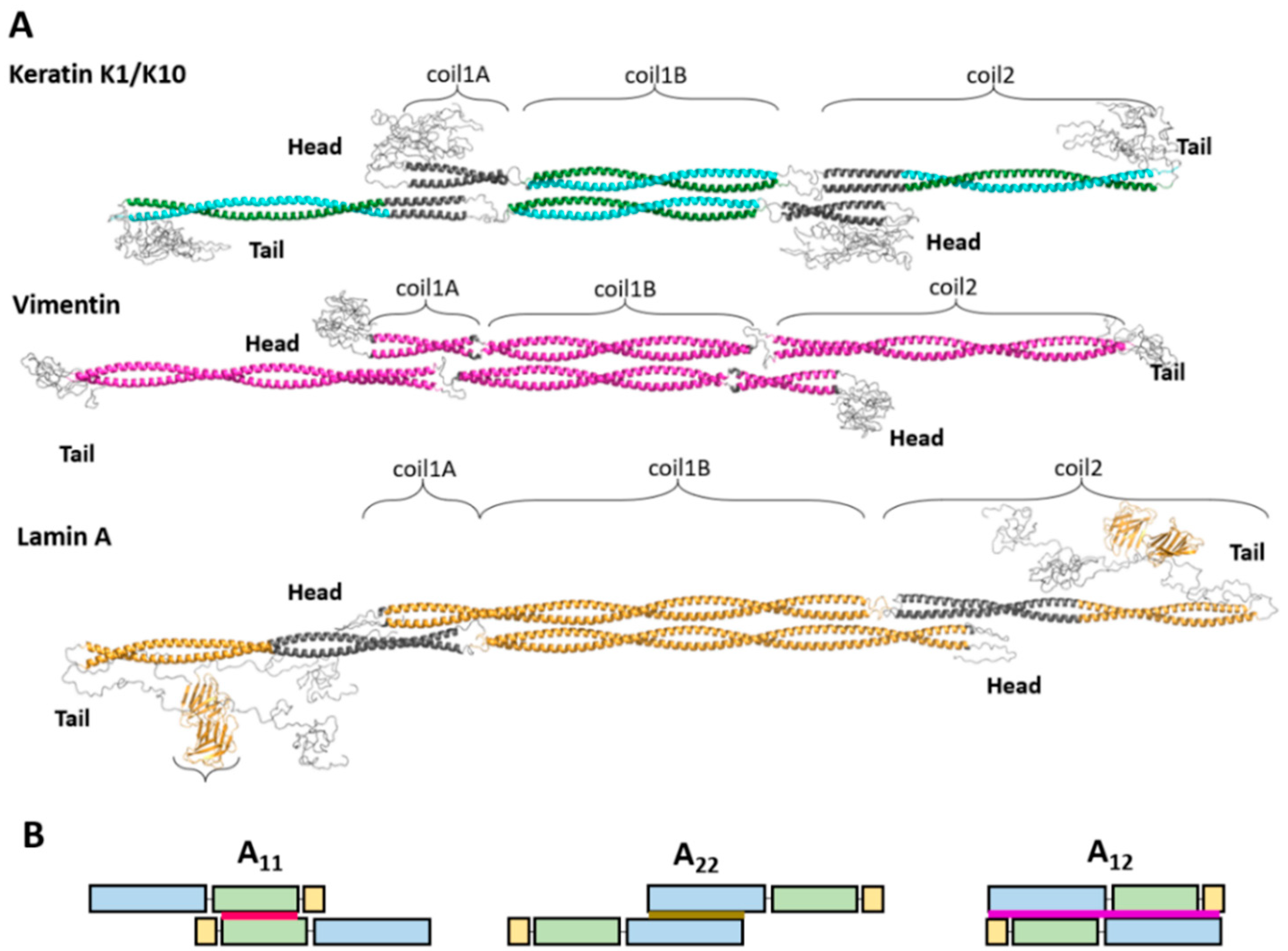
:1. Structural Principles and Biological Role of IFs
2. Atomic Structure of the Elementary IF Dimer and A11 Tetramer
2.1. Elementary Dimer
2.2. A11 Tetramer of Cytoplasmic and Nuclear IF Proteins
3. Use of Chemical Cross-Linking to Reveal the 3D Architecture of Complete Filaments
3.1. Starting Material for Cross-Linking Studies
3.2. Chemical Cross-Linking Approach
3.3. Cross-Linking Based Models of Cytoplasmic IF Architecture by Steinert’s Group
3.4. Cross-Linking Studies of Nuclear Lamins
4. Discussion and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrmann, H.; Bär, H.; Kreplak, L.; Strelkov, S.V.; Aebi, U. Intermediate filaments: From cell architecture to nanomechanics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Kreplak, L.; Buehler, M.J. Nanomechanical properties of vimentin intermediate filament dimers. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 425101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeverenyi, I.; Cassidy, A.J.; Chung, C.W.; Lee, B.T.; Common, J.E.; Ogg, S.C.; Chen, H.; Sim, S.Y.; Goh, W.L.; Ng, K.W.; et al. The Human Intermediate Filament Database: Comprehensive information on a gene family involved in many human diseases. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzenko, D.; Chernyatina, A.A.; Strelkov, S.V. Crystallographic Studies of Intermediate Filament Proteins. Subcell Biochem. 2017, 82, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgay, Y.; Eibauer, M.; Goldman, A.E.; Shimi, T.; Khayat, M.; Ben-Harush, K.; Dubrovsky-Gaupp, A.; Sapra, K.T.; Goldman, R.D.; Medalia, O. The molecular architecture of lamins in somatic cells. Nature 2017, 543, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aebi, U.; Cohn, J.; Buhle, L.; Gerace, L. The nuclear lamina is a meshwork of intermediate-type filaments. Nature 1986, 323, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyatina, A.A.; Guzenko, D.; Strelkov, S.V. Intermediate filament structure: The bottom-up approach. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 32, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldirany, S.A.; Lomakin, I.B.; Ho, M.; Bunick, C.G. Recent insight into intermediate filament structure. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2020, 68, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.K.; Coulombe, P.A.; Fuchs, E. The roles of K5 and K14 head, tail, and R/K L L E G E domains in keratin filament assembly in vitro. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 119, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mucke, N.; Wedig, T.; Burer, A.; Marekov, L.N.; Steinert, P.M.; Langowski, J.; Aebi, U.; Herrmann, H. Molecular and biophysical characterization of assembly-starter units of human vimentin. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 340, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, H.; Haner, M.; Brettel, M.; Muller, S.A.; Goldie, K.N.; Fedtke, B.; Lustig, A.; Franke, W.W.; Aebi, U. Structure and assembly properties of the intermediate filament protein vimentin: The role of its head, rod and tail domains. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 264, 933–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, H.; Haner, M.; Brettel, M.; Ku, N.O.; Aebi, U. Characterization of distinct early assembly units of different intermediate filament proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 286, 1403–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucke, N.; Kammerer, L.; Winheim, S.; Kirmse, R.; Krieger, J.; Mildenberger, M.; Bassler, J.; Hurt, E.; Goldmann, W.H.; Aebi, U.; et al. Assembly Kinetics of Vimentin Tetramers to Unit-Length Filaments: A Stopped-Flow Study. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 2408–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Premchandar, A.; Mücke, N.; Poznański, J.; Wedig, T.; Kaus-Drobek, M.; Herrmann, H.; Dadlez, M. Structural Dynamics of the Vimentin Coiled-coil Contact Regions Involved in Filament Assembly as Revealed by Hydrogen-Deuterium Exchange. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 24931–24950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirmse, R.; Portet, S.; Mücke, N.; Aebi, U.; Herrmann, H.; Langowski, J. A quantitative kinetic model for the in vitro assembly of intermediate filaments from tetrameric vimentin. