The Importance of Respiratory Rate Monitoring: From Healthcare to Sport and Exercise
Abstract
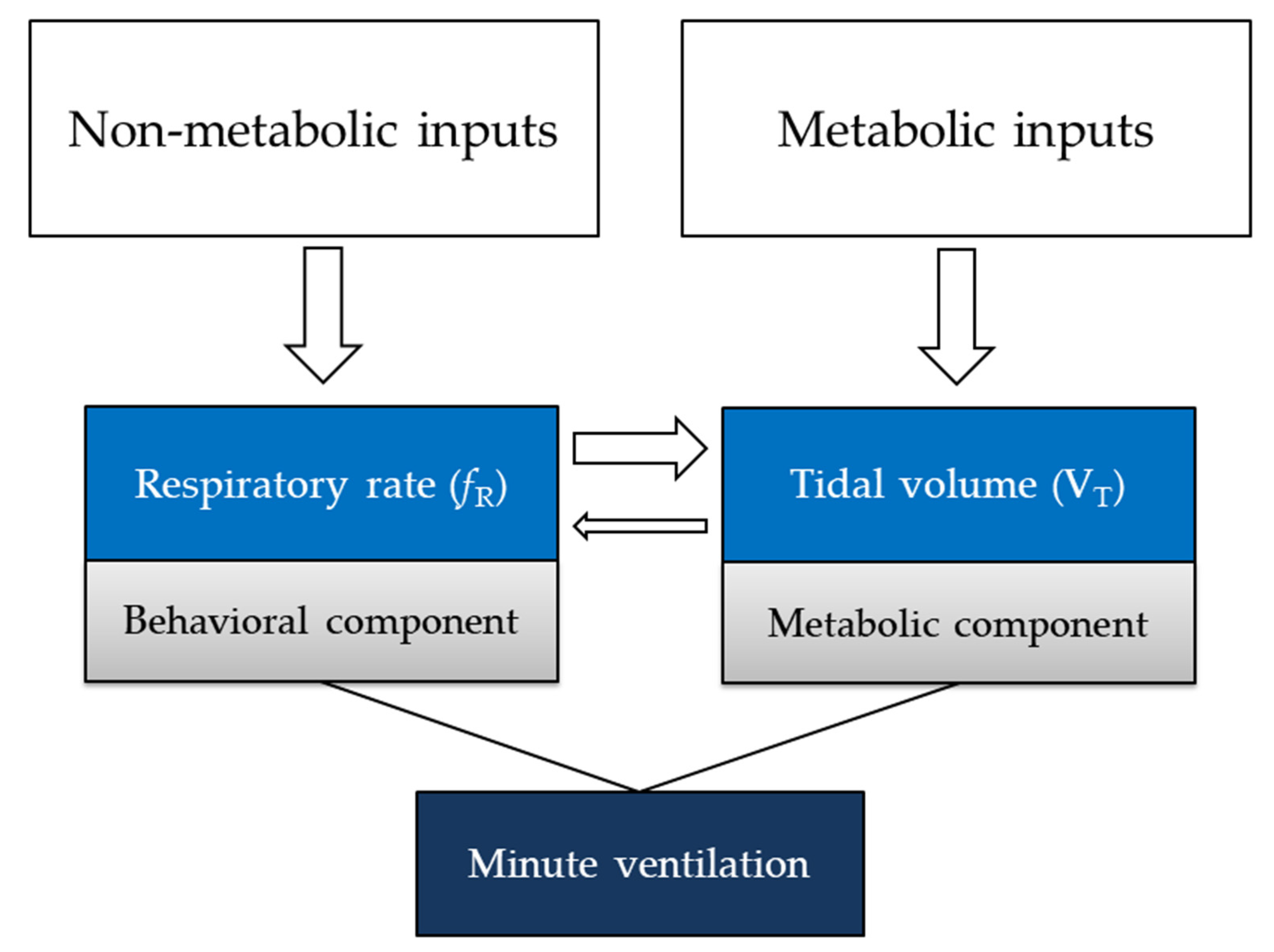
:1. Introduction
2. Goals and Measurement Scenarios Requiring Respiratory Rate Monitoring
2.1. Presence of Breathing
2.1.1. Current Evidence
2.1.2. Measurement and Computing
2.2. Adverse Cardiac Events
2.2.1. Current Evidence
2.2.2. Measurement and Computing
2.3. Apnea
2.3.1. Current Evidence
2.3.2. Measurement and Computing
2.4. Pneumonia
2.4.1. Current Evidence
2.4.2. Measurement and Computing
2.5. Clinical Deterioration
2.5.1. Current Evidence
2.5.2. Measurement and Computing
2.6. Dyspnea
2.6.1. Current Evidence
2.6.2. Measurement and Computing
2.7. Pain
2.7.1. Current Evidence
2.7.2. Measurement and Computing
2.8. Emotional Stress
2.8.1. Current Evidence
2.8.2. Measurement and Computing
2.9. Cognitive Load
2.9.1. Current Evidence
2.9.2. Measurement and Computing
2.10. Environment-Induced Stress
2.10.1. Current Evidence
2.10.2. Measurement and Computing
2.11. Physical Effort and Fatigue during Sport and Exercise
2.11.1. Current Evidence
2.11.2. Measurement and Computing
2.12. Respiratory Artifacts
2.12.1. Current Evidence
2.12.2. Measurement and Computing
2.13. Respiratory Biofeedback
2.13.1. Current Evidence
2.13.2. Measurement and Computing
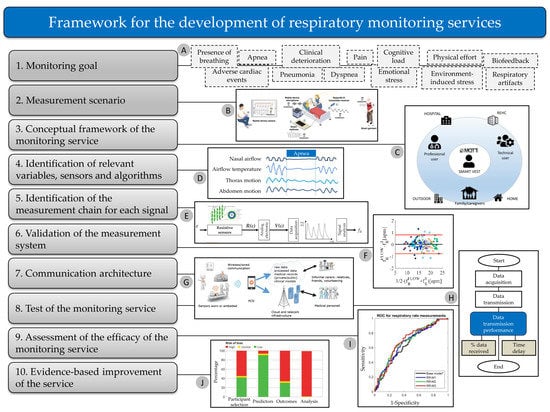
3. A Conceptual Framework for the Development of Respiratory Monitoring Services
4. Perspectives and Challenges of Respiratory Rate Monitoring
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHI | Apnea-Hypopnea Index |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CSA | Central sleep apnea |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| ECG | Electrocardiography |
| fR | Respiratory frequency |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| LOAs | Limits of agreement |
| MEWS | Modified Early Warning Score |
| MOD | Mean of difference |
| mos | Months |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NEWS | National Early Warning Score |
| OSA | Obstructive sleep apnea |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| PPG | Photoplethysmography |
| RGB | Red green blue |
| RIP | Respiratory inductive plethysmography |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| SQI | Signal quality index |
| UWB | Ultra-wideband |
| VT | Tidal volume |
References
- Cretikos, M.A.; Bellomo, R.; Hillman, K.; Chen, J.; Finfer, S.; Flabouris, A. Respiratory rate: The neglected vital sign. Med. J. Aust. 2008, 188, 657–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churpek, M.M.; Yuen, T.C.; Park, S.Y.; Meltzer, D.O.; Hall, J.B.; Edelson, D.P. Derivation of a cardiac arrest prediction model using ward vital signs. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 2102–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodman, D.; Crocker, M.E.; Pervaiz, F.; McCollum, E.D.; Steenland, K.; Simkovich, S.M.; Miele, C.H.; Hammitt, L.L.; Herrera, P.; Zar, H.J.; et al. Challenges in the diagnosis of paediatric pneumonia in intervention field trials: Recommendations from a pneumonia field trial working group. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 1068–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nannan Panday, R.S.; Minderhoud, T.C.; Alam, N.; Nanayakkara, P.W.B. Prognostic value of early warning scores in the emergency department (ED) and acute medical unit (AMU): A narrative review. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 45, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaroni, C.; Nicolò, A.; Schena, E.; Sacchetti, M. Remote Respiratory Monitoring in the Time of COVID-19. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, S. Behavioural and arousal-related influences on breathing in humans. Exp. Physiol. 1996, 81, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipton, M.J.; Harper, A.; Paton, J.F.R.; Costello, J.T. The human ventilatory response to stress: Rate or depth? J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 5729–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, I.; Masaoka, Y. Breathing rhythms and emotions. Exp. Physiol. 2008, 93, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grassmann, M.; Vlemincx, E.; von Leupoldt, A.; Mittelstädt, J.M.; Van den Bergh, O. Respiratory Changes in Response to Cognitive Load: A Systematic Review. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 8146809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolò, A.; Bazzucchi, I.; Haxhi, J.; Felici, F.; Sacchetti, M. Comparing Continuous and Intermittent Exercise: An “Isoeffort” and “Isotime” Approach. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolò, A.; Girardi, M.; Bazzucchi, I.; Felici, F.; Sacchetti, M. Respiratory frequency and tidal volume during exercise: Differential control and unbalanced interdependence. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicolò, A.; Marcora, S.M.; Bazzucchi, I.; Sacchetti, M. Differential control of respiratory frequency and tidal volume during high-intensity interval training. Exp. Physiol. 2017, 102, 934–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolò, A.; Marcora, S.M.; Sacchetti, M. Respiratory frequency is strongly associated with perceived exertion during time trials of different duration. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolò, A.; Massaroni, C.; Passfield, L. Respiratory Frequency during Exercise: The Neglected Physiological Measure. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolò, A.; Montini, M.; Girardi, M.; Felici, F.; Bazzucchi, I.; Sacchetti, M. Respiratory Frequency as a Marker of Physical Effort During High-Intensity Interval Training in Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2020, 15, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolò, A.; Sacchetti, M.; Girardi, M.; McCormick, A.; Angius, L.; Bazzucchi, I.; Marcora, S.M. A comparison of different methods to analyse data collected during time-to-exhaustion tests. Sport Sci. Health 2019, 15, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girardi, M.; Nicolò, A.; Bazzucchi, I.; Felici, F.; Sacchetti, M. The effect of pedalling cadence on respiratory frequency: Passive vs. active exercise of different intensities. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, A.; Alghamdi, B.J.; Ciavaglia, C.E.; Elbehairy, A.F.; Webb, K.A.; Ora, J.; Neder, J.A.; O’Donnell, D.E. Common Mechanisms of Dyspnea in Chronic Interstitial and Obstructive Lung Disorders. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
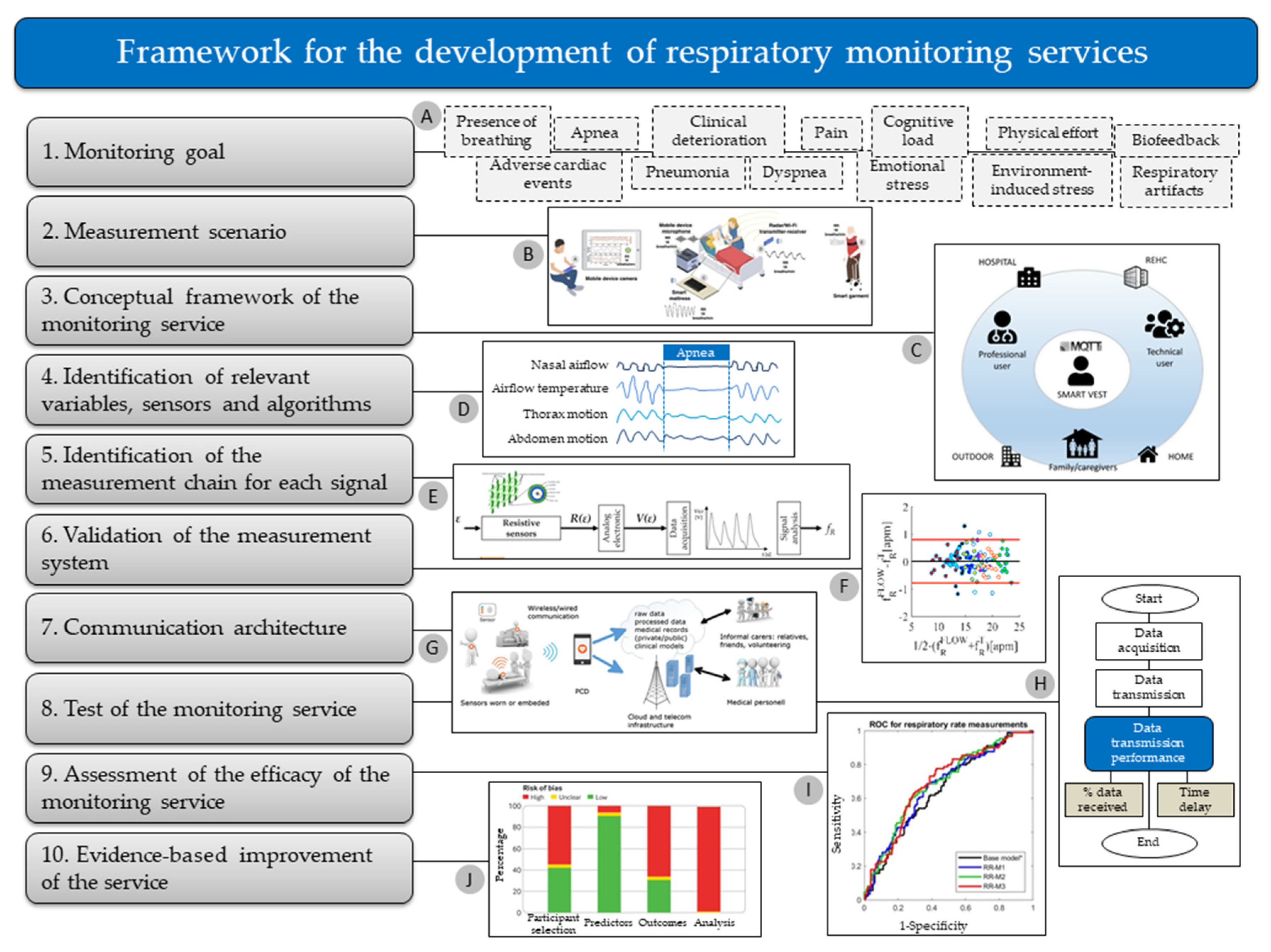
- Nicolò, A.; Girardi, M.; Sacchetti, M. Control of the depth and rate of breathing: Metabolic vs. non-metabolic inputs. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 6363–6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolò, A.; Marcora, S.M.; Sacchetti, M. Last Word on Viewpoint: Time to reconsider how ventilation is regulated above the respiratory compensation point during incremental exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 128, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolò, A.; Marcora, S.M.; Sacchetti, M. Time to reconsider how ventilation is regulated above the respiratory compensation point during incremental exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 128, 1447–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolò, A.; Sacchetti, M. A new model of ventilatory control during exercise. Exp. Physiol. 2019, 104, 1331–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaroni, C.; Nicolò, A.; Sacchetti, M.; Schena, E. Contactless Methods For Measuring Respiratory Rate: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaroni, C.; Nicolò, A.; Lo Presti, D.; Sacchetti, M.; Silvestri, S.; Schena, E. Contact-Based Methods for Measuring Respiratory Rate. Sensors 2019, 19, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Allen, J.; Zheng, D.; Chen, F. Recent development of respiratory rate measurement technologies. Physiol. Meas. 2019, 40, 07TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanegas, E.; Igual, R.; Plaza, I. Sensing systems for respiration monitoring: A technical systematic review. Sensors 2020, 20, 5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, A.; Aliverti, A. Telemonitoring systems for respiratory patients: Technological aspects. Pulmonology 2020, 26, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaroni, C.; Zaltieri, M.; Lo Presti, D.; Nicolò, A.; Tosi, D.; Schena, E. Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors for Cardiorespiratory Monitoring: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughlin, P.C.; Sebat, F.; Kellett, J.G. Respiratory Rate: The Forgotten Vital Sign—Make It Count! Jt. Comm. J. Qual. Patient Saf. 2018, 44, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Drost, N.; McIvor, R. Respiratory Rate and Breathing Pattern. McMaster Univ. Med. J. 2013, 10, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, S.; Thompson, M.; Stevens, R.; Heneghan, C.; Plüddemann, A.; Maconochie, I.; Tarassenko, L.; Mant, D. Normal ranges of heart rate and respiratory rate in children from birth to 18 years of age: A systematic review of observational studies. Lancet 2011, 377, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Liu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, F. Advanced Signal Processing for Vital Sign Extraction With Applications in UWB Radar Detection of Trapped Victims in Complex Environments. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantonen, T.; Jalonen, J.; Grönlund, J.; Antila, K.; Southall, D.; Välimäki, I. Increased amplitude modulation of continuous respiration precedes sudden infant death syndrome. Early Hum. Dev. 1998, 53, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Akangire, G.; Sullivan, B.; Fairchild, K.; Sampath, V. Continuous vital sign analysis for predicting and preventing neonatal diseases in the twenty-first century: Big data to the forefront. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 87, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, G.D.; Stephenson, B.; Hulme, J.; Monsieurs, K.G. Birmingham assessment of breathing study (BABS). Resuscitation 2005, 64, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppert, M.; Reith, M.W.; Widmann, J.H.; Lackner, C.K.; Kerkmann, R.; Schweiberer, L.; Peter, K. Checking for Breathing: Evaluation of the Diagnostic Capability of Emergency Medical Services Personnel, Physicians, Medical Students, and Medical Laypersons. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1999, 34, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M. Why is Respiratory Rate the Neglected Vital Sign? A Narrative Review. Int. Arch. Nurs. Health Care 2016, 2, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flenady, T.; Dwyer, T.; Applegarth, J. Accurate respiratory rates count: So should you! Australas. Emerg. Nurs. J. 2017, 20, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nizami, S.; Green, J.R.; McGregor, C. Implementation of Artifact Detection in Critical Care: A Methodological Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 6, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birrenkott, D.A.; Pimentel, M.A.F.; Watkinson, P.J.; Clifton, D.A. A Robust Fusion Model for Estimating Respiratory Rate From Photoplethysmography and Electrocardiography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 2033–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaroni, C.; Di Tocco, J.; Bravi, M.; Carnevale, A.; Lo Presti, D.; Sabbadini, R.; Miccinilli, S.; Sterzi, S.; Formica, D.; Schena, E. Respiratory Monitoring During Physical Activities With a Multi-Sensor Smart Garment and Related Algorithms. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 2173–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaroni, C.; Di Tocco, J.; Sabbadini, R.; Carnevale, A.; Lo Presti, D.; Schena, E.; Raiano, L.; Formica, D.; Miccinilli, S.; Bravi, M.; et al. Influence of torso movements on a multi-sensor garment for respiratory monitoring during walking and running activities. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira, A.; Spirandeli, A.F.; Moraes, R.; Zarzoso, V. Respiratory Waveform Estimation From Multiple Accelerometers: An Optimal Sensor Number and Placement Analysis. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 23, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.B.; Yu, X.; Goos, T.; Reiss, I.; Orlikowsky, T.; Heimann, K.; Venema, B.; Blazek, V.; Leonhardt, S.; Teichmann, D. Noncontact Monitoring of Respiratory Rate in Newborn Infants Using Thermal Imaging. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhsarmast, F.; Lyu, T.; Liang, X.; Zhang, H.; Gulliver, T. Random-Noise Denoising and Clutter Elimination of Human Respiration Movements Based on an Improved Time Window Selection Algorithm Using Wavelet Transform. Sensors 2018, 19, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.; Deng, J.; Zhang, H.; Gulliver, T.A. Ultra-Wideband Impulse Radar Through-Wall Detection of Vital Signs. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.; Lv, T.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Fang, G. Through-wall human being detection using UWB impulse radar. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2018, 2018, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fieselmann, J.F.; Hendryx, M.S.; Helms, C.M.; Wakefield, D.S. Respiratory rate predicts cardiopulmonary arrest for internal medicine inpatients. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 1993, 8, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgetts, T.J.; Kenward, G.; Vlachonikolis, I.G.; Payne, S.; Castle, N. The identification of risk factors for cardiac arrest and formulation of activation criteria to alert a medical emergency team. Resuscitation 2002, 54, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churpek, M.M.; Yuen, T.C.; Huber, M.T.; Park, S.Y.; Hall, J.B.; Edelson, D.P. Predicting Cardiac Arrest on the Wards. Chest 2012, 141, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Churpek, M.M.; Yuen, T.C.; Winslow, C.; Hall, J.; Edelson, D.P. Differences in Vital Signs Between Elderly and Nonelderly Patients Prior to Ward Cardiac Arrest. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthel, P.; Wensel, R.; Bauer, A.; Muller, A.; Wolf, P.; Ulm, K.; Huster, K.M.; Francis, D.P.; Malik, M.; Schmidt, G. Respiratory rate predicts outcome after acute myocardial infarction: A prospective cohort study. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dommasch, M.; Sinnecker, D.; Barthel, P.; Müller, A.; Dirschinger, R.J.; Hapfelmeier, A.; Huster, K.M.; Laugwitz, K.-L.; Malik, M.; Schmidt, G. Nocturnal Respiratory Rate Predicts Non–Sudden Cardiac Death in Survivors of Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2432–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinnecker, D.; Dommasch, M.; Barthel, P.; Müller, A.; Dirschinger, R.J.; Hapfelmeier, A.; Huster, K.M.; Laugwitz, K.-L.; Malik, M.; Schmidt, G. Assessment of mean respiratory rate from ECG recordings for risk stratification after myocardial infarction. J. Electrocardiol. 2014, 47, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumert, M.; Linz, D.; Stone, K.; McEvoy, R.D.; Cummings, S.; Redline, S.; Mehra, R.; Immanuel, S. Mean nocturnal respiratory rate predicts cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in community-dwelling older men and women. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1802175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, M.E.H.; Perkins, G.D.; Cariou, A. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: Prehospital management. Lancet 2018, 391, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.; Rea, T.; Gollakota, S.; Sunshine, J.E. Contactless cardiac arrest detection using smart devices. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, J.; Nguyen, O.K.; Clark, C.; Halm, E.A.; Makam, A.N. Is everyone really breathing 20 times a minute? Assessing epidemiology and variation in recorded respiratory rate in hospitalised adults. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2017, 26, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flenady, T.; Dwyer, T.; Applegarth, J. Explaining transgression in respiratory rate observation methods in the emergency department: A classic grounded theory analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2017, 74, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.; Kelly, E.; Horswill, M.S.; Watson, M.O. The effects of awareness and count duration on adult respiratory rate measurements: An experimental study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2018, 27, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walsh, J.A.; Topol, E.J.; Steinhubl, S.R. Novel Wireless Devices for Cardiac Monitoring. Circulation 2014, 130, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, P.H.; Birrenkott, D.A.; Bonnici, T.; Pimentel, M.A.F.; Johnson, A.E.W.; Alastruey, J.; Tarassenko, L.; Watkinson, P.J.; Beale, R.; Clifton, D.A. Breathing Rate Estimation From the Electrocardiogram and Photoplethysmogram: A Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 11, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varon, C.; Morales, J.; Lázaro, J.; Orini, M.; Deviaene, M.; Kontaxis, S.; Testelmans, D.; Buyse, B.; Borzée, P.; Sörnmo, L.; et al. A Comparative Study of ECG-derived Respiration in Ambulatory Monitoring using the Single-lead ECG. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanata, A.; Scilingo, E.P.; Nardini, E.; Loriga, G.; Paradiso, R.; De-Rossi, D. Comparative Evaluation of Susceptibility to Motion Artifact in Different Wearable Systems for Monitoring Respiratory Rate. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermer, S.; Brewer, L.; Orr, J.; Egan, T.D.; Johnson, K. Comparison of 7 Different Sensors for Detecting Low Respiratory Rates Using a Single Breath Detection Algorithm in Nonintubated, Sedated Volunteers. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 129, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliverti, A. Wearable technology: Role in respiratory health and disease. Breathe 2017, 13, e27–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjafield, A.V.; Ayas, N.T.; Eastwood, P.R.; Heinzer, R.; Ip, M.S.M.; Morrell, M.J.; Nunez, C.M.; Patel, S.R.; Penzel, T.; Pépin, J.-L.; et al. Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of obstructive sleep apnoea: A literature-based analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Javaheri, S.; Barbe, F.; Campos-Rodriguez, F.; Dempsey, J.A.; Khayat, R.; Javaheri, S.; Malhotra, A.; Martinez-Garcia, M.A.; Mehra, R.; Pack, A.I.; et al. Sleep Apnea. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 841–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, V.K.; Auckley, D.H.; Chowdhuri, S.; Kuhlmann, D.C.; Mehra, R.; Ramar, K.; Harrod, C.G. Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 479–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randerath, W.; Bassetti, C.L.; Bonsignore, M.R.; Farre, R.; Ferini-Strambi, L.; Grote, L.; Hedner, J.; Kohler, M.; Martinez-Garcia, M.-A.; Mihaicuta, S.; et al. Challenges and perspectives in obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1702616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.B.; Budhiraja, R.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Gozal, D.; Iber, C.; Kapur, V.K.; Marcus, C.L.; Mehra, R.; Parthasarathy, S.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Rules for Scoring Respiratory Events in Sleep: Update of the 2007 AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2012, 8, 597–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendonça, F.; Mostafa, S.S.; Ravelo-García, A.G.; Morgado-Dias, F.; Penzel, T. Devices for home detection of obstructive sleep apnea: A review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 41, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collop, N.A.; Tracy, S.L.; Kapur, V.; Mehra, R.; Kuhlmann, D.; Fleishman, S.A.; Ojile, J.M. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Devices for Out-Of-Center (OOC) Testing: Technology Evaluation. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2011, 7, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farré, R.; Montserrat, J.M.; Rotger, M.; Ballester, E.; Navajas, D. Accuracy of thermistors and thermocouples as flow-measuring devices for detecting hypopnoeas. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 11, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, P.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, R. Smart Sensing Strip Using Monolithically Integrated Flexible Flow Sensor for Noninvasively Monitoring Respiratory Flow. Sensors 2015, 15, 31738–31750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, A.T.; Singh, P.; Ruehland, W.R.; Rochford, P.D. AASM Criteria for Scoring Respiratory Events: Interaction between Apnea Sensor and Hypopnea Definition. Sleep 2012, 35, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, V.; Crainiceanu, C.M.; Punjabi, N.M.; Redline, S.; Gottlieb, D.J. Calibration Model for Apnea-Hypopnea Indices: Impact of Alternative Criteria for Hypopneas. Sleep 2015, 38, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzel, T.; Sabil, A. The use of tracheal sounds for the diagnosis of sleep apnoea. Breathe 2017, 13, e37–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabil, A.; Glos, M.; Günther, A.; Schöbel, C.; Veauthier, C.; Fietze, I.; Penzel, T. Comparison of Apnea Detection Using Oronasal Thermal Airflow Sensor, Nasal Pressure Transducer, Respiratory Inductance Plethysmography and Tracheal Sound Sensor. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glos, M.; Sabil, A.; Jelavic, K.S.; Baffet, G.; Schöbel, C.; Fietze, I.; Penzel, T. Tracheal sound analysis for detection of sleep disordered breathing. Somnologie 2019, 23, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakano, H.; Furukawa, T.; Tanigawa, T. Tracheal Sound Analysis Using a Deep Neural Network to Detect Sleep Apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, L.-P.; Meng, Z.-M.; Lin, S.-S. R&D for Home Sleep Apnea Syndrome Observation System. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Computer Sciences and Applications, Wuhan, China, 14–15 December 2013; pp. 474–478. [Google Scholar]
- Olvera, D.L.D.; Lopez, D.S.; Prado, M.A.M.; Resendiz, J.R.; Rivera, Y.O. Noninvasive monitoring system for early detection of apnea in newborns and infants. In Proceedings of the IECBES 2016—IEEE-EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 494–498. [Google Scholar]
- Schätz, M.; Procházka, A.; Kuchyňka, J.; Vyšata, O. Sleep Apnea Detection with Polysomnography and Depth Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sadek, I.; Seet, E.; Biswas, J.; Abdulrazak, B.; Mokhtari, M. Nonintrusive Vital Signs Monitoring for Sleep Apnea Patients: A Preliminary Study. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 2506–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defaye, P.; Mendelson, M.; Tamisier, R.; Jacon, P.; Venier, S.; Arnol, N.; Pépin, J.-L. Validation of an apnea and hypopnea detection algorithm implemented in implantable cardioverter defibrillators. The AIRLESS study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shokoueinejad, M.; Fernandez, C.; Carroll, E.; Wang, F.; Levin, J.; Rusk, S.; Glattard, N.; Mulchrone, A.; Zhang, X.; Xie, A.; et al. Sleep apnea: A review of diagnostic sensors, algorithms, and therapies. Physiol. Meas. 2017, 38, R204–R252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, K.; Alfvén, T.; Mucunguzi, A.; Wharton-Smith, A.; Dantzer, E.; Habte, T.; Matata, L.; Nanyumba, D.; Okwir, M.; Posada, M.; et al. Performance of Four Respiratory Rate Counters to Support Community Health Workers to Detect the Symptoms of Pneumonia in Children in Low Resource Settings: A Prospective, Multicentre, Hospital-Based, Single-Blinded, Comparative Trial. EClinicalMedicine 2019, 12, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ginsburg, A.S.; Lenahan, J.L.; Izadnegahdar, R.; Ansermino, J.M. A Systematic Review of Tools to Measure Respiratory Rate in Order to Identify Childhood Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.-S.; Macfarlane, J.T. Defining prognostic factors in the elderly with community acquired pneumonia: A case controlled study of patients aged ≥75 yrs. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 17, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez, F.; Masiá, M. Improving Outcomes of Elderly Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Drugs Aging 2008, 25, 585–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liapikou, A.; Polverino, E.; Ewig, S.; Cillóniz, C.; Marcos, M.A.; Mensa, J.; Bello, S.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Menéndez, R.; Torres, A. Severity and outcomes of hospitalised community-acquired pneumonia in COPD patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 39, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kissler, S.M.; Tedijanto, C.; Goldstein, E.; Grad, Y.H.; Lipsitch, M. Projecting the transmission dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 through the postpandemic period. Science 2020, 368, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandell, L.A.; Wunderink, R.G.; Anzueto, A.; Bartlett, J.G.; Campbell, G.D.; Dean, N.C.; Dowell, S.F.; File, T.M.; Musher, D.M.; Niederman, M.S.; et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society Consensus Guidelines on the Management of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, S27–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.S.; Van Der Eerden, M.M.; Laing, R.; Boersma, W.G.; Karalus, N.; Town, G.I.; Lewis, S.A.; Macfarlane, J.T. Defining community acquired pneumonia severity on presentation to hospital: An international derivation and validation study. Thorax 2003, 58, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, W.S.; Lewis, S.; Macfarlane, J.T. Severity prediction rules in community acquired pneumonia: A validation study. Thorax 2000, 55, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strauß, R.; Ewig, S.; Richter, K.; König, T.; Heller, G.; Bauer, T.T. The Prognostic Significance of Respiratory Rate in Patients With Pneumonia. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2014, 111, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dwyer, R.; Hedlund, J.; Henriques-Normark, B.; Kalin, M. Improvement of CRB-65 as a prognostic tool in adult patients with community-acquired pneumonia. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2014, 1, e000038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.; Bachur, R.; Kim, D.; Neuman, M.I. Lack of Predictive Value of Tachypnea in the Diagnosis of Pneumonia in Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2010, 29, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansermino, J.M.; Dumont, G.; Ginsburg, A.S. How Uncertain Is Our Reference Standard for Respiratory Rate Measurement? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1036–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, D.R.; Davies, E.V.; Harlow, E.R.; Hsu, J.J.; Knighton, S.C.; Walker, T.A.; Voos, J.E.; Drummond, C.K. Wearable Sensors for COVID-19: A Call to Action to Harness Our Digital Infrastructure for Remote Patient Monitoring and Virtual Assessments. Front. Digit. Health 2020, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naji, A.; Chahl, J. Remote respiratory monitoring system based on developing motion magnification technique. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2016, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naji, A.; Gibson, K.; Lee, S.-H.; Chahl, J. Real Time Apnoea Monitoring of Children Using the Microsoft Kinect Sensor: A Pilot Study. Sensors 2017, 17, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kebe, M.; Gadhafi, R.; Mohammad, B.; Sanduleanu, M.; Saleh, H.; Al-Qutayri, M. Human Vital Signs Detection Methods and Potential Using Radars: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chow, P.; Nagendra, G.; Abisheganaden, J.; Wang, Y.T. Respiratory monitoring using an air-mattress system. Physiol. Meas. 2000, 21, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalise, L.; Ercoli, I.; Marchionni, P.; Tomasini, E.P. Measurement of respiration rate in preterm infants by laser Doppler vibrometry. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications, Bari, Italy, 30–31 May 2011; pp. 657–661. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso-Álvarez, M.L.; Terán-Santos, J.; Ordax Carbajo, E.; Cordero-Guevara, J.A.; Navazo-Egüia, A.I.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Gozal, D. Reliability of Home Respiratory Polygraphy for the Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea in Children. Chest 2015, 147, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mochizuki, K.; Shintani, R.; Mori, K.; Sato, T.; Sakaguchi, O.; Takeshige, K.; Nitta, K.; Imamura, H. Importance of respiratory rate for the prediction of clinical deterioration after emergency department discharge: A single-center, case-control study. Acute Med. Surg. 2017, 4, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.-H.; Schwartz, J.; Moy, A.; Knaplund, C.; Kang, M.-J.; Schnock, K.O.; Garcia, J.P.; Jia, H.; Dykes, P.C.; Cato, K.; et al. Development and validation of early warning score system: A systematic literature review. J. Biomed. Inform. 2020, 105, 103410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerry, S.; Bonnici, T.; Birks, J.; Kirtley, S.; Virdee, P.S.; Watkinson, P.J.; Collins, G.S. Early warning scores for detecting deterioration in adult hospital patients: Systematic review and critical appraisal of methodology. BMJ 2020, 369, m1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonafide, C.P.; Brady, P.W.; Keren, R.; Conway, P.H.; Marsolo, K.; Daymont, C. Development of Heart and Respiratory Rate Percentile Curves for Hospitalized Children. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e1150–e1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, G.B.; Prytherch, D.R.; Meredith, P.; Schmidt, P.E.; Featherstone, P.I. The ability of the National Early Warning Score (NEWS) to discriminate patients at risk of early cardiac arrest, unanticipated intensive care unit admission, and death. Resuscitation 2013, 84, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbe, C.P.; Kruger, M.; Rutherford, P.; Gemmel, L. Validation of a modified early warning score in medical admissions. QJM 2001, 94, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martín-Rodríguez, F.; López-Izquierdo, R.; del Pozo Vegas, C.; Sánchez-Soberón, I.; Delgado-Benito, J.F.; Martín-Conty, J.L.; Castro-Villamor, M.A. Can the prehospital National Early Warning Score 2 identify patients at risk of in-hospital early mortality? A prospective, multicenter cohort study. Heart Lung 2020, 49, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marik, P.E.; Taeb, A.M. SIRS, qSOFA and new sepsis definition. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 943–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinten, V.M.; van Meurs, M.; Olgers, T.J.; Vonk, J.M.; Ligtenberg, J.J.M.; ter Maaten, J.C. Repeated vital sign measurements in the emergency department predict patient deterioration within 72 hours: A prospective observational study. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2018, 26, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, W.T.; Fang, A.H.; Loo, C.M.; Wong, K.S.; Balakrishnan, T. Use of the National Early Warning Score (NEWS) to Identify Acutely Deteriorating Patients with Sepsis in Acute Medical Ward. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2019, 48, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weenk, M.; Koeneman, M.; van de Belt, T.H.; Engelen, L.J.L.P.G.; van Goor, H.; Bredie, S.J.H. Wireless and continuous monitoring of vital signs in patients at the general ward. Resuscitation 2019, 136, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynn, L.A.; Curry, J.P. Patterns of unexpected in-hospital deaths: A root cause analysis. Patient Saf. Surg. 2011, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eckart, A.; Hauser, S.I.; Kutz, A.; Haubitz, S.; Hausfater, P.; Amin, D.; Amin, A.; Huber, A.; Mueller, B.; Schuetz, P. Combination of the National Early Warning Score (NEWS) and inflammatory biomarkers for early risk stratification in emergency department patients: Results of a multinational, observational study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e024636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viglino, D.; L’her, E.; Maltais, F.; Maignan, M.; Lellouche, F. Evaluation of a new respiratory monitoring tool “Early Warning ScoreO2” for patients admitted at the emergency department with dyspnea. Resuscitation 2020, 148, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellett, J.; Li, M.; Rasool, S.; Green, G.C.; Seely, A. Comparison of the heart and breathing rate of acutely ill medical patients recorded by nursing staff with those measured over 5min by a piezoelectric belt and ECG monitor at the time of admission to hospital. Resuscitation 2011, 82, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, W.; Dugas, A.F.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Saheed, M.; Hill, P.; Lindauer, C.; Terzis, A.; Rothman, R.E. Revitalizing a Vital Sign: Improving Detection of Tachypnea at Primary Triage. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2013, 61, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latten, G.H.P.; Spek, M.; Muris, J.W.M.; Cals, J.W.L.; Stassen, P.M. Accuracy and interobserver-agreement of respiratory rate measurements by healthcare professionals, and its effect on the outcomes of clinical prediction/diagnostic rules. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semler, M.W.; Stover, D.G.; Copland, A.P.; Hong, G.; Johnson, M.J.; Kriss, M.S.; Otepka, H.; Wang, L.; Christman, B.W.; Rice, T.W. Flash Mob Research. Chest 2013, 143, 1740–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charlton, P.H.; Bonnici, T.; Tarassenko, L.; Clifton, D.A.; Beale, R.; Watkinson, P.J. An assessment of algorithms to estimate respiratory rate from the electrocardiogram and photoplethysmogram. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 610–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergese, S.D.; Mestek, M.L.; Kelley, S.D.; McIntyre, R.; Uribe, A.A.; Sethi, R.; Watson, J.N.; Addison, P.S. Multicenter Study Validating Accuracy of a Continuous Respiratory Rate Measurement Derived From Pulse Oximetry. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 124, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Touw, H.R.W.; Verheul, M.H.; Tuinman, P.R.; Smit, J.; Thöne, D.; Schober, P.; Boer, C. Photoplethysmography respiratory rate monitoring in patients receiving procedural sedation and analgesia for upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2017, 31, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharp, C.; Soleimani, V.; Hannuna, S.; Camplani, M.; Damen, D.; Viner, J.; Mirmehdi, M.; Dodd, J.W. Toward Respiratory Assessment Using Depth Measurements from a Time-of-Flight Sensor. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zito, D.; Pepe, D.; Mincica, M.; Zito, F.; Tognetti, A.; Lanata, A.; De Rossi, D. SoC CMOS UWB Pulse Radar Sensor for Contactless Respiratory Rate Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2011, 5, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Matsui, T. Rapid and stable measurement of respiratory rate from Doppler radar signals using time domain autocorrelation model. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; Volume 2015, pp. 5985–5988. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, R.; Wang, W.; Moço, A.; de Haan, G. Video-based respiration monitoring with automatic region of interest detection. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subbe, C.; Kinsella, S. Continuous Monitoring of Respiratory Rate in Emergency Admissions: Evaluation of the RespiraSenseTM Sensor in Acute Care Compared to the Industry Standard and Gold Standard. Sensors 2018, 18, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weenk, M.; van Goor, H.; Frietman, B.; Engelen, L.J.; van Laarhoven, C.J.; Smit, J.; Bredie, S.J.; van de Belt, T.H. Continuous Monitoring of Vital Signs Using Wearable Devices on the General Ward: Pilot Study. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2017, 5, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, N.; Serradori, M. Determining the cause of dyspnoea: Linguistic and biological descriptors. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2006, 3, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yañez, A.M.; Guerrero, D.; Pérez de Alejo, R.; Garcia-Rio, F.; Alvarez-Sala, J.L.; Calle-Rubio, M.; de Molina, R.M.; Valle Falcones, M.; Ussetti, P.; Sauleda, J.; et al. Monitoring Breathing Rate at Home Allows Early Identification of COPD Exacerbations. Chest 2012, 142, 1524–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, V.; Babb, T.G. Exertional dyspnoea in obesity. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2016, 25, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, S.F. Dyspnoea and quality of life in older people at home. Age Ageing 2001, 30, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waschki, B.; Spruit, M.A.; Watz, H.; Albert, P.S.; Shrikrishna, D.; Groenen, M.; Smith, C.; Man, W.D.-C.; Tal-Singer, R.; Edwards, L.D.; et al. Physical activity monitoring in COPD: Compliance and associations with clinical characteristics in a multicenter study. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wasserman, K.; Casaburi, R. Dyspnea: Physiological and Pathophysiological Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Med. 1988, 39, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Iglesia, F.; Valino, P.; Pita, S.; Ramos, V.; Pellicer, C.; Nicolas, R.; Diz-Lois, F. Factors predicting a hospital stay of over 3 days in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Intern. Med. 2002, 251, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franciosi, L.G.; Page, C.P.; Celli, B.R.; Cazzola, M.; Walker, M.J.; Danhof, M.; Rabe, K.F.; Pasqua, E.D.O. Markers of exacerbation severity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.A.; Velardo, C.; Farmer, A.; Tarassenko, L. Exacerbations in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Identification and Prediction Using a Digital Health System. J. Med. Internet Res. 2017, 19, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.M.; Guz, A.; Murphy, K.; Griffith, A.R.; Pedersen, D.L.; Kardos, A.; Leff, A.; Adams, L.; Casadei, B.; Paterson, D.J. Identification of higher brain centres that may encode the cardiorespiratory response to exercise in humans. J. Physiol. 2001, 533, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviolette, L.; Laveneziana, P. Dyspnoea: A multidimensional and multidisciplinary approach. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 1750–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marlow, L.L.; Faull, O.K.; Finnegan, S.L.; Pattinson, K.T.S. Breathlessness and the brain. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2019, 13, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansing, R.W.; Im, B.S.H.; Thwing, J.I.; Legedza, A.T.R.; Banzett, R.B. The perception of respiratory work and effort can be independent of the perception of air hunger. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minagar, A.; Weiner, W.J. Adolf Kussmaul and His Respiratory Sign. J. Med. Biogr. 2001, 9, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victorson, D.E.; Anton, S.; Hamilton, A.; Yount, S.; Cella, D. A Conceptual Model of the Experience of Dyspnea and Functional Limitations in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Value Health 2009, 12, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fekr, A.R.; Janidarmian, M.; Radecka, K.; Zilic, Z. Respiration Disorders Classification With Informative Features for m-Health Applications. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekr, A.R.; Radecka, K.; Zilic, Z. Design and Evaluation of an Intelligent Remote Tidal Volume Variability Monitoring System in E-Health Applications. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2015, 19, 1532–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesareo, A.; Previtali, Y.; Biffi, E.; Aliverti, A. Assessment of Breathing Parameters Using an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)-Based System. Sensors 2018, 19, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, M.; Nguyen, T.; Pandey, V.; Zhou, Y.; Pham, H.N.; Bar-Yoseph, R.; Radom-Aizik, S.; Jain, R.; Cooper, D.M.; Khine, M. Respiration rate and volume measurements using wearable strain sensors. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaroni, C.; Nicolò, A.; Lo Presti, D.; Sacchetti, M.; Schena, E. Respiratory monitoring during cycling exercise: Performance assessment of a smart t-shirt embedding fiber optic sensors. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 & IoT, Roma, Italy, 3–5 June 2020; pp. 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, M.C.; Porras, D.C.; Lunardi, A.C.; da Silva, C.C.B.M.; Barbosa, R.C.C.; Cardenas, L.Z.; Pletsch, R.; Ferreira, J.G.; de Castro, I.; de Carvalho, C.R.F.; et al. Thoracoabdominal asynchrony: Two methods in healthy, COPD, and interstitial lung disease patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaroni, C.; Carraro, E.; Vianello, A.; Miccinilli, S.; Morrone, M.; Levai, I.K.; Schena, E.; Saccomandi, P.; Sterzi, S.; Dickinson, J.W.; et al. Optoelectronic Plethysmography in Clinical Practice and Research: A Review. Respiration 2017, 93, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo-Hernández, D.; Talaminos-Barroso, A.; Reina-Tosina, J.; Roa, L.; Barbarov-Rostan, G.; Cejudo-Ramos, P.; Márquez-Martín, E.; Ortega-Ruiz, F. Smart Vest for Respiratory Rate Monitoring of COPD Patients Based on Non-Contact Capacitive Sensing. Sensors 2018, 18, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Langford, R.M. Pain management today—What have we learned? Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 25, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunwoody, C.J.; Krenzischek, D.A.; Pasero, C.; Rathmell, J.P.; Polomano, R.C. Assessment, Physiological Monitoring, and Consequences of Inadequately Treated Acute Pain. Pain Manag. Nurs. 2008, 9, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan-Otto, A.; Salmir, N.; Johan, H.; Erik, H.; Christer, A. The intensity of pain in the prehospital setting is most strongly reflected in the respiratory rate among physiological parameters. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 37, 2125–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, M.S.; Eikermann, M. Contact-free respiratory monitoring using bed wheel sensors: A valid respiratory monitoring technique with significant potential impact on public health. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 1430–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Courtois, I.; Van den Bergh, O.; Vlaeyen, J.W.S.; Van Diest, I. Pain and respiration. Pain 2017, 158, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman, C.; Askanazi, J.; Forse, R.A.; Hyman, A.I.; Milic-Emili, J.; Kinney, J.M. The metabolic and ventilatory response to the infusion of stress hormones. Ann. Surg. 1986, 203, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willer, J. Influence de l’anticipation de la douleur sur les fréquences cardiaque et respiratoire et sur le réflexe nociceptif chez l’homme. Physiol. Behav. 1975, 15, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendall, J.C.; Simpson, P.M.; Middleton, P.M. Prehospital vital signs can predict pain severity. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 18, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.A.; Caplan, R.A.; Stephens, L.S.; Posner, K.L.; Terman, G.W.; Voepel-Lewis, T.; Domino, K.B. Postoperative Opioid-induced Respiratory Depression. Anesthesiology 2015, 122, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargo, J.J.; Zuccaro, G.; Dumot, J.A.; Conwell, D.L.; Morrow, J.B.; Shay, S.S. Automated graphic assessment of respiratory activity is superior to pulse oximetry and visual assessment for the detection of early respiratory depression during therapeutic upper endoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2002, 55, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gélinas, C.; Johnston, C. Pain assessment in the critically ill ventilated adult: Validation of the critical-care pain observation tool and physiologic indicators. Clin. J. Pain 2007, 23, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kabes, A.M.; Graves, J.K.; Norris, J. Further Validation of the Nonverbal Pain Scale in Intensive Care Patients. Crit. Care Nurse 2009, 29, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arsenault, M.; Ladouceur, A.; Lehmann, A.; Rainville, P.; Piché, M. Pain modulation induced by respiration: Phase and frequency effects. Neuroscience 2013, 252, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heck, D.H.; McAfee, S.S.; Liu, Y.; Babajani-Feremi, A.; Rezaie, R.; Freeman, W.J.; Wheless, J.W.; Papanicolaou, A.C.; Ruszinkó, M.; Sokolov, Y.; et al. Breathing as a Fundamental Rhythm of Brain Function. Front. Neural Circuits 2017, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jafari, H.; Van de Broek, K.; Plaghki, L.; Vlaeyen, J.W.S.; Van den Bergh, O.; Van Diest, I. Respiratory hypoalgesia? Breath-holding, but not respiratory phase modulates nociceptive flexion reflex and pain intensity. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2016, 101, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermer, S.C.; Farney, R.J.; Johnson, K.B.; Orr, J.A.; Egan, T.D.; Brewer, L.M. An Automated Algorithm Incorporating Poincaré Analysis Can Quantify the Severity of Opioid-Induced Ataxic Breathing. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 130, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, G.B.; Bates, A.; Mann, J.; Arvind, D.K. Characterization of breathing patterns during patient-controlled opioid analgesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 111, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sessler, D.I. Preventing Respiratory Depression. Anesthesiology 2015, 122, 484–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isono, S.; Nozaki-Taguchi, N.; Hasegawa, M.; Kato, S.; Todoroki, S.; Masuda, S.; Iida, N.; Nishimura, T.; Noto, M.; Sato, Y. Contact-free unconstraint respiratory measurements with load cells under the bed in awake healthy volunteers: Breath-by-breath comparison with pneumotachography. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 1432–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, Z.T.; Hayes, T.L.; Guilleminault, C.; Hagen, C.C. Accurate scoring of the apnea-hypopnea index using a simple non-contact breathing sensor. J. Sleep Res. 2013, 22, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jarzyna, D.; Jungquist, C.R.; Pasero, C.; Willens, J.S.; Nisbet, A.; Oakes, L.; Dempsey, S.J.; Santangelo, D.; Polomano, R.C. American Society for Pain Management Nursing Guidelines on Monitoring for Opioid-Induced Sedation and Respiratory Depression. Pain Manag. Nurs. 2011, 12, 118–145.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaoka, Y.; Homma, I. The effect of anticipatory anxiety on breathing and metabolism in humans. Respir. Physiol. 2001, 128, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhan, Q.; Yang, T.; Xia, S. Respiration-based emotion recognition with deep learning. Comput. Ind. 2017, 92–93, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, J.M.; Kent, J.; Martinez, J.; Browne, S.; Coplan, J.; Papp, L.A. Physiological Changes During Carbon Dioxide Inhalation in Patients With Panic Disorder, Major Depression, and Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2001, 58, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, M.; Caldirola, D.; Di Chiaro, N.V.; Riva, A.; Daccò, S.; Pompili, M.; Perna, G. Are Respiratory Abnormalities Specific for Panic Disorder? A Meta-Analysis. Neuropsychobiology 2014, 70, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, J.L.; Khuvis, S.; Yeagle, E.; Cerf, M.; Mehta, A.D. Breathing above the brain stem: Volitional control and attentional modulation in humans. J. Neurophysiol. 2018, 119, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerath, R.; Crawford, M.W.; Barnes, V.A.; Harden, K. Self-Regulation of Breathing as a Primary Treatment for Anxiety. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2015, 40, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Ley, M.; Hanke, S. Emotion Recognition from Physiological Signal Analysis: A Review. Electron. Notes Theor. Comput. Sci. 2019, 343, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzedzickis, A.; Kaklauskas, A.; Bucinskas, V. Human Emotion Recognition: Review of Sensors and Methods. Sensors 2020, 20, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, M.-H.; Zhai, G.-T.; Li, D.; Fan, Y.-Z.; Chen, X.-H.; Yang, X.-K. Synergetic use of thermal and visible imaging techniques for contactless and unobtrusive breathing measurement. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 036006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwasniewska, A.; Ruminski, J.; Szankin, M. Improving accuracy of contactless respiratory rate estimation by enhancing thermal sequences with deep neural networks. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, B.; He, X.; Zhang, C.; Wu, X. Non-contact, synchronous dynamic measurement of respiratory rate and heart rate based on dual sensitive regions. Biomed. Eng. Online 2017, 16, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khanam; Al-Naji; Chahl Remote Monitoring of Vital Signs in Diverse Non-Clinical and Clinical Scenarios Using Computer Vision Systems: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4474. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlemincx, E.; Abelson, J.L.; Lehrer, P.M.; Davenport, P.W.; Van Diest, I.; Van den Bergh, O. Respiratory variability and sighing: A psychophysiological reset model. Biol. Psychol. 2013, 93, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, T.; Zhou, G.; Schuele, S.; Templer, J.; Zelano, C. Automated analysis of breathing waveforms using BreathMetrics: A respiratory signal processing toolbox. Chem. Senses 2018, 43, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wientjes, C.J.E.; Grossman, P.; Gaillard, A.W.K. Influence of drive and timing mechanisms on breathing pattern and ventilation during mental task performance. Biol. Psychol. 