The Use of 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-4-Oxo-2-(4-Antipyrinyl)-Butanoic Acid in the Preparation of Some New Heterocyclic Compounds With Expected Biological Activity
Abstract
:Introduction
Results and Discussion

Biological Screening
| Compound No. | Gram positive bacteria | Gram negative bacteria | Fungi | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus (NCTC-7447) | Bacillus cereus (ATCC-14579) | Serratia marcescens (IMRU-70) | Proteus merabilis (NCTC-289) | Aspergillus fungytus (PP-29) | |
| 3 | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ |
| 4 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| 6 | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| 8 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| 10 | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ |
| 12a | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ |
| 13 | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ |
| 17 | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
Experimental
General
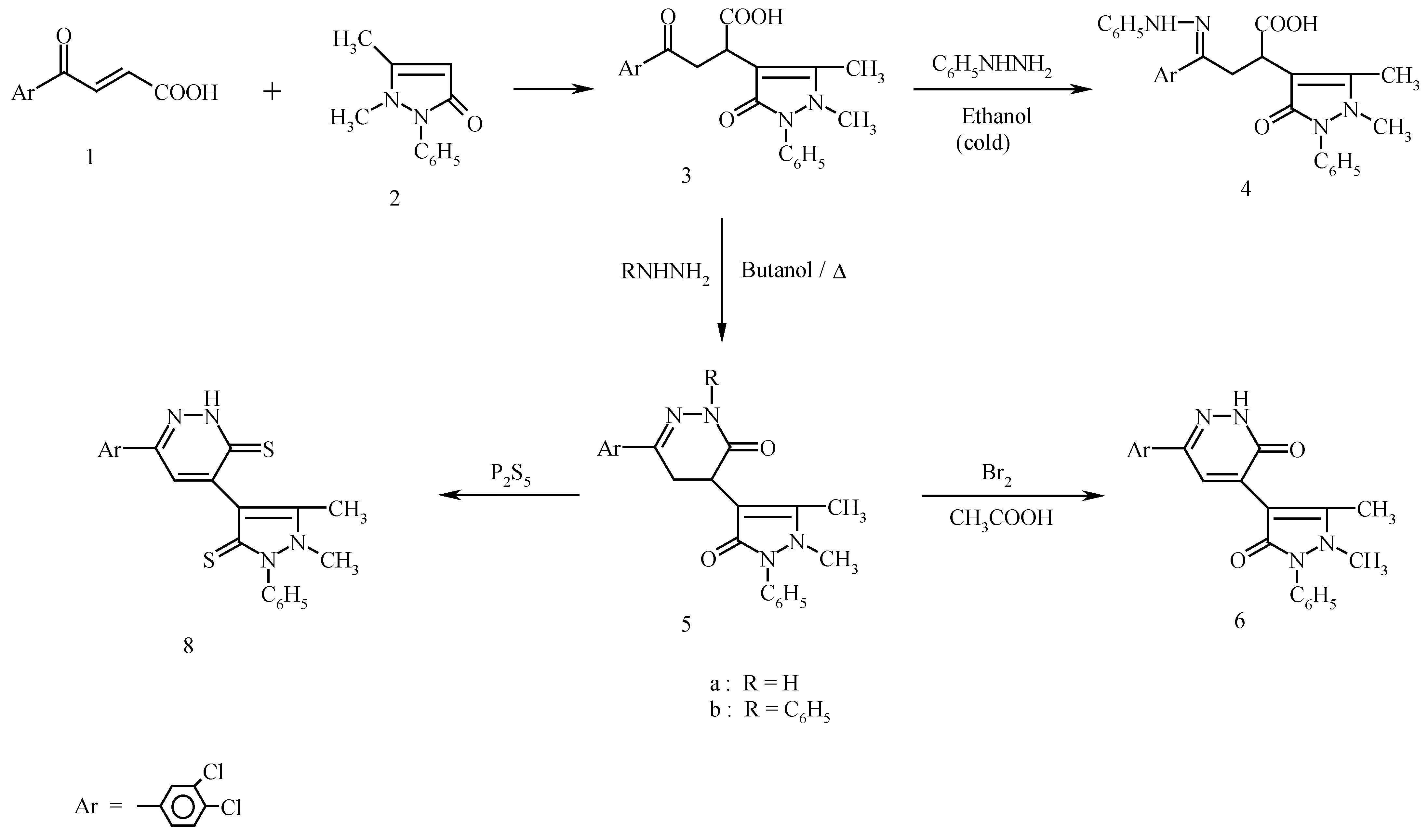
Synthesis of 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-oxo-2-(4-antipyrinyl) butanoic acid (3).