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 18563–18572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portet, S.; Mücke, N.; Kirmse, R.; Langowski, J.; Beil, M.; Herrmann, H. Vimentin intermediate filament formation: In vitro measurement and mathematical modeling of the filament length distribution during assembly. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2009, 25, 8817–8823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasse, B.; Aebi, U.; Stuurman, N. A tailless Drosophila lamin Dm0 fragment reveals lateral associations of dimers. J. Str. Biol. 1998, 123, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitlinger, E.; Peter, M.; Häner, M.; Lustig, A.; Aebi, U.; Nigg, E.A. Expression of chicken lamin B2 in Escherichia coli: Characterization of its structure, assembly, and molecular interactions. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 113, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foeger, N.; Wiesel, N.; Lotsch, D.; Mücke, N.; Kreplak, L.; Aebi, U.; Gruenbaum, Y.; Herrmann, H. Solubility properties and specific assembly pathways of the B-type lamin from Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Str. Biol. 2006, 155, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, H.; Aebi, U. Intermediate Filaments: Molecular Structure, Assembly Mechanism, and Integration Into Functionally Distinct Intracellular Scaffolds. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 749–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne-Manneville, S. Cytoplasmic Intermediate Filaments in Cell Biology. Ann. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 34, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, N.T.; Omary, M.B. Post-translational modifications of intermediate filament proteins: Mechanisms and functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, Y.; Kasahara, K.; Inagaki, M. Intermediate filaments and IF-associated proteins: From cell architecture to cell proliferation. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phy. Biol. Sci. 2019, 95, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eriksson, J.E.; He, T.; Trejo-Skalli, A.V.; Härmälä-Braskén, A.S.; Hellman, J.; Chou, Y.H.; Goldman, R.D. Specific in vivo phosphorylation sites determine the assembly dynamics of vimentin intermediate filaments. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gruenbaum, Y.; Aebi, U. Intermediate filaments: A dynamic network that controls cell mechanics. F1000prime Rep. 2014, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chernyatina, A.A.; Hess, J.F.; Guzenko, D.; Voss, J.C.; Strelkov, S.V. How to Study Intermediate Filaments in Atomic Detail. Methods Enzymol. 2016, 568, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strelkov, S.V.; Herrmann, H.; Geisler, N.; Lustig, A.; Ivaninskii, S.; Zimbelmann, R.; Burkhard, P.; Aebi, U. Divide-and-conquer crystallographic approach towards an atomic structure of intermediate filaments. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 306, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, N.; Schünemann, J.; Weber, K.; Häner, M.; Aebi, U. Assembly and architecture of invertebrate cytoplasmic intermediate filaments reconcile features of vertebrate cytoplasmic and nuclear lamin-type intermediate filaments. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 282, 601–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, A.C.; Steinert, P.M.; Parry, D.A. Coiled-coil stutter and link segments in keratin and other intermediate filament molecules: A computer modeling study. Proteins 1994, 20, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalmans, G.; Lilina, A.V.; Vermeire, P.J.; Fiala, J.; Novák, P.; Strelkov, S.V. Addressing the Molecular Mechanism of Longitudinal Lamin Assembly Using Chimeric Fusions. Cells 2020, 9, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolet, S.; Herrmann, H.; Aebi, U.; Strelkov, S.V. Atomic structure of vimentin coil 2. J. Str. Biol. 2010, 170, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernyatina, A.A.; Nicolet, S.; Aebi, U.; Herrmann, H.; Strelkov, S.V. Atomic structure of the vimentin central α-helical domain and its implications for intermediate filament assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13620–13625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korkmaz, E.N.; Taylor, K.C.; Andreas, M.P.; Ajay, G.; Heinze, N.T.; Cui, Q.; Rayment, I. A composite approach towards a complete model of the myosin rod. Proteins 2016, 84, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzenko, D.; Strelkov, S.V. CCFold: Rapid and accurate prediction of coiled-coil structures and application to modelling intermediate filaments. