Strain-Dependent Photoacoustic Characteristics of Free-Standing Carbon-Nanocomposite Transmitters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Transmitter Fabrication
2.2. PA Characterization of Nanocomposite Transmitters on Glass Substrate
2.3. Strain-Dependent PA Characterization of Free-Standing Nanocomposite Transmitters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PA Characteristics of Nanocomposite Transmitters on Glass Substrates
3.2. Strain-Dependent PA Characteristics of Free-Standing Nanocomposite Transmitters
3.3. Dynamic Endurance Test (DET)
3.4. Mechanical Robustness against Input Optical Fluence
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, L.; Gutbrod, S.R.; Bonifas, A.P.; Su, Y.; Sulkin, M.S.; Lu, N.; Chung, H.-J.; Jang, K.-I.; Liu, Z.; Ying, M.; et al. 3D Multifunctional Integumentary Membranes for Spatiotemporal Cardiac Measurements and Stimulation across the Entire Epicardium. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Choi, T.K.; Lee, Y.B.; Cho, H.R.; Ghaffari, R.; Wang, L.; Choi, H.J.; Chung, T.D.; Lu, N.; Hyeon, T.; et al. A Graphene-Based Electrochemical Device with Thermoresponsive Microneedles for Diabetes Monitoring and Therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltenbrunner, M.; Sekitani, T.; Reeder, J.; Yokota, T.; Kuribara, K.; Tokuhara, T.; Drack, M.; Schwödiauer, R.; Graz, I.; Bauer-Gogonea, S.; et al. An Ultra-Lightweight Design for Imperceptible Plastic Electronics. Nature 2013, 499, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Lu, N.; Ma, R.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, R.-H.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Won, S.M.; Tao, H.; Islam, A.; et al. Epidermal Electronics. Science 2011, 333, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, M.K.; Yang, J.; Kim, D.C.; Dai, Z.; Kim, J.; Seung, H.; Kale, V.S.; Sung, S.J.; Park, C.R.; Lu, N.; et al. Extremely Vivid, Highly Transparent, and Ultrathin Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.; Lee, J.; Qiao, S.; Ghaffari, R.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.E.; Song, C.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, D.J.; Jun, S.W.; et al. Multifunctional Wearable Devices for Diagnosis and Therapy of Movement Disorders. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Kobayashi, S.; Nagase, M.; Jimbo, Y.; Saito, I.; Inoue, Y.; Yambe, T.; Sekino, M.; Malliaras, G.G.; Yokota, T.; et al. Nonthrombogenic, Stretchable, Active Multielectrode Array for Electroanatomical Mapping. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Heo, S.W.; Lee, W.; Inoue, D.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, K.; Jinno, H.; Hashizume, D.; Sekino, M.; Yokota, T.; et al. Self-Powered Ultra-Flexible Electronics via Nano-Grating-Patterned Organic Photovoltaics. Nature 2018, 561, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, L.; Mathewson, K.E.; Jang, K.-I.; Kim, J.; Fu, H.; Huang, X.; Chava, P.; Wang, R.; et al. Soft Microfluidic Assemblies of Sensors, Circuits, and Radios for the Skin. Science 2014, 344, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, T.; Zalar, P.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Jinno, H.; Matsuhisa, N.; Kitanosako, H.; Tachibana, Y.; Yukita, W.; Koizumi, M.; Someya, T. Ultraflexible Organic Photonic Skin. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Shim, H.J.; Yang, J.; Choi, M.K.; Kim, D.C.; Kim, J.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.-H. Ultrathin Quantum Dot Display Integrated with Wearable Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, W.; Vinciguerra, V.; Lorenzelli, L.; Dahiya, R. Printable Stretchable Interconnects. Flex. Print. Electron. 2017, 2, 013003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monchalin, J.P. Laser-Ultrasonics: Principles and Industrial Applications. In Ultrasonic and Advanced Methods for Nondestructive Testing and Material Characterization; World Scientific: Singapore, 2007; pp. 79–115. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Lee, S.; Huang, Z.; Chen, R.; Chen, Z.; Wang, C.; et al. Stretchable Ultrasonic Transducer Arrays for Three-Dimensional Imaging on Complex Surfaces. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Escoffre, J.M.; Bouakaz, A. Therapeutic Ultrasound; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heilderberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Baac, H.W.; Ok, J.G.; Park, H.J.; Ling, T.; Chen, S.-L.; Hart, A.J.; Guo, L.J. Carbon Nanotube Composite Optoacoustic Transmitters for Strong and High Frequency Ultrasound Generation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 234104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baac, H.W.; Ok, J.G.; Maxwell, A.; Lee, K.-T.; Chen, Y.