Synthesis of 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-phenylhydrazono-2-(4-antipyrinyl)butanoic acid (4).
Synthesis of 6-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-(4-antipyrinyl)-4,5-dihydropyridazin-3(2H)-one (5a) and 6-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-phenyl-4-(4-antipyrinyl)4,5-dihydropyridazin-3(2H)-one (5b).
Synthesis of 6-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-(4-antipyrinyl)pyridazin-3(2H)-one (6).
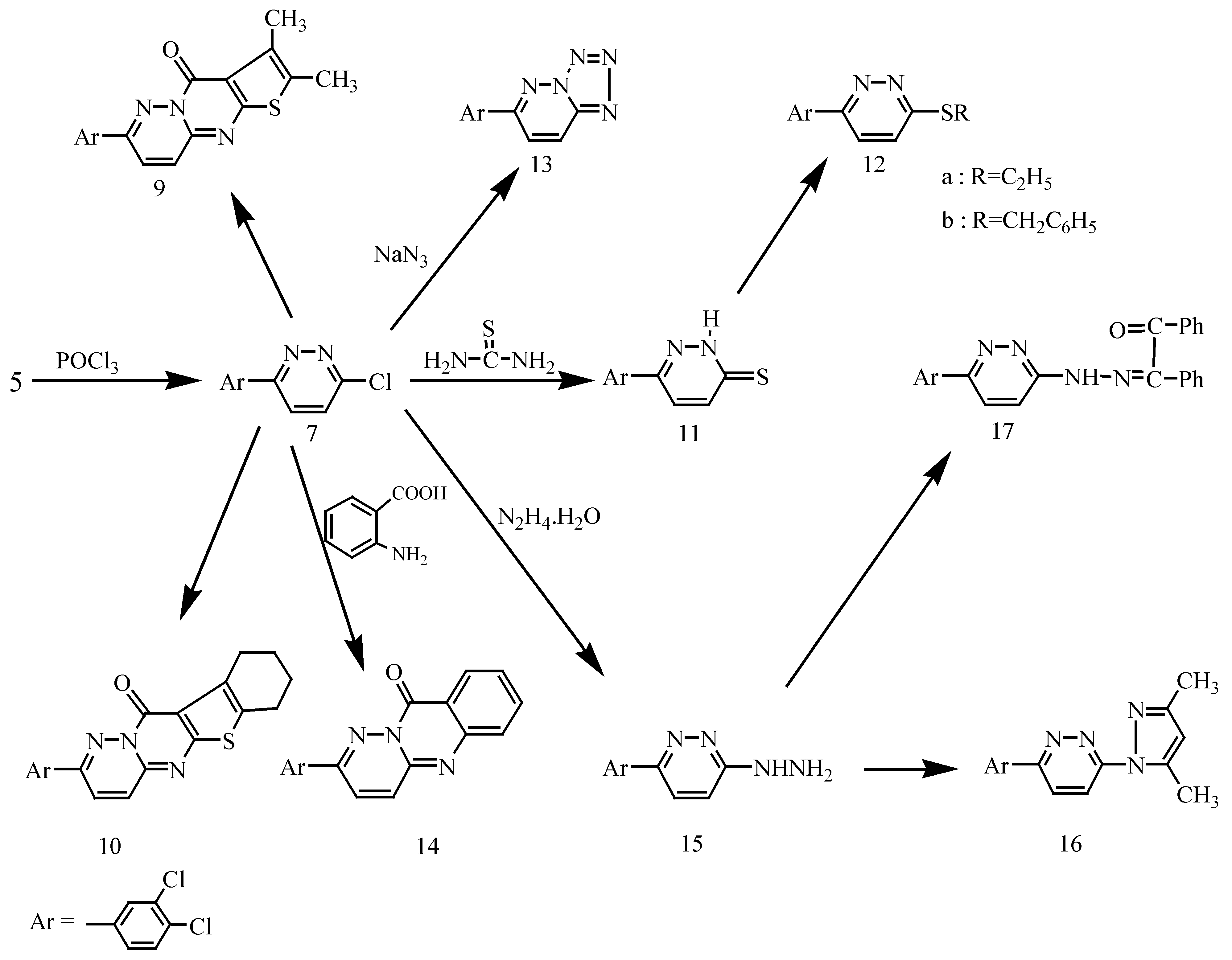
Synthesis of 6-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3-chloropyridazine (7).
