An Air-Ground Wireless Sensor Network for Crop Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction

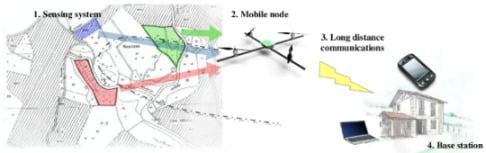
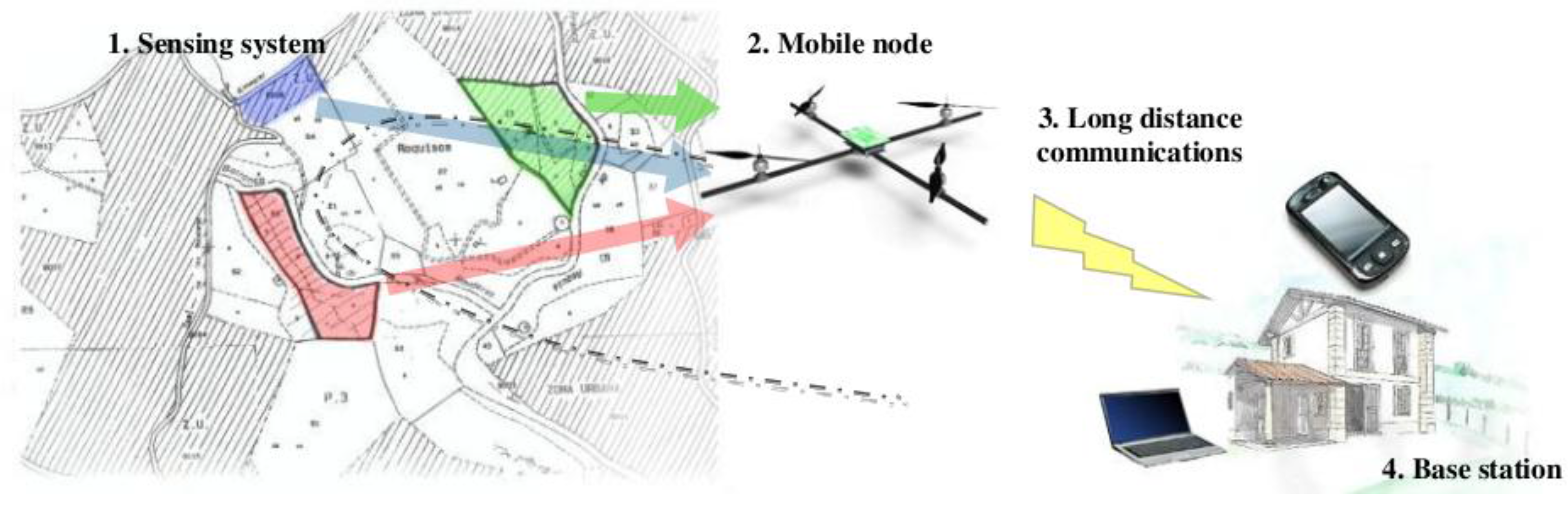
2. System Overview
- Sensing system (WSN). It is made up of a split ground static wireless sensor network, which monitors the crop acquiring information in an intelligent manner (i.e., optimal sampling, storing and routing). This will be described in detail in Section 2.1.
