Proof-of-Concept of a Millimeter-Wave Integrated Heterogeneous Network for 5G Cellular
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. mmWave-Integrated Cellular Networks
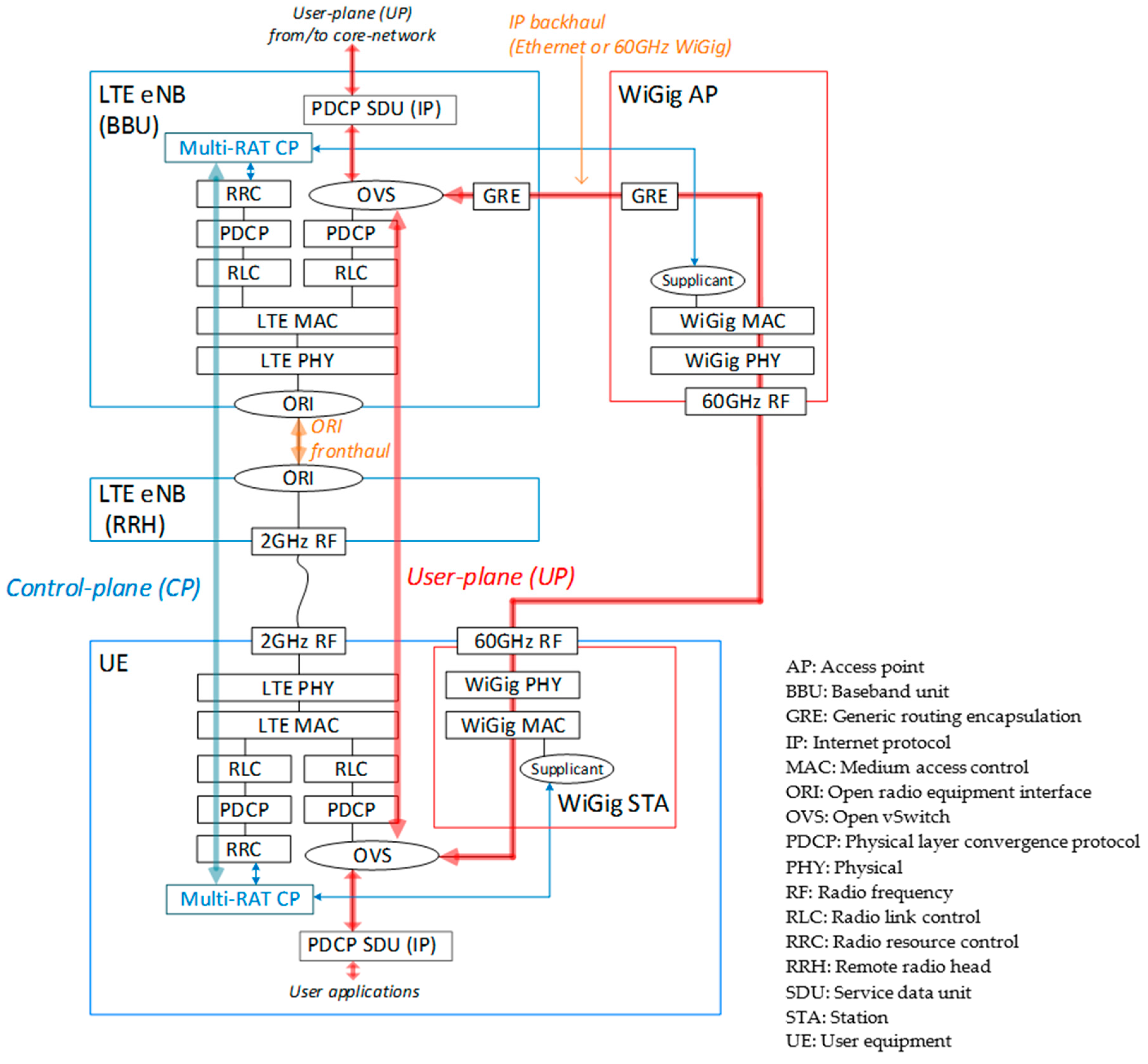
2.1. Control/User Plane Splitting for HetNet
2.2. 60-GHz mmWave WLAN
2.3. LTE-WLAN Interworking and Aggregation
- Non-seamless WLAN offload (NSWO): In NSWO, the traffic is not sent via the EPC, but directly from the Internet to the WLAN-AP. An offloading scheme that bypasses the EPC is called non-seamless WLAN offload (NSWO). In NSWO, the IP flow between the network and UE is interrupted during LTE-WLAN handover, because a different IP address will be allocated to each RAT. In addition, the UE cannot use the operator’s private IP services via WLAN.
