COVID-19 Detection from Chest X-ray Images Using Feature Fusion and Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Literature
3. Proposed Methodology
3.1. System Architecture
3.2. Dataset Used
| Algorithm 1 Proposed Algorithm for COVID-19 Detection |
| Input: COVID-19 Chest X-ray image dataset (D) with resize image (M) Extraction: Extract Feature Matrix (f). CNN Feature Vector (Fc). Step 1: Initialize ≥ Step 2: Extract each image feature Step 3: = + Step 4: = overall CNN features. Histogram Oriented Gradient (HOG). Step 1: Initialize. ,. Step 2: HOG = + . Step 3: HOG = overall Histogram Oriented Gradient Fusion of features in Vector (V). . . Extract test feature (T) = repeat step 1, 2 from test_image. . Output: |
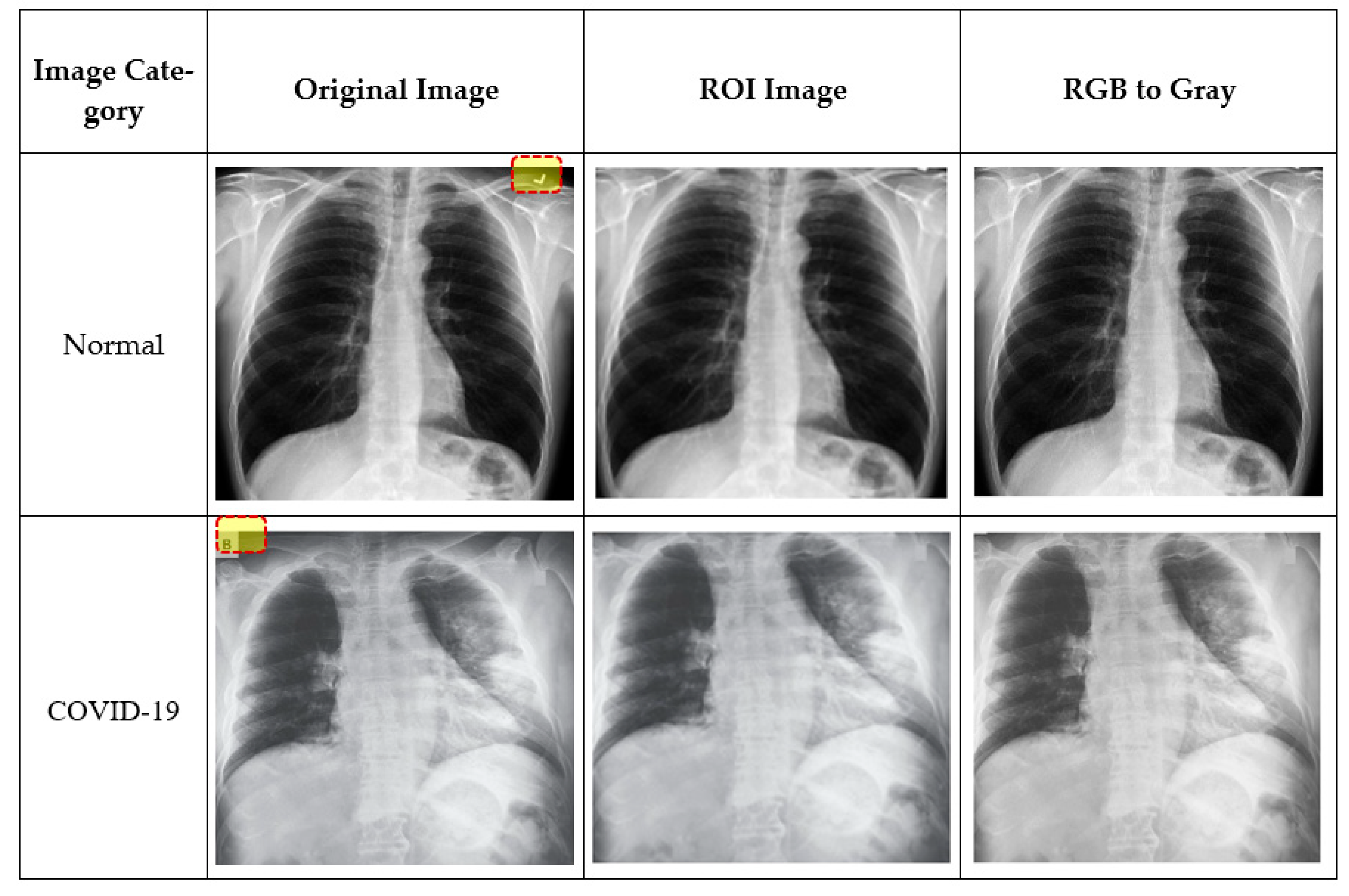
3.3. Data Preprocessing
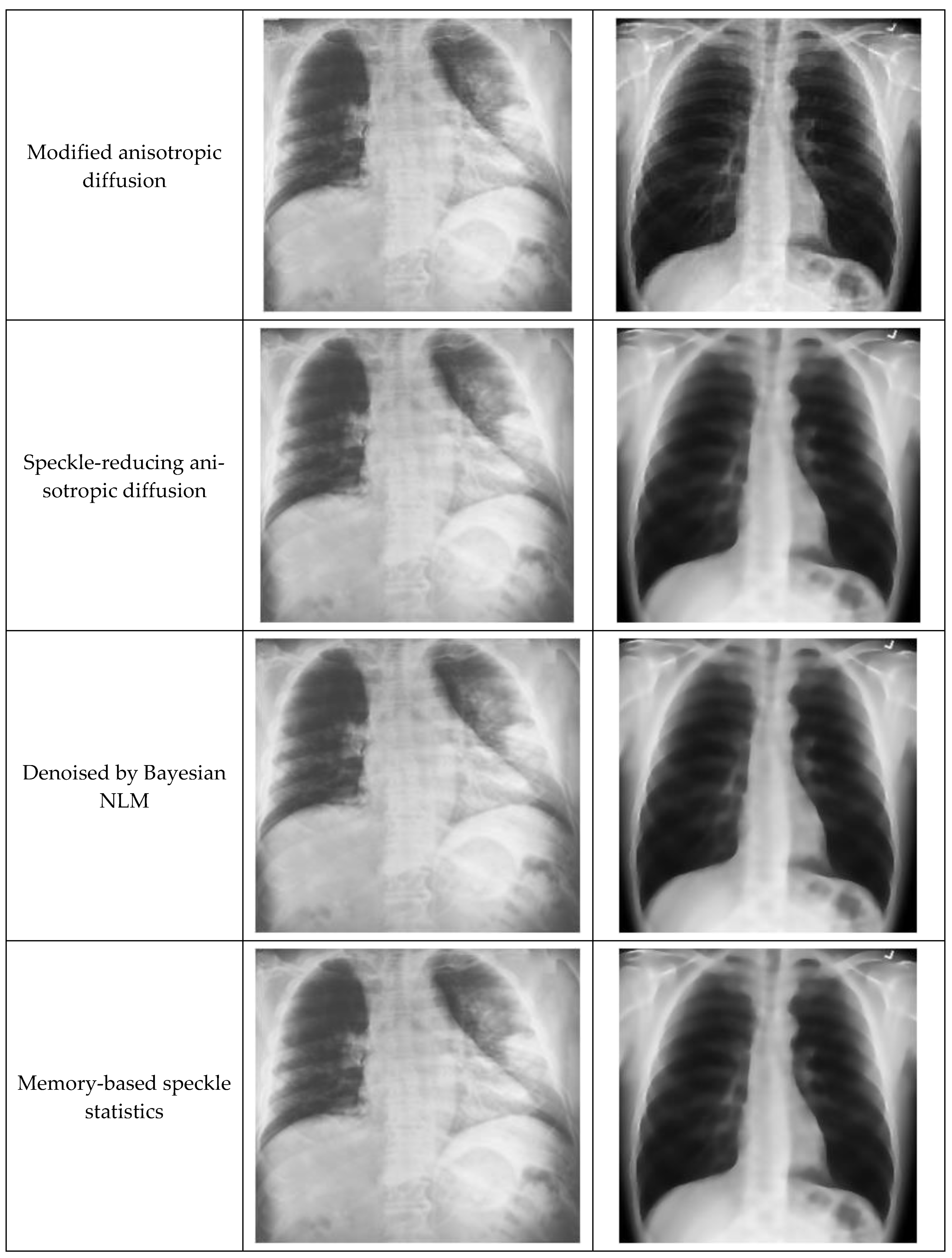
3.4. Modified Anisotropic Diffusion Filtering (MADF)
3.5. Feature Extractor
3.5.1. Histogram-Oriented Gradient (HOG) Feature Extractor
3.5.2. CNN Based Feature Extractor and Classification
3.6. Feature Fusion and Classification
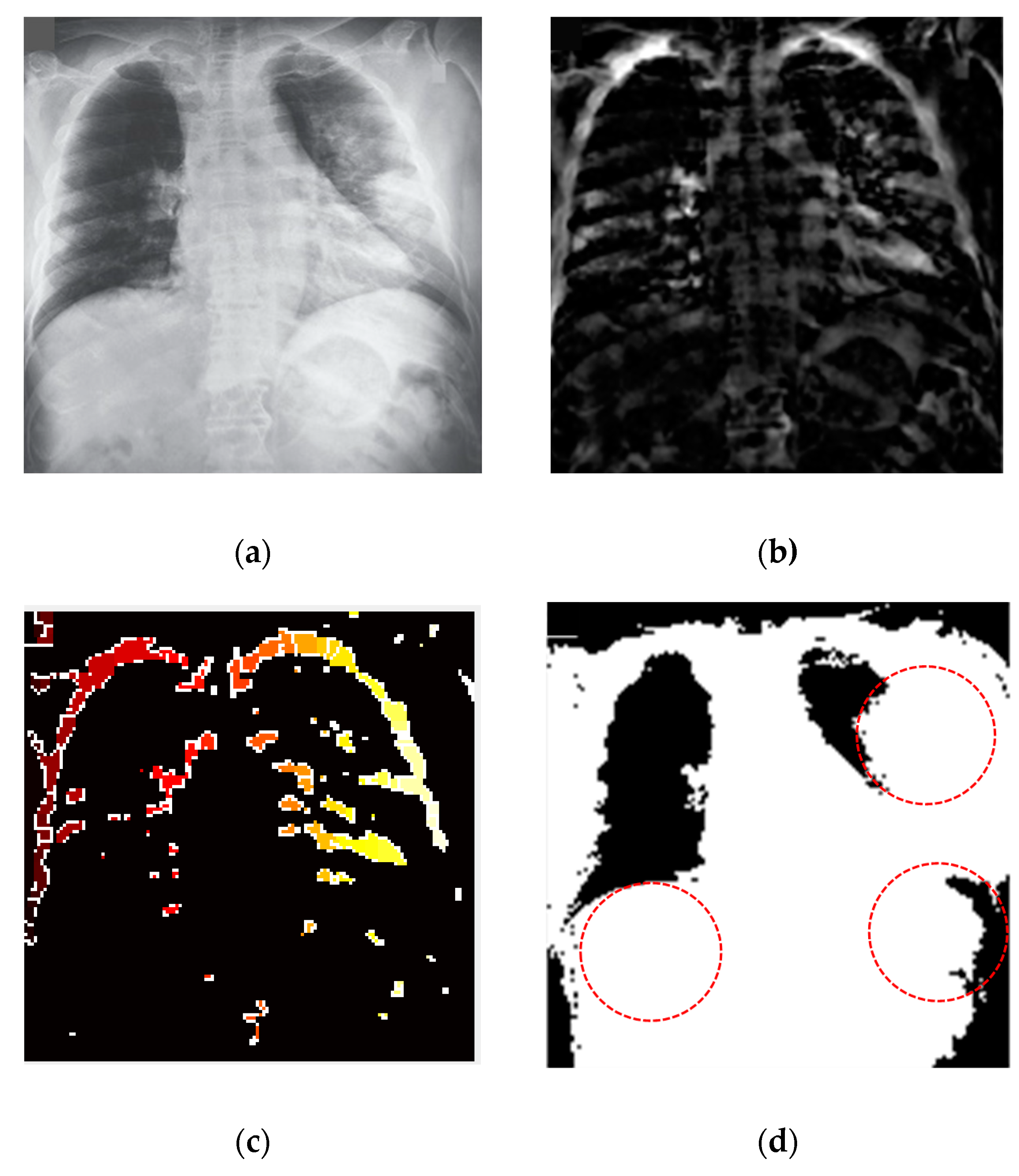
3.7. Segmentation of the COVID-19-Affected Region
4. Experimental Details and Results
4.1. Datasets and Overall Performance
4.2. Filtering Performance
4.3. Feature Extraction Performance
4.4. Classification Performance
5. Discussion
5.1. System Validation
5.2. Comparative Analysis
5.3. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.W.; Tian, J.H.; Pei, Y.Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.; et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. 2020. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Ren, R.; Leung, K.S.; Lau, E.H.; Wong, J.Y.; et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holshue, M.L.; DeBolt, C.; Lindquist, S.; Lofy, K.H.; Wiesman, J.; Bruce, H.; Spitters, C.; Ericson, K.; Wilkerson, S.; Tural, A.; et al. First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/?gclid=CjwKCAjw5p_8BRBUEiwAPpJO682JEO1UwRkSSDosfqaqGeAncQYeiEeTcnMSFJd55I0lzYlHrvi4SxoCAeUQAvD_BwE (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Ledford, H.; Cyranoski, D.; Van, N.R. The UK has approved a COVID vaccine-here’s what scientists now want to know. Nature 2020, 588, 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anon. The COVID vaccine challenges that lie ahead. Nature 2020, 587, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Marks, F.; Clemens, J.D. Looking beyond COVID-19 vaccine phase 3 trials. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logunov, D.Y.; Dolzhikova, I.V.; Shcheblyakov, D.V.; Tukhvatulin, A.I.; Zubkova, O.V.; Dzharullaeva, A.S.; Kovyrshina, A.V.; Lubenets, N.L.; Grousova, D.M.; Erokhova, A.S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of an rAd26 and rAd5 vector-based heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccine: An interim analysis of a randomised controlled phase 3 trial in Russia. Lancet 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, L. Meet the Challenges of Mass Vaccination against COVID-19. Explor. Res. Hypothesis Med. 2021, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, L. Skin lesion analysis towards melanoma detection using deep learning network. Sensors 2018, 18, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Q.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, Z.L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q. Multi-task deep convolutional neural network for cancer diagnosis. Neurocomputing 2019, 348, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Gujrathi, I.; Haider, M.A.; Khalvati, F. Prostate cancer detection using deep convolutional neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 2017, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wong, A. Covid-net: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of covid-19 cases from chest X-ray images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, A. Molecular diagnostic technologies for COVID-19: Limitations and challenges. J. Adv. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization: Use of Chest Imaging in Covid-19. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/use-of-chest-imaging-in-covid-19 (accessed on 7 January 2021).
- Davies, H.E.; Wathen, C.G.; Gleeson, F.V. The risks of radiation exposure related to diagnostic imaging and how to minimise them. BMJ 2011, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, T.; Mulholland, E.K.; Carlin, J.B.; Ostensen, H.; Amin, R.; Campo, M.D.; Greenberg, D.; Lagos, R.; Lucero, M.; Madhi, S.A.; et al. Standardized interpretation of paediatric chest radiographs for the diagnosis of pneumonia in epidemiological studies. Bull. World Health Organ 2005, 83, 353–359. [Google Scholar]