- Mobile node. Stationary nodes are combined with a mobile node carried by a mini aerial vehicle, employed as a remote dynamic data collector, analyzed in Section 2.2.
- Long distance communications. Finally, the system is endowed with a packet oriented mobile data service connection, which provides a long distance communication channel. This is presented in Section 2.3.
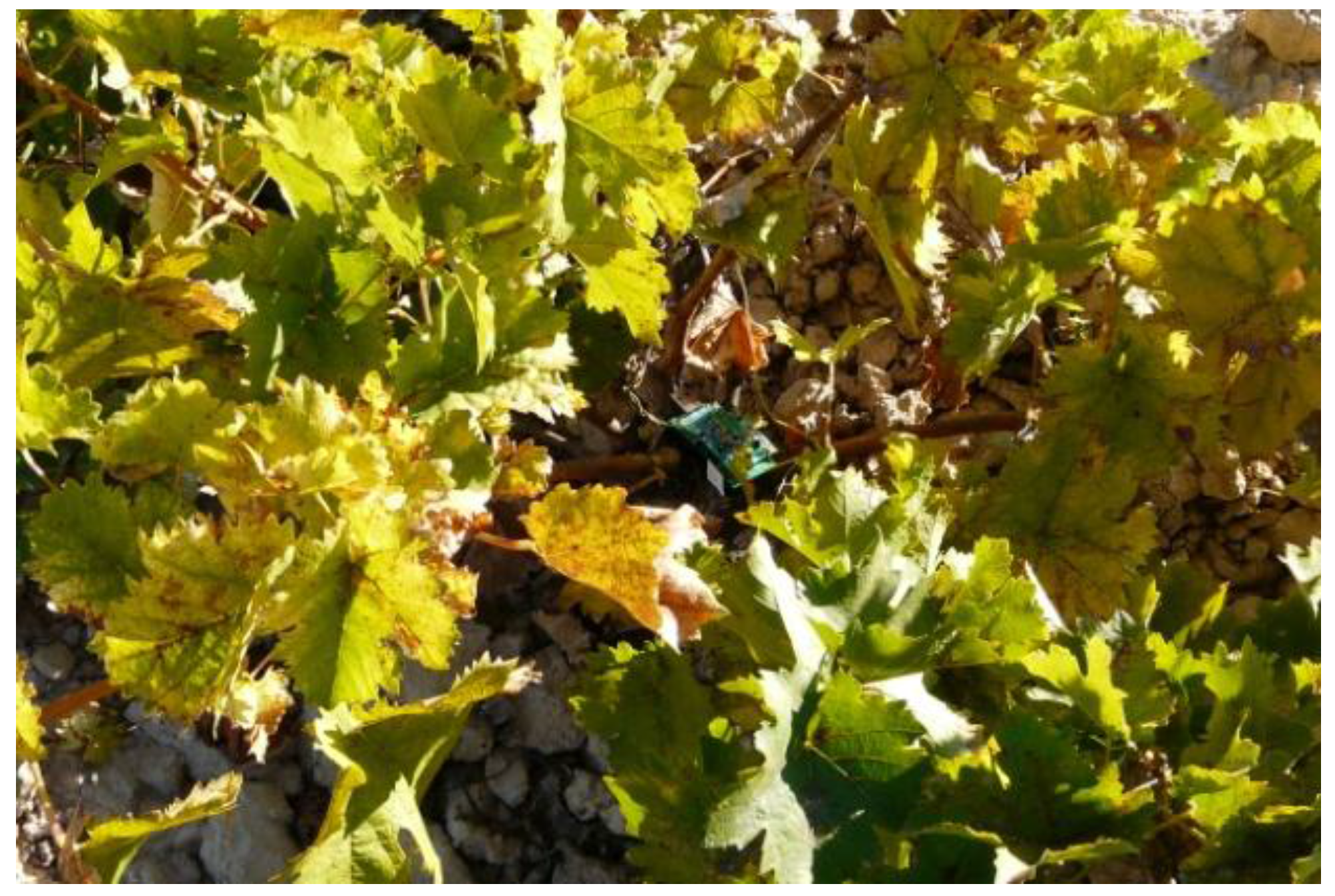
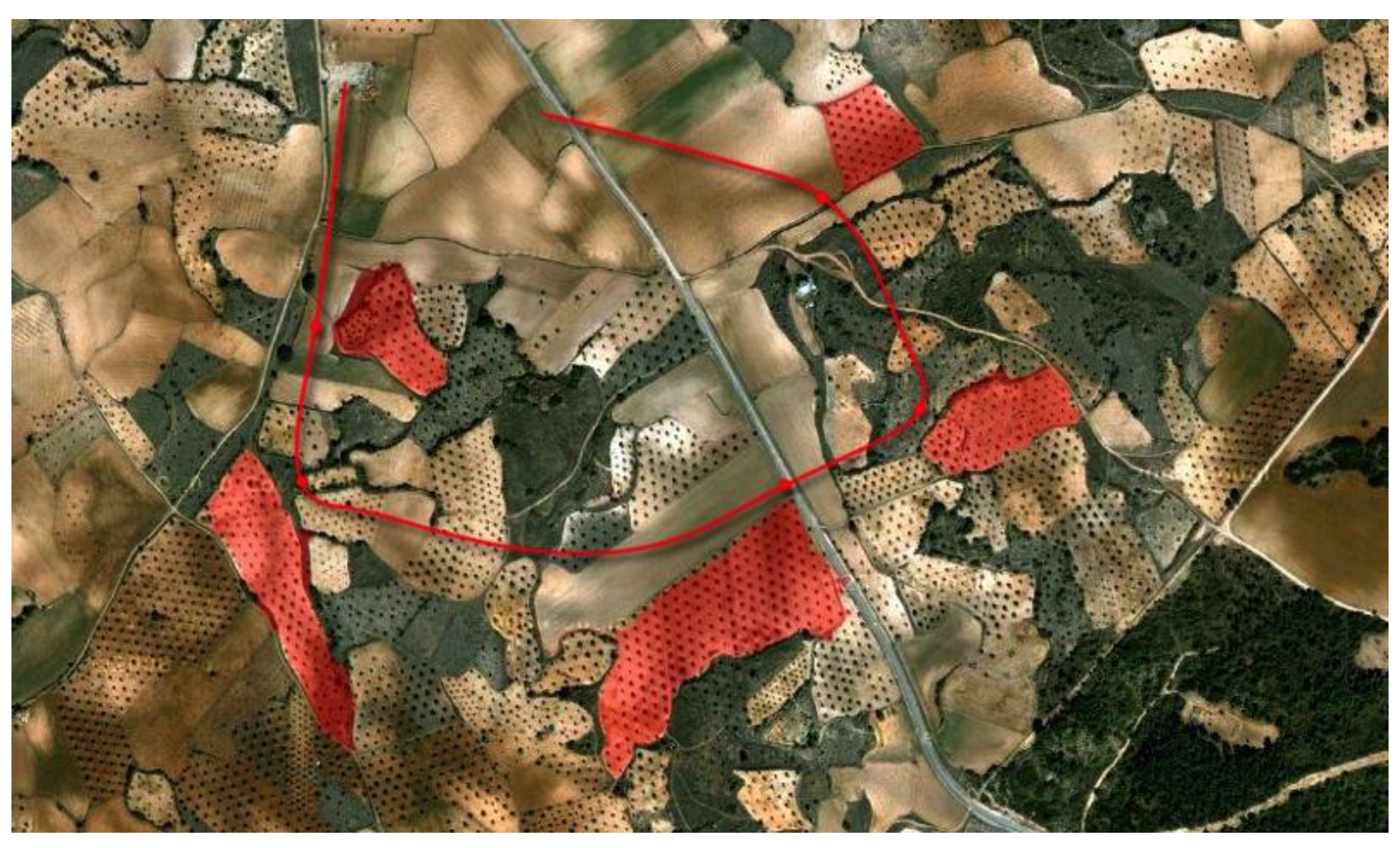
2.1. Sensing System: WSNs for Specific Data Acquisition
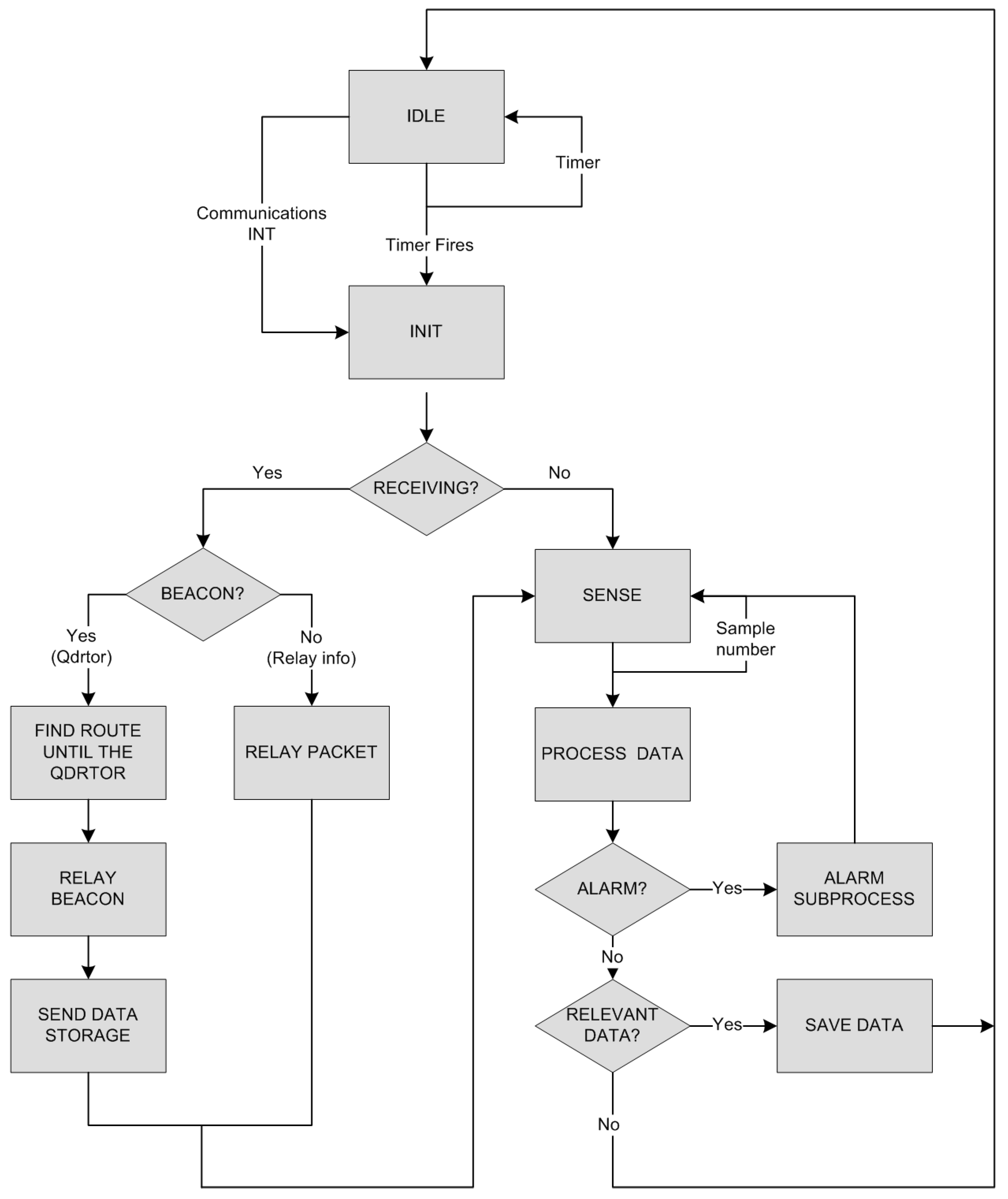
