Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio Might Serve as a Prognostic Marker in Young Patients with Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Results
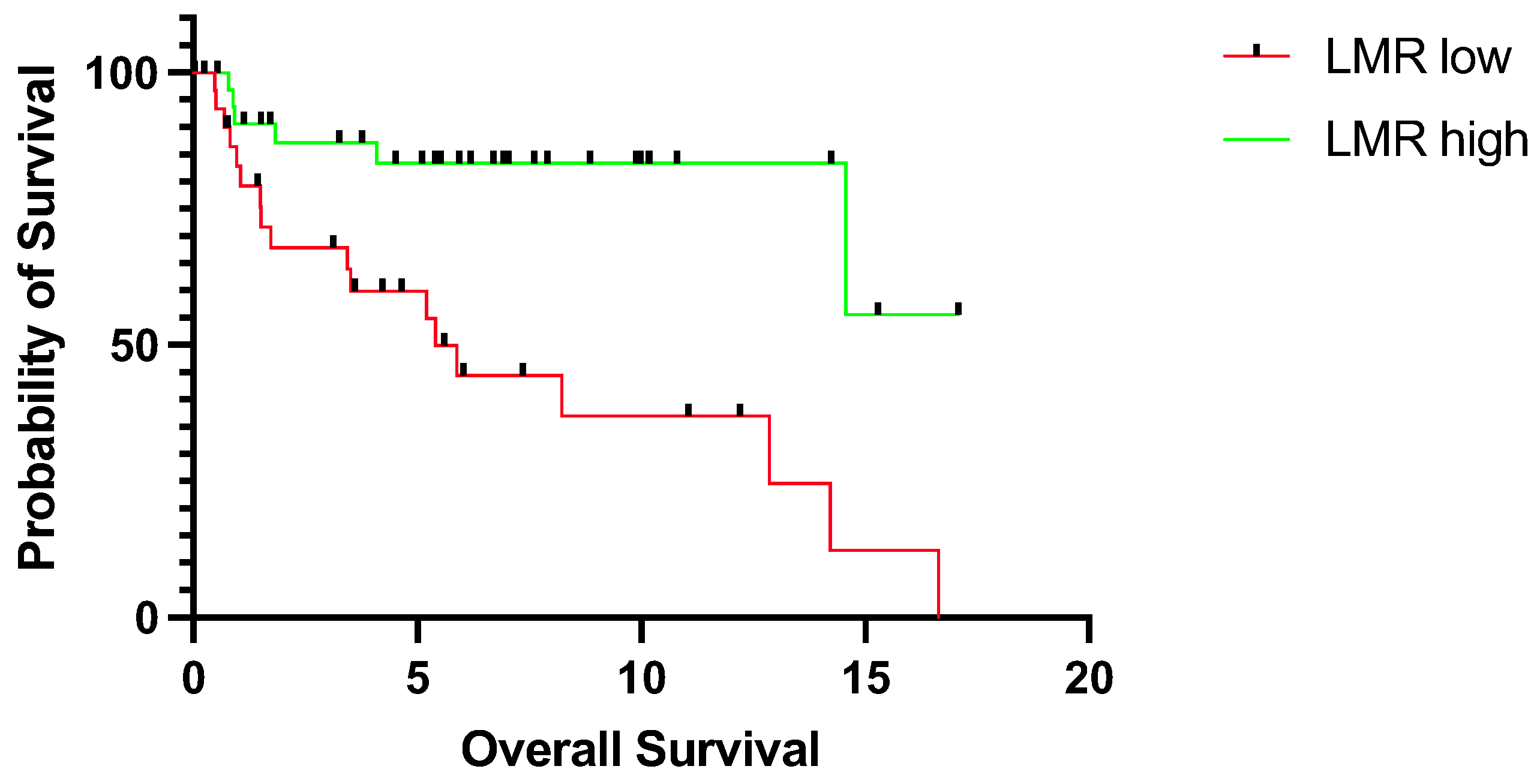
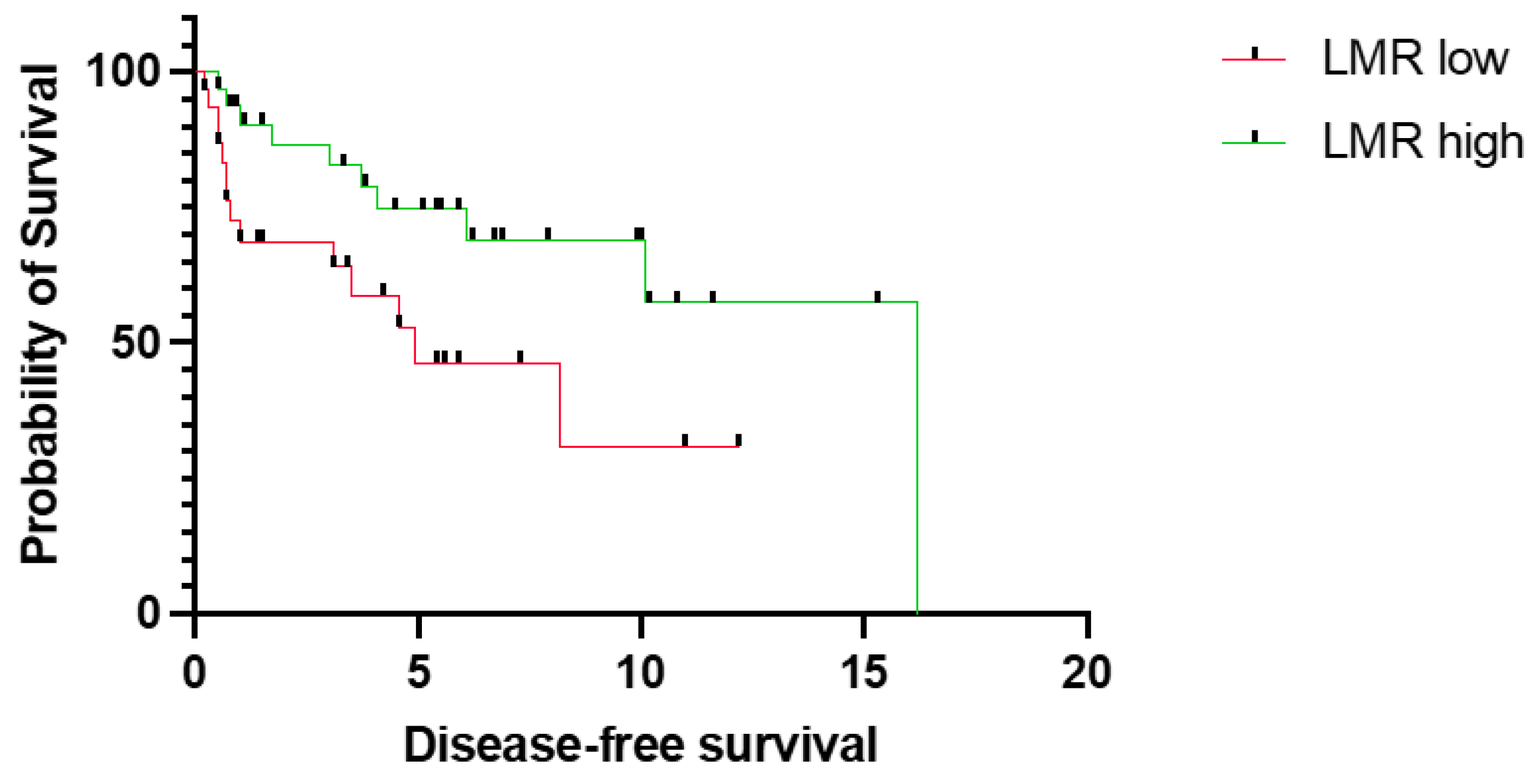
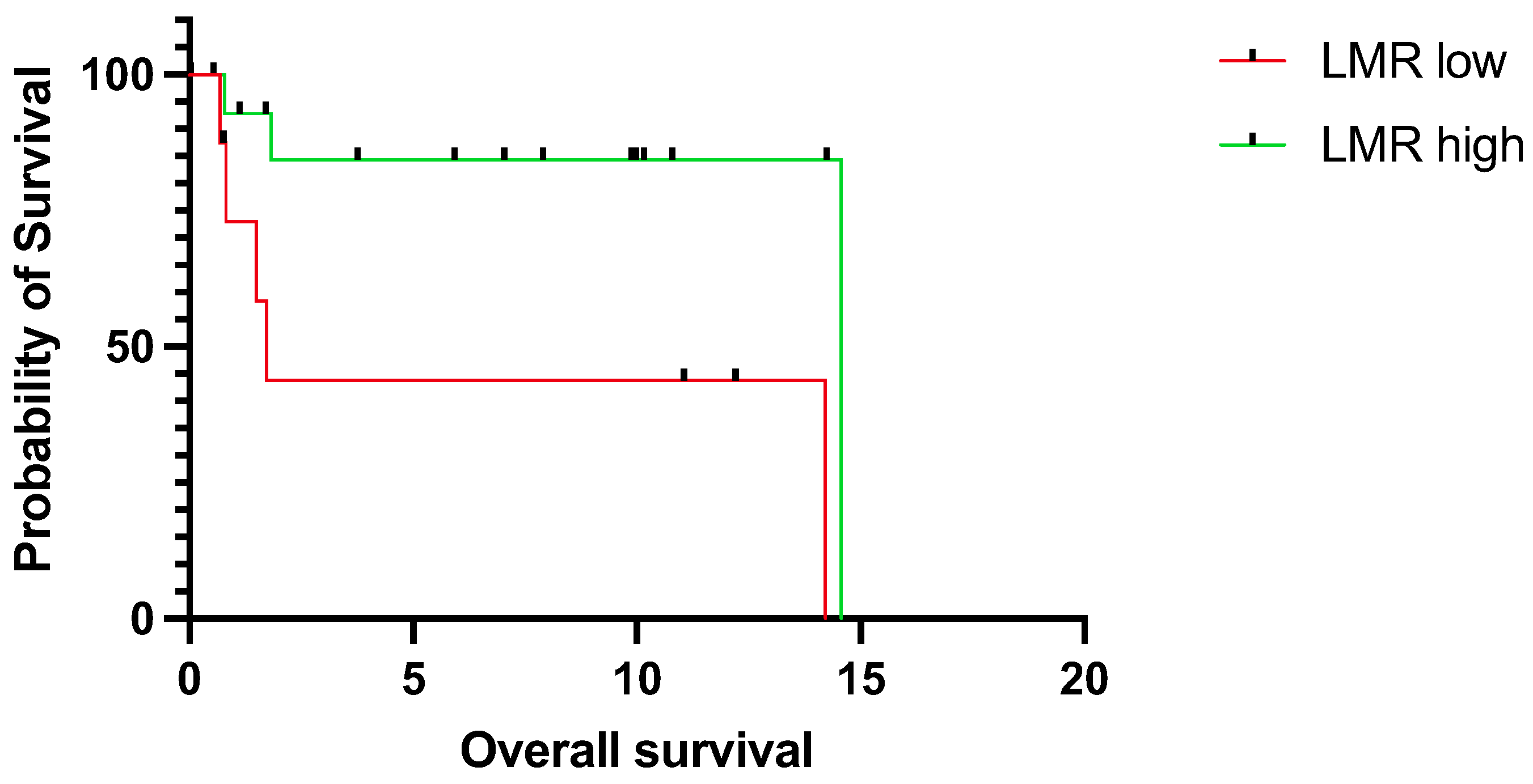
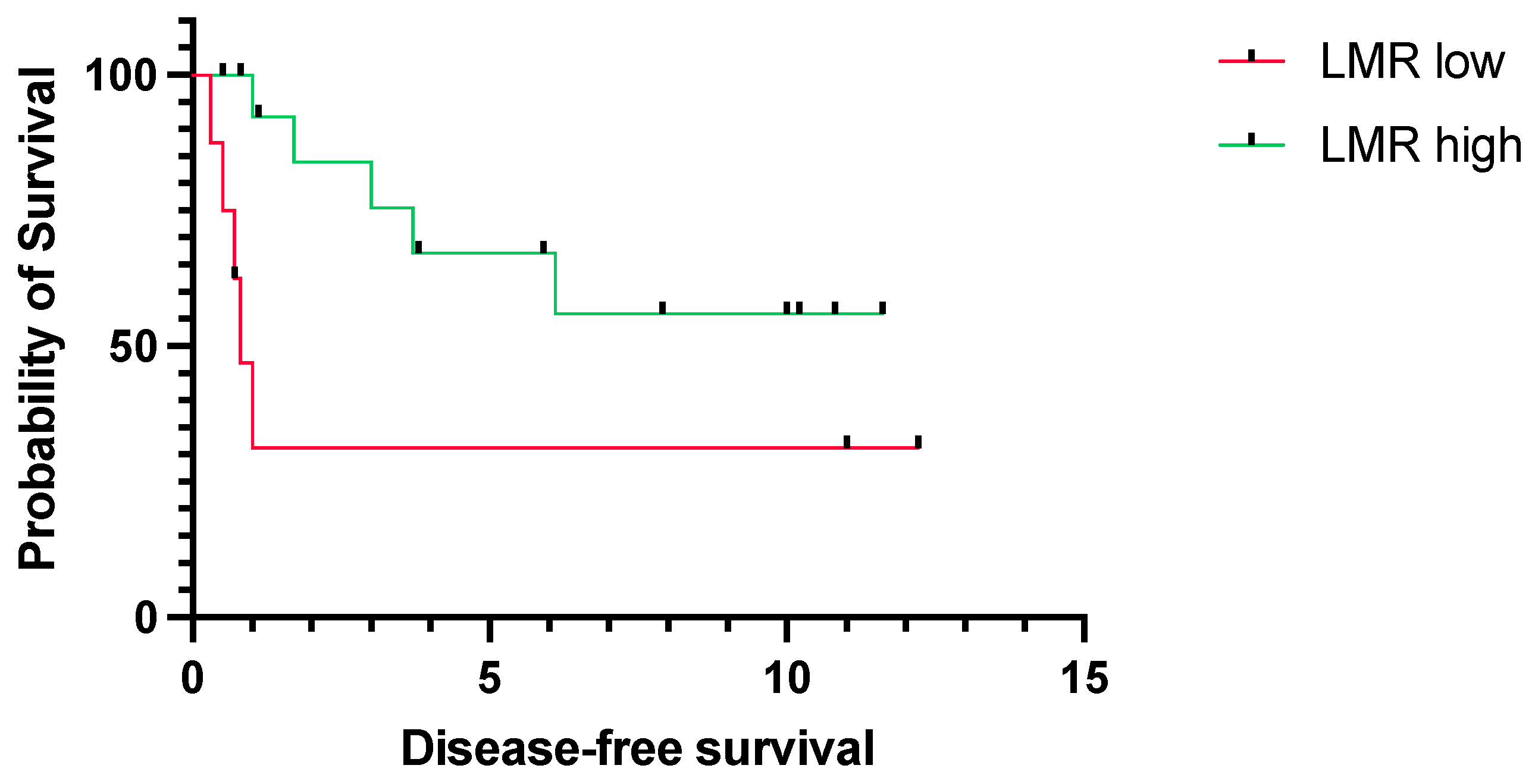
3.2. Prognostic Relevance of LMR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Bsc, M.F.B.; Me, J.F.; Soerjomataram, M.I.; et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.H.; Iyer, N.G.; Tan, M.-H.; Edgren, G. Changing epidemiology of oral squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: A global study. Head Neck 2017, 39, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deneuve, S.; Pérol, O.; Dantony, E.; Guizard, A.; Bossard, N.; Virard, F.; Fervers, B.; FRANCIM Network. Diverging incidence trends of oral tongue cancer compared to other head and neck cancers in young adults in France. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 150, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerman, P.S.; Hayes, D.N.; Grandis, J.R. Therapeutic insights from genomic studies of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, R.L. Immunology and Immunotherapy of Head and Neck Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3293–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G., Jr.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Nivolumab for Recurrent Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiwert, T.Y.; Burtness, B.; Mehra, R.; Weiss, J.; Berger, R.; Eder, J.P.; Heath, K.; McClanahan, T.; Lunceford, J.; Gause, C.; et al. Safety and clinical activity of pembrolizumab for treatment of recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-012): An open-label, multicentre, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.E.W.; Soulières, D.; Le Tourneau, C.; Dinis, J.; Licitra, L.; Ahn, M.-J.; Soria, A.; Machiels, J.-P.; Mach, N.; Mehra, R.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus methotrexate, docetaxel, or cetuximab for recurrent or metastatic head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-040): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2019, 393, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burtness, B.; Harrington, K.J.; Greil, R.; Soulières, D.; Tahara, M.; de Castro, G., Jr.; Psyrri, A.; Basté, N.; Neupane, P.; Bratland, Å.; et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2019, 394, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, S.I.; Faivre, S.; Licitra, L.; Machiels, J.