- Seamless WLAN offload: When the UE is capable of IP flow mobility (IFOM), the traffic can be transferred to the UE via the WLAN-AP and a PDN GW, an evolved packet data gateway (ePDG) or a trusted wireless access gateway (TWAG). In this scheme, the UE can offload the same IP flow from LTE to WLAN. The PDN GW is an anchor point between the LTE and WLAN accesses.
3. mmWave Beamforming Antenna and Backhaul
3.1. Passive Reflectarray Antennas
3.2. Highly Directional Steerable mmWave Antennas
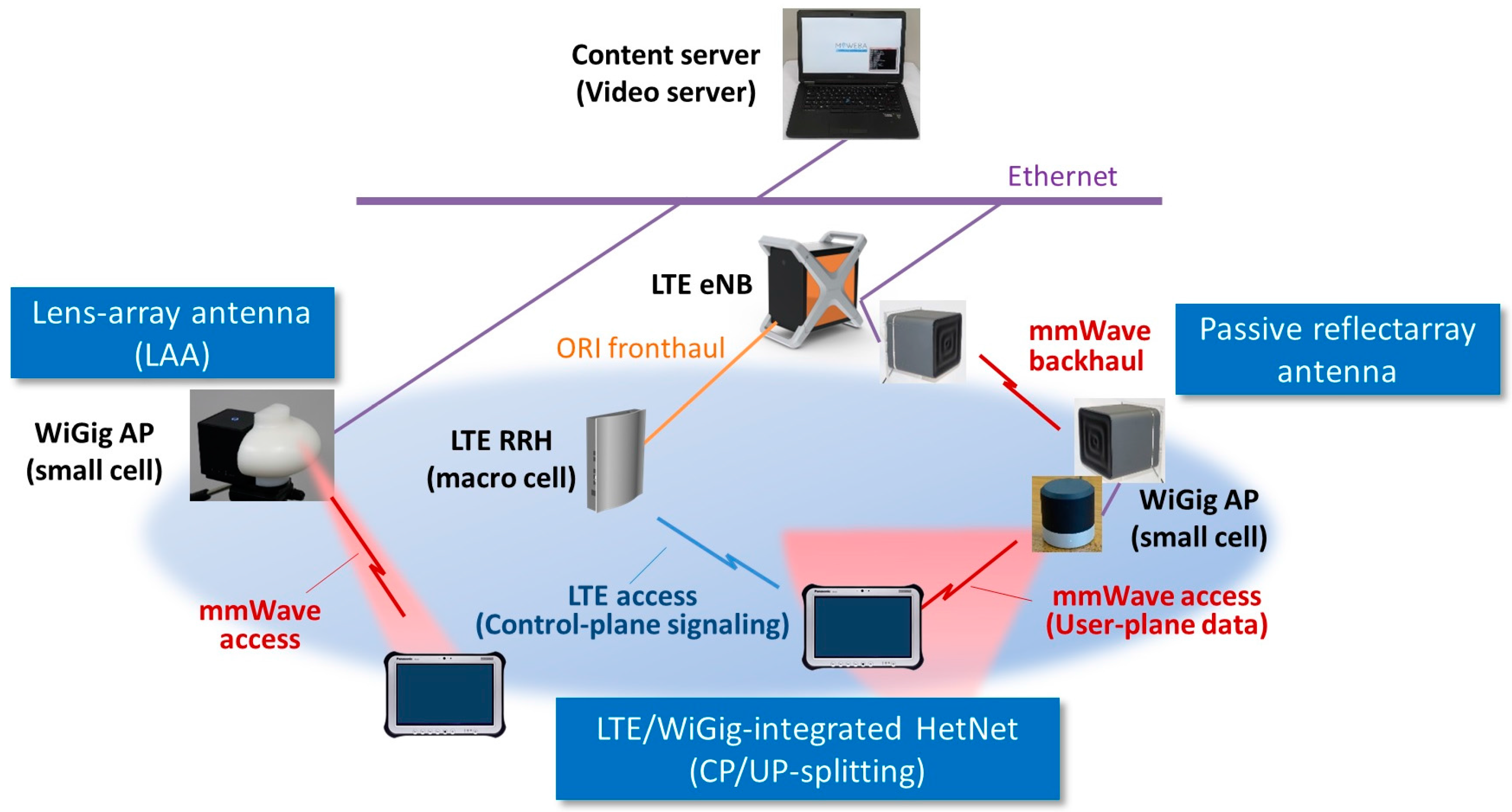
4. Proof of Concept Implementation and Integration
4.1. LTE/WiGig-Integrated HetNet Prototype
4.2. PoC Applications
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3GPP | Third Generation Partnership Project |
| 5G | Fifth generation mobile networks |
| AAA | Authentication, authorization and accounting |
| ANDSF | Access network discovery and selection function |
| AP | Access point |
| BBU | Baseband unit |
| BS | Base station |
| CAPEX | Capital expenditure |
| CP | Control plane |
| CPRI | Common public radio interface |
| CN | Core network |
| C-RAN | Centralized-RAN |
| D2D | Device-to-device |
| DC | Dual connectivity |
| eNB | Evolved Node B |
| EPC | Evolved packet core |
| ePDG | Evolved packet data gateway |
| GRE | Generic routing encapsulation |
| HetNet | Heterogeneous network |
| HSS | Home subscriber server |
| IEEE | Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers |
| IF | Intermediate frequency |
| IFOM | IP flow mobility |
| IP | Internet Protocol |
| IPsec | IP security |
| ITU-R | International Telecommunications Union-Radiocommunication Sector |
| IMS | IP multimedia subsystem |
| IMT-2020 | International Mobile Telecommunications for 2020 and beyond |
| LAA | Lens array antenna |
| LNA | Low-noise amplifier |
| LTE(-A) | Long-Term Evolution (-Advanced) |
| MAC | Medium access control |