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.; Xu, C.; Bian, C.; Lam, R.; Wang, J.P.; Kania, J.; Min, J.; Zang, J. Crystal structures of the coil 2B fragment and the globular tail domain of human lamin B1. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gohara, R.; Tang, D.; Inada, H.; Inagaki, M.; Takasaki, Y.; Ando, S. Phosphorylation of vimentin head domain inhibits interaction with the carboxyl-terminal end of α-helical rod domain studied by surface plasmon resonance measurements. FEBS Lett. 2001, 489, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pittenger, J.T.; Hess, J.F.; Budamagunta, M.S.; Voss, J.C.; Fitzgerald, P.G. Identification of phosphorylation-induced changes in vimentin intermediate filaments by site-directed spin labeling and electron paramagnetic resonance. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 10863–10870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinert, P.M.; Mack, J.W.; Korge, B.P.; Gan, S.-Q.; Haynes, S.R.; Steven, A.C. Glycine loops in proteins: Their occurence in certain intermediate filament chains, loricrins and single-stranded RNA binding proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1991, 13, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badowski, C.; Sim, A.Y.L.; Verma, C.; Szeverényi, I.; Natesavelalar, C.; Terron-Kwiatkowski, A.; Harper, J.; O′Toole, E.A.; Lane, E.B. Modeling the Structure of Keratin 1 and 10 Terminal Domains and their Misassembly in Keratoderma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1914–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bousquet, O.; Ma, L.; Yamada, S.; Gu, C.; Idei, T.; Takahashi, K.; Wirtz, D.; Coulombe, P.A. The nonhelical tail domain of keratin 14 promotes filament bundling and enhances the mechanical properties of keratin intermediate filaments in vitro. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hess, J.F.; Budamagunta, M.S.; Shipman, R.L.; FitzGerald, P.G.; Voss, J.C. Characterization of the Linker 2 Region in Human Vimentin Using Site-Directed Spin Labeling and Electron Paramagnetic Resonance. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 11737–11743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hess, J.F.; Voss, J.C.; FitzGerald, P.G. Real-time Observation of Coiled-coil Domains and Subunit Assembly in Intermediate Filaments. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35516–35522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hess, J.F.; Budamagunta, M.S.; FitzGerald, P.G.; Voss, J.C. Characterization of Structural Changes in Vimentin Bearing an Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex-like Mutation Using Site-directed Spin Labeling and Electron Paramagnetic Resonance. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 2141–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aziz, A.; Hess, J.F.; Budamagunta, M.S.; Voss, J.C.; FitzGerald, P.G. Site-directed Spin Labeling and Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Determination of Vimentin Head Domain Structure. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 15278–15285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, A.; Hess, J.F.; Budamagunta, M.S.; FitzGerald, P.G.; Voss, J.C. Head and Rod 1 Interactions in Vimentin. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 7330–7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hess, J.F.; Budamagunta, M.S.; Aziz, A.; FitzGerald, P.G.; Voss, J.C. Electron paramagnetic resonance analysis of the vimentin tail domain reveals points of order in a largely disordered region and conformational adaptation upon filament assembly. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 2013, 22, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hess, J.F.; Budamagunta, M.S.; Voss, J.C.; FitzGerald, P.G. Structural Characterization of Human Vimentin Rod 1 and the Sequencing of Assembly Steps in Intermediate Filament Formation in Vitro Using Site-directed Spin Labeling and Electron Paramagnetic Resonance. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44841–44846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budamagunta, M.S.; Hess, J.F.; Fitzgerald, P.G.; Voss, J.C. Describing the structure and assembly of protein filaments by EPR spectroscopy of spin-labeled side chains. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 48, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Hess, J.F.; Budamagunta, M.S.; Voss, J.C.; Kuzin, A.P.; Huang, Y.J.; Xiao, R.; Montelione, G.T.; FitzGerald, P.G.; Hunt, J.F. The Structure of Vimentin Linker 1 and Rod 1B Domains Characterized by Site-directed Spin-labeling Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (SDSL-EPR) and X-ray Crystallography. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 28349–28361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinert, P.M.; Marekov, L.N.; Parry, D.A. Diversity of intermediate filament structure. Evidence that the alignment of coiled-coil molecules in vimentin is different from that in keratin intermediate filaments. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 24916–24925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldirany, S.A.; Ho, M.; Hinbest, A.J.; Lomakin, I.B.; Bunick, C.G. Human keratin 1/10-1B tetramer structures reveal a knob-pocket mechanism in intermediate filament assembly. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Kim, S.; Jin, M.S. Crystal structure of the human glial fibrillary acidic protein 1B domain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 2899–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.; Jo, I.; Kang, S.-m.; Hong, S.; Kim, S.; Jeong, S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Park, B.-J.; Ha, N.-C. Structural basis for lamin assembly at the molecular level. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilina, A.V.; Chernyatina, A.A.; Guzenko, D.; Strelkov, S.V. Lateral A11 type tetramerization in lamins. J. Str. Biol. 2020, 209, 107404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernot, K.M.; Lee, C.H.; Coulombe, P.A. A small surface hydrophobic stripe in the coiled-coil domain of type I keratins mediates tetramer stability. J Cell Biol. 2005, 168, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, D.A.; Steinert, P.M. Intermediate filaments: Molecular architecture, assembly, dynamics and polymorphism. Q Rev. Biophys. 1999, 32, 99–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarov, A.A.; Zou, J.; Houston, D.R.; Spanos, C.; Solovyova, A.S.; Cardenal-Peralta, C.; Rappsilber, J.; Schirmer, E.C. Lamin A molecular compression and sliding as mechanisms behind nucleoskeleton elasticity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, H.; Kreplak, L.; Aebi, U. Isolation, Characterization, and In Vitro Assembly of Intermediate Filaments. In Methods in Cell Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; Volume 78, pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann, H.; Wedig, T.; Porter, R.M.; Lane, E.B.; Aebi, U. Characterization of early assembly intermediates of recombinant human keratins. J. Str. Biol. 2002, 137, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, A.V.; Kreplak, L.; Wedig, T.; Mücke, N.; Svergun, D.I.; Herrmann, H.; Aebi, U.; Strelkov, S.V. Monitoring intermediate filament assembly by small-angle x-ray scattering reveals the molecular architecture of assembly intermediates. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weber, M.S.; Eibauer, M.; Sivagurunathan, S.; Magin, T.M.; Goldman, R.D.; Medalia, O. Structural heterogeneity of cellular K5/K14 filaments as revealed by cryo-electron microscopy. Elife 2021, 10, e70307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinz, A. Divide and conquer: Cleavable cross-linkers to study protein conformation and protein-protein interactions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobucci, C.; Piotrowski, C.; Aebersold, R.; Amaral, B.C.; Andrews, P.; Bernfur, K.; Borchers, C.; Brodie, N.I.; Bruce, J.E.; Cao, Y.; et al. First Community-Wide, Comparative Cross-Linking Mass Spectrometry Study. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 6953–6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, D.; Brockmeyer, A.; Mueller, F.; Musacchio, A.; Bange, T. Simplified Protocol for Cross-linking Mass Spectrometry Using the MS-Cleavable Cross-linker DSBU with Efficient Cross-link Identification. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 10990–10999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.Q.; Dreiocker, F.; Ihling, C.H.; Schäfer, M.; Sinz, A. Cleavable cross-linker for protein structure analysis: Reliable identification of cross-linking products by tandem MS. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6958–6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozbesky, D.; Rosulek, M.; Kukacka, Z.; Chmelik, J.; Man, P.; Novak, P. Impact of Chemical Cross-Linking on Protein Structure and Function. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.K.; Tetaert, D.; Debuire, B.; Dautrevaux, M.; Biserte, G. (Sequential Edman degredation). Biochimie 1977, 59, 557–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinz, A. Cross-Linking/Mass Spectrometry for Studying Protein Structures and Protein-Protein Interactions: Where Are We Now and Where Should We Go from Here? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 6390–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobucci, C.; Gotze, M.; Ihling, C.H.; Piotrowski, C.; Arlt, C.; Schafer, M.; Hage, C.; Schmidt, R.; Sinz, A. A cross-linking/mass spectrometry workflow based on MS-cleavable cross-linkers and the MeroX software for studying protein structures and protein-protein interactions. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 2864–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, J.D.; Mohr, J.P.; Mathay, M.; Zhong, X.; Keller, A.; Bruce, J.E. Systems structural biology measurements by in vivo cross-linking with mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2318–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, D.A.; Marekov, L.N.; Steinert, P.M. Subfilamentous protofibril structures in fibrous proteins: Cross-linking evidence for protofibrils in intermediate filaments. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 39253–39258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinert, P.M.; Marekov, L.N.; Parry, D.A. Conservation of the structure of keratin intermediate filaments: Molecular mechanism by which different keratin molecules integrate into preexisting keratin intermediate filaments during differentiation. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 10046–10056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinert, P.M.; Marekov, L.N.; Fraser, R.D.; Parry, D.A. Keratin intermediate filament structure. Crosslinking studies yield quantitative information on molecular dimensions and mechanism of assembly. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 230, 436–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinert, P.M.; Marekov, L.N.; Parry, D.A. Molecular parameters of type IV alpha-internexin and type IV-type III alpha-internexin-vimentin copolymer intermediate filaments. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinert, P.M.; Roop, D.R. Molecular and cellular biology of intermediate filaments. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1988, 57, 593–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norlen, L.; Masich, S.; Goldie, K.N.; Hoenger, A. Structural analysis of vimentin and keratin intermediate filaments by cryo-electron tomography. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 2217–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strelkov, S.V.; Herrmann, H.; Aebi, U. Molecular architecture of intermediate filaments. BioEssays News Rev. Mol. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2003, 25, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapinos, L.E.; Schumacher, J.; Mücke, N.; Machaidze, G.; Burkhard, P.; Aebi, U.; Strelkov, S.V.; Herrmann, H. Characterization of the head-to-tail overlap complexes formed by human lamin A, B1 and B2 “half-minilamin” dimers. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 396, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitlinger, E.; Peter, M.; Lustig, A.; Villiger, W.; Nigg, E.A.; Aebi, U. The role of the head and tail domain in lamin structure and assembly: Analysis of bacterially expressed chicken lamin A and truncated B2 lamins. J. Str. Biol. 1992, 108, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, H.; Aebi, U. Intermediate Filaments: Structure and Assembly. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a018242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, M.S.; Chung, B.M.; Leahy, D.J.; Coulombe, P.A. Structural basis for heteromeric assembly and perinuclear organization of keratin filaments. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.-H.; Kim, M.-S.; Li, S.; Leahy, D.J.; Coulombe, P.A. Structure-Function Analyses of a Keratin Heterotypic Complex Identify Specific Keratin Regions Involved in Intermediate Filament Assembly. Structure 2020, 28, 355–362.e354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomakin, I.B.; Hinbest, A.J.; Ho, M.; Eldirany, S.A.; Bunick, C.G. Crystal Structure of Keratin 1/10(C401A) 2B Heterodimer Demonstrates a Proclivity for the C-Terminus of Helix 2B to Form Higher Order Molecular Contacts. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2020, 93, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bunick, C.G.; Milstone, L.M. The X-Ray Crystal Structure of the Keratin 1-Keratin 10 Helix 2B Heterodimer Reveals Molecular Surface Properties and Biochemical Insights into Human Skin Disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russel, D.; Lasker, K.; Webb, B.; Velázquez-Muriel, J.; Tjioe, E.; Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Peterson, B.; Sali, A. Putting the Pieces Together: Integrative Modeling Platform Software for Structure Determination of Macromolecular Assemblies. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toivola, D.M.; Boor, P.; Alam, C.; Strnad, P. Keratins in health and disease. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 32, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymkowsky, M.W. Filaments and phenotypes: Cellular roles and orphan effects associated with mutations in cytoplasmic intermediate filament proteins. F1000Research 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, E. Intermediate filaments and disease: Mutations that cripple cell strength. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 125, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikitis, M.; Galata, Z.; Mavroidis, M.; Psarras, S.; Capetanaki, Y. Intermediate filaments in cardiomyopathy. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 1007–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamcheu, J.C.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Syed, D.N.; Adhami, V.M.; Liovic, M.; Mukhtar, H. Keratin gene mutations in disorders of human skin and its appendages. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 508, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alastalo, T.P.; West, G.; Li, S.P.; Keinanen, A.; Helenius, M.; Tyni, T.; Lapatto, R.; Turanlahti, M.; Heikkila, P.; Kaariainen, H.; et al. LMNA Mutation c.917T>G (p.L306R) Leads to Deleterious Hyper-Assembly of Lamin A/C and Associates with Severe Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy and Premature Aging. Hum. Mutat. 2015, 36, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibauer, M.; Weber, M.S.; Turgay, Y.; Sivagurunathan, S.; Goldman, R.D.; Medalia, O. The molecular architecture of vimentin filaments. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vermeire, P.-J.; Stalmans, G.; Lilina, A.V.; Fiala, J.; Novak, P.; Herrmann, H.; Strelkov, S.V. Molecular Interactions Driving Intermediate Filament Assembly. Cells 2021, 10, 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092457
Vermeire P-J, Stalmans G, Lilina AV, Fiala J, Novak P, Herrmann H, Strelkov SV. Molecular Interactions Driving Intermediate Filament Assembly. Cells. 2021; 10(9):2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092457
Chicago/Turabian StyleVermeire, Pieter-Jan, Giel Stalmans, Anastasia V. Lilina, Jan Fiala, Petr Novak, Harald Herrmann, and Sergei V. Strelkov. 2021. "Molecular Interactions Driving Intermediate Filament Assembly" Cells 10, no. 9: 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092457
APA StyleVermeire, P.-J., Stalmans, G., Lilina, A. V., Fiala, J., Novak, P., Herrmann, H., & Strelkov, S. V. (2021). Molecular Interactions Driving Intermediate Filament Assembly. Cells, 10(9), 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092457