-P.; Vermorken, J.B.; Bruzzi, P.; Gruenwald, V.; Giglio, R.E.; Leemans, C.R.; Seiwert, T.Y.; et al. Comparative analysis of the phase III clinical trials of anti-PD1 monotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients (CheckMate 141 and KEYNOTE 040). J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, R.I.; Harrington, K.; Tahara, M.; Ferris, R.L.; Gillison, M.; Fayette, J.; Daste, A.; Koralewski, P.; Zurawski, B.; Taberna, M.; et al. Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab Versus EXTREME Regimen as First-Line Treatment for Recurrent/Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: The Final Results of CheckMate 651. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2166–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello, F.W.; Melo, G.; Pasetto, J.J.; Silva, C.A.B.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Rivero, E.R.C. The synergistic effect of tobacco and alcohol consumption on oral squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 2849–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, Q.; Maddineni, S.; Arnaud, E.H.; Divi, V.; Megwalu, U.C.; Topf, M.C.; Sunwoo, J.B. Oral cavity cancer in young, non-smoking, and non-drinking patients: A contemporary review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2023, 190, 104112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, R.; Sinha, D.N.; Mehrotra, R. Relationship between type of smokeless tobacco & risk of cancer: A systematic review. Indian J. Med. Res. 2018, 148, 56–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Picon, H.; Guddati, A.K. Mechanisms of resistance in head and neck cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 2742–2751. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, A.A.; Helder, M.N.; de Visscher, J.G.; Leemans, C.R.; Braakhuis, B.J.; de Vet, H.C.W.; Forouzanfar, T. Global incidence of oral and oropharynx cancer in patients younger than 45 years versus older patients: A systematic review. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 82, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paderno, A.; Morello, R.; Piazza, C. Tongue carcinoma in young adults: A review of the literature. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2018, 38, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toporcov, T.N.; Znaor, A.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Yu, G.-P.; Winn, D.M.; Wei, Q.; Vilensky, M.; Vaughan, T.; Thomson, P.; Talamini, R.; et al. Risk factors for head and neck cancer in young adults: A pooled analysis in the INHANCE consortium. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, H.S.; Gokavarapu, S.; Wang, L.Z.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, C.P. Low Pretreatment Lymphocyte-Monocyte Ratio and High Platelet-Lymphocyte Ratio Indicate Poor Cancer Outcome in Early Tongue Cancer. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 1762–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, K.; Kawasaki, G.; Naruse, T.; Umeda, M. Prognostic Significance of Pretreatment Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio in Patients with Tongue Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, R.L.; Haddad, R.; Even, C.; Tahara, M.; Dvorkin, M.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Clement, P.; Mesia, R.; Kutukova, S.; Zholudeva, L.; et al. Durvalumab with or without tremelimumab in patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: EAGLE, a randomized, open-label phase III study. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nøst, T.H.; Alcala, K.; Urbarova, I.; Byrne, K.S.; Guida, F.; Sandanger, T.M.; Johansson, M. Systemic inflammation markers and cancer incidence in the UK Biobank. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 36, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolan, R.D.; Lim, J.; McSorley, S.T.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C. The role of the systemic inflammatory response in predicting outcomes in patients with operable cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brkic, F.F.; Kadletz, L.; Jank, B.; Cede, J.; Seemann, R.; Schneider, S.; Haymerle, G.; Parzefall, T.; Kenner, L.; Heiduschka, G. Pretreatment assessment of hematologic and inflammatory markers in adenoid cystic carcinoma: Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio is associated with multiple recurrences. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2019, 127, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brkic, F.F.; Kadletz, L.; Jank, B.; Mayer, C.; Heiduschka, G.; Brunner, M. Impact of pretherapeutic neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, serum albumin, body-mass index, and advanced lung cancer inflammation index on clinical outcome in sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2020, 48, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brkic, F.F.; Stoiber, S.; Friedl, M.; Maier, T.; Heiduschka, G.; Kadletz-Wanke, L. The Potential Prognostic Value of a Novel Hematologic Marker Fibrinogen-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Head and Neck Adenoid-Cystic Carcinoma. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szkandera, J.; Gerger, A.; Liegl-Atzwanger, B.; Absenger, G.; Stotz, M.; Friesenbichler, J.; Trajanoski, S.; Stojakovic, T.; Eberhard, K.; Leithner, A.; et al. The lymphocyte/monocyte ratio predicts poor clinical outcome and improves the predictive accuracy in patients with soft tissue sarcomas. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Shen, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Q.; Du, J. Prognostic significance of systemic inflammation-based lymphocyte- monocyte ratio in patients with lung cancer: Based on a large cohort study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutterer, G.C.; Stoeckigt, C.; Stojakovic, T.; Jesche, J.; Eberhard, K.; Pummer, K.; Zigeuner, R.; Pichler, M. Low preoperative lymphocyte-monocyte ratio (LMR) represents a potentially poor prognostic factor in nonmetastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stotz, M.; Pichler, M.; Absenger, G.; Szkandera, J.; Arminger, F.; Schaberl-Moser, R.; Samonigg, H.; Stojakovic, T.; Gerger, A. The preoperative lymphocyte to monocyte ratio predicts clinical outcome in patients with stage III colon cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.-H.; Jia, Y.-B.; Song, Q.-X.; Wang, J.-B.; Wang, N.-N.; Cheng, Y.-F. Prognostic significance of preoperative lymphocyte-monocyte ratio in patients with resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 2245–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-M.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, L.; Wan, F.-N.; Zhu, Y.-P.; Sun, L.-J.; Ye, D.-W. Preoperative lymphocyte-monocyte and platelet-lymphocyte ratios as predictors of overall survival in patients with bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 8537–8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.-X.; Ruan, D.-Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, D.-H.; Ma, X.-K.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.-H.; Li, X.; Wang, T.-T.; Lin, Q.; et al. Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio predicts survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 10898–10906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, T.; Fujimoto, N.; Nishi, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Hara, N.; Asano, M.; Fuchimoto, Y.; Wada, S.; Kitamura, K.; Ozaki, S.; et al. Prognostic significance of the lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T.; Ishihara, S.; Kawai, K.; Kazama, S.; Yamaguchi, H.; Sunami, E.; Kitayama, J.; Watanabe, T. Impact of a lymphocyte to monocyte ratio in stage IV colorectal cancer. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 199, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.C.Y.; Chan, D.L.; Diakos, C.I.; Engel, A.; Pavlakis, N.; Gill, A.; Clarke, S.J. The Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio is a Superior Predictor of Overall Survival in Comparison to Established Biomarkers of Resectable Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2017, 265, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Wang, D.-C.; Su, J.-Z.; Jia, L.-F.; Peng, X.; Yu, G.