Pupil and Glint Detection Using Wearable Camera Sensor and Near-Infrared LED Array
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Proposed Method
2.1. Proposed Gaze Tracking Device
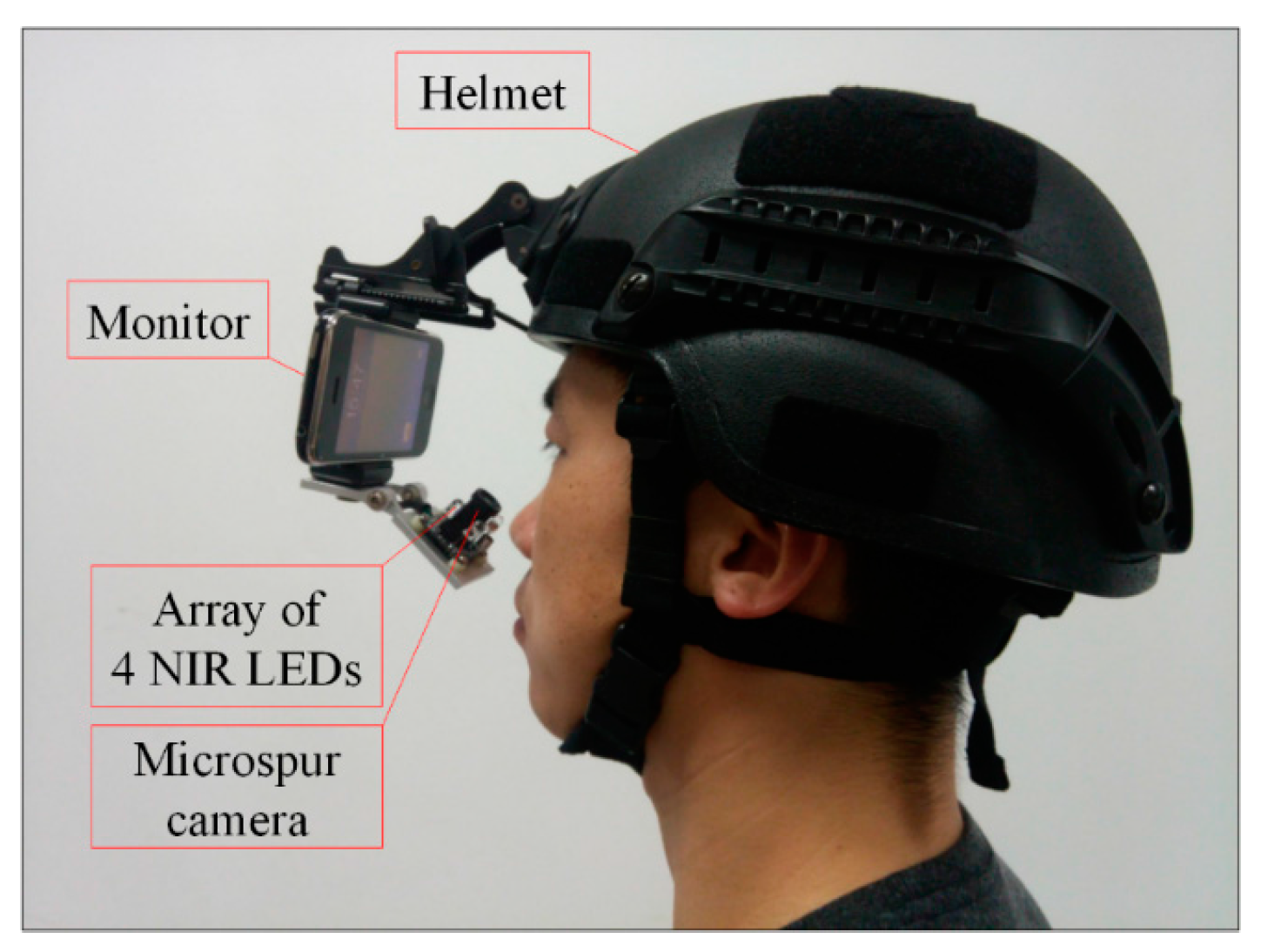
2.2. Pupil Detection
2.2.1. Binarization and Opening-and-Closing Operation

| Method | Original Otsu | Improved Otsu |
|---|---|---|
| Time/ms | 32.4 | 17.1 |


