Machine Learning Based Single-Frame Super-Resolution Processing for Lensless Blood Cell Counting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
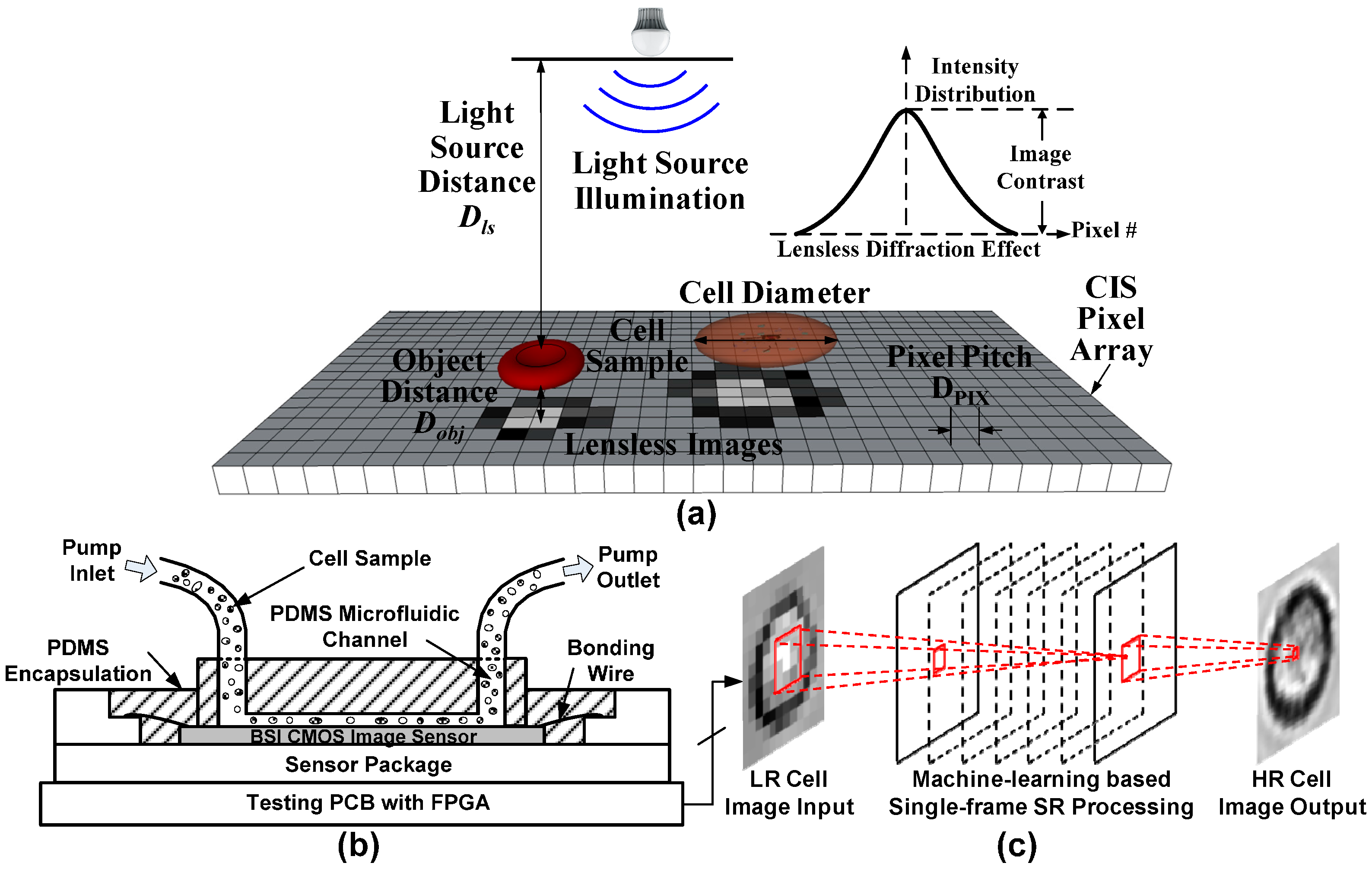
2.1. Lensless Cell Counting System Design
2.1.1. System Overview
2.1.2. CMOS Image Sensor
2.1.3. Microfluidic Channel
2.1.4. Testing Board
2.1.5. Sample Preparation
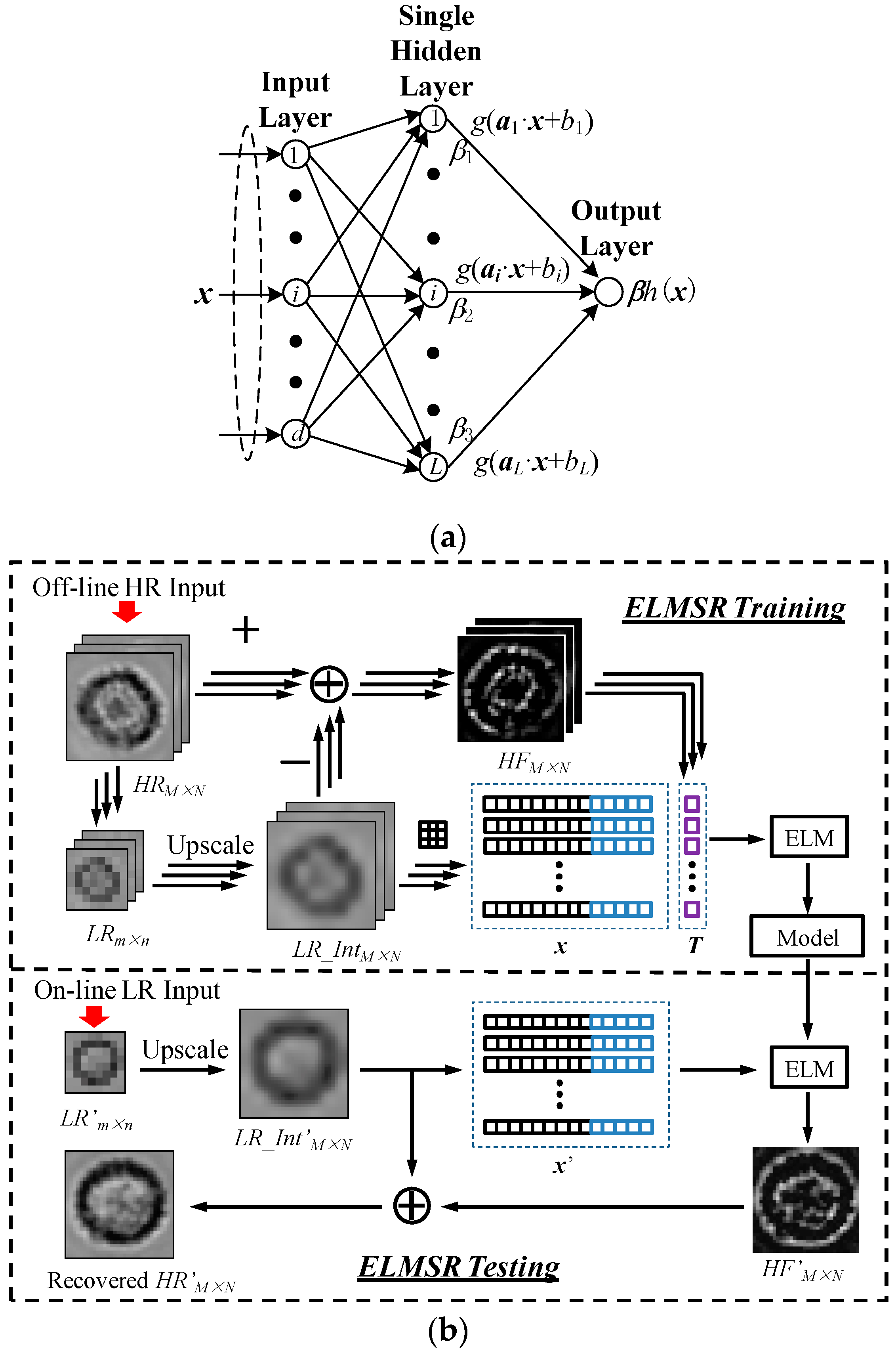
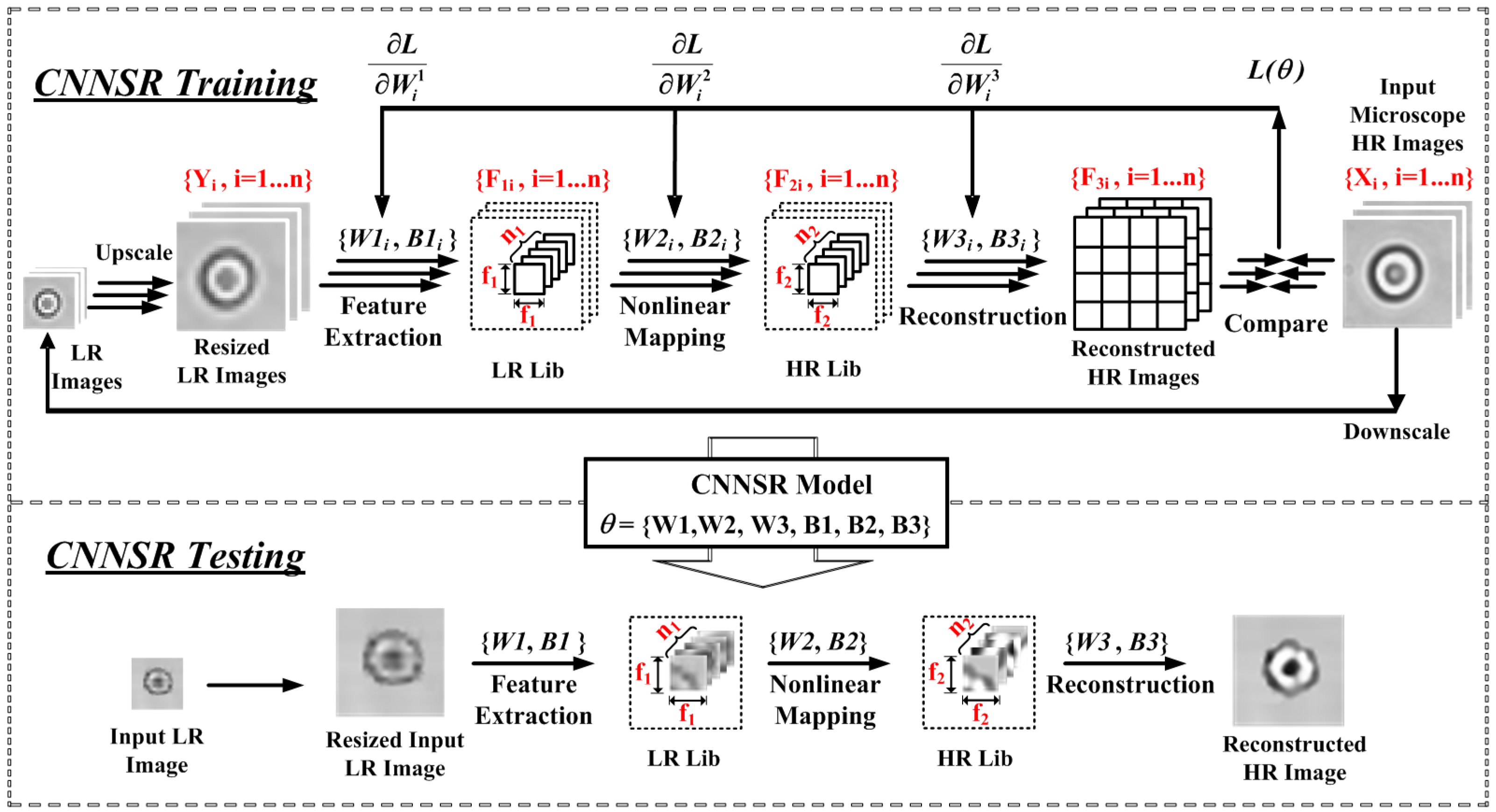
2.2. Machine-Learning Based Single-Frame SR Processing
2.2.1. ELMSR
2.2.2. CNNSR
2.2.3. Comparison of ELMSR and CNNSR
3. Results and Discussion
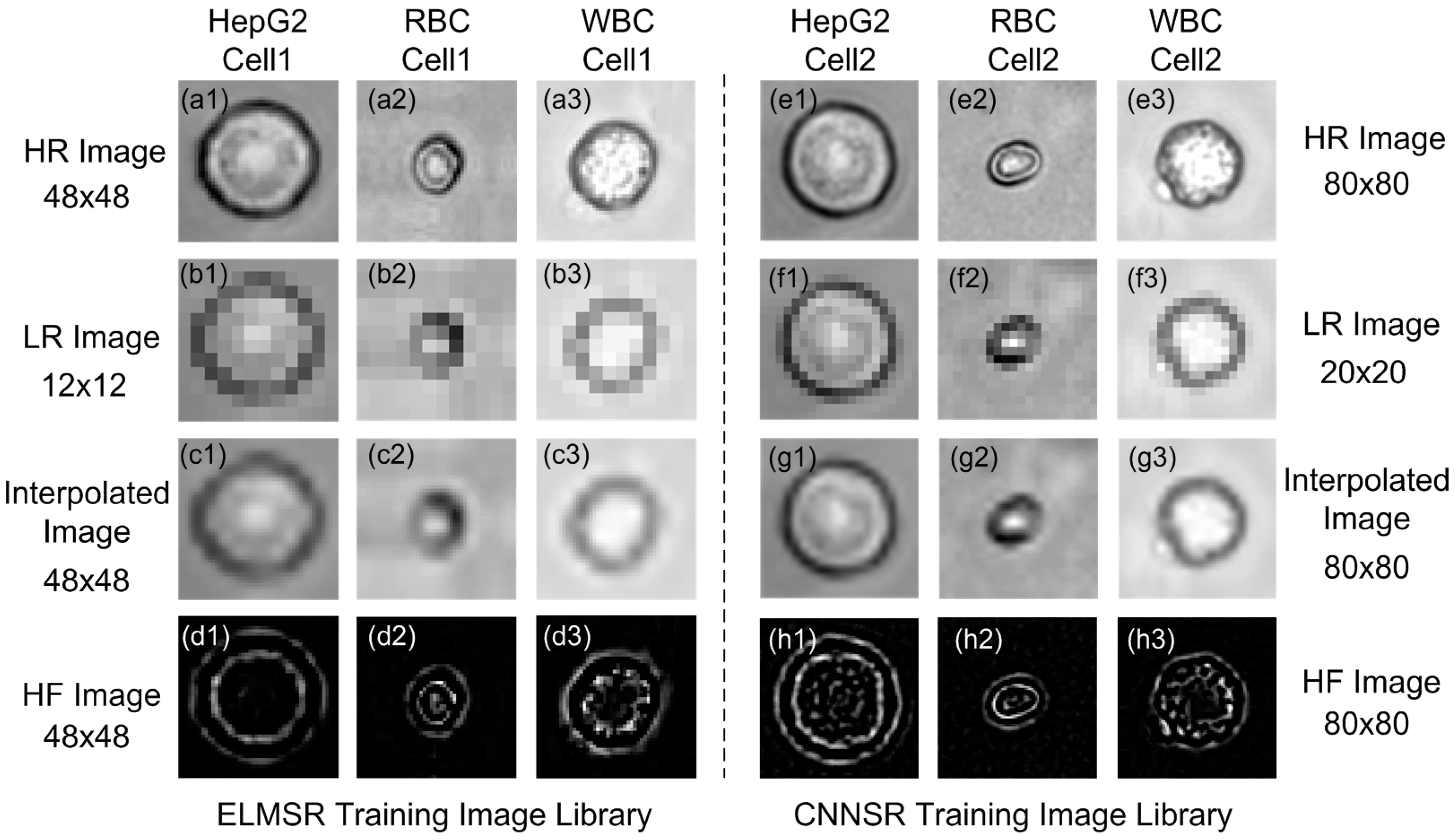
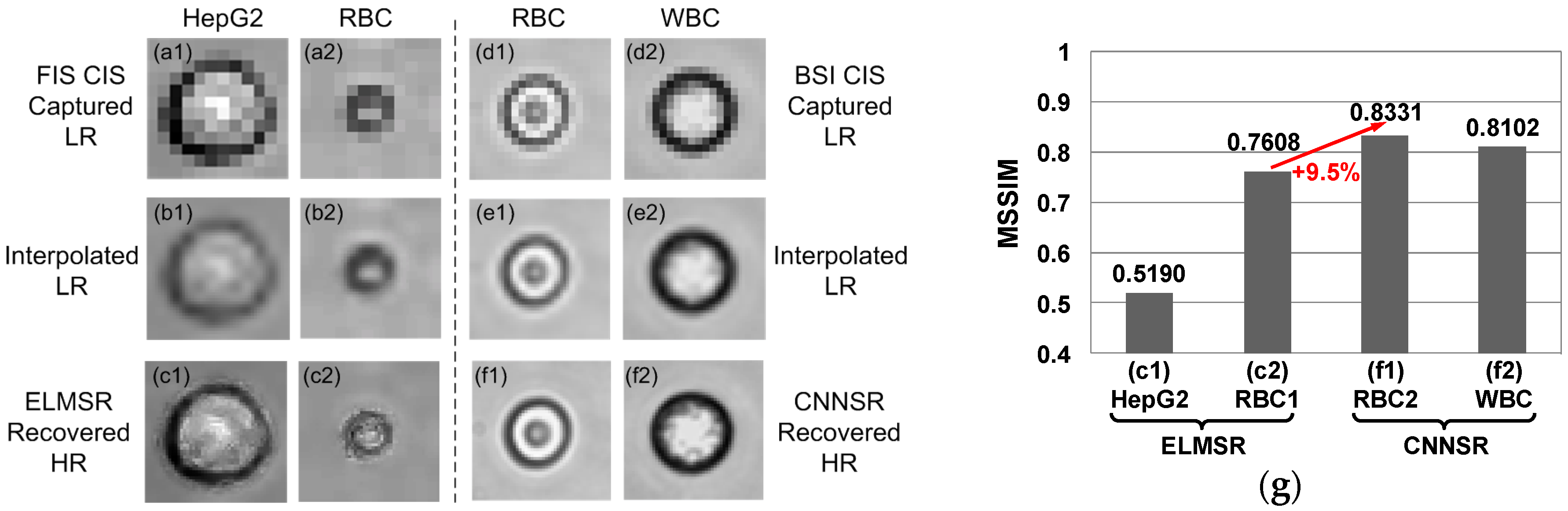
3.1. Off-Line SR Training
3.2. On-Line SR Testing
3.3. On-Line Cell Recognition and Counting
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, W.; Han, J.; Choi, J.-W.; Ahn, C.H. Point-of-care testing (POCT) diagnostic systems using microfluidic lab-on-a-chip technologies. Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 132, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Berkel, C.; Gwyer, J.D.; Deane, S.; Green, N.; Holloway, J.; Hollis, V.; Morgan, H. Integrated systems for rapid point of care (POC) blood cell analysis. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, A.; McLeod, E. Lensless imaging and sensing. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 18, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Guo, J.; Yan, M.; Kang, Y.; Yu, H. A contact-imaging based microfluidic cytometer with machine-learning for single-frame super-resolution processing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, M.; Yu, H. A robust recognition error recovery for micro-flow cytometer by machine-learning enhanced single-frame super-resolution processing. Integration 2015, 51, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, A.; Demirci, U. Ultra wide-field lens-free monitoring of cells on-chip. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Lee, S.A.; Yang, S.; Yang, C. Sub-pixel resolving optofluidic microscope for on-chip cell imaging. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 3125–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Saeki, T.; Sunaga, Y.; Matsunaga, T. High-content analysis of single cells directly assembled on CMOS sensor based on color imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, G.; Yoo, I.; Pack, S.P.; Yang, J.; Ha, U.; Paek, S.; Seo, S. Lens-free shadow image based high-throughput continuous cell monitoring technique. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Sander, D.; Haas, A.; Abshire, P.A. Contact imaging: Simulation and experiment. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2007, 54, 1698–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yu, H.; Liu, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, M.; Wu, D. A dual-mode large-arrayed CMOS ISFET sensor for accurate and high-throughput pH sensing in biomedical diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 2224–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.C.; Park, M.K.; Kang, M.G. Super-resolution