-Y. Clinicopathological characteristics and outcomes of squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue in different age groups. Head Neck 2017, 39, 2276–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Kubota, A.; Yokose, T.; Furukawa, M.; Matsushita, T.; Katsumata, N.; Oridate, N. Prognostic Role of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Tumor Budding in Early Oral Tongue Carcinoma. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, 2512–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangush, A.; Pirinen, M.; Heikkinen, I.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Salo, T.; Leivo, I. Tumour budding in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi, M.; Patsias, A.; Posner, M.; Sikora, A. The role of inflammation in head and neck cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 816, 107–127. [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie, G.J.K.; Charles, K.A.; Roxburgh, C.S.D.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C.; Clarke, S.J. The systemic inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: Experience in patients with cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2013, 88, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Templeton, A.J.; Ace, O.; McNamara, M.G.; Al-Mubarak, M.; Vera-Badillo, F.E.; Hermanns, T.; Šeruga, B.; Ocaña, A.; Tannock, I.F.; Amir, E. Prognostic role of platelet to lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2014, 23, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishijima, T.F.; Muss, H.B.; Shachar, S.S.; Tamura, K.; Takamatsu, Y. Prognostic value of lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio in patients with solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, A.D.; Fritz, J.M.; Lenardo, M.J. A guide to cancer immunotherapy: From T cell basic science to clinical practice. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, A.; Burtness, B. Treating Head and Neck Cancer in the Age of Immunotherapy: A 2023 Update. Drugs 2023, 83, 217–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanmee, T.; Ontong, P.; Konno, K.; Itano, N. Tumor-associated macrophages as major players in the tumor microenvironment. Cancers 2014, 6, 1670–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tham, T.; Olson, C.; Khaymovich, J.; Herman, S.W.; Costantino, P.D. The lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio as a prognostic indicator in head and neck cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 275, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, Q.; Chen, Y.; Su, C.; Lin, W.; Wei, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H. Prognostic Evaluation of Metastasis-Related Lymphocyte/Monocyte Ratio in Stage I–III Breast Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 782383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-H.; Sun, H.