-C.; Hart, A.J.; Xu, Z.; Yoon, E.; Guo, L.J. Carbon-Nanotube Optoacoustic Lens for Focused Ultrasound Generation and High-Precision Targeted Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baac, H.W.; Ok, J.G.; Lee, T.; Jay Guo, L. Nano-Structural Characteristics of Carbon Nanotube–Polymer Composite Films for High-Amplitude Optoacoustic Generation. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 14460–14468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Xie, B.; Li, X.; Lei, S.; Ou-Yang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Multilayered Carbon Nanotube Yarn Based Optoacoustic Transducer with High Energy Conversion Efficiency for Ultrasound Application. Nano Energy 2018, 46, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Ashkenazi, S.; Huang, S.-W.; O’Donnell, M. An Integrated Optoacoustic Transducer Combining Etalon and Black PDMS Structures. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2008, 55, 2719–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buma, T.; Spisar, M.; O’Donnell, M. High-Frequency Ultrasound Array Element Using Thermoelastic Expansion in an Elastomeric Film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Chang, W.-Y.; Lindsey, B.D.; Dayton, P.A.; Dai, X.; Stavas, J.M.; Jiang, X. Laser-Generated-Focused Ultrasound Transducers for Microbubble-Mediated, Dual-Excitation Sonothrombolysis. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Tours, France, 18–21 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, B.Y.; Kim, J.; Zhu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, X. A Laser Ultrasound Transducer Using Carbon Nanofibers–Polydimethylsiloxane Composite Thin Film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 021902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, W.Y.; Huang, W.; Kim, J.; Li, S.; Jiang, X. Candle Soot Nanoparticles-Polydimethylsiloxane Composites for Laser Ultrasound Transducers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 161903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Chang, W.Y.; Kim, J.; Li, S.; Huang, S.; Jiang, X. A Novel Laser Ultrasound Transducer Using Candle Soot Carbon Nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2016, 15, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.Y.; Zhang, X.A.; Kim, J.; Huang, W.; Chang, C.H.; Jiang, X. Photoacoustic Transduction Efficiency Evaluation of Candle Soot Nanoparticles/PDMS Composites. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 17th International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–27 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.Y.; Zhang, X.A.; Kim, J.; Huang, W.; Bagal, A.; Chang, C.H.; Fang, T.; Wu, H.F.; Jiang, X. Evaluation of Photoacoustic Transduction Efficiency of Candle Soot Nanocomposite Transmitters. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2018, 17, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, G.; Chen, S.L. Miniature Fiber-Optic High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Device Using a Candle Soot Nanoparticles-Polydimethylsiloxane Composites-Coated Photoacoustic Lens. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 21700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraz, M.; Abbasi, M.A.; Sang, P.; Son, D.; Baac, H.W. Stretchable and Robust Candle-Soot Nanoparticle-Polydimethylsiloxane Composite Films for Laser-Ultrasound Transmitters. Micromachines 2020, 11, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Kim, J.S.; Ashkenazi, S.; O’Donnell, M.; Guo, L.J. Optical Generation of High Frequency Ultrasound Using Two-Dimensional Gold Nanostructure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 093901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.X.; Choi, J.W. Patterning Conductive PDMS Nanocomposite in an Elastomer Using Microcontact Printing. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 085019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, M.A.; Chou, H.-P.; Thorsen, T.; Scherer, A.; Quake, S.R. Monolithic Microfabricated Valves and Pumps by Multilayer Soft Lithography. Science 2000, 288, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilkner, T.; Janasek, D.; Manz, A. Micro Total Analysis Systems. Recent Developments. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 3373–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, K.A.; Ryu, K.S.; Goluch, E.D.; Nam, J.M.; Liu, J.; Thaxton, C.S.; Chiesl, T.N.; Barron, A.E.; Lu, Y.; Mirkin, C.A.; et al. A Modular Microfluidic Architecture for Integrated Biochemical Analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9745–9750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDonald, J.C.; Whitesides, G.M. Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) as a Material for Fabricating Microfluidic Devices. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, B.; Sundqvist, B. Resistivity of a Composite Conducting Polymer as a Function of Temperature, Pressure, and Environment: Applications as a Pressure and Gas Concentration Transducer. J. Appl. Phys. 1986, 60, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, E.; Tchoudakov, R.; Narkis, M.; Siegmann, A. Sensing of Liquids by Electrically Conductive Immiscible Polypropylene/Thermoplastic Polyurethane Blends Containing Carbon Black. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2003, 41, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lu, M.; Bermak, A.; Lee, Y.K. Study of Piezoresistance Effect of Carbon Nanotube-PDMS Composite Materials for Nanosensors. In Proceedings of the 2007 7th IEEE Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE NANO), Hong Kong, China, 2–5 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, X.Z.; Peng, S.L.; Liu, L.Y.; Wen, W.J.; Sheng, P. Characterizing and Patterning of PDMS-Based Conducting Composites. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2682–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, F.; Hu, S.; Liu, P.; Li, A.; Chen, J. Optimized CNT-PDMS Flexible Composite for Attachable Health-Care Device. Sensors 2020, 20, 4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hong, S.K.; Ryu, J.-K.; Park, S.H. Effect of Filler Alignment on Piezo-Resistive and Mechanical Properties of Carbon Nanotube Composites. Materials 2020, 13, 2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.A.; Faraz, M.; Joo, M.G.; Son, D.; Won, S.M.; Ok, J.G.; Park, H.J.; Baac, H.W. Variable-Focus Optoacoustic Lens with Wide Dynamic Range and Long Focal Length by Using a Flexible Polymer Nano-Composite Membrane. Ultrasonics 2021, 117, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Park, J.Y.; Nam, H.J.; Choa, S.H. Highly Stretchable, Durable, and Printable Textile Conductor. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 20th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference (EPTC), Singapore, 4–7 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, M.G.; Lee, K.T.; Sang, P.; Heo, J.; Park, H.J.; Baac, H.W. Laser-Generated Focused Ultrasound Transmitters with Frequency-Tuned Outputs over Sub-10-MHz Range. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 154103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Dai, J.; Fan, X.; Song, T.; Tao, Y.T.; Wang, K.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Bai, X.; Lu, P.; et al. Self-Cleaning Flexible Infrared Nanosensor Based on Carbon Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4007–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.H.; Chen, H.L.; Ju, S.P.; Chen, H.Y.; Shih, C.W.; Pan, C.T.; You, T.