2.2. Mobile Node: Aerial Robot as a Mobile WSN Node
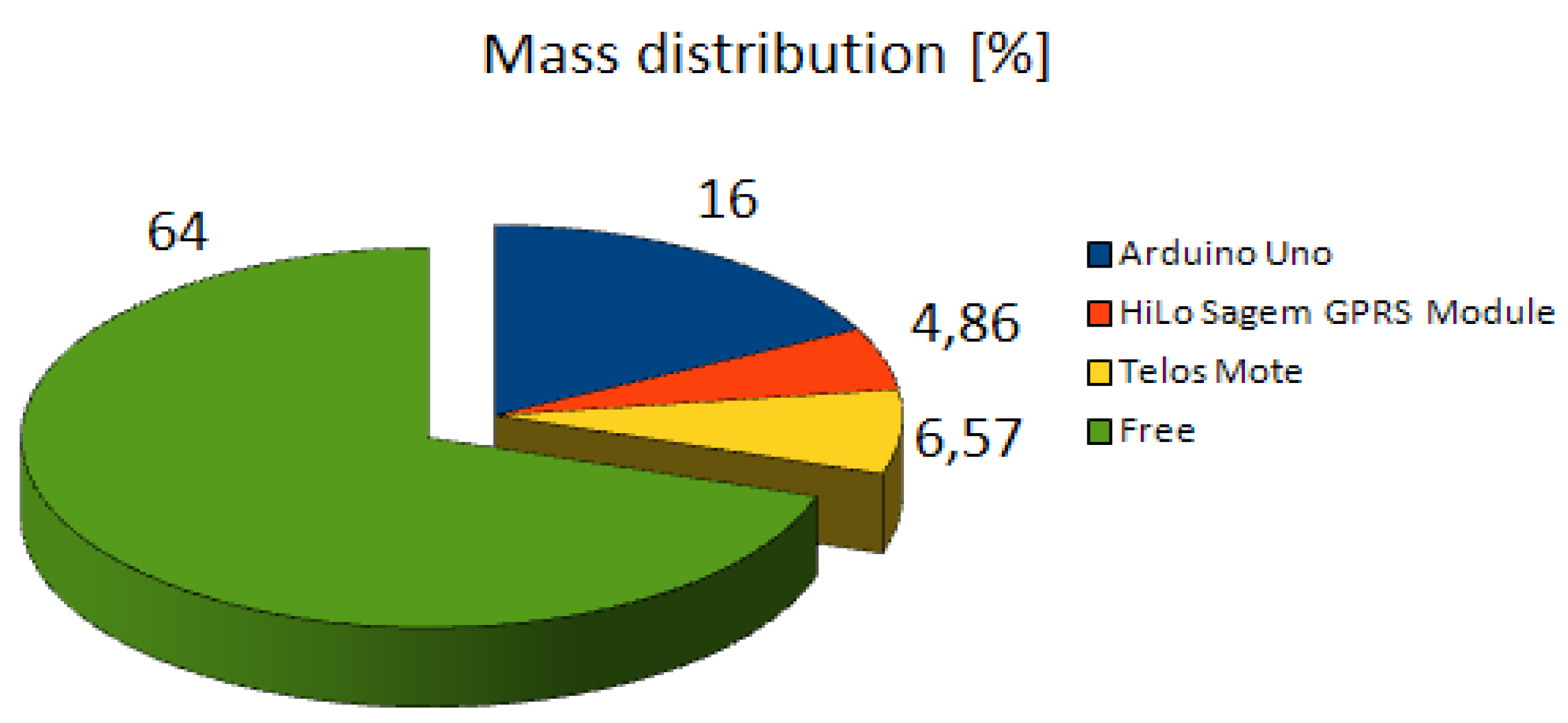
- Width: 0.63 m
- Dimensions: 40 × 40 × 10 cm
- Total weight: 550 grams
- Payload: 200 grams
- Spektrum DX7SE 2.4 GHz remote control
- X-Bee 2.4 GHz data link
- LiPo 11.1 V 2100 mAh
- Maximum height: 500 m
- The four rotors are made up of X-BL-52s brushless motors and their controllers.
- Sensing capacity: GPS, IMU, 3D-MAG, pressure sensor.
- The mainframe is made up of a power board and an autopilot card.