2.2.2. Rough Location of Pupil Area and Center

2.2.3. Collection of Pupil Boundary Points

2.2.4. Ellipse Fitting

2.3. Glint Detection
2.3.1. Rough Location of Glint Region

2.3.2. Gaussian Fitting


3. Experimental Results
3.1. Pupil Detection
3.1.1. Pupil Detection of Single Subject

3.1.2. Pupil Detection of Different Subjects

3.2. Glint Detection

| Detected Glint Center () | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glint Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Figure 11a | (212.39, 214.42) | (268.28, 214.64) | (213.53, 241.31) | (266.76, 241.24) |
| Figure 11b | (293.85, 201.79) | (345.34, 202.49) | (294.15, 227.63) | (343.94, 227.71) |
| Figure 11c | (296.90, 191.21) | (348.58, 191.36) | (298.34, 217.17) | (347.55, 217.43) |
| Figure 11d | (314.53, 196.17) | (366.49, 197.12) | (316.03, 221.18) | (365.87, 222.52) |
| Figure 12a | (264.25, 207.31) | (318.64, 208.15) | (265.12, 235.43) | (317.20, 235.98) |
| Figure 12b | (211.39, 133.26) | (252.13, 134.68) | (221.64, 149.52) | (251.54, 149.22) |
| Figure 12c | (265.47, 186.29) | (321.40, 186.24) | (263.68, 216.44) | (319.87, 215.31) |
| Figure 12d | (284.31, 152.37) | (331.82, 152.21) | (283.14, 176.33) | (329.13, 176.45) |
3.3. Stability and Error
| Method | Pupil Detection | Glint Detection | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stability | Error (Pixels) | Time (ms) | Stability | Error (Pixels) | Time (ms) | |
| Proposed method | 99.4% | 2.17 | 43.6 | 98.7% | 0.69 | 21.5 |
| Paper [13] | 94.9% | 6.48 | 92.1 | 90.9% | 1.73 | 38.6 |
| Paper [20] | 95.2% | 7.86 | 65.5 | 94.1% | 1.28 | 34.1 |
| Paper [21] | 97.9% | 5.43 | 54.3 | - | - | - |
| Paper [22] | 96.6% | 5.95 | 126.4 | - | - | - |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blondon, K.; Wipfli, R.; Lovis, C. Use of eye-tracking technology in clinical reasoning: a systematic review. Stud. Health Technol. Inf. 2015, 210, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Higins, E.; Leinenger, M.; Rayner, K. Eye movements when viewing advertisements. Front. Psychol. 2014, 210. Available online: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00210/full (accessed on 30 November 2015). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spakov, O.; Majaranta, P. Scrollable keyboards for casual eye typing. Psychol. J. 2009, 7, 159–173. [Google Scholar]
- Noureddin, B.; Lawrence, P.D.; Man, C.F. A non-contact device for tracking gaze in human computer interface. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2005, 98, 52–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.; Langdon, P. Multimodal intelligent eye-gaze tracking system. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2015, 31, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.J.; Kim, D. Development of gaze tracking interface for controlling 3D contents. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2012, 185, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarbus, A.L. Eye Movements and Vision; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Dodge, R.; Cline, T.S. The angle velocity of eye movements. Psychol. Rev. 1901, 8, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditchburn, R.W. Eye movements and Visual Perception; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, W. The peep-hole method for observing eye movements in reading. J. Gen. Psychol. 1928, 1, 373–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A. A method of measuring eye movements using a scleral search coil in a magnetic field. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1963, 10, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cornsweet, T.N.; Crane, H.S. Accurate two-dimensional eye tracker using first and fourth Purkinje images. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1973, 63, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, T.; Mukawa, N.; Yoshikawa, A. Free gaze: a gaze tracking system for everyday gaze interaction. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications Symposium, New Orleans, LA, USA, 25–27 March 2002; pp. 125–132.
- Goñi, S.; Echeto, J.; Villanueva, A.; Cabeza, R. Robust algorithm for pupil-glint vector detection in a video-oculography eye tracking system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cambridge, UK, 23–26 August 2004; pp. 941–944.