-D. The Mechanical Behaviors of Polyethylene/Silver Nanoparticle Composites: An Insight from Molecular Dynamics Study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipomi, D.J.; Vosgueritchian, M.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Hellstrom, S.L.; Lee, J.A.; Fox, C.H.; Bao, Z. Skin-like Pressure and Strain Sensors Based on Transparent Elastic Films of Carbon Nanotubes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.E.; Jang, H.-W.; Kim, G.-H.; Kim, S.K.; Yoon, S.-M. Improvement in Mechanical Durability of Stretchable Charge-Trap Memory Transistors with Engineered Wavy-Dimensional Structures. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 2984–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Baac, H.W.; Li, Q.; Guo, L.J. Efficient Photoacoustic Conversion in Optical Nanomaterials and Composites. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1800491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

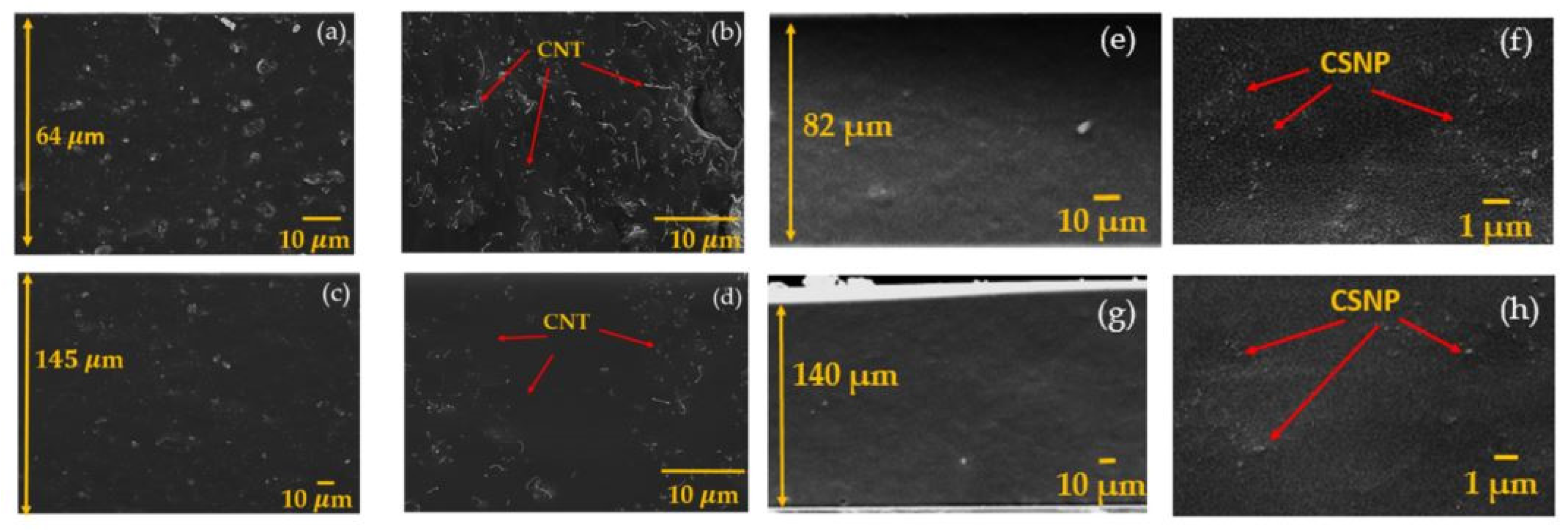



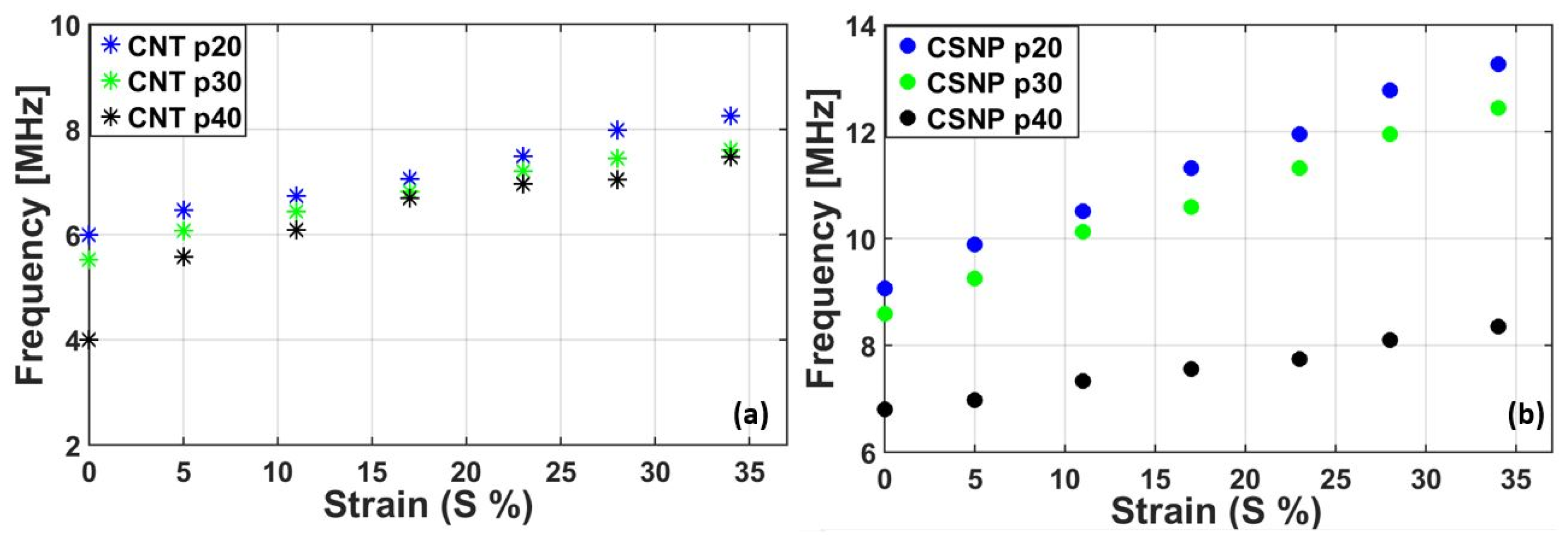

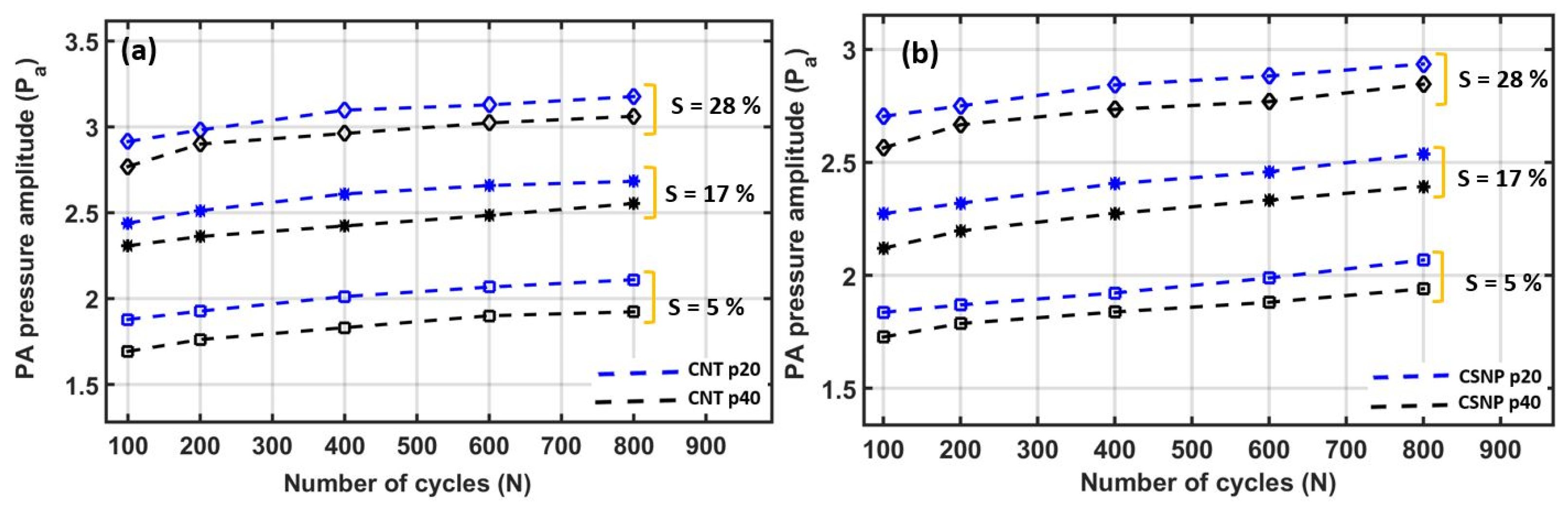

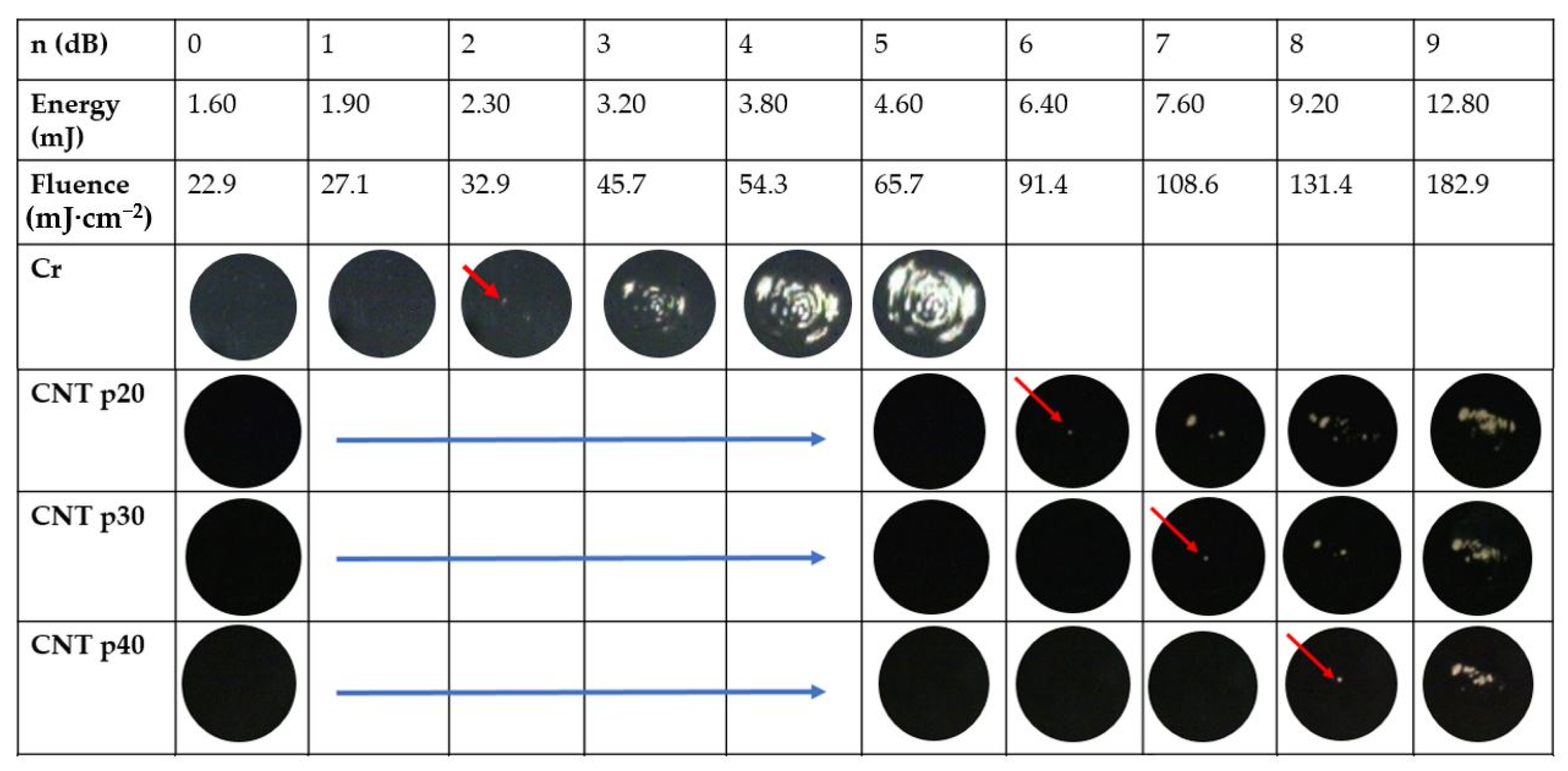
| Applied Strain (%) | Dynamic Endurance (E) (%) (Pressure Variation between N = 100 and 800 per Strain) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNT p20 | CNT p40 | CSNP p20 | CSNP p40 | |
| 5 | 2.4 | 2.8 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
| 17 | 0.58 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.76 |
| 28 | 0.28 | 0.35 | 0.28 | 0.35 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faraz, M.; Abbasi, M.A.; Son, D.; Shin, C.; Lee, K.-T.; Won, S.M.; Baac, H.W. Strain-Dependent Photoacoustic Characteristics of Free-Standing Carbon-Nanocomposite Transmitters. Sensors 2022, 22, 3432. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093432
Faraz M, Abbasi MA, Son D, Shin C, Lee K-T, Won SM, Baac HW. Strain-Dependent Photoacoustic Characteristics of Free-Standing Carbon-Nanocomposite Transmitters. Sensors. 2022; 22(9):3432. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093432
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaraz, Muhammad, Muhammad Awais Abbasi, Donghee Son, Changhwan Shin, Kyu-Tae Lee, Sang Min Won, and Hyoung Won Baac. 2022. "Strain-Dependent Photoacoustic Characteristics of Free-Standing Carbon-Nanocomposite Transmitters" Sensors 22, no. 9: 3432. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093432