-F.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Liao, Z.-J.; Zhao, L.; Cui, J.; Wu, T.; Lu, J.-R.; Nan, K.-J.; Wang, S.-H. The clinical use of the platelet/lymphocyte ratio and lymphocyte/monocyte ratio as prognostic predictors in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 20011–20024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neofytou, K.; Smyth, E.C.; Giakoustidis, A.; Khan, A.Z.; Williams, R.; Cunningham, D.; Mudan, S. The Preoperative Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio is Prognostic of Clinical Outcomes for Patients with Liver-Only Colorectal Metastases in the Neoadjuvant Setting. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 4353–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.-N.; Peng, J.-W.; Xiao, J.-J.; Liu, D.-Y.; Xia, Z.-J. Prognostic impact of circulating monocytes and lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio on previously untreated metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving platinum-based doublet. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eo, W.K.; Chang, H.J.; Kwon, S.H.; Koh, S.B.; Kim, Y.O.; Ji, Y.I.; Kim, H.-B.; Lee, J.Y.; Suh, D.S.; Kim, K.H.; et al. The Lymphocyte-Monocyte Ratio Predicts Patient Survival and Aggressiveness of Ovarian Cancer. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Geng, Y.; Sun, M.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z. Clinical implications of systemic inflammatory response markers as independent prognostic factors for advanced pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology 2015, 15, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Luo, X. Prognostic significance of elevated pretreatment systemic inflammatory markers for patients with prostate cancer: A meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, M.; Katoh, H.; Nishimiya, H.; Kikuchi, M.; Kosaka, Y.; Sengoku, N.; Watanabe, M.; Yamashita, K. Lymphocyte-Monocyte Ratio Significantly Predicts Recurrence in Papillary Thyroid Cancer. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 246, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kürten, C.H.L.; Kulkarni, A.; Cillo, A.R.; Santos, P.M.; Roble, A.K.; Onkar, S.; Reeder, C.; Lang, S.; Chen, X.; Duvvuri, U.; et al. Investigating immune and non-immune cell interactions in head and neck tumors by single-cell RNA sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arutyunyan, I.; Jumaniyazova, E.; Makarov, A.; Fatkhudinov, T. In Vitro Models of Head and Neck Cancer: From Primitive to Most Advanced. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeSavage, B.L.; Suhar, R.A.; Broguiere, N.; Lutolf, M.P.; Heilshorn, S.C. Next-generation cancer organoids. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontheimer-Phelps, A.; Hassell, B.A.; Ingber, D.E. Modelling cancer in microfluidic human organs-on-chips. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Cao, L. Use and application of organ-on-a-chip platforms in cancer research. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 17, 1163–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, A.; Mayr, M.; Schwaiger, T.; Sprung, S.; Chetta, P.; Gottfried, T.; Dudas, J.; Greier, M.C.; Glatz, M.C.; Haybaeck, J.; et al. Patient-derived head and neck tumor slice cultures: A versatile tool to study oncolytic virus action. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; He, M.; Xie, C.; Zhong, R.; Liu, J.; Tang, C.; Li, C.; Xiong, S.; et al. Multiplex immunofluorescence and single-cell transcriptomic profiling reveal the spatial cell interaction networks in the non-small cell lung cancer microenvironment. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühn, J.P.; Schmid, W.; Körner, S.; Bochen, F.; Wemmert, S.; Rimbach, H.; Smola, S.; Radosa, J.C.; Wagner, M.; Morris, L.G.; et al. HPV Status as Prognostic Biomarker in Head and Neck Cancer-Which Method Fits the Best for Outcome Prediction? Cancers 2021, 13, 4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbichler, T.B.; Alshaimaa, A.; Maria, M.V.; Daniel, D.; Herbert, R.; Jozsef, D.; Ira-Ida, S. Epithelial-mesenchymal crosstalk induces radioresistance in HNSCC cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 3641–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starska-Kowarska, K. The Role of Different Immunocompetent Cell Populations in the Pathogenesis of Head and Neck Cancer-Regulatory Mechanisms of Pro- and Anti-Cancer Activity and Their Impact on Immunotherapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsetto, D.; Tomasoni, M.; Payne, K.; Polesel, J.; Deganello, A.; Bossi, P.; Tysome, J.R.; Masterson, L.; Tirelli, G.; Tofanelli, M.; et al. Prognostic Significance of CD4+ and CD8+ Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, C.C.L.; Kao, J.; Sikora, A.G. Recognizing and reversing the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment of head and neck cancer. Immunol. Res. 2012, 54, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Xie, Y.; Tan, Y.S.; Prince, M.E.; Moyer, J.S.; Nör, J.; Wolf, G.T. Telltale tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) in oral, head & neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 2016, 61, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feller, G.; Khammissa, R.A.G.; Nemutandani, M.S.; Feller, L. Biological consequences of cancer radiotherapy in the context of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Face Med. 2021, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuyama, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yanamoto, S. Relationship between Tumor Budding and Partial Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Young Cohort (<45 years, n = 27) | Whole Cohort (n = 74) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| Median, years (range) | 34.2 (21.6–44.9) | 53.7 (21.6–76.1) |