Preparation of an authentic sample of 7.
Synthesis of 6-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-(1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-3-thioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-3(2H)pyridazine thione (8).
Synthesis of 7-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-2,3-dimethyl-4H-thieno-[2′,3′:4,5] pyrimido-[1,2-b]-pyridazin-4-one (9) and 2-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-11H-[1]-benzothieno-[2′,3′:4,5]-pyrimido-[1,2-b]-pyridazin-11-one (10).
Synthesis of 6-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3(2H)pyridazine thione (11).
Synthesis of 6-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3-(ethylsulfanyl)pyridazine (12a) and 6-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3-(benzylsulfanyl)pyridazine (12b).
Synthesis of 6-(3,4-dichlorophenyl) [1,2,3,4] tetrazolo [1,5-b] pyridazine (13).
Synthesis of 2-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-10H-pyridazino (6,1-b)quinazolin-10-one (14).
Synthesis of 6-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3-hydrazinopyridazine (15).
Synthesis of 6-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3-(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyridazine (16) and 1,2-diphenyl-1,2-ethanedione-1-{N-[6-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-3-pyridazonyl]- hydrazone} (17).
| Comp. No. | M.P. (°C) (cryst. solvent) | Molecular formula (mol. mass) | Analysis % Calc. / Found | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | N | S | |||
| 3 | 213 (ethanol) | C21H18Cl2N2O4 (433.28) | 58.21 58.19 | 4.19 3.98 | 6.47 6.44 | |
| 4 | 148 (ethanol) | C27H24Cl2N4O3 (523.41) | 61.96 61.89 | 4.62 4.48 | 10.70 10.58 | |
| 5a | 255 (methanol) | C21H18Cl2N4O2 (429.30) | 58.75 58.47 | 4.23 3.99 | 13.05 12.84 | |
| 5b | 185 (pet. ether b.p. 80-100°C) | C27H22Cl2N4O2 (505.39) | 64.17 64.04 | 4.39 4.05 | 11.09 10.92 | |
| 6 | 227 (acetic acid) | C21H16Cl2N4O2 (427.28) | 59.03 59.30 | 3.77 3.58 | 13.11 12.83 | |
| 7 | 182 (pet. ether b.p. 80-100°C) | C10H5Cl3N2 (259.52) | 46.28 46.16 | 1.94 1.64 | 10.79 10.58 | |
| 8 | 238 (benzene) | C21H16Cl2N4S2 (459.42) | 54.90 54.96 | 3.51 3.29 | 12.20 12.41 | 13.96 14.1 |
| 9 | 313 (ethanol) | C17H11Cl2N3OS (376.26) | 54.27 54.31 | 2.95 3.17 | 11.17 10.99 | 8.52 8.75 |
| 10 | 325 (ethanol) | C19H13Cl2N3OS (402.30) | 56.73 56.41 | 3.26 2.97 | 10.45 10.41 | 7.97 7.77 |
| 11 | 203 (ethanol) | C10H6Cl2N2S (257.14) | 46.71 46.94 | 2.35 2.30 | 10.89 10.62 | 12.47 12.72 |
| 12a | 124 (pet. ether b.p. 80-100°C) | C12H10Cl2N2S (285.19) | 50.54 50.78 | 3.53 3.63 | 9.82 10.12 | 11.24 11.06 |
| 12b | 155 (pet. ether b.p. 80-100°C) | C17H12Cl2N2S (347.26) | 58.80 58.67 | 3.48 3.58 | 8.07 7.93 | 9.23 9.50 |
| 13 | 202 (benzene) | C10H5Cl2N5 (266.09) | 45.14 45.11 | 1.89 1.70 | 26.32 26.12 | |
| 14 | 325 (acetic acid) | C17H9Cl2N3O (342.18) | 59.67 59.51 | 2.65 2.50 | 12.28 12.42 | |
| 15 | 135 (methanol) | C10H8Cl2N4 (255.10) | 47.08 47.30 | 3.16 3.40 | 21.96 22.12 | |
| 16 | 166 (methanol) | C15H12Cl2N4 (319.19) | 56.44 56.69 | 3.79 3.98 | 17.55 17.39 | |
| 17 | 172 (pet. ether b.p. 80-100°C) | C24H16Cl2N4O (447.31) | 64.44 64.16 | 3.61 3.38 | 12.53 12.78 | |
Biological testing
References