| MCS | Modulation and coding scheme |
| MEC | Mobile edge computing |
| MIMO | Multiple-input multiple-output |
| MME | Mobility management entity |
| MUST | Multi-user superposition transmission |
| NOMA | Non-orthogonal multiple access |
| NSWO | Non-seamless WLAN offload |
| mmWave | Millimeter wave |
| OFDM | Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing |
| OPEX | Operational expenditure |
| ORI | Open radio equipment interface |
| OVS | Open vSwitch |
| PAPR | Peak to average power ratio |
| PA | Power amplifier |
| PAA | Phased antenna array |
| PC | Personal computer |
| PCB | Printed circuit board |
| PDCP | Packet data convergence protocol |
| PDN | Packet data network |
| PDU | Protocol data unit |
| PHY | Physical |
| PoC | Proof-of-concept |
| QAM | Quadrature amplitude modulation |
| QPSK | Quadrature phase shift keying |
| RAN | Radio access network |
| RAT | Radio access technology |
| RF | Radio frequency |
| RRC | Radio resource control |
| RRH | Remote radio head |
| RRM | Radio resource management |
| RSSI | Received signal strength indicator |
| SC | Single carrier |
| SDU | Service data unit |
| STA | Station |
| TDD | Time division duplex |
| TWAG | Trusted wireless access gateway |
| UE | User equipment |
| UP | User plane |
| WiGig | Wireless Gigabit |
| WLAN | Wireless local area network |
References
- Association of Radio Industries and Businesses (ARIB) 2020 and Beyond Ad Hoc Group. Mobile Communications Systems for 2020 and beyond. In ARIB 2020 and Beyond Ad Hoc Group White Paper; v1.0.0; Association of Radio Industries and Businesses: Tokyo, Japan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- G-Infrastructure PPP Vision Document, 5G Vision Brochure. 2015. Available online: http://5g-ppp.eu/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/5G-Vision-Brochure-v1.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2016).