| Sex, n (%) | ||
| m | 18 (66.7) | 49 (66.2) |
| f | 9 (33.3) | 25 (33.8) |
| T classification, n (%) | ||
| T1 | 13 (48.1) | 25 (33.8) |
| T2 | 8 (29.6) | 36 (48.6) |
| T3 | 1 (3.7) | 2 (2.7) |
| T4 | 5 (18.5) | 11 (14.9) |
| N classification, n (%) | ||
| N0 | 15 (55.6) | 41 (55.4) |
| N1 | 4 (14.8) | 17 (23.0) |
| N2 | 8 (29.6) | 16 (21.6) |
| N3 | 0 | 0 |
| M classification, n (%) | ||
| M0 | 26 (96.3) | 71 (95.9) |
| M1 | 1 (3.7) | 3 (4.1) |
| Primary therapy, n (%) | ||
| Surgery | 20 (74.1) | 52 (70.3) |
| Radio ± chemotherapy | 6 (22.2) | 14 (18.9) |
| Palliative systemic therapy | 1 (3.7) | 8 (10.8) |
| Clinical outcome, n (%) | ||
| Median OS, years (range) | 3.8 (0.0–14.6) | 5.2 (0.0–17.1) |
| Median DFS, years (range) | 1.7 (0.0–12.2) | 3.5 (0.0–16.2) |
| Mortality | 9 (33.3) | 29 (39.2) |
| Recurrence | 12 (44.4) | 28 (37.8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kandathil, S.A.; Peter Truta, I.; Kadletz-Wanke, L.; Heiduschka, G.; Stoiber, S.; Kenner, L.; Herrmann, H.; Huskic, H.; Brkic, F.F. Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio Might Serve as a Prognostic Marker in Young Patients with Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14020159
Kandathil SA, Peter Truta I, Kadletz-Wanke L, Heiduschka G, Stoiber S, Kenner L, Herrmann H, Huskic H, Brkic FF. Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio Might Serve as a Prognostic Marker in Young Patients with Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(2):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14020159
Chicago/Turabian StyleKandathil, Sam Augustine, Ina Peter Truta, Lorenz Kadletz-Wanke, Gregor Heiduschka, Stefan Stoiber, Lukas Kenner, Harald Herrmann, Harun Huskic, and Faris F. Brkic. 2024. "Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio Might Serve as a Prognostic Marker in Young Patients with Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 2: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14020159
APA StyleKandathil, S. A., Peter Truta, I., Kadletz-Wanke, L., Heiduschka, G., Stoiber, S., Kenner, L., Herrmann, H., Huskic, H., & Brkic, F. F. (2024). Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio Might Serve as a Prognostic Marker in Young Patients with Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(2), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14020159








