Multi-Sensor Perception Strategy to Enhance Autonomy of Robotic Operation for Uncertain Peg-in-Hole Task
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Description
- (1)
- how to perceive the features of the uncertain operating object,
- (2)
- how to achieve make an automatic decision for the robotic operation,
- (3)
- how to achieve safety interaction between the robot and the uncertain operating object.
3. Design of Multi-Sensor Perception Strategy
3.1. Interactive Exploration
3.1.1. Initialization
3.1.2. Random Wandering of Sampled Particles
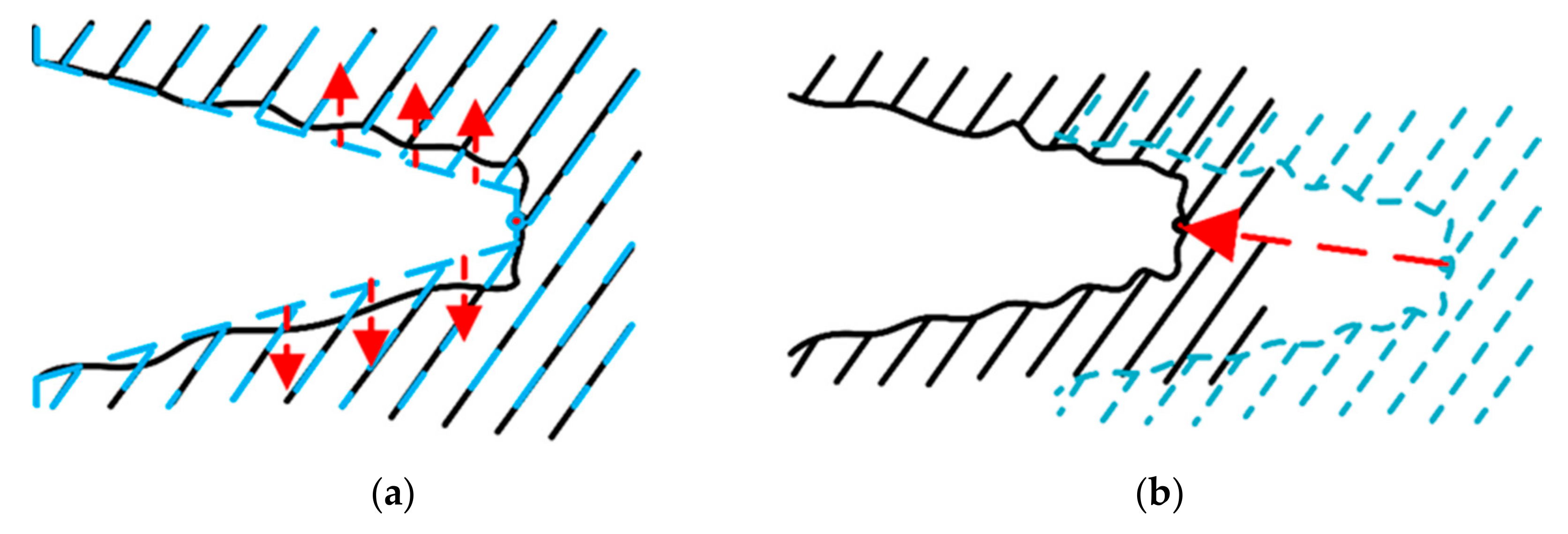
3.1.3. Estimating the Probability of the Features of the Uncertain Object Based on Position Information
3.1.4. Estimating the Probability of the Features of the Uncertain Object Based on Force Information
3.1.5. Estimating the Probability of the Features of the Uncertain Object Based on Visual Information
3.1.6. Weighted Integration
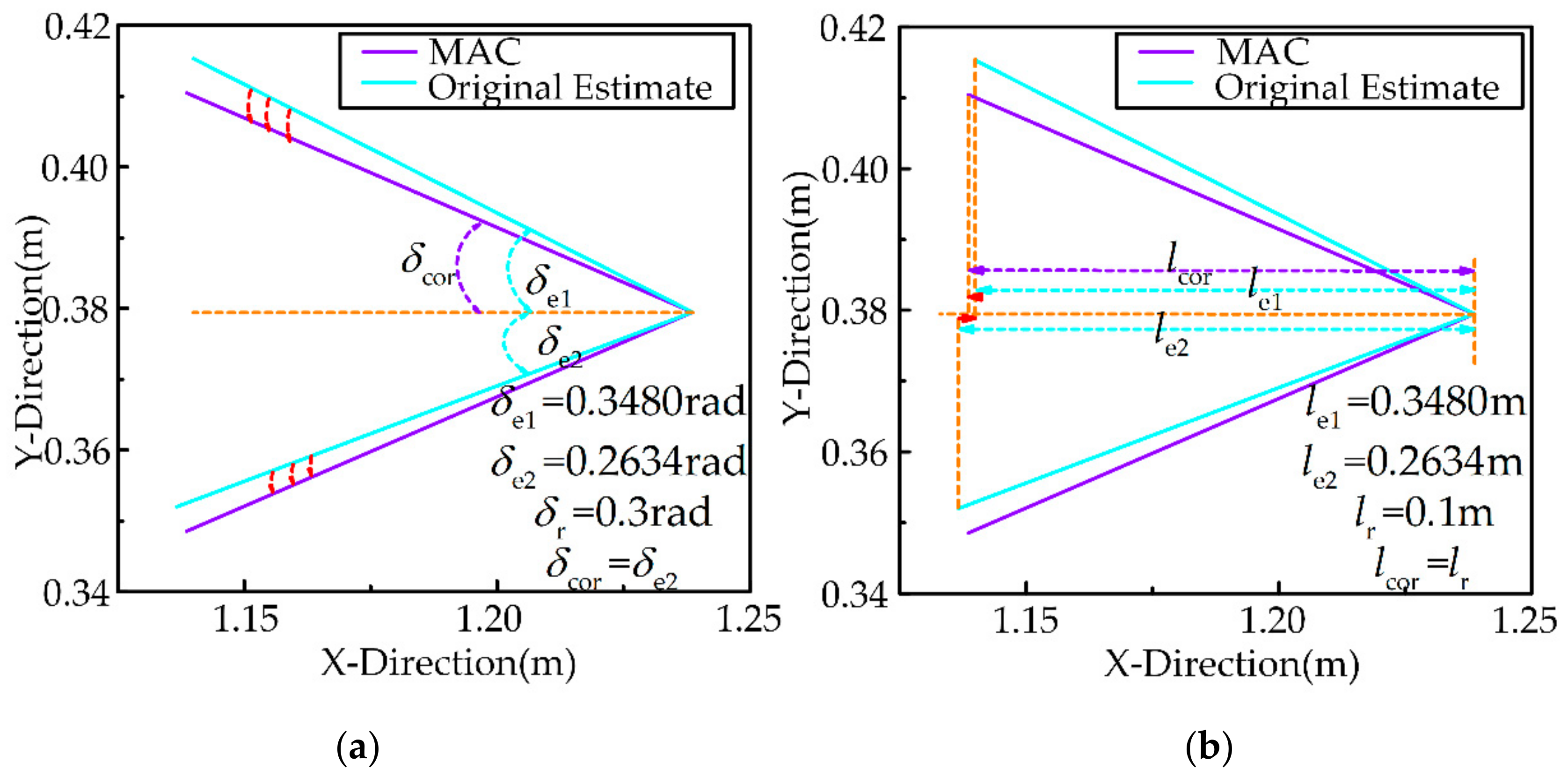
3.1.7. Correcting the Estimated Features of the Uncertain Object
3.2. Fusion Decision Based on D-S Theory
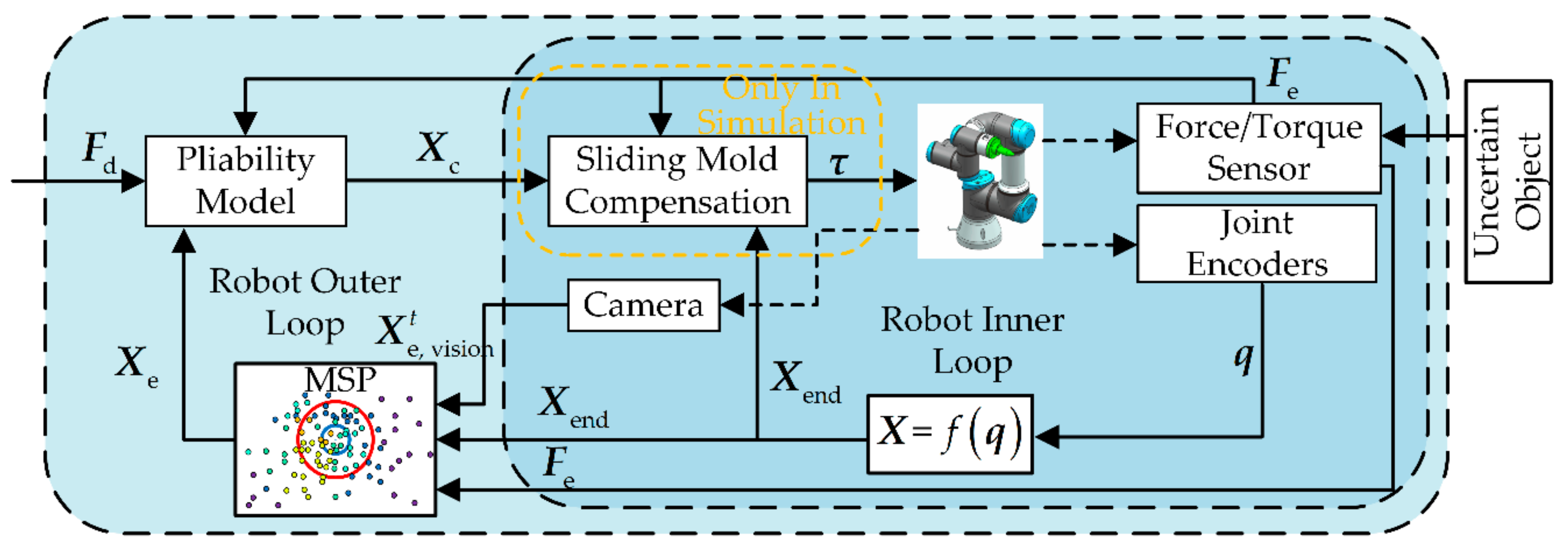
4. Design of Control System
4.1. Dynamics Model