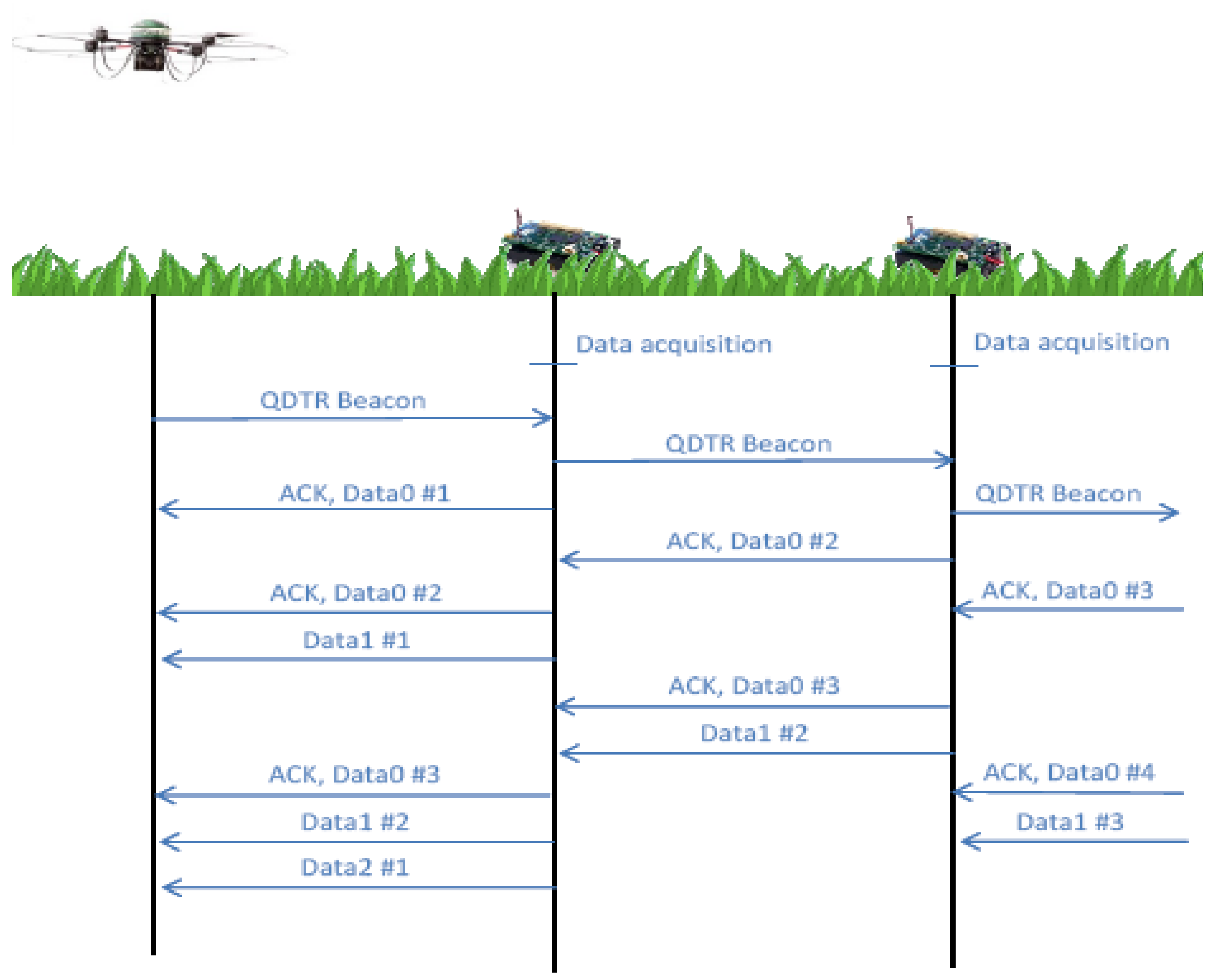
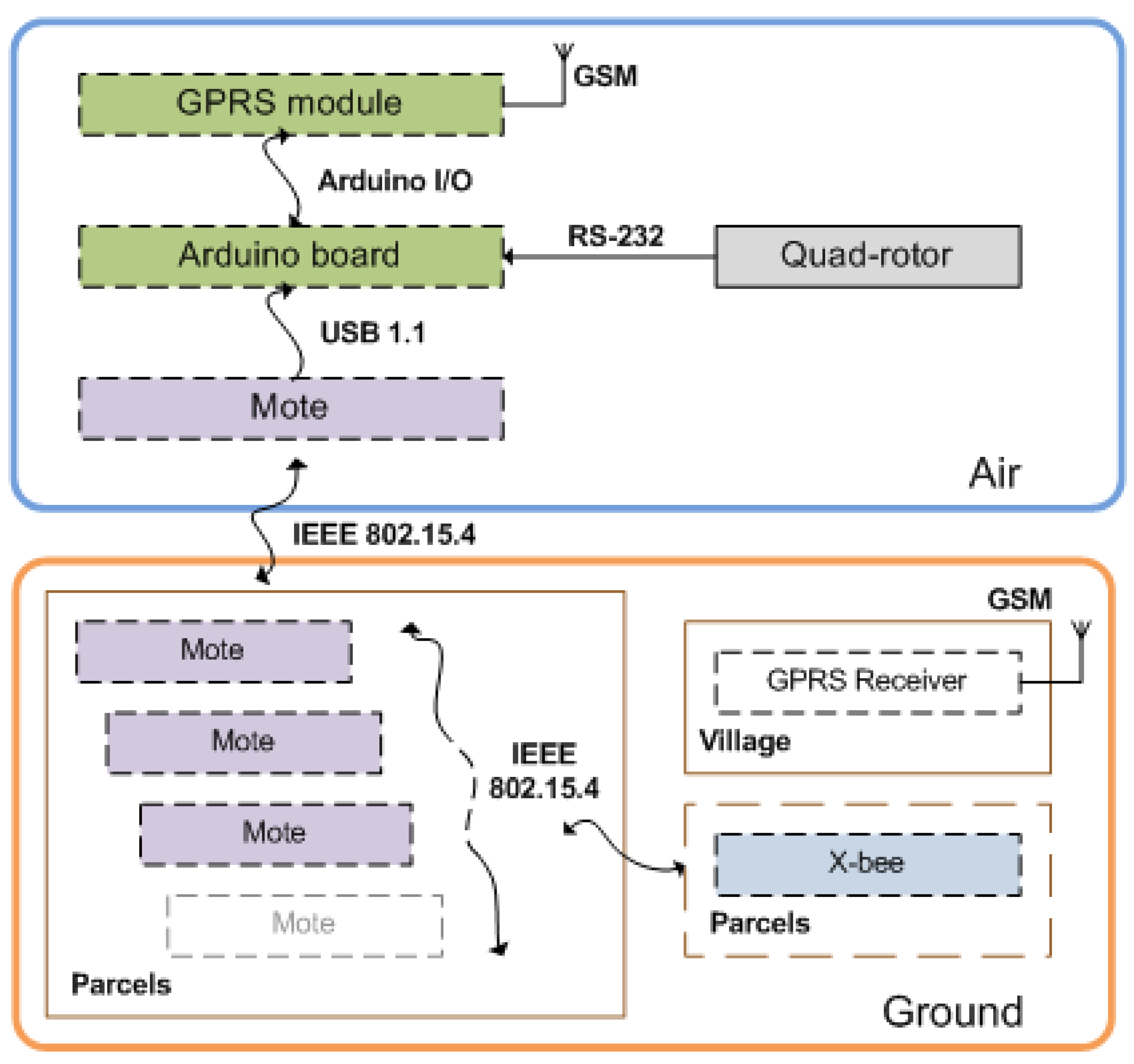
2.3. Communications Workflow: Relaying Data to the Base Station
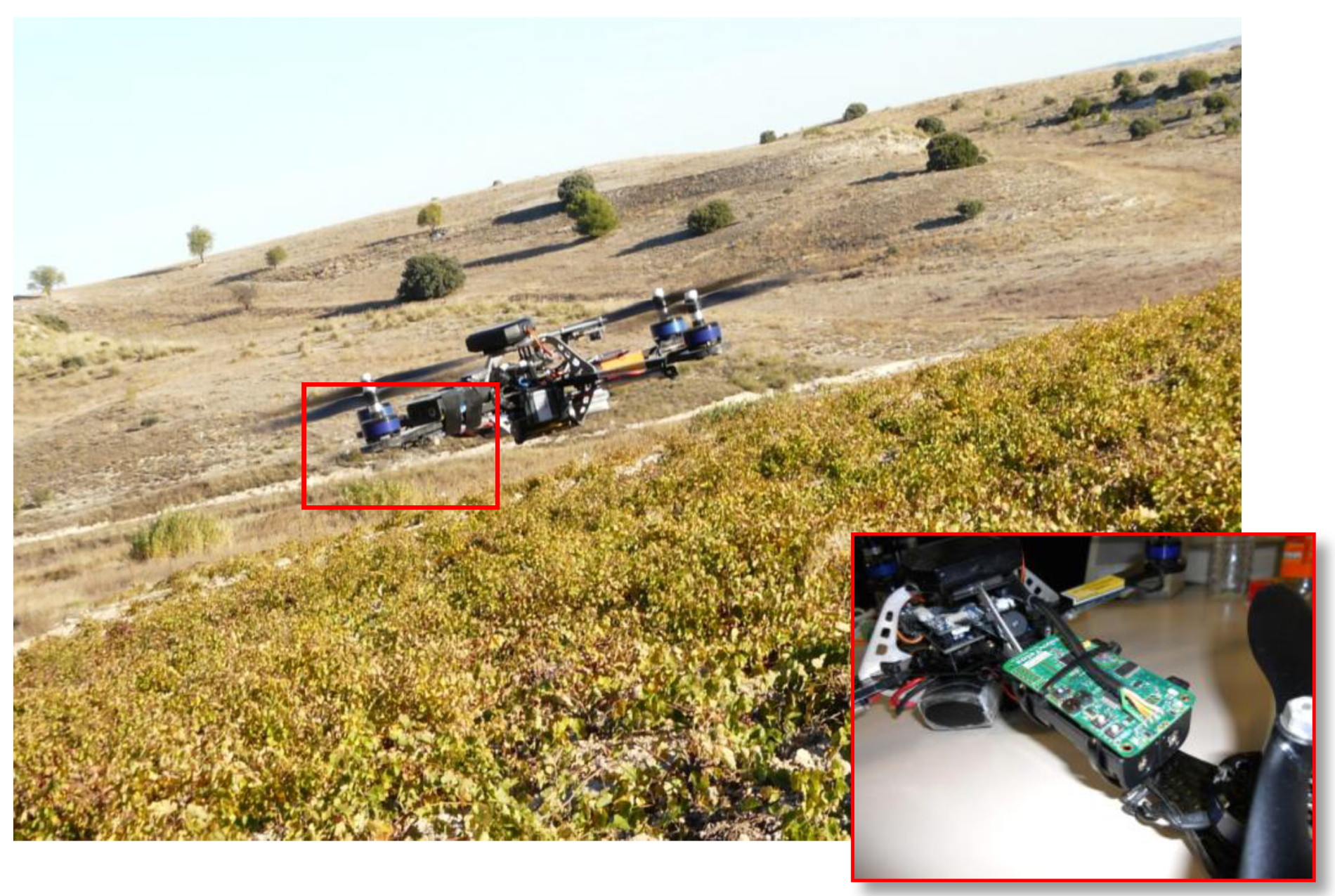


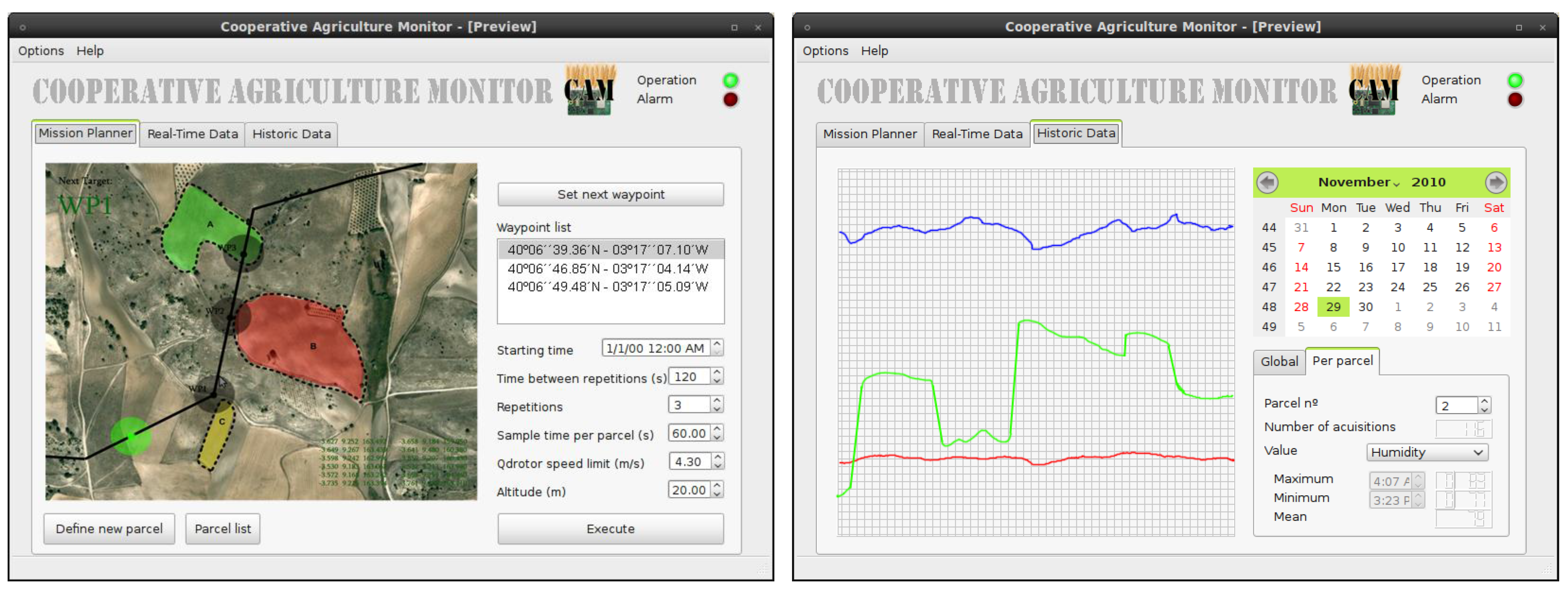
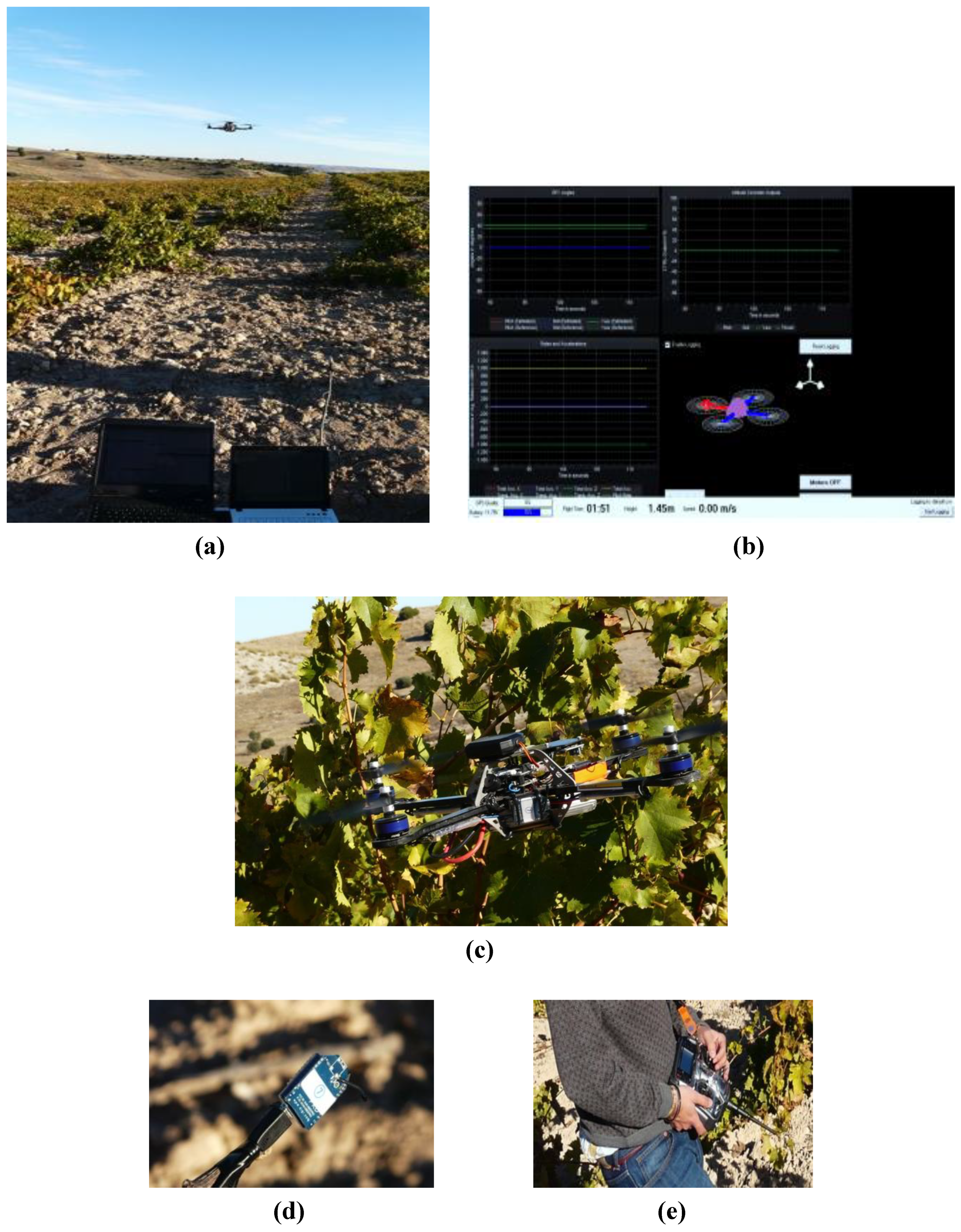
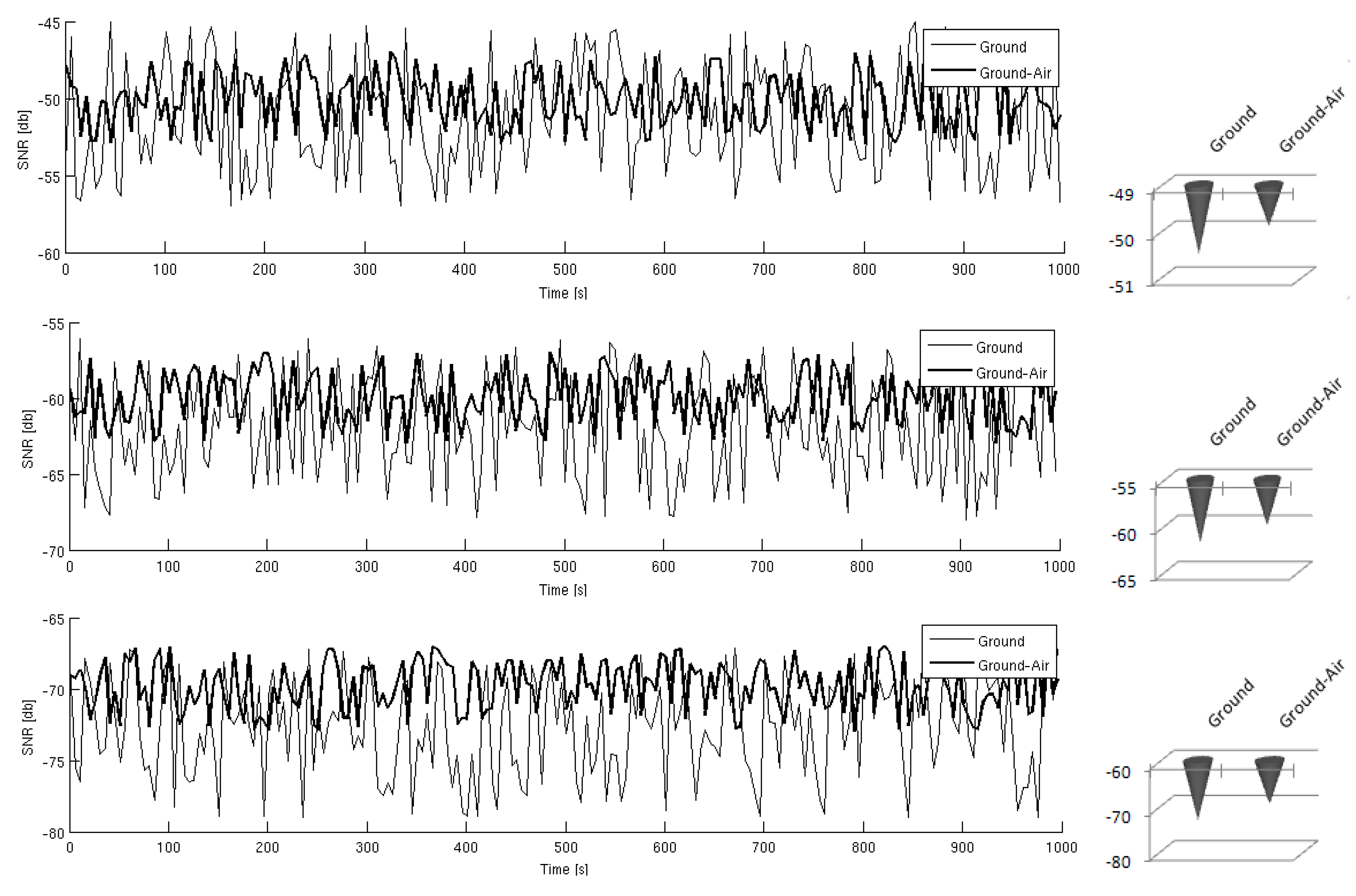
3. Case Study and Experimental Results
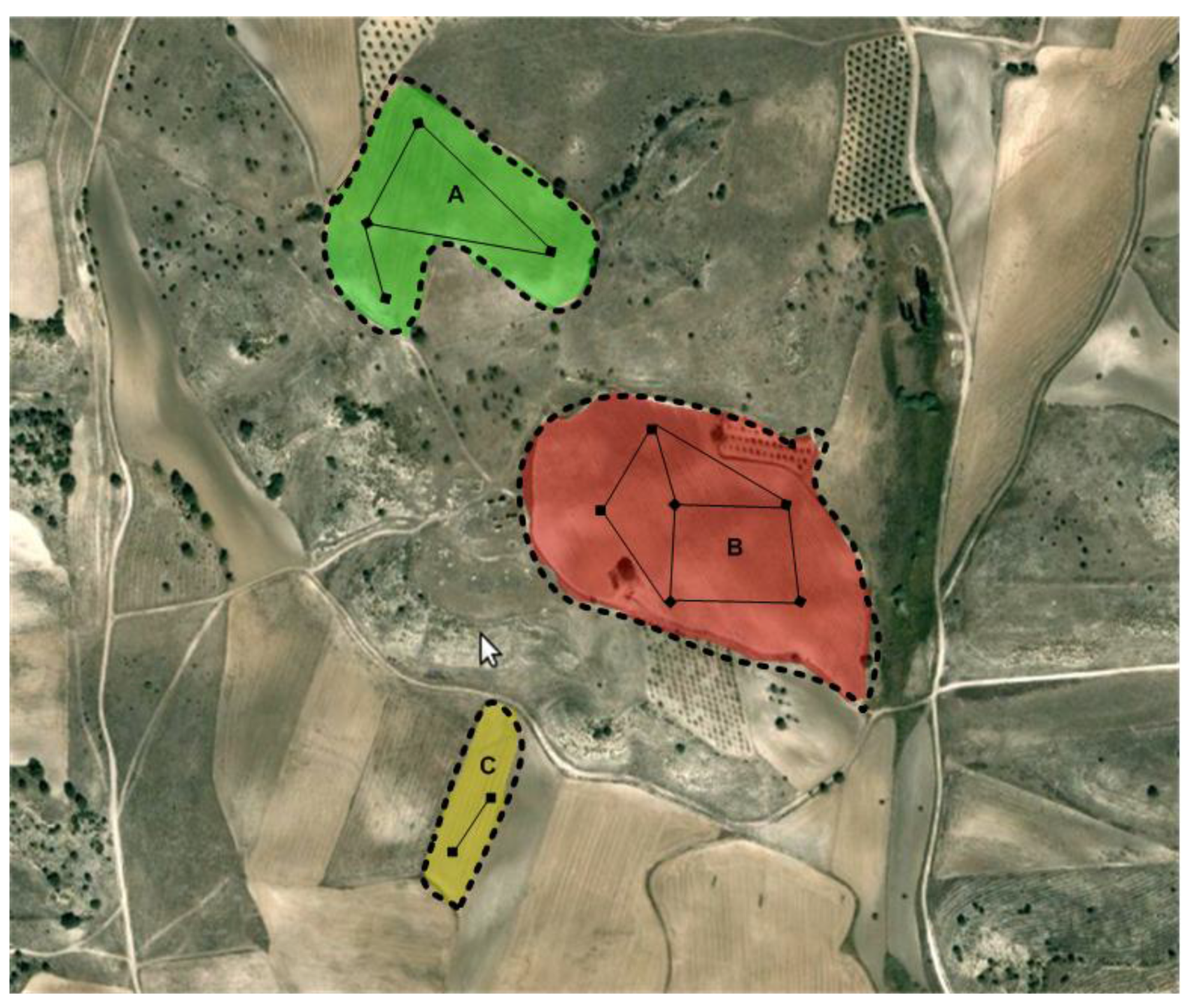

| Parcels | Average dispersion [m] | Signal quality [%] | Packets lost [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 10 | 80.3 | 4.1 |
| B | 20 | 73.2 | 6 |
| C | 30 | 59.9 | 6.7 |
| Parcels | Flight height [m] | Signal quality [%] | Packets lost [%] | Nodes covered |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 10 | 95.2 | 0.8 | 100% |
| A | 20 | 93.9 | 1.7 | 100% |
| A | 30 | 84 | 1.1 | 100% |
| B | 10 | 93.8 | 1.2 | 100% |
| B | 20 | 90.2 | 1.3 | 100% |
| B | 30 | 83.7 | 1.4 | 91% (10/11) |
| C | 10 | 95 | 0.9 | 100% |
| C | 20 | 91 | 1 | 100% |
| C | 30 | 87.4 | 3 | 100% |
| Parcels | Time | Way-point | Update Time | Battery | Quadrotor speed | Signal quality | Packets lost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 17 h:45 m:14 s 08/12/2010 | 40°06''49.48'N 03°17''05.09'W | 71 s | 12.51 V | 5 m/s | 92.3% | 2% |