- Franquet, T. Imaging of pneumonia: Trends and algorithms. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 18, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, M.Y.; Lee, E.Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, F.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Lui, M.; Lo, C.; Leung, B.; Khong, P.; et al. Imaging profile of the covid-19 infection: Radiologic findings and literature review. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, S.G.; Prakash, S. Pneumonia classification using deep learning in healthcare. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2020, 9, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaowei, X.; Xiangao, J.; Chunlian, M.; Peng, D.; Xukun, L.; Shuangzhi, L.; Liang, Y.; Qin, N.; Yanfei, C.; Junwei, S.; et al. A deep learning system to screen novel coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia. Engineering 2020, 6, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, F.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Z.; He, K.; Shi, Y.; Shen, D. Review of artificial intelligence techniques in imaging data acquisition, segmentation and diagnosis for covid-19. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Ahammed, K.; Satu, M.S.; Abedin, M.Z.; Rahaman, M.A.; Islam, S.M.S. Early Detection of Coronavirus Cases Using Chest X-ray Images Employing Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches. medRxiv 2020. medRxiv 2020.06.07.20124594. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, N.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Kabir, M.A. PDCOVIDNet: A parallel-dilated convolutional neural network architecture for detecting COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2020, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.; Abdelsamea, M.M.; Gaber, M.M. Classification of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images using DeTraC deep convolutional neural network. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Azemin, M.Z.; Hassan, R.; Mohd Tamrin, M.I.; Md Ali, M.A. COVID-19 Deep Learning Prediction Model Using Publicly Available Radiologist-Adjudicated Chest X-Ray Images as Training Data: Preliminary Findings. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rashidy, N.; El-Sappagh, S.; Islam, S.M.R.; El-Bakry, H.M.; Abdelrazek, S. End-To-End Deep Learning Framework for Coronavirus (COVID-19) Detection and Monitoring. Electronics 2020, 9, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.U.; Aslam, N. A Deep-Learning-Based Framework for Automated Diagnosis of COVID-19 Using X-ray Images. Information 2020, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loey, M.; Smarandache, F.M. Khalifa, N.E. Within the Lack of Chest COVID-19 X-ray Dataset: A Novel Detection Model Based on GAN and Deep Transfer Learning. Symmetry 2020, 12, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minaee, S.; Kafieh, R.; Sonka, M.; Yazdani, S.; Soufi, G. Deep-COVID: Predicting COVID-19 from chest X-ray images using deep transfer learning. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 65, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekeroglu, B.; Ozsahin, I. Detection of COVID-19 from Chest X-Ray Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks. SLAS Technol. Transl. Life Sci. Innov. 2020, 25, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Liu, H.; Xu, C. Deep Learning for The Detection of COVID-19 Using Transfer Learning and Model Integration. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 10th International Conference on Electronics Information and Emergency Communication (ICEIEC), Beijing, China, 17–19 July 2020; pp. 281–284. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, S.H.; Geng, H.; Chiu, T.L.; Yu, S.K.; Cho, D.C.; Heo, J.; Choi, M.S.; Choi, I.H.; Van, C.C.; Nhung, N.V. Deep Learning-Based Decision-Tree Classifier for COVID-19 Diagnosis From Chest X-ray Imaging. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, N.E.M.; Taha, M.H.N.; Manogaran, G.; Loey, M. A deep learning model and machine learning methods for the classification of potential coronavirus treatments on a single human cell. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2020, 22, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Mo, J.; Zhou, G.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y. An efficient mixture of deep and machine learning models for COVID-19 diagnosis in chest X-ray images. PloS ONE 2020, 15, e0242535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlol, A.T.; Yousri, D.; Ewees, A.A.; Al-Qaness, M.A.; Damasevicius, R.; Abd Elaziz, M. COVID-19 image classification using deep features and fractional-order marine predators algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.E.; Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Mazhar, R.; Kadir, M.A.; Mahbub, Z.B.; Islam, K.R.; Khan, M.S.; Iqbal, A.; Al-Emadi, N.; et al. Can ai help in screening viral and covid-19 pneumonia? arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.13145. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.P.; Morrison, P.; Dao, L. COVID-19 Image Data Collection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11597v1. [Google Scholar]