- Villanueva, A.; Cabeza, R. A novel gaze estimation system with one calibration point. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2008, 38, 1123–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gneo, M.; Schmid, M.; Conforto, S.; D’Alessio, T. A free geometry model-independent neural eye-gaze tracking system. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2002, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blignaut, P. Mapping the pupil-glint vector to gaze coordinates in a simple video-based eye tracker. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2014, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.C.; Shih, S.W.; Hung, Y.P. Hybrid method for 3-D gaze tracking using glint and contour features. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2015, 25, 24–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ebisawa, Y. Unconstrained pupil detection technique using two light sources and the image difference method. Visual. Intell. Des. Engine Arch. 1995, 15, 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, D.H.; Chung, M.J.; Ju, D.B.; Choi, I.H. Non-intrusive eye gaze estimation using a projective invariant under head movement. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2006; pp. 3443–3448.
- Gwon, S.Y.; Cho, C.W.; Lee, H.C. Robust eye and pupil detection method for gaze tracking. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2013, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.H.; Winfield, D.W.; Parkhurst, D.J. Starburst: A hybrid algorithm for video-based eye tracking combining feature-based and model-based approaches. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Diego, CA, USA, 25–25 June 2005; pp. 79–86.
- Krishnamoorthi, R.; Annapoorani, G. A simple boundary extraction technique for irregular pupil localization with orthogonal polynomials. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2012, 116, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliney, D.; Aron-Rosa, D.; DeLori, F.; Fankhauser, F.; Landry, R.; Mainster, M.; Marshall, J.; Rassow, B.; Stuck, B.; Trokel, S.; et al. Adjustment of guidelines for exposure of the eye to optical radiation from ocular instruments: Statement from a task group of the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 2162–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Truchetet, F.; Nicolier, F.; Laligant, O. Subpixel edge detection for dimensional control by artificial vision. J. Electron. Imaging 2001, 10, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Philos. Mag. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, G.H.; Van Loan, C.F. An analysis of the total least squares problem. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1980, 177, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gander, W.; Golub, G.H.; Strebel, R. Least-squares fitting of circles and ellipses. BIT Numer. Math. 1994, 34, 558–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortis, M.R.; Clarke, T.A.; Short, T. A comparison of some techniques for the subpixel location of discrete target images. In Photonics for Industrial Applications, Proceedings of the International Society for Optics and Photonics, Boston, MA, USA, 6 October 1994; pp. 239–259.
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Shi, J. Pupil and Glint Detection Using Wearable Camera Sensor and Near-Infrared LED Array. Sensors 2015, 15, 30126-30141. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151229792
Wang J, Zhang G, Shi J. Pupil and Glint Detection Using Wearable Camera Sensor and Near-Infrared LED Array. Sensors. 2015; 15(12):30126-30141. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151229792
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jianzhong, Guangyue Zhang, and Jiadong Shi. 2015. "Pupil and Glint Detection Using Wearable Camera Sensor and Near-Infrared LED Array" Sensors 15, no. 12: 30126-30141. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151229792
APA StyleWang, J., Zhang, G., & Shi, J. (2015). Pupil and Glint Detection Using Wearable Camera Sensor and Near-Infrared LED Array. Sensors, 15(12), 30126-30141. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151229792