| B | 17 h:47 m:32 s 08/12/2010 | 40°06''46.85'N 03°17''04.14'W | 83 s | 12.37 V | 5 m/s | 89.7% | 3% |
| C | 17 h:50 m:43 s 08/12/2010 | 40°06''39.36'N 03°17''07.10'W | 76 s | 12.02 V | 5 m/s | 96% | 1% |
| Experiments | Wind speed | Aerial Robot velocity | Battery status | Mission duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.2 m/s | 5 m/s | 10.23 V | 191 s |
| 2 | 8.9 m/s | 5 m/s | 9.25 V | 276 s |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Kropff, M.; Wallinga, J.; Lotz, L. Modelling for Precision Weed Management. In Proceedings of Ciba Foundation Symposium 210—Precision Agriculture: Spatial and Temporal Variability of Environmental Quality, Chichester, UK, 27 September 2007; pp. 182–207.
- Blackmore, S.; Wheeler, P.; Earl, R. Precision Farming: The Management of Variability. Landwards 1996, 51, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, A. Handbook of Precision Agriculture: Principles and Applications; CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sudduth, K.; Hummel, J.; Birrell, S. Sensors for Site-Specific Managemen. In The State of Site Specific Management for Agriculture; ASA-CSSA-SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1997; pp. 183–210. [Google Scholar]
- Akyildiz, I.F.; Su, W.; Sankarasubramaniam, Y.; Cayirci, E. Wireless Sensor Networks: A Survey. Comput. Netw. 2002, 38, 393–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.-M.; Wang, L.-M.; Qu, X.-Q.; Zhan, Y.-Z. Application Research of WSN in Precise Agriculture Irrigation. In Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Application Technology, Wuhan, China, 4–5 July 2009; Volume 2, pp. 297–300.
- de Lima, G.H.E.L.; e Silva, L.C.; Neto, P.F.R. WSN as a Tool for Supporting Agriculture in the Precision Irrigation. In Proceedings of International Conference on Networking and Services, Cancun, Mexico, 7–13 March 2010; pp. 137–142.
- Kim, Y.; Evans, R.; Iversen, W. Remote Sensing and Control of an Irrigation System Using a Distributed Wireless Sensor Network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2008, 57, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar]
- Shinghal, K.; Noor, D.; Srivastava, D.; Singh, D. Wireless Sensor Networks in Agriculture: For Potato Farming. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2010, 2, 3955–3963. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasi, G.; Farruggia, O.; Re, G.L.; Ortolani, M. Monitoring High-Quality Wine Production using Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 42nd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Big Island, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2009; pp. 1–7.
- Yoo, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.; Ahn, S.; Sung, J.; Kim, D. A2S: Automated Agriculture System Based on WSN. In Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Consumer Electronics, Dallas, TX, USA, 20–23 June 2007; pp. 1–5.
- Siuli Roy, A.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Agro-Sense: Precision Agriculture Using Sensor-Based Wireless Mesh Networks. Innovations in NGN—Future Network and Services. In Proceedings of An IT U-T Kaleidoscope Conference, Geneva, Switzerland, 12–13 May 2008; pp. 383–388.
- Yamaha Inc. Yamaha autonomous-flight unmanned helicopter deployed for observation illegal dumping around Mt. fuji., 2011.