- COVID-19 X-ray Image Data Sets. Available online: https://drive.google.com/uc?id=1coM7x3378f-Ou2l6Pg2wldaOI7Dntu1a (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Cleverley, J.; Piper, J.; Jones, M.M. The role of chest radiography in confirming covid-19 pneumonia. BMJ 2020, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Kang, B.; Feng, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W. Anisotropic Diffusion Based Multiplicative Speckle Noise Removal. Sensors 2019, 19, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaoxin, Z.; Da-Wen, S. 2-Image Segmentation Techniques. In Food Science and Technology, Computer Vision Technology for Food Quality Evaluation; Da-Wen, S., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 37–56. [Google Scholar]
- Dandıl, E.; Çakiroğlu, M.; Ekşi, Z.; Özkan, M.; Kurt, Ö.K.; Canan, A. Artificial neural network-based classification system for lung nodules on computed tomography scans. In Proceedings of the 2014 6th International Conference of Soft Computing and Pattern Recognition (soCPar), Tunis, Tunisia, 11–14 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Llordén, G.; Vegas-Sánchez-Ferrero, G.; Martin-Fernández, M.; Alberola-López, C.; Aja-Fernández, S. Anisotropic diffusion filter with memory based on speckle statistics for ultrasound images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, Z.; Tan, H.; Ye, W. The excellent properties of a dense grid-based HOG feature on face recognition compared to Gabor and LBP. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 29306–29319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbhuiya, A.A.; Karsh, R.K.; Jain, R. CNN based feature extraction and classification for sign language. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafiz, R.; Rahman, M.M.; Uddin, M.S. Gastrointestinal polyp classification through empirical mode decomposition and neural features. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, T.; Mohamed, A.S.; El-Affendi, M.; Amin, J.; Sharif, M. Brain tumor detection using fusion of hand crafted and deep learning features. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2020, 59, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; Pagani, L.; Zeng, W.; Jiang, X.; Scott, P.J. Watershed segmentation of topographical features on freeform surfaces and its application to additively manufactured surfaces. Precis. Eng. 2020, 63, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ludwig, S.A. Color image segmentation using fuzzy C-regression model. Adv. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Academic Torrents. Available online: https://academictorrents.com/ (accessed on 10 August 2020).