4.2. Control System Designed with MSP
5. Simulation and Experimental Results
5.1. Simulation Studies
5.1.1. Simulation Settings
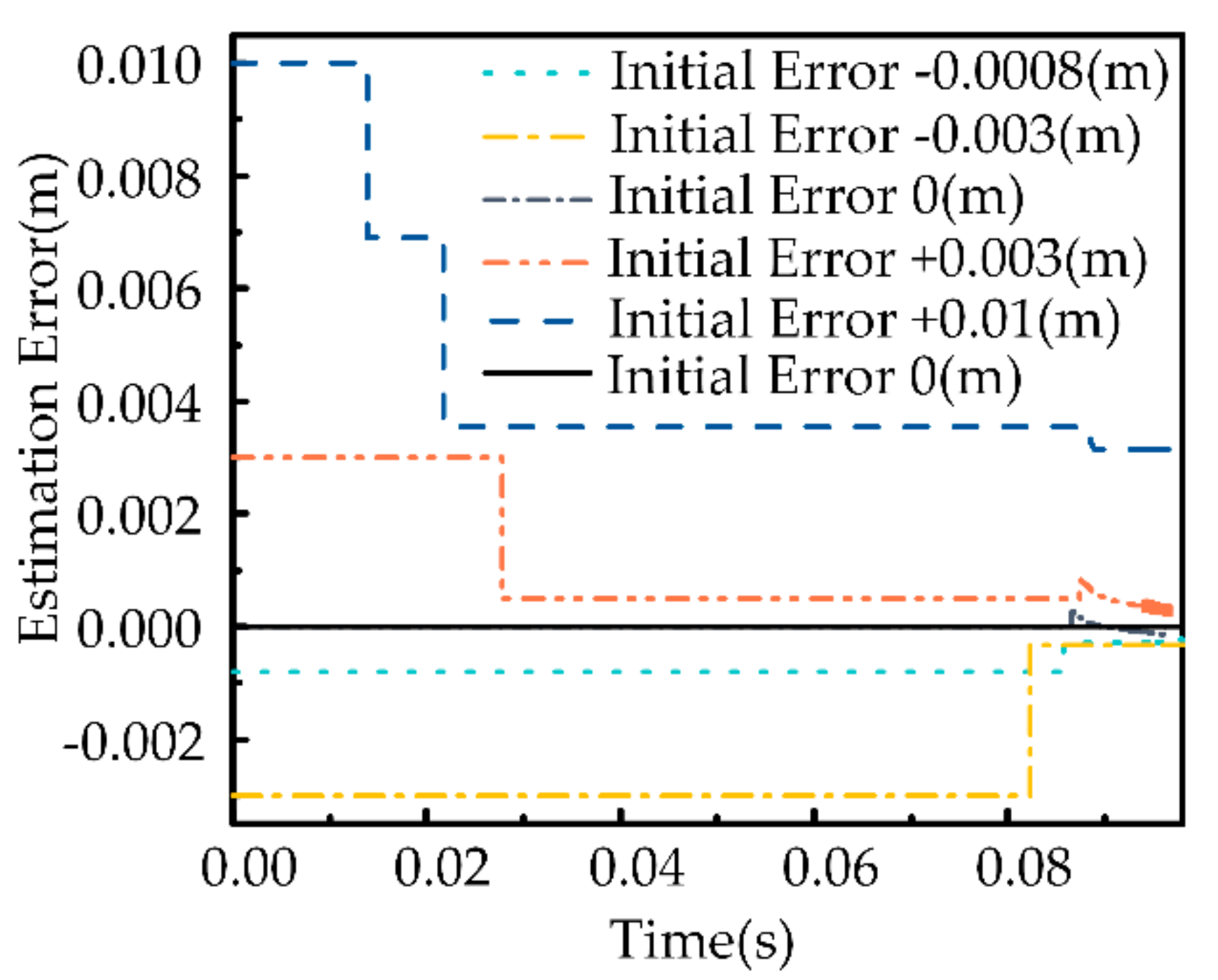
5.1.2. Intelligibility Evaluation
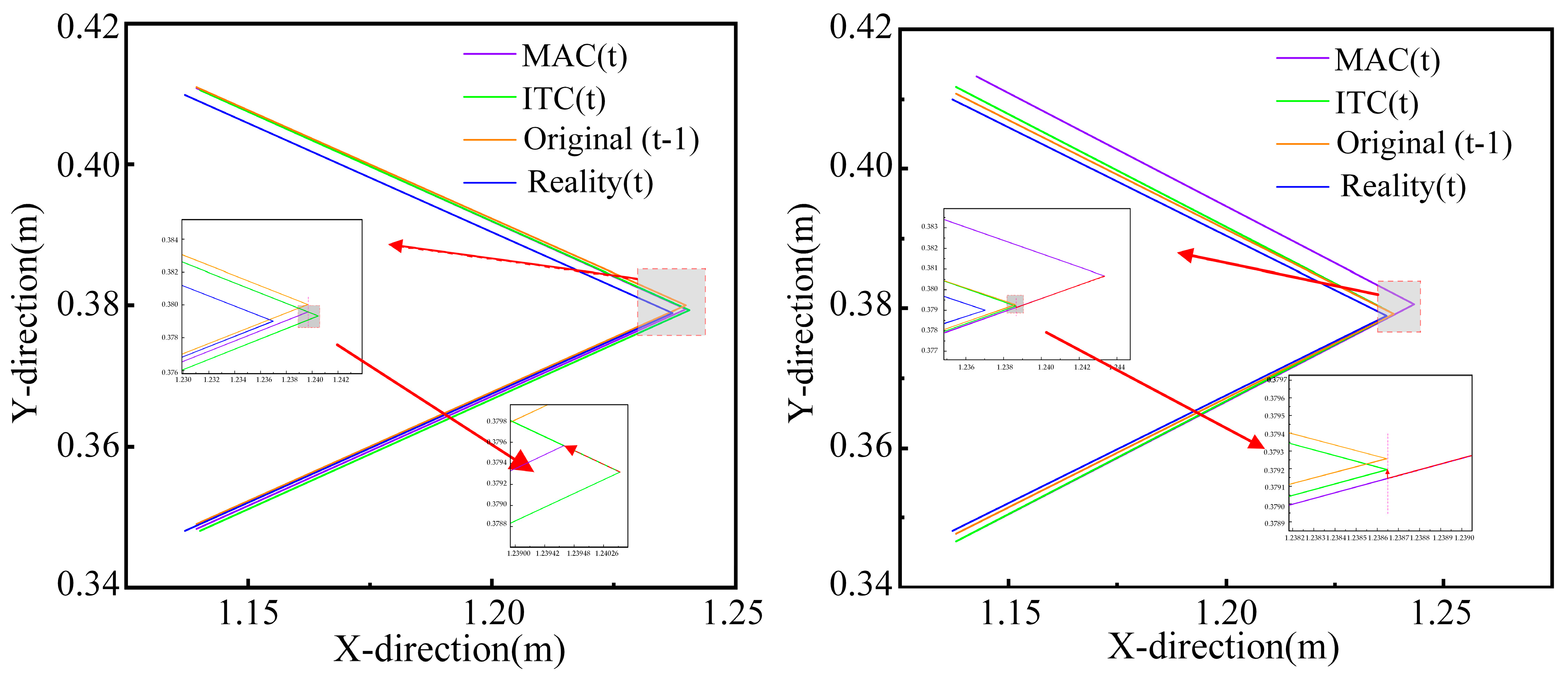
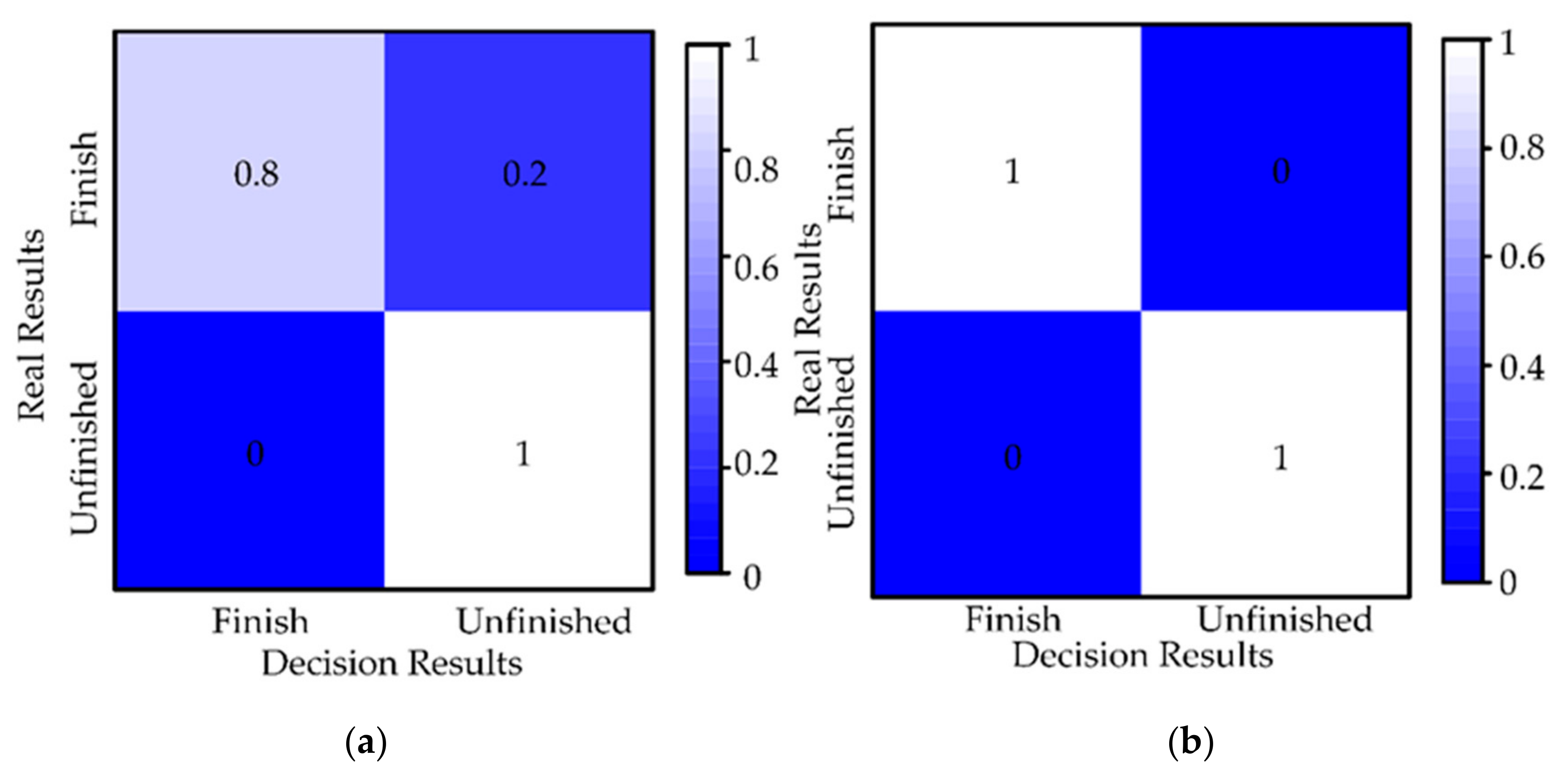
5.1.3. Autonomy Evaluation
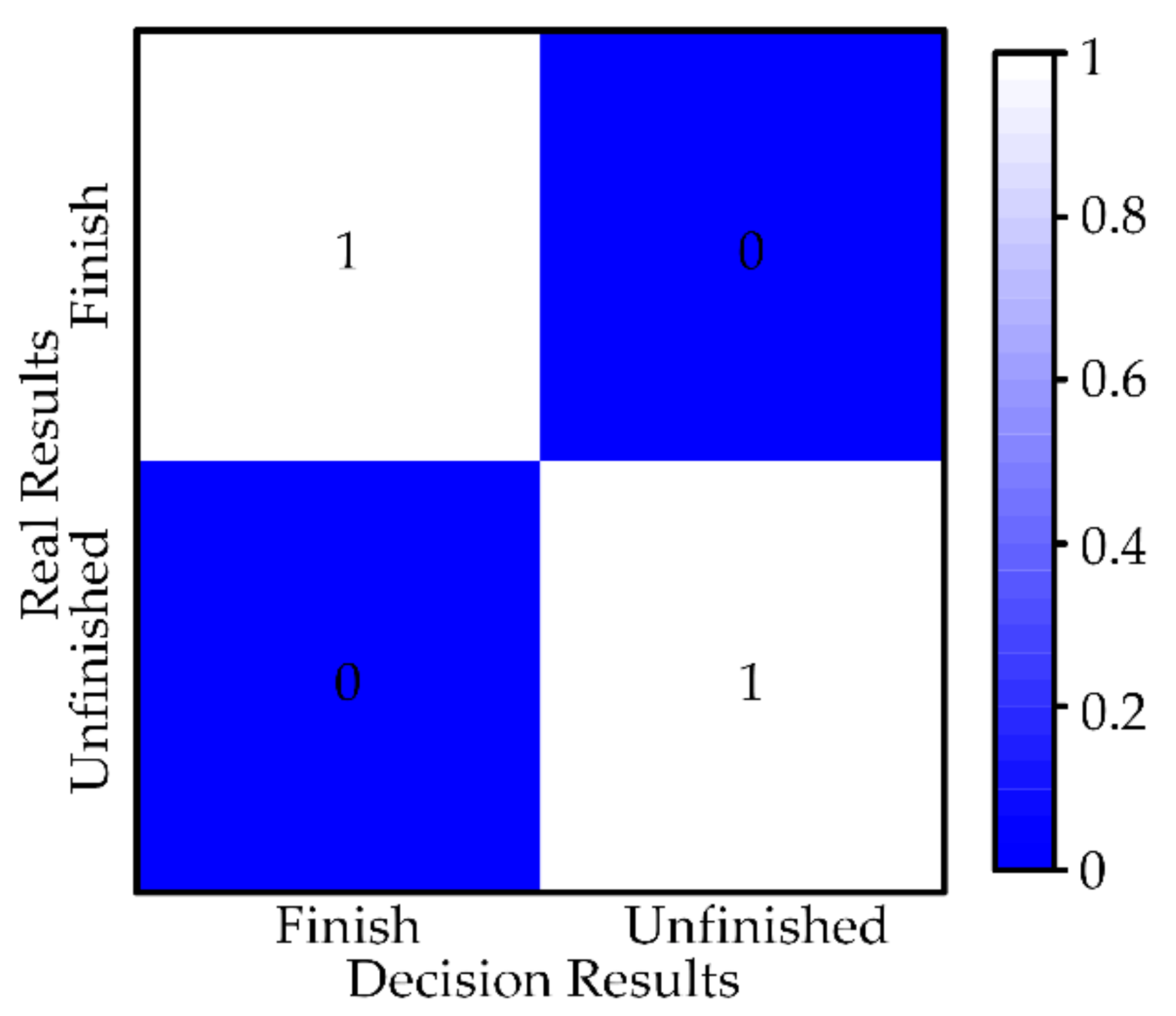
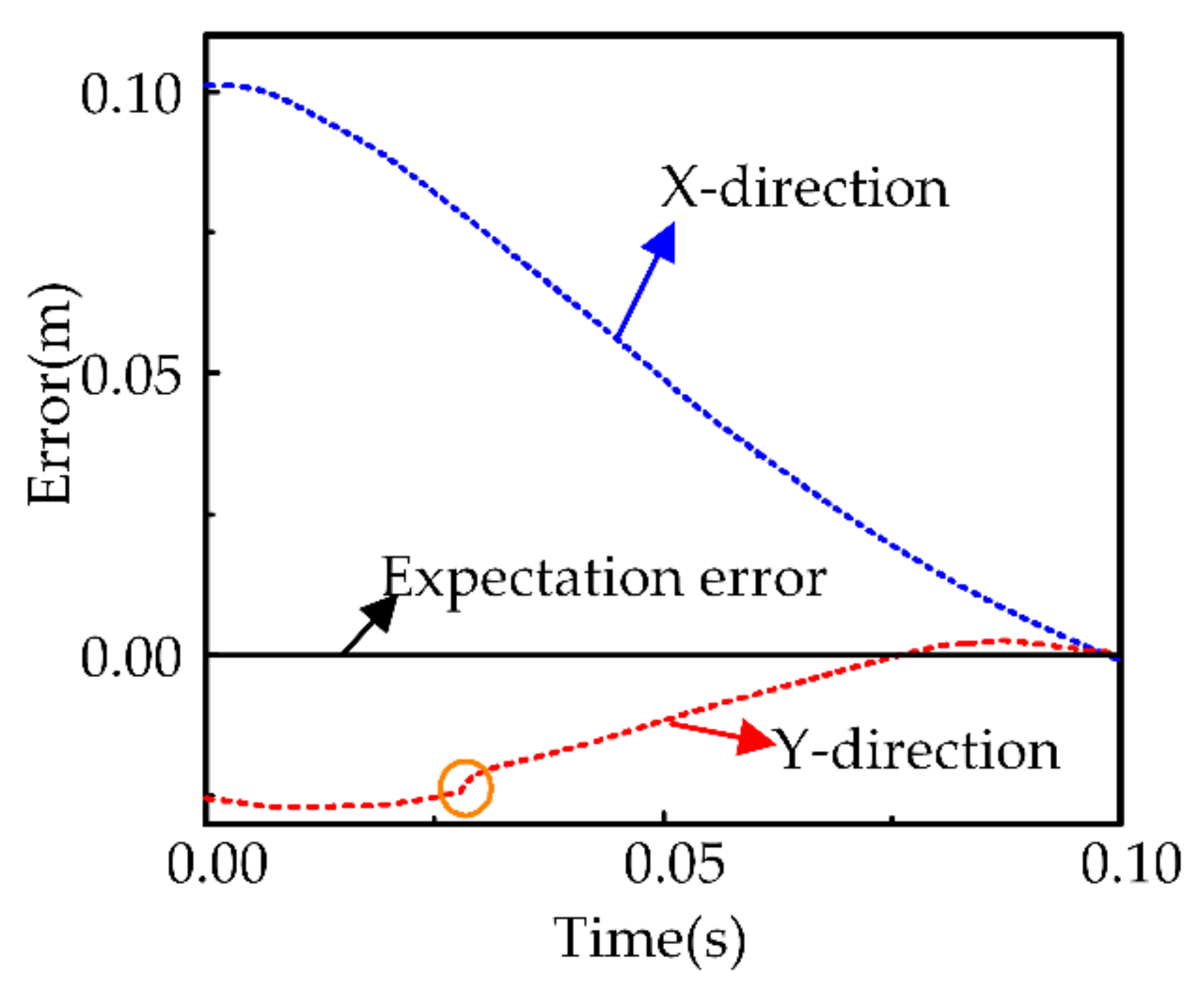
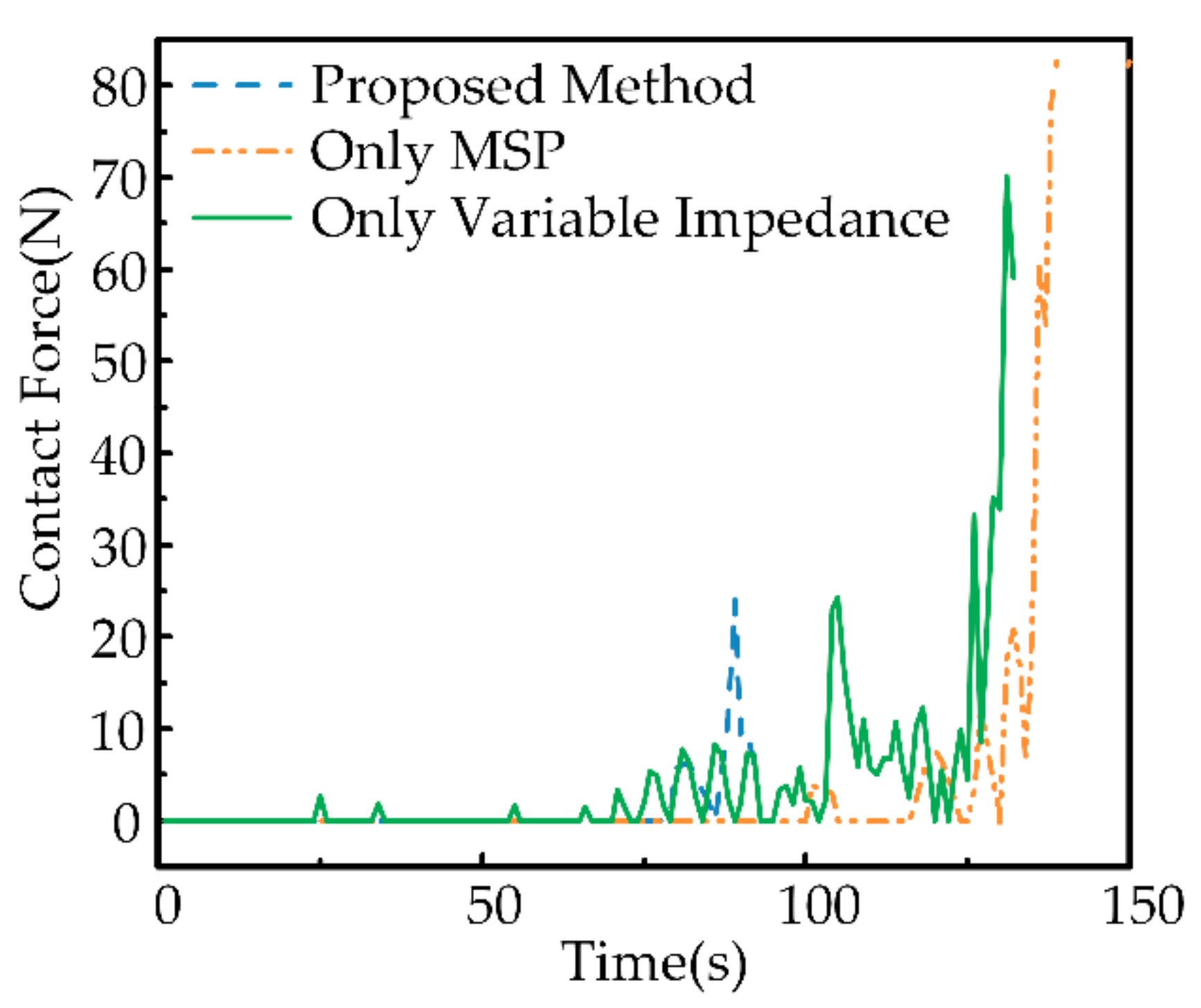
5.1.4. Safety Evaluation
5.2. Experimental Studies
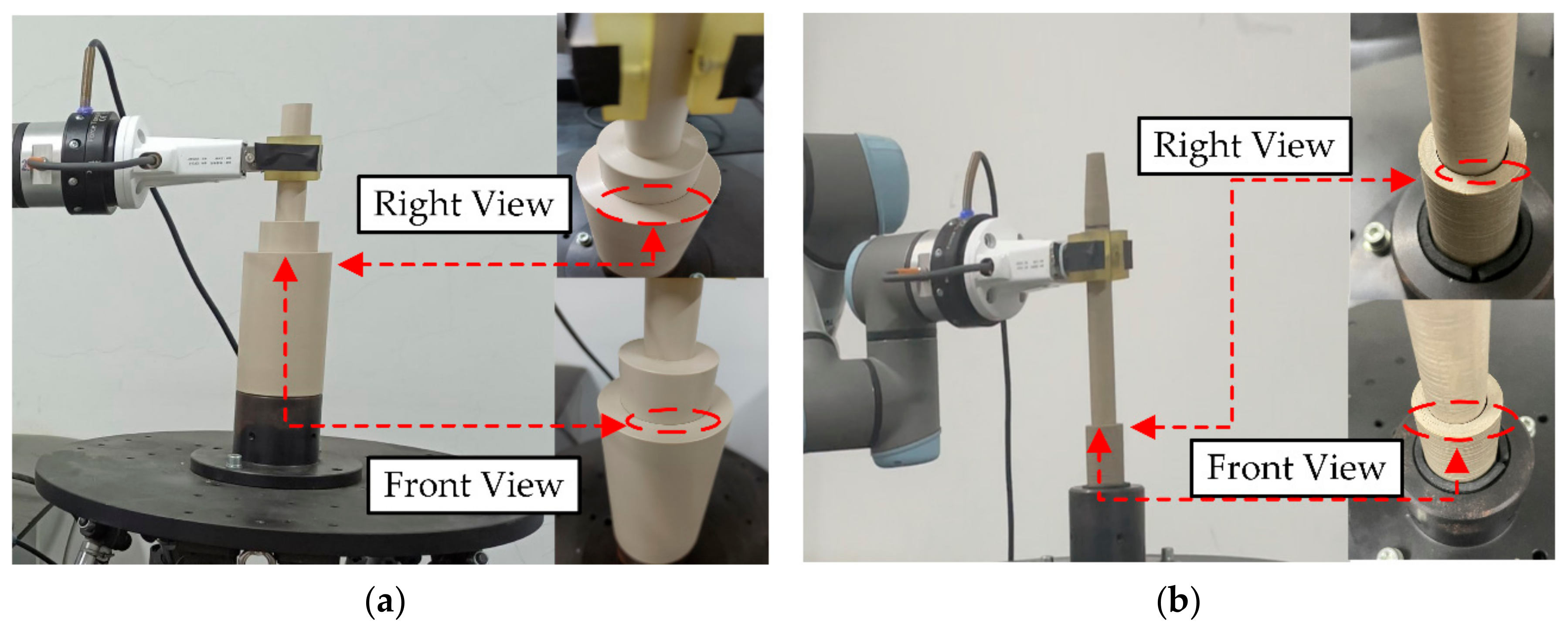
5.2.1. Experimental Settings
5.2.2. Autonomy Evaluation
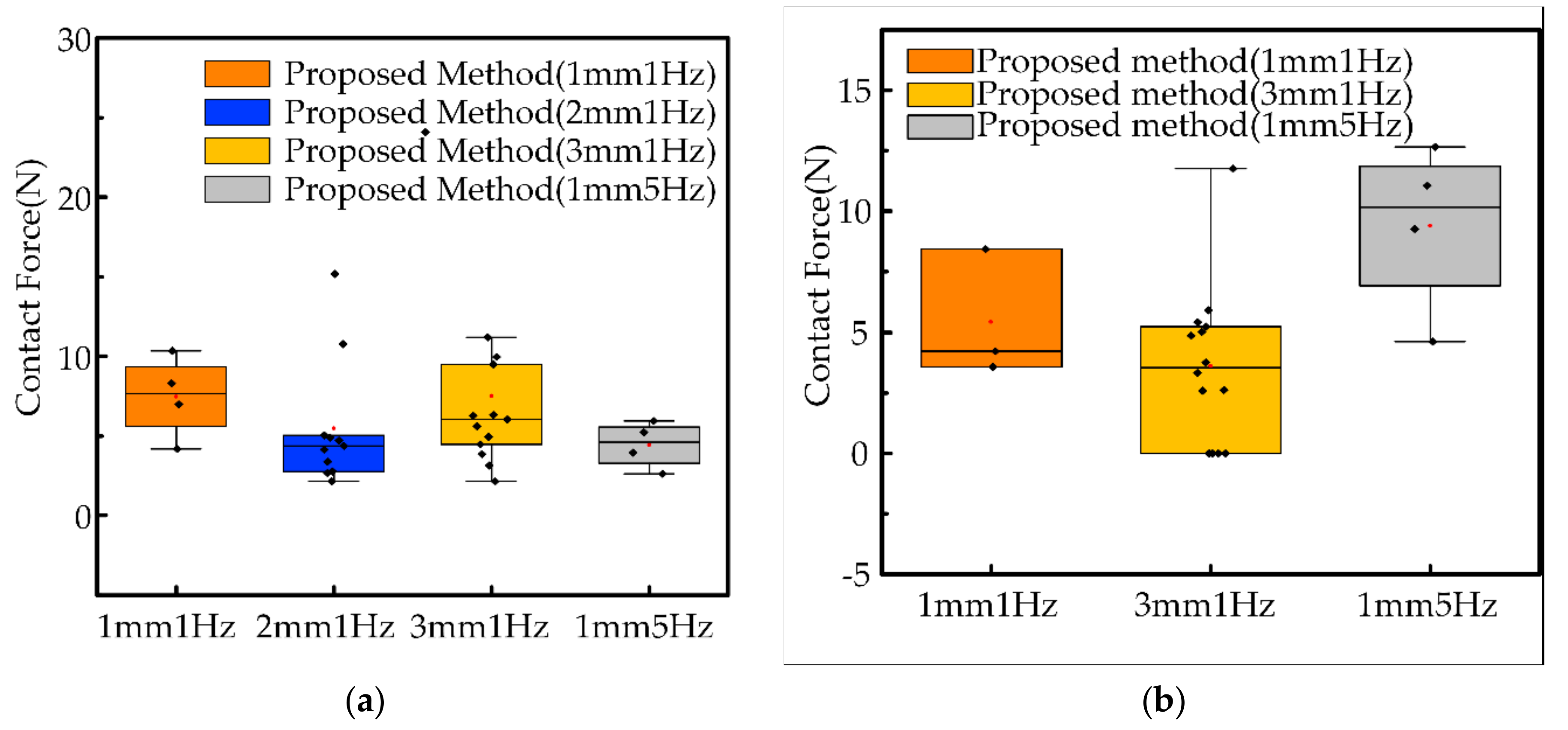
5.2.3. Safety Evaluation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, Z.; Chen, B.; Liu, J.; Yuan, F.; Shao, Z.; Yang, H.; Domel, A.G.; Zhang, J.; Wen, L. A Tapered Soft Robotic Oropharyngeal Swab for Throat Testing: A New Way to Collect Sputa Samples. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2021, 28, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Li, F.; Quan, W.; Yang, X.; Zhao, J. Skill learning for robotic assembly based on visual perspectives and force sensing. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2021, 135, 103651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Liu, H.; Ke, Y. Sensor-Based Control Using an Image Point and Distance Features for Rivet-in-Hole Insertion. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 4692–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Cui, H.; Cheng, X.; Tian, W. A Measurement Method for Robot Peg-in-Hole Prealignment Based on Combined Two-Level Visual Sensors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J. Predictive visual control framework of mobile robot for solving occlusion. Neurocomputing 2021, 423, 474–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, K.; Yamazaki, K. Learning from Demonstration Based on a Mechanism to Utilize an Object’s Invisibility. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macao, China, 3–8 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.; Chung, W.-Y.; Lee, J. Artificial Intelligence-Based Optimal Grasping Control. Sensors 2020, 20, 6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatkowski, J.; Lavertu, J.-S.; Gourrat, C.; Duchaine, V. Determining Object Properties from Tactile Events During Grasp Failure. In Proceedings of the IEEE 15th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 22–26 August 2019; Okamura, A.M., Amato, N., Asfour, T., Choi, Y.J., Chong, N.Y., Ding, H., Lee, D.H., Lerma, C.C., Li, J.S., Marchand, E., et al., Eds.; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1692–1698. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.; Ebert, F.; Jayaraman, D.; Mudigonda, M.; Finn, C.; Calandra, R.; Levine, S. Manipulation by Feel: Touch-Based Control with Deep Predictive Models. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 818–824. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, D.F.; Paoletti, P.; Luo, S. Generation of GelSight Tactile Images for Sim2Real Learning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 4177–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geier, A.; Tucker, R.; Somlor, S.; Sawada, H.; Sugano, S. End-to-End Tactile Feedback Loop: From Soft Sensor Skin Over Deep GRU-Autoencoders to Tactile Stimulation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 6467–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billard, A.; Kragic, D. Trends and challenges in robot