- Zarco-Tejada, P.; Berni, J.; Suárez, L.; Fereres, E. A new era in remote sensing of crops with unmanned robots. SPIE Newsroom 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwitz, S.; Dunagan, S.; Sullivan, D.; Higgins, R.; Johnson, L.; Zheng, J.; Slye, R.; Brass, J.; Leung, J.; Gallmeyer, B.; Aoyagi, M. Solar-Powered UAV Mission for Agricultural Decision Support. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 3, pp. 1692–1694.
- Herwitz, S.; Johnson, L.; Dunagan, S.; Higgins, R.; Sullivan, D.; Zheng, J.; Lobitz, B.; Leung, J.; Gallmeyer, B.; Aoyagi, M.; et al. Imaging from an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle: Agricultural Surveillance and Decision Support. Comput. Electr. Agr. 2004, 44, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.; Herwitz, S.; Dunagan, S.; Lobitz, B.; Sullivan, D.; Slye, R. Collection of Ultra High Spatial and Spectral Resolution Image Data over California Vineyards with a Small UAV. In Proceedings of the 30th International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment, Honolulu, HI, USA, 10–14 November 2003.
- Herwitz, S.; Slye, R.; Dunagan, S.; Lobitz, B.; Johnson, L. Nighttime UAV Vineyard Mission: Challenges of See-and-Avoid in the U.S. National Airspace. In Proceedings of AIAA 3rd Unmanned Unlimited Technical Conference, Workshop and Exhibit, Chicago, IL, USA, 20–23 September 2004.
- Sugiura, R.; Noguchi, N.; Ishii, K. Remote-sensing Technology for Vegetation Monitoring using an Unmanned Helicopter. Biosyst. Eng. 2005, 90, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahori, T.; Noguchi, N.; Ishii, K.; Sugiura, R. Development of GIS Map Generation System Using an Unmanned Helicopter; Technical Report 051020; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rovira-Más, F.; Zhang, Q.; Reid, J. Creation of Three-Dimensional Crop Maps based on Aerial Stereoimages. Biosyst. Eng. 2005, 90, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.; Baumann, M.; Jensen, A.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ren, W.; McKee, M. Band-Reconfigurable Multi-UAV-Based Cooperative Remote Sensing for Real-Time Water Management and Distributed Irrigation Control. In Proceedings of IFAC World Congress, Seoul, Korea, 6–11 July 2008.
- Johnson, H.; Robinson, J.; Limited, O.P.G. The World Atlas of Wine; Mitchell Beazley: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tongrod, N.; Tuantranont, A.; Kerdcharoen, T. Adoption of Precision Agriculture in Vineyard. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology, Pattaya, Thailand, 6–9 May 2009; Volume 2, pp. 735–738.
- Beckwith, R.; Teibel, D.; Bowen, P. Unwired Wine: Sensor Networks in Vineyards. Proc. IEEE Sensors 2004, 2, 561–564. [Google Scholar]
- Burrell, J.; Brooke, T.; Beckwith, R. Vineyard Computing: Sensor Networks in Agricultural Production. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2004, 3, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero Risalde, F.J. Central termica de biomasa de 5 Mw de potencia. Anexo 5: Estudio de la distribucion del viñedo por superficie y numero de parcelas. M.S. Thesis, Universidad de Castilla-La Mancha, Ciudad Real, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Teh, S.K.; Mejias, L.; Corke, P.; Hu, W. Experiments in Integrating Autonomous Uninhabited Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the Australasian Conference on Robotics and Automation, Canberra, Australia, 3–5 December 2008.
- Dang, P.; Lewis, F.L.; Popa, D.O. Dynamic Localization of Air-Ground Wireless Sensor Networks. In Advances in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles; Valavanis, K.P., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 431–453. [Google Scholar]
- Poe, W.Y.; Schmitt, J.B. Node Deployment in Large Wireless Sensor Networks: Coverage, Energy Consumption, and Worst-Case Delay. In Proceedings of Asian Internet Engineering Conference, Bangkok, Thailand, 18–20 November 2009; pp. 77–84.
- Puccinelli, D.; Haenggi, M. Arbutus: Network-Layer Load Balancing for Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 March–3 April 2008; pp. 2063–2068.
- Xiang, X.; Guo, X. Zigbee Wireless Sensor Network Nodes Deployment Strategy for Digital Agricultural Data Acquisition. In Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture III; Li, D., Zhao, C., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; Volume 317. [Google Scholar]
- Salhieh, A.; Weinmann, J.; Kochhal, M.; Schwiebert, L. Power Efficient Topologies for Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of International Conference on Parallel Processing, Valencia, Spain, 3–7 September 2001; pp. 156–163.
- Förster, A.; Murphy, A.L. A Critical Survey and Guide to Evaluating WSN Routing Protocols. In Proceedings of The First International Workshop on Networks of Cooperating Objects, Stockholm, Sweden, 12 April 2010.
- Abramson, N. The ALOHA System: Another Alternative for Computer Communications. In Proceedings of the Fall Joint Computer Conference, Montvale, NJ, USA, 17–19 November 1970; pp. 281–285.
- Ziouva, E.; Antonakopoulos, T. CSMA/CA Performance under High Traffic Conditions: Throughput and Delay Analysis. Comput. Commun. 2002, 25, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, R.; Hagenauer, J. On Variable Length Codes for Iterative Source/Channel Decoding. In Proceedings of Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, UT, USA, 2001; pp. 273–282.
- The experiments were carried using TelosB motes. Available online: http://bullseye.xbow.com:81/Products/Product_pdf_files/Wireless_pdf/TelosB_Datasheet.pdf/ (accessed on 26 May 2011).
- The experiments were carried from 25 October–December 2010.
- Sensirion SHT11: Temperature and Relative Humidity Sensor. Available online: http://www.sensirion.com/en/pdf/product_information/Datasheet-humidity-sensor-SHT1x.pdf/ (accessed on 26 May 2011).
- Hamamatsu S108: Visible light sensor. Available online: http://sales.hamamatsu.com/assets/pdf/parts_S/S1087_etc.pdf/ (accessed on 26 May 2011).
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Valente, J.; Sanz, D.; Barrientos, A.; Cerro, J.d.; Ribeiro, Á.; Rossi, C. An Air-Ground Wireless Sensor Network for Crop Monitoring. Sensors 2011, 11, 6088-6108. https://doi.org/10.3390/s110606088
Valente J, Sanz D, Barrientos A, Cerro Jd, Ribeiro Á, Rossi C. An Air-Ground Wireless Sensor Network for Crop Monitoring. Sensors. 2011; 11(6):6088-6108. https://doi.org/10.3390/s110606088
Chicago/Turabian StyleValente, João, David Sanz, Antonio Barrientos, Jaime del Cerro, Ángela Ribeiro, and Claudio Rossi. 2011. "An Air-Ground Wireless Sensor Network for Crop Monitoring" Sensors 11, no. 6: 6088-6108. https://doi.org/10.3390/s110606088
APA StyleValente, J., Sanz, D., Barrientos, A., Cerro, J. d., Ribeiro, Á., & Rossi, C. (2011). An Air-Ground Wireless Sensor Network for Crop Monitoring. Sensors, 11(6), 6088-6108. https://doi.org/10.3390/s110606088