- International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R). IMT-Vision–Framework and Overall Objectives of the Future Development of IMT for 2020 and Beyond; Recommendation ITU-R M.2083-0; International Telecommunications Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Flore, D.; Bertenyi, B. “5G” Timeline in 3GPP; 3GPP Tdoc SP-140149; 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP): Sophia Antipolis, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ABI Research. ABI Research Projects 5G Worldwide Service Revenue to Reach $247 Billion in 2025. Available online: https://www.abiresearch.com/press/abi-research-projects-5g-worldwide-service-revenue/ (accessed on 9 August 2016).
- Bryzek, J. Trillion Sensors Movement in Support of Abundance and Internet of Everything. In Proceedings of the VP Development, MEMS and Sensing Solutions & Chair, TSensors Summit, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 30 January 2014.
- International Telecommunications Union Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R). Assessment of the Global Mobile Broadband Deployments and Forecasts for International Mobile Telecommunications; Recommendation ITU-R M.2243; Internationnal Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- International Telecommunications Union Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R). IMT Traffic Estimates for the Years 2020 to 2030; Report ITU-R M.2370-0; International Telecommunications Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, J.G.; Buzzi, S.; Choi, W.; Hanly, S.V.; Lozano, A.; Soong, A.C.K.; Zhang, J.C. What Will 5G Be? IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2014, 32, 1065–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Telecommunications Union Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R). Future Technology Trends of Terrestrial IMT Systems; Report ITU-R M.2320-0; International Telecommunications Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- MediaTek Inc. Study on Downlink Multiuser Superposition Transmission; 3GPP Tdoc RP-150496; 3rd Generation Parnership Project (3GPP): Sofia Antipolis, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rangan, S.; Rappaport, T.S.; Erkip, E. Millimeter-Wave Cellular Wireless Networks: Potentials and Challenges. IEEE Proc. 2014, 102, 366–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, N.; Li, J.; Malladi, D.; Gilmore, R.; Brenner, D.; Damnjanovic, A.; Sukhavasi, R.T.; Patel, C.; Geirhofer, R. Network Densification: The Dominant Theme for Wireless Evolution into 5G. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, K.; Tran, G.K.; Shimodaira, H.; Nanba, S.; Sakurai, T.; Takinami, K.; Siaud, I.; Strinati, E.C.; Capone, A.; Karls, I.; et al. Millimeter-Wave Evolution for 5G Cellular Networks. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2015, E98-B, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiler, R.J.; Peter, M.; Keusgen, W.; Strinati, E.C.; Domenico, A.D.; Filippini, I.; Capone, A.; Siaud, I.; Ulmer-Moll, A.; Maltsev, A.; et al. Enabling 5G Backhaul and access with millimeter-waves. In Proceedings of the 2014 European Conference on Networks and Communications (EuCNC), Bologna, Italy, 23–26 June 2014.
- International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R). Technical Feasibility of IMT in Bands above 6 GHz; Report ITU-R M.2376-0; International Telecommunications Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- NGMN Alliance. Backhaul Provisioning for LTE-Advanced & Small Cells. Available online: https://www.ngmn.org/uploads/media/150929_NGMN_P-SmallCells_Backhaul_for_LTE-Advanced_and_Small_Cells.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- Hur, S.; Kim, T.; Love, D.J.; Krogmeier, J.V.; Thomas, A. Millimeter Wave Beamforming for Wireless Backhaul and Access in Small Cell Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2013, 61, 4391–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Z.; Choi, J.; Heath, R., Jr. Millimeter-Wave Gigabit Broadband Evolution Toward 5G: Fixed Access and Backhaul. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2016, 54, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, T.; Keusgen, W.; Weiler, R.J. Dual-Polarized Square-Shaped Offset-Fed Reflectarray Antenna with High Gain and High Bandwidth in the 60 GHz Domain. In Proceedings of the 2015 9th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), Lisbon, Portugal, 12–17 April 2015.
- Maltsev, A.; Sadri, A.; Pudeyev, A.; Bolotin, I. Highly Directional Steerable antennas. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2016, 11, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MiWEBA Website. Available online: http://www.miweba.eu/ (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- Ishii, H.; Kishiyama, Y.; Takahashi, H. A novel architecture for LTE-B: C-plane/U-plane split and phantom cell concept. In Proceedings of the IEEE Globecom Workshops, Anaheim, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2012.