1998, 49, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattyn, N.; Migeotte, P.-F.; Neyt, X.; van den Nest, A.; Cluydts, R. Comparing real-life and laboratory-induced stress reactivity on cardio-respiratory parameters: Differentiation of a tonic and a phasic component. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 101, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassmann, M.; Vlemincx, E.; von Leupoldt, A.; Van den Bergh, O. The role of respiratory measures to assess mental load in pilot selection. Ergonomics 2016, 59, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acevedo, E.; Webb, H.; Weldy, M.; Fabianke, E.; Orndorff, G.; Starks, M. Cardiorespiratory Responses of Hi Fit and Low Fit Subjects to Mental Challenge during Exercise. Int. J. Sports Med. 2006, 27, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, H.E.; Weldy, M.L.; Fabianke-Kadue, E.C.; Orndorff, G.R.; Kamimori, G.H.; Acevedo, E.O. Psychological stress during exercise: Cardiorespiratory and hormonal responses. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker Steege, L.M.; Nussbaum, M.A. Dimensions of Fatigue as Predictors of Performance: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach Among Registered Nurses. IIE Trans. Occup. Ergon. Hum. Factors 2013, 1, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, L. Experienced mental workload, perception of usability, their interaction and impact on task performance. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nindl, B.C.; Billing, D.C.; Drain, J.R.; Beckner, M.E.; Greeves, J.; Groeller, H.; Teien, H.K.; Marcora, S.; Moffitt, A.; Reilly, T.; et al. Perspectives on resilience for military readiness and preparedness: Report of an international military physiology roundtable. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2018, 21, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rastgoo, M.N.; Nakisa, B.; Rakotonirainy, A.; Chandran, V.; Tjondronegoro, D. A critical review of proactive detection of driver stress levels based on multimodal measurements. ACM Comput. Surv. 2018, 51, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bridger, R.S.; Brasher, K. Cognitive task demands, self-control demands and the mental well-being of office workers. Ergonomics 2011, 54, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhardt, S.; Leicht, L.; Teichmann, D. Unobtrusive Vital Sign Monitoring in Automotive Environments—A Review. Sensors 2018, 18, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wusk, G.; Gabler, H. Non-Invasive Detection of Respiration and Heart Rate with a Vehicle Seat Sensor. Sensors 2018, 18, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massaroni, C.; Lopes, D.S.; Lo Presti, D.; Schena, E.; Silvestri, S. Contactless Monitoring of Breathing Patterns and Respiratory Rate at the Pit of the Neck: A Single Camera Approach. J. Sens. 2018, 2018, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaroni, C.; Lo Presti, D.; Formica, D.; Silvestri, S.; Schena, E. Non-Contact Monitoring of Breathing Pattern and Respiratory Rate via RGB Signal Measurement. Sensors 2019, 19, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruser, C.; Antink, C.H.; Wartzek, T.; Walter, M.; Leonhardt, S. Ambient and Unobtrusive Cardiorespiratory Monitoring Techniques. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 8, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaroni, C.; Schena, E.; Silvestri, S.; Maji, S. Comparison of two methods for estimating respiratory waveforms from videos without contact. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Istanbul, Turkey, 26–28 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, A.N.; Walsh, M.L.; White, M.D. Influence of passive hyperthermia on human ventilation during rest and isocapnic hypoxia. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2007, 32, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Honda, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Kondo, N.; Nishiyasu, T. Relationship between ventilatory response and body temperature during prolonged submaximal exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, L.L.; Rosenberg, H.R. Preventing Heat-Related Illness Among Agricultural Workers. J. Agromed. 2010, 15, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, R.A.I.; Epstein, Y.; Kjellstrom, T. Excessive occupational heat exposure: A significant ergonomic challenge and health risk for current and future workers. Extrem. Physiol. Med. 2014, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parsons, K. Heat stress standard ISO 7243 and its global application. Ind. Health 2006, 44, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, A.W.; Gonzalez, J.A.; Xu, X. Ebola Response: Modeling the Risk of Heat Stress from Personal Protective Clothing. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tipton, M.J.; Stubbs, D.A.; Elliott, D.H. Human initial responses to immersion in cold water at three temperatures and after hyperventilation. J. Appl. Physiol. 1991, 70, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Wakabayashi, H.; Sengoku, Y.; Tsubakimoto, S.; Nishiyasu, T. Maximal workload but not peak oxygen uptake is decreased during immersed incremental exercise at cooler temperatures. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 116, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.L.; Hayward, J.S. Wet-cold exposure and hypothermia: Thermal and metabolic responses to prolonged exercise in rain. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 81, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, C.J.; Howard, K.A.; Neifer, S.K. How much did cold shock and swimming failure contribute to drowning deaths in the fishing industry in British Columbia 1976–2002? Occup. Med. 2005, 55, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koglin, L.; Kayser, B. Control and sensation of breathing during cycling exercise in hypoxia under naloxone: A randomised controlled crossover trial. Extrem. Physiol. Med. 2013, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aqueveque, P.; Gutierrez, C.; Saavedra, F.; Pino, E.J.; Morales, A.S.; Wiechmann, E. Monitoring physiological variables of mining workers at high altitude. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 2628–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angerer, P.; Nowak, D. Working in permanent hypoxia for fire protection—Impact on health. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2003, 76, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, J.; Beauchamp, G.; Suyama, J.; Guyette, F.X.; Reis, S.E.; Callaway, C.W.; Hostler, D. Cognitive function following treadmill exercise in thermal protective clothing. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Xiao, P.; Shi, J.; Liang, Y.; Lu, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Théato, P.; Kuo, S.-W.; Chen, T. High Performance Humidity Fluctuation Sensor for Wearable Devices via a Bioinspired Atomic-Precise Tunable Graphene-Polymer Heterogeneous Sensing Junction. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 4343–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Roberge, R.; Powell, J.; Shafer, A.; Jon Williams, W. Measurement Accuracy of Heart Rate and Respiratory Rate during Graded Exercise and Sustained Exercise in the Heat Using the Zephyr BioHarnessTM. Int. J. Sports Med. 2012, 34, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, S.H.; Wang, G.H.; Ye, F.; Li, P.Z. Validity and Reliability of Multiparameter Physiological Measurements Recorded by the Equivital Lifemonitor During Activities of Various Intensities. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2013, 10, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, J.D.; Fisher, J.R.K.O.; Guenette, J.A.; Cheong, K.A.; Wilson, B.J.; Sheel, A.W. Measurement of exercise ventilation by a portable respiratory inductive plethysmograph. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2006, 154, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, C.A.; Hamlin, M.J.; Lizamore, C.A. Validity and Reliability of the Hexoskin Wearable Biometric Vest During Maximal Aerobic Power Testing in Elite Cyclists. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torreblanca González, J.; García Ovejero, R.; Lozano Murciego, Á.; Villarrubia González, G.; De Paz, J.F. Effects of Environmental Conditions and Composition on the Electrical Properties of Textile Fabrics. Sensors 2019, 19, 5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lo Presti, D.; Massaroni, C.; Jorge Leitao, C.S.; De Fatima Domingues, M.; Sypabekova, M.; Barrera, D.; Floris, I.; Massari, L.; Oddo, C.M.; Sales, S.; et al. Fiber Bragg Gratings for Medical Applications and Future Challenges: A Review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 156863–156888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesisoglou, A.; Nicolò, A.; Passfield, L. Cycling Performance and Training Load: Effects of Intensity and Duration. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolò, A.; Bazzucchi, I.; Lenti, M.; Haxhi, J.; di Palumbo, A.S.; Sacchetti, M. Neuromuscular and Metabolic Responses to High-Intensity Intermittent Cycling Protocols With Different Work-to-Rest Ratios. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcora, S. Perception of effort during exercise is independent of afferent feedback from skeletal muscles, heart, and lungs. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 2060–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zenon, A.; Sidibe, M.; Olivier, E. Disrupting the Supplementary Motor Area Makes Physical Effort Appear Less Effortful. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 8737–8744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loe, H.; Steinshamn, S.; Wisløff, U. Cardio-Respiratory Reference Data in 4631 Healthy Men and Women 20-90 Years: The HUNT 3 Fitness Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolò, A.; Bazzucchi, I.; Felici, F.; Patrizio, F.; Sacchetti, M. Mechanical and electromyographic responses during the 3-min all-out test in competitive cyclists. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2015, 25, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiano, L.; Di Tocco, J.; Massaroni, C.; Di Pino, G.; Schena, E.; Formica, D. Clean-Breathing: A Novel Sensor Fusion Algorithm Based on ICA to Remove Motion Artifacts from Breathing Signal. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 & IoT, Roma, Italy, 3–5 June 2020; pp. 734–739. [Google Scholar]