- Hasan, M.M.; Islam, N.; Rahman, M.M. Gastrointestinal polyp detection through a fusion of contourlet transform and Neural features. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasar, H.; Ceylan, M. A new deep learning pipeline to detect Covid-19 on chest X-ray images using local binary pattern, dual tree complex wavelet transform and convolutional neural networks. Appl. Intell. 2020, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, H.; Gupta, P.K.; Siddiqui, M.K.; Morales-Menendez, R.; Singh, V. Application of deep learning for fast detection of COVID-19 in X-rays using nCOVnet. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 138, 109944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, T.; Talo, M.; Yildirim, E.A.; Baloglu, U.B.; Yildirim, O.; Acharya, U.R. Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.I.; Shah, J.L.; Bhat, M.M. Coronet: A deep neural network for detection and diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest x-ray images. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 2020, 196, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, I.D.; Mpesiana, T.A. Covid-19: Automatic detection from x-ray images utilizing transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmud, T.; Rahman, M.A.; Fattah, S.A. CovXNet: A multidilation convolutional neural network for automatic COVID-19 and other pneumonia detection from chest X-ray images with transferable multi-receptive feature optimization. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 122, 103869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbrahim, H.; Hachimi, H.; Amine, A. Deep transfer learning with apache spark to detect COVID-19 in chest X-ray images. Romanian J. Inform. Sci. Technol. 2020, 23, S117–S129. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, F.; Martínez, F.; Jacinto, E. Performance evaluation of the NASNet convolutional network in the automatic identification of COVID-19. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inform. Technol. 2020, 10, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraman, S.; Alakus, T.B.; Turkoglu, I. Convolutional capsnet: A novel artificial neural network approach to detect COVID-19 disease from X-ray images using capsule networks. Chaos Solitons Fract. 2020, 140, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Lopez, L.; Dominguez-Morales, J.P.; Corral-Jaime, J.; Vicente- Diaz, S.; Linares-Barranco, A. COVID-XNet: A custom deep learning system to diagnose and locate COVID-19 in chest X-ray images. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.P.; Hashir, M.; Brooks, R.; Bertrand, H. On the limits of cross-domain generalization in automated X-ray prediction. In Medical Imaging with Deep Learning; Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.02497 (accessed on 7 January 2021).