image reconstruction: A technical overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2003, 20, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishara, W.; Sikora, U.; Mudanyali, O.; Su, T.; Yaglidere, O.; Luckhart, S.; Ozcan, A. Holographic pixel super-resolution in portable lensless on-chip microscopy using a fiber-optic array. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1276–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobieranski, A.C.; Inci, F.; Tekin, H.C.; Yuksekkaya, M.; Comunello, E.; Cobra, D.; von Wangenheim, A.; Demirci, U. Portable lensless wide-field microscopy imaging platform based on digital inline holography and multi-frame pixel super-resolution. Light Sci. Appl. 2015, 4, e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yu, H.; Liu, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, M. A single-frame superresolution algorithm for lab-on-a-chip lensless microfluidic imaging. IEEE Des. Test. 2015, 32, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, X.; Jia, Q.; Yan, M.; Yu, H.; Yeo, K.-S. A super-resolution CMOS image sensor for bio-microfluidic imaging. In Proceedings of the Biomedical Circuits and Systems, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 28–30 November 2012; pp. 388–391.
- Koydemir, H.C.; Gorocs, Z.; Tseng, D.; Cortazar, B.; Feng, S.; Chan, R.Y.L.; Burbano, J.; McLeod, E.; Ozcan, A. Rapid imaging, detection and quantification of giardia lamblia cysts using mobile-phone based fluorescent microscopy and machine learning. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, C.; Gerlich, D.W. Machine learning in cell biology—Teaching computers to recognize phenotypes. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 5529–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, W.T.; Pasztor, E.C.; Carmichael, O.T. Learning low-level vision. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2000, 40, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, W.T.; Jones, T.R.; Pasztor, E.C. Example-based super-resolution. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2002, 22, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, G.; Fattal, R. Image and video upscaling from local self-examples. ACM Trans. Graph. 2011, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lin, Z.; Cohen, S.D. Fast Image Super-Resolution Based on in-Place Example Regression. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013.
- Sun, J.; Zheng, N.; Tao, H.; Shum, H. Image Hallucination with Primal Sketch Priors. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, WI, USA, 16–22 June 2003.
- Yang, J.; Wright, J.C.; Huang, T.S.; Ma, Y. Image super-resolution via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 2861–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, K.; Lohit, S.; Turaga, P.; Kerviche, R.; Ashok, A. ReconNet: Non-Iterative Reconstruction of Images from Compressively Sensed Random Measurements. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016.