- Di Tocco, J.; Massaroni, C.; Raiano, L.; Formica, D.; Schena, E. A wearable system for respiratory and pace monitoring in running activities: A feasibility study. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 & IoT, Roma, Italy, 3–5 June 2020; pp. 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Massaroni, C.; Nicolò, A.; Girardi, M.; La Camera, A.; Schena, E.; Sacchetti, M.; Silvestri, S.; Taffoni, F. Validation of a Wearable Device and an Algorithm for Respiratory Monitoring During Exercise. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 4652–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, T.; Choi, J.; Reeder, J.; Lee, S.P.; Aranyosi, A.J.; Ghaffari, R.; Rogers, J.A. Soft, skin-interfaced wearable systems for sports science and analytics. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 9, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servati, A.; Zou, L.; Wang, Z.; Ko, F.; Servati, P. Novel Flexible Wearable Sensor Materials and Signal Processing for Vital Sign and Human Activity Monitoring. Sensors 2017, 17, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Halhouli, A.; Al-Ghussain, L.; El Bouri, S.; Liu, H.; Zheng, D. Fabrication and Evaluation of a Novel Non-Invasive Stretchable and Wearable Respiratory Rate Sensor Based on Silver Nanoparticles Using Inkjet Printing Technology. Polymers 2019, 11, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Chen, Y.-C.; Nicolini, L.; Pasupathy, P.; Sacks, J.; Su, B.; Yang, R.; Sanchez, D.; Chang, Y.-F.; Wang, P.; et al. “Cut-and-Paste” Manufacture of Multiparametric Epidermal Sensor Systems. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6423–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Li, X.; Zang, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, K.; Wu, D.; Zhu, H. Wearable and Highly Sensitive Graphene Strain Sensors for Human Motion Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4666–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; He, Q.; Meng, K.; Tan, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Machine-knitted washable sensor array textile for precise epidermal physiological signal monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nehmeh, S.A.; Erdi, Y.E. Respiratory Motion in Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography: A Review. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2008, 38, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzadi, I.; Siddiqui, M.F.; Aslam, I.; Omer, H. Respiratory motion compensation using data binning in dynamic contrast enhanced golden-angle radial MRI. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 70, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavedon, C. Real-time control of respiratory motion: Beyond radiation therapy. Phys. Med. 2019, 66, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, J.R.; Hawkes, D.J.; Schaeffter, T.; King, A.P. Respiratory motion models: A review. Med. Image Anal. 2013, 17, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boda-Heggemann, J.; Knopf, A.-C.; Simeonova-Chergou, A.; Wertz, H.; Stieler, F.; Jahnke, A.; Jahnke, L.; Fleckenstein, J.; Vogel, L.; Arns, A.; et al. Deep Inspiration Breath Hold—Based Radiation Therapy: A Clinical Review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 94, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, R.; Chung, T.D.; Vedam, S.S.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Mohan, R.; Weiss, E.; Keall, P.J. Audio-visual biofeedback for respiratory-gated radiotherapy: Impact of audio instruction and audio-visual biofeedback on respiratory-gated radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2006, 65, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temko, A.; Thomas, E.; Marnane, W.; Lightbody, G.; Boylan, G. EEG-based neonatal seizure detection with Support Vector Machines. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Littmann, L. The diagnostic use of respiratory artifact. J. Electrocardiol. 2010, 43, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brümmer, V.; Schneider, S.; Strüder, H.K.; Askew, C.D. Primary motor cortex activity is elevated with incremental exercise intensity. Neuroscience 2011, 181, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaza, E.; Symonds-Tayler, R.; Collins, D.J.; McDonald, F.; McNair, H.A.; Scurr, E.; Koh, D.-M.; Leach, M.O. First MRI application of an active breathing coordinator. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 1681–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glide-Hurst, C.K.; Chetty, I.J. Improving radiotherapy planning, delivery accuracy, and normal tissue sparing using cutting edge technologies. J. Thorac. Dis. 2014, 6, 303–318. [Google Scholar]
- Heinz, C.; Reiner, M.; Belka, C.; Walter, F.; Söhn, M. Technical evaluation of different respiratory monitoring systems used for 4D CT acquisition under free breathing. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2015, 16, 334–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, S.; Tang, J.; Rodgers, J.; Cleary, K. Skin respiratory motion tracking for stereotactic radiosurgery using the CyberKnife. Int. Congr. Ser. 2003, 1256, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, A.M.; Emery, R.; Rodriguez, L.; Richards, G.M.; Ng, T.; Sanghavi, S.; Barsa, J. Clinical experience using respiratory gated radiation therapy: Comparison of free-breathing and breath-hold techniques. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2004, 60, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, L.-L.; Chuang, H.-C.; Liao, A.-H.; Kuo, C.-C.; Yu, H.-W.; Tsai, H.-C.; Tien, D.-C.; Jeng, S.-C.; Chiou, J.-F. Tumor motion tracking based on a four-dimensional computed tomography respiratory motion model driven by an ultrasound tracking technique. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2020, 10, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, L.-L.; Chuang, H.-C.; Liao, A.-H.; Kuo, C.-C.; Yu, H.-W.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Tien, D.-C.; Jeng, S.-C.; Chiou, J.-F. Experimental verification of a two-dimensional respiratory motion compensation system with ultrasound tracking technique in radiation therapy. Phys. Medica 2018, 49, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaerer, J.; Fassi, A.; Riboldi, M.; Cerveri, P.; Baroni, G.; Sarrut, D. Multi-dimensional respiratory motion tracking from markerless optical surface imaging based on deformable mesh registration. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverstein, E.; Snyder, M. Comparative analysis of respiratory motion tracking using Microsoft Kinect v2 sensor. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2018, 19, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schein, M.; Gavish, B.; Herz, M.; Rosner-Kahana, D.; Naveh, P.; Knishkowy, B.; Zlotnikov, E.; Ben-Zvi, N.; Melmed, R. Treating hypertension with a device that slows and regularises breathing: A randomised, double-blind controlled study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2001, 15, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kapitza, K.P.; Passie, T.; Bernateck, M.; Karst, M. First Non-Contingent Respiratory Biofeedback Placebo versus Contingent Biofeedback in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain: A Randomized, Controlled, Double-Blind Trial. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2010, 35, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purwandini Sutarto, A.; Abdul Wahab, M.N.; Mat Zin, N. Resonant Breathing Biofeedback Training for Stress Reduction Among Manufacturing Operators. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2012, 18, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morarend, Q.A.; Spector, M.L.; Dawson, D.V.; Clark, S.H.; Holmes, D.C. The Use of a Respiratory Rate Biofeedback Device to Reduce Dental Anxiety: An Exploratory Investigation. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2011, 36, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.P.; Gerbarg, P.L.; Muench, F. Breathing Practices for Treatment of Psychiatric and Stress-Related Medical Conditions. Psychiatr. Clin. 2013, 36, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giggins, O.M.; Persson, U.; Caulfield, B. Biofeedback in rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2013, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Yue, Z.-Q.; Gong, Z.-Q.; Zhang, H.; Duan, N.-Y.; Shi, Y.-T.; Wei, G.-X.; Li, Y.-F. The Effect of Diaphragmatic Breathing on Attention, Negative Affect and Stress in Healthy Adults. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laborde, S.; Allen, M.S.; Göhring, N.; Dosseville, F. The effect of slow-paced breathing on stress management in adolescents with intellectual disability. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2017, 61, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, R.; Kaushik, R.M.; Mahajan, S.K.; Rajesh, V. Biofeedback assisted diaphragmatic breathing and systematic relaxation versus propranolol in long term prophylaxis of migraine. Complement. Ther. Med. 2005, 13, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachowska, K.; Bellwon, J.; Moryś, J.; Gruchała, M.; Hering, D. Slow breathing improves cardiovascular reactivity to mental stress and health-related quality of life in heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction. Cardiol. J. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parati, G.; Malfatto, G.; Boarin, S.; Branzi, G.; Caldara, G.; Giglio, A.; Bilo, G.; Ongaro, G.; Alter, A.; Gavish, B.; et al. Device-Guided Paced Breathing in the Home Setting. Circ. Heart Fail. 2008, 1, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Diest, I.; Verstappen, K.; Aubert, A.E.; Widjaja, D.; Vansteenwegen, D.; Vlemincx, E. Inhalation/Exhalation Ratio Modulates the Effect of Slow Breathing on Heart Rate Variability and Relaxation. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2014, 39, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Funk, M.; Hu, J.; Wang, Q.; Feijs, L. Biofeedback for Everyday Stress Management: A Systematic Review. Front. ICT 2018, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagaduan, J.; Wu, S.S.; Kameneva, T.; Lambert, E. Acute effects of resonance frequency breathing on cardiovascular regulation. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e14295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Vigon Uriarte, I.d.L.; Garcia-Zapirain, B.; Garcia-Chimeno, Y. Game design to measure reflexes and attention based on biofeedback multi-sensor interaction. Sensors 2015, 15, 6520–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Osman, H.; Dong, H.; El Saddik, A. Ubiquitous Biofeedback Serious Game for Stress Management. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 1274–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerink, W.J.; Dorrius, M.D.; Groen, H.J.M.; Van Ooijen, P.M.A.; Vliegenthart, R.; Oudkerk, M. Respiratory level tracking with visual biofeedback for consistent breath-hold level with potential application in image-guided interventions. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2018, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Jung, Y.-J.; Choi, S.; Kim, D. Design and Evaluation of a MEMS Magnetic Field Sensor-Based Respiratory Monitoring and Training System for Radiotherapy. Sensors 2018, 18, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schein, M.H.; Gavish, B.; Baevsky, T.; Kaufman, M.; Levine, S.; Nessing, A.; Alter, A. Treating hypertension in type II diabetic patients with device-guided breathing: A randomized controlled trial. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2009, 23, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, M.; Frishman, W.H.; Gandhi, K. RESPeRATE. Cardiol. Rev. 2011, 19, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernes, R.; Zimlichman, R. RESPeRATE: The role of paced breathing in hypertension treatment. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2015, 9, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuret, A.E.; Wilhelm, F.H.; Ritz, T.; Roth, W.T. Feedback of end-tidal pCO2 as a therapeutic approach for panic disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2008, 42, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tolin, D.F.; McGrath, P.B.; Hale, L.R.; Weiner, D.N.; Gueorguieva, R. A Multisite Benchmarking Trial of Capnometry Guided Respiratory Intervention for Panic Disorder in Naturalistic Treatment Settings. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2017, 42, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, H.; Pirbhulal, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Zhang, Y.-T. Assessment of Biofeedback Training for Emotion Management Through Wearable Textile Physiological Monitoring System. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 7087–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Pirbhulal, S.; Zhang, H.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Quantitative Assessment for Self-Tracking of Acute Stress Based on Triangulation Principle in a Wearable Sensor System. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Informatics 2019, 23, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Shi, B.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, Z. Wearable and Implantable Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giavarina, D. Understanding Bland Altman analysis. Biochem. Med. 2015, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo Presti, D.; Romano, C.; Massaroni, C.; D’Abbraccio, J.; Massari, L.; Caponero, M.A.; Oddo, C.M.; Formica, D.; Schena, E. Cardio-Respiratory Monitoring in Archery Using a Smart Textile Based on Flexible Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, R.A.; Pathan, A.-S.K. The state-of-the-art wireless body area sensor networks: A survey. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albahri, O.S.; Zaidan, A.A.; Zaidan, B.B.; Hashim, M.; Albahri, A.S.; Alsalem, M.A. Real-Time Remote Health-Monitoring Systems in a Medical Centre: A Review of the Provision of Healthcare Services-Based Body Sensor Information, Open Challenges and Methodological Aspects. J. Med. Syst. 2018, 42, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasic, I.; Tomasic, N.; Trobec, R.; Krpan, M.; Kelava, T. Continuous remote monitoring of COPD patients—Justification and explanation of the requirements and a survey of the available technologies. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2018, 56, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talaminos-Barroso, A.; Estudillo-Valderrama, M.A.; Roa, L.M.; Reina-Tosina, J.; Ortega-Ruiz, F. A Machine-to-Machine protocol benchmark for eHealth applications—Use case: Respiratory rehabilitation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 129, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naggar, N.Q.; Al-Hammadi, H.M.; Al-Fusail, A.M.; AL-Shaebi, Z.A. Design of a Remote Real-Time Monitoring System for Multiple Physiological Parameters Based on Smartphone. J. Healthc. Eng. 2019, 2019, 5674673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faezipour, M.; Faezipour, M. Sustainable Smartphone-Based Healthcare Systems: A Systems Engineering Approach to Assess the Efficacy of Respiratory Monitoring Apps. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, N.; Hobbelink, E.L.; van Tienhoven, A.J.; van de Ven, P.M.; Jansma, E.P.; Nanayakkara, P.W.B. The impact of the use of the Early Warning Score (EWS) on patient outcomes: A systematic review. Resuscitation 2014, 85, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.E.B.; Chiovaro, J.C.; O’Neil, M.; Kansagara, D.; Quiñones, A.R.; Freeman, M.; Motu’apuaka, M.L.; Slatore, C.G. Early Warning System Scores for Clinical Deterioration in Hospitalized Patients: A Systematic Review. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, 1454–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmitri, M.; Fourati, H.; Vuillerme, N. Human activities and postures recognition: From inertial measurements to quaternion-based approaches. Sensors 2019, 19, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douglas, N.J.; White, D.P.; Pickett, C.K.; Weil, J.V.; Zwillich, C.W. Respiration during sleep in normal man. Thorax 1982, 37, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutierrez, G.; Williams, J.; Alrehaili, G.A.; McLean, A.; Pirouz, R.; Amdur, R.; Jain, V.; Ahari, J.; Bawa, A.; Kimbro, S. Respiratory rate variability in sleeping adults without obstructive sleep apnea. Physiol. Rep. 2016, 4, e12949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, G. Borg’s Perceived Exertion and Pain Scales; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Von Leupoldt, A.; Sommer, T.; Kegat, S.; Baumann, H.J.; Klose, H.; Dahme, B.; Büchel, C. Dyspnea and pain share emotion-related brain network. NeuroImage 2009, 48, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.-Y.; Joshi, H.; Tandon, P.; Freeman, R.; Reich, D.L.; Mazumdar, M.; Kohli-Seth, R.; Levin, M.A.; Timsina, P.; Kia, A. Using Machine Learning to Predict ICU Transfer in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chester, J.G.; Rudolph, J.L. Vital Signs in Older Patients: Age-Related Changes. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2011, 12, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Monitoring Goal | Contact-Based Methods | Contactless Methods | Information Detail | Type of Recording | Main Measurement/Computing Challenge | Need for VT * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Presence of breathing | XXX | XX | b-by-b | P/C | respiratory signal quality | - |
| 2. Adverse cardiac events | XXX | X | 60 s | C | wearable and unobtrusive systems | - |
| 3. Apnea | XXX | X | raw data | C | hypopnea detection | ●●● |
| 4. Pneumonia | XXX | XX | 60 s | P/C | solutions for low-income countries | - |
| 5. Clinical deterioration | XXX | XX | 60 s | P/C | acceptance of technologies | - |
| 6. Dyspnea | XXX | X | b-by-b | C | motion artifacts | ●● |
| 7. Pain | XXX | X | b-by-b/60s | C | detection of respiratory depression | ●● |
| 8. Emotional stress | XXX | XX | b-by-b | P/C | processing of video images | ● |
| 9. Cognitive load | XXX | XX | b-by-b/60 s | C | accurate and unobtrusive systems | - |
| 10. Environment-induced stress | XXX | X | 60 s | C | change of sensor properties | ● |
| 11. Physical effort | XXX | X | b-by-b/5 s | C | motion artifacts | - |
| 12. Respiratory artifacts | XX | XXX | raw data | P | respiratory features in real-time | ●●● |
| 13. Respiratory biofeedback | XXX | XX | raw data | P | respiratory features in real-time | ●● |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicolò, A.; Massaroni, C.; Schena, E.; Sacchetti, M. The Importance of Respiratory Rate Monitoring: From Healthcare to Sport and Exercise. Sensors 2020, 20, 6396. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216396
Nicolò A, Massaroni C, Schena E, Sacchetti M. The Importance of Respiratory Rate Monitoring: From Healthcare to Sport and Exercise. Sensors. 2020; 20(21):6396. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216396
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicolò, Andrea, Carlo Massaroni, Emiliano Schena, and Massimo Sacchetti. 2020. "The Importance of Respiratory Rate Monitoring: From Healthcare to Sport and Exercise" Sensors 20, no. 21: 6396. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216396
APA StyleNicolò, A., Massaroni, C., Schena, E., & Sacchetti, M. (2020). The Importance of Respiratory Rate Monitoring: From Healthcare to Sport and Exercise. Sensors, 20(21), 6396. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216396