- Tartaglione, E.; Barbano, C.A.; Berzovini, C.; Calandri, M.; Grangetto, M. Unveiling covid-19 from chest x-ray with deep learning: A hurdles race with small data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguolo, G.; Nanni, L. A critic evaluation of methods for covid-19 automatic detection from x-ray images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.12823. [Google Scholar]















| Data Sets | Number of Images | Ratio of Normal to the COVID-19 Images | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | COVID-19 | ||
| Training | 2489 | 1584 | 1.57 |
| Validation | 70 | 70 | 1.0 |
| Testing | 622 | 395 | 1.57 |
| Feature Extraction Methods | Fold 1 | Fold 2 | Fold 3 | Fold 4 | Fold 5 | Mean Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOG | 0.8732 | 0.8789 | 0.8741 | 0.8675 | 0.8730 | 0.8734 |
| CNN | 0.9378 | 0.9367 | 0.9387 | 0.9367 | 0.9321 | 0.9364 |
| Proposed fusion (HOG+CNN) | 0.9856 | 0.9847 | 0.9813 | 0.9827 | 0.9833 | 0.9836 |
| References | Dataset | Methods | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ahammed et al. [29] | 2971 chest X-ray images (COVID-19 = 285, normal = 1341, pneumonia = 1345) | CNN | 94.03% |
| Chowdhury et al. [30] | 2905 chest X-ray images (COVID-19 = 219, normal = 1341 and pneumonia = 1345) | Parallel-dilated CNN | 96.58% |
| Abbas et al. [31] | 196 CXR images (COVID-19 = 105, normal = 80, and SARScases = 11) | Deep CNN (DeTraC) | 93.1% |
| Azemin et al. [32] | 5982 (COVID-19 = 154 and normal = 5828) | ResNet-101 CNN | 71.9% |
| El-Rashidy et al. [33] | 750 chest X-ray images(COVID-19 = 250 and normal = 500) | CNN/ConvNet | 97.95% |
| Khan et al. [34] | 1057 X-ray images (COVID-19 = 195 and normal = 862) | VGG16+VGG19 | 99.3% |
| Loey et al. [35] | 307 X-ray images (COVID-19 = 69, normal = 79, Pneumonia_bac = 79 and Pneumonia_vir = 79) | AlexNet+ Googlenet+Restnet18 | 100% |
| Minaee et al. [36] | 50,184 chest X-ray images (COVID-19 = 184 and normal = 5000) | ResNet18 + ResNet50 + SqueezeNet + DenseNet-121 | 98% |
| Sekeroglu et al. [37] | 6100 X-ray images (COVID-19 = 225, normal = 1583 and pneumonia = 4292) | CNN | 98.50% |
| Wang et al. [38] | 18,567 X-ray images (COVID-19 = 140, normal = 8851 and Pneumonia = 9576) | ResNet-101 + ResNet-152 | 96.1% |
| Panwar et al. [60] | 284 images (COVID-19 = 142 and normal = 142) | Convolutional neural network (nCOVnet) | 88.1% |
| Ozturk et al. [61] | 625 images (COVID-19 = 125 and normal = 500) | Convolutional neural network (DarkNet) | 98.08% |
| Khan et al. [62] | 594 images (COVID-19 = 284 and normal = 310) | Convolutional neural network (CoroNet (Xception)) | 99% |
| Apostolopoulos and Mpesiana [63] | 728 images (COVID-19 = 224 and normal = 504) | Transfer learning with convolutional neural networks(VGG19, MobileNet v2, Inception, Xception, InceptionResNet v2) | 96.78% |
| Mahmud et al. [64] | 610 images (COVID-19 = 305 and normal = 305) | Transfer learning with convolutional neural networks(stacked MultiResolution CovXNet) | 97.4% |
| Benbrahim et al. [65] | 320 images (COVID-19 = 160 and normal = 160) | Transfer learning with convolutional neural networks(Inceptionv3 and ResNet50) | 99.01% |
| Martínez et al. [66] | 240 images (COVID-19 = 120 and normal = 120) | Convolutional neural network (Neural Architecture Searchnetwork (NASNet)) | 97% |
| Toraman et al. [67] | 1281 images (COVID-19 = 231 and normal = 1050) | Convolutional neural network (CapsNet) | 97.24% |
| Duran-Lopezet al. [68] | 6926 images (COVID-19 = 2589 and normal = 4337) | Convolutional neural network | 94.43% |
| Proposed Method | 5090 chest X-ray images (COVID-19 = 1979 and normal = 3111) | Fusion features (CNN+HOG) + VGG19 pre-train model | 99.49% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alam, N.-A.-; Ahsan, M.; Based, M.A.; Haider, J.; Kowalski, M. COVID-19 Detection from Chest X-ray Images Using Feature Fusion and Deep Learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041480
Alam N-A-, Ahsan M, Based MA, Haider J, Kowalski M. COVID-19 Detection from Chest X-ray Images Using Feature Fusion and Deep Learning. Sensors. 2021; 21(4):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041480
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlam, Nur-A-, Mominul Ahsan, Md. Abdul Based, Julfikar Haider, and Marcin Kowalski. 2021. "COVID-19 Detection from Chest X-ray Images Using Feature Fusion and Deep Learning" Sensors 21, no. 4: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041480
APA StyleAlam, N.-A.-, Ahsan, M., Based, M. A., Haider, J., & Kowalski, M. (2021). COVID-19 Detection from Chest X-ray Images Using Feature Fusion and Deep Learning. Sensors, 21(4), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041480