- Huang, G.; Zhu, Q.; Siew, C.K. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Shih, W.; Hui, C.; Chen, S.; Lee, C. Bonding strength of pressurized microchannels fabricated by polydimethylsiloxane and silicon. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 115032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ref. | Description | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| [6] | LUCAS, static cell counting based on one single captured low-resolution (LR) image of a droplet of cell solution in between two cover glasses on CIS surface | Simple architecture and large field for cell counting | Low resolution single cell image |
| [7] | SROFM, drop and capillary flow cells through microchannel, capture multiple LR image to generate one high-resolution (HR) image | High resolution single cell image | Low throughput for cell counting |
| [8] | Static cell counting by dropping cell sample in a chamber over CMOS image sensor (CIS) | Multi-color imaging | Low resolution single cell image |
| [9] | Continuously monitor cells in incubator above CIS | Non-label continuous imaging | Low resolution single cell image |
| ELMSR Training: |
|---|
| 1 Downscale the input to obtain images |
| 2 Upscale images to |
| 3 Generate feature matrix X from |
| 4 Generate p and row vector T |
| 5 Generate the weight vector with [X, T] |
| , |
| ELMSR Testing: |
| 6 Input LR image for testing |
| 7 Upscale to |
| 8 Generate feature matrix X' from |
| 9 Calculate image, |
| 10 Generate final SR output with HF components |
| CNNSR Training |
|---|
| Input: LR cell images {Yi} and corresponding HR cell images {Xi} |
| Output: Model parameter |
| 1 are initialized by drawing randomly from Gaussian Distribution () |
| 2 For // n is the number of training image |
| 3 For = 1 to 3 // 3 layers to tune |
| 4 Calculate based on Equations (13)–(15) |
| 5 End For |
| 6 Calculate |
| 7 If // is closed to zero |
| 8 Calculate , |
| 9 End If |
| 10 End For |
| CNNSR Testing |
| Input: LR cell image {Y’} and Model parameter |
| Output: Corresponding HR cell images F{Y’} |
| 11. For = 1 to 3 // 3-layer network |
| 12 Calculate based on Equations (13)–(15) |
| 13 End For |
| Group | RBC (# μL−1) | HepG2 (# μL−1) | RBC/HepG2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 239 (54.32%) | 201 (45.68%) | 1.19 |
| 2 | 338 (50.22%) | 335 (49.78%) | 1.01 |
| 3 | 260 (53.72%) | 224 (46.28%) | 1.06 |
| 4 | 435 (52.98%) | 386 (47.02%) | 1.12 |
| 5 | 340 (55.74%) | 270 (44.26%) | 1.26 |
| 6 | 334 (49.85%) | 336 (50.15%) | 0.99 |
| Mean | 324 (52.60%) | 292 (47.40%) | 1.11 |
| Stdev | 70 | 72 | 0.11 |
| CV | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.10 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Han, Z.; Rong, H.; Yang, H.; Yan, M.; Yu, H. Machine Learning Based Single-Frame Super-Resolution Processing for Lensless Blood Cell Counting. Sensors 2016, 16, 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111836
Huang X, Jiang Y, Liu X, Xu H, Han Z, Rong H, Yang H, Yan M, Yu H. Machine Learning Based Single-Frame Super-Resolution Processing for Lensless Blood Cell Counting. Sensors. 2016; 16(11):1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111836
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xiwei, Yu Jiang, Xu Liu, Hang Xu, Zhi Han, Hailong Rong, Haiping Yang, Mei Yan, and Hao Yu. 2016. "Machine Learning Based Single-Frame Super-Resolution Processing for Lensless Blood Cell Counting" Sensors 16, no. 11: 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111836
APA StyleHuang, X., Jiang, Y., Liu, X., Xu, H., Han, Z., Rong, H., Yang, H., Yan, M., & Yu, H. (2016). Machine Learning Based Single-Frame Super-Resolution Processing for Lensless Blood Cell Counting. Sensors, 16(11), 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111836