- Turan-Zitouni, G.; Sivaci, M.; Kilic, F.S.; Erol, K. Synthesis of some triazolyl-antypyrine derivatives and investigation of analgesic activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 36, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondhi, S.M.; Sharma, V.K.; Singhal, N.; Verma, R.P; Shukla, R.; Raghubir, R.; Dubey, M. P. Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity evaluation of some acridinyl amino antypyrine, acridinyl amino anthraquinone, acridino thiourea and thiazolino thiourea derivatives. Phosphorus, Sulfur, Silicon Relat. Elem. 2000, 156, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdulene, D.; Palaima, A.; Stumbryavichyute, Z.; Talaikite, Z. Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity of 4-aminoantipyrine derivatives of succinamides. Pharm. Chem. J. 1999, 33, 191–193. [Google Scholar]
- Evstopov, A.N.; Yavorovskaya, V.E; Vorob`ev, E.S.; Kudonogova, Z.P.; Gritsenko, L.N.; Schmidt, E.N; Medevedeva, S.G; Filimonov, V.D.; Prishchep, T.P.; Saratikov, A.S. Pharm. Chem. J. 1992, 26, 426–429.
- Sayed, G.H.; Radwan, A.; Mohamed, S.M.; Shiba, S.A.; Khalil, M. Synthesis and reactions of some 6-aryl and 2,6-diaryl-4(4`-antipyrinyl)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridazin-3-ones and screening for their antibacterial activities. Chin. J. Chem. 1992, 10, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, G.N.; Yonova, P.A.; Bohland, H.; Vassilev, N.G.; Yordanov, B. Synthesis and grouth-regulating activity of some metal coordination compounds with thioureas and antipyrines. Dokl Bulg Akad Nauk 1997, 50, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Cosmetic, Toiletry and Fragrance Association, Inc. Final report on the safety assessment of phenyl(methyl)pyrazolone. J. Am. Coll. Toxicol. 1992, 11, 475–488. [Google Scholar]
- Verleye, M.; Heurald, I.; Gillardin, J.-M. Phenazone potentiates the local anaethetic effect of lidocaine in Mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2000, 41, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, G.H.; El-Kady, M.Y.; Abd Elhalim, M.S. Synthesis and reactions of some α-aryl-β-(4-bromobenzoyl)-propionic acids. Indian J. Chem. 1981, 20, 845–848. [Google Scholar]
- El-Hashash, M.A.; Amine, M.S.; Soliman, F.M.; Morsi, M.A. Behavior of β-aroylacrylic acids toward hydrazine hydrate and some studies on the cyclized products. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 1992, 57, 563–569. [Google Scholar]
- Gould, J.C.; Bowie, J.M. Determination of bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics. Edinburgh Med. J. 1952, 59, 178–199. [Google Scholar]
- Sample availability: Available from MDPI.
© 2003 by MDPI ( http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Sayed, G.H.; Hamed, A.A.; Meligi, G.A.; Boraie, W.E.; Shafik, M. The Use of 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-4-Oxo-2-(4-Antipyrinyl)-Butanoic Acid in the Preparation of Some New Heterocyclic Compounds With Expected Biological Activity. Molecules 2003, 8, 322-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/80300322
Sayed GH, Hamed AA, Meligi GA, Boraie WE, Shafik M. The Use of 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-4-Oxo-2-(4-Antipyrinyl)-Butanoic Acid in the Preparation of Some New Heterocyclic Compounds With Expected Biological Activity. Molecules. 2003; 8(3):322-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/80300322
Chicago/Turabian StyleSayed, G. H., A. A. Hamed, G. A. Meligi, W. E. Boraie, and M. Shafik. 2003. "The Use of 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-4-Oxo-2-(4-Antipyrinyl)-Butanoic Acid in the Preparation of Some New Heterocyclic Compounds With Expected Biological Activity" Molecules 8, no. 3: 322-332. https://doi.org/10.3390/80300322