manipulation. Science 2019, 364, eaat8414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekiroglu, Y.; Detry, R.; Kragic, D. Learning tactile characterizations of object- and pose-specific grasps. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; pp. 1554–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Calandra, R.; Owens, A.; Jayaraman, D.; Lin, J.; Yuan, W.; Malik, J.; Adelson, E.; Levine, S. More Than a Feeling: Learning to Grasp and Regrasp Using Vision and Touch. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watkins-Valls, D.; Varley, J.; Allen, P. Multi-Modal Geometric Learning for Grasping and Manipulation. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 7339–7345. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X.; Chen, G.; Hu, H.; Lou, Y. A Robotic Charging Scheme for Electric Vehicles Based on Monocular Vision and Force Perception. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Dali, China, 6–8 December 2019; pp. 2958–2963. [Google Scholar]
- Jusoh, S.; Almajali, S. A Systematic Review on Fusion Techniques and Approaches Used in Applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 14424–14439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.A.; Zhu, Y.; Zachares, P.; Tan, M.; Srinivasan, K.; Savarese, S.; Fei-Fei, L.; Garg, A.; Bohg, J. Making Sense of Vision and Touch: Learning Multimodal Representations for Contact-Rich Tasks. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2020, 36, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, F.; García-González, J.; Gandarias, J.; Medina, D.; Closas, P.; Garcia, A.; Gomez-de-Gabriel, J. Bayesian and Neural Inference on LSTM-Based Object Recognition from Tactile and Kinesthetic Information. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 6, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izatt, G.; Mirano, G.; Adelson, E.; Tedrake, R. Tracking objects with point clouds from vision and touch. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 4000–4007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Cully, A.; Demiris, Y. Probabilistic Real-Time User Posture Tracking for Personalized Robot-Assisted Dressing. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2019, 35, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nottensteiner, K.; Sachtler, A.; Albu-Schäffer, A. Towards Autonomous Robotic Assembly: Using Combined Visual and Tactile Sensing for Adaptive Task Execution. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2021, 101, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachtler, A.; Nottensteiner, K.; Kaßecker, M.; Albu-Schäffer, A. Combined Visual and Touch-based Sensing for the Autonomous Registration of Objects with Circular Features. In Proceedings of the 2019 19th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2–6 December 2019; pp. 426–433. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, U.; Molkenstruck, S.; Iser, R.; Wahl, F.M. Multi Sensor Fusion in Robot Assembly Using Particle Filters. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Rome, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; pp. 3837–3843. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, K.; Wang, H. Combined and interactive effects of interference fit and preloads on composite joints. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2014, 27, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Pal, N.R.; Marathe, A.R.; Wang, Y.-K.; Lin, C.-T. Fuzzy Decision-Making Fuser (FDMF) for Integrating Human-Machine Autonomous (HMA) Systems with Adaptive Evidence Sources. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, L.; Wang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Qin, S. Multi-Sensor Perception Strategy to Enhance Autonomy of Robotic Operation for Uncertain Peg-in-Hole Task. Sensors 2021, 21, 3818. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113818
Qin L, Wang H, Yuan Y, Qin S. Multi-Sensor Perception Strategy to Enhance Autonomy of Robotic Operation for Uncertain Peg-in-Hole Task. Sensors. 2021; 21(11):3818. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113818
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Li, Hongyu Wang, Yazhou Yuan, and Shufan Qin. 2021. "Multi-Sensor Perception Strategy to Enhance Autonomy of Robotic Operation for Uncertain Peg-in-Hole Task" Sensors 21, no. 11: 3818. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113818
APA StyleQin, L., Wang, H., Yuan, Y., & Qin, S. (2021). Multi-Sensor Perception Strategy to Enhance Autonomy of Robotic Operation for Uncertain Peg-in-Hole Task. Sensors, 21(11), 3818. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113818