- Inoue, M.; Wu, G.; Hase, Y.; Sugitani, A.; Kawakami, E.; Shimizu, S.; Tokuda, K. An IP-Over-Ethernet-Based Ultrahigh-Speed Wireless LAN Prototype Operating in the 60-GHz Band. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2000, E83-B, 1720–1730. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE Standards Association. IEEE Standard for Information Technology—Telecommunications and Information Exchange between Systems—Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Specific Requirements—Part 15.3: Amendment 2: Millimeter-Wave-Based Alternative Physical Layer Extension; 802.15.3c-2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, K.; Kondou, K.; Miyahara, M.; Shinagawa, M.; Asada, H.; Minami, R.; Yamaguchi, T.; Musa, A.; Tsukui, Y.; Asakura, Y.; et al. Full Four-Channel 6.3-Gb/s 60-GHz CMOS Transceiver With Low-Power Analog and Digital Baseband Circuitry. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 46–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, N.; Tsukizawa, T.; Shirakata, N.; Morita, T.; Tanaka, K.; Sato, J.; Morishita, Y.; Kanemaru, M.; Kitamura, R.; Shima, T.; et al. A Fully Integrated 60-GHz CMOS Transceiver Chipset Based on WiGig/IEEE802.11ad With Built-in Self Calibration for Mobile Usage. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 3146–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, K.; Mohamed, E.M.; Kusano, H.; Mizukami, M.; Miyamoto, S.; Rezagah, R.E.; Takinami, K.; Takahashi, K.; Shirakata, N.; Peng, H.; et al. Millimeter-Wave Wireless LAN and Its Extension toward 5G Heterogeneous networks. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2015, E98-B, 1932–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Standards Association. IEEE Standard for Information Technology—Telecommunications and Information Exchange between Systems—Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Specific Requirements Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications Amendment 3: Enhancements for Very High Throughput in the 60 GHz Band; 802.11adTM-2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wireless Gigabit (WiGig) Alliance. WiGig MAC and PHY Specification; v1.0; WiGig Alliance: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Intel Corporation. Intel® Wireless Docking Overview. Available online: http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/wireless-products/wireless-docking.html (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- Snapdragon Staff. Get to Know the Snapdragon 810 Processor. Available online: https://www.qualcomm.com/news/snapdragon/2014/12/02/get-know-snapdragon-810-processor (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- TP-LINK Technologies Co., Ltd. Talon AD7200 Multi-Band Wi-Fi Router. Available online: http://www.tp-link.com/en/products/details/AD7200.html (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. Samsung Electronics and Deutsche Telekom Demonstrate World’s First End-to-End 5G Solution at Mobile World Congress 2016. Available online: https://news.samsung.com/global/samsung-electronics-and-deutsche-telekom-demonstrate-worlds-first-end-to-end-5g-solution-at-mobile-world-congress-2016 (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- Branda, M. Qualcomm Research Demonstrates Robust mmWave Design for 5G. Available online: https://www.qualcomm.com/news/onq/2015/11/19/qualcomm-research-demonstrates-robust-mmwave-design-5g (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. 5G Vision White Paper. Available online: http://www.samsung.com/global/business-images/insights/2015/Samsung-5G-Vision-0.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. Huawei to Bring 73 GHz mmWave Mu-MIMO live Demo to Deutsche Telekom. Available online: http://www.huawei.com/en/news/2016/2/73GHzmm-Wave-Mu-MIM-live-demo (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- Nokia Networks. Nokia Networks Showcases 5G speed of 10Gbps with NI at the Brooklyn 5G Summit. Available online: http://networks.nokia.com/news-events/press-room/press-releases/nokia-networks-showcases-5g-speed-of-10gbps-with-ni-at-the-brooklyn-5g-summit (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- Goovaerts, D. Verizon, T-Mobile Seek Permission to Test 5G Tech at 28 GHz. Available online: http://www.wirelessweek.com/news/2016/03/verizon-t-mobile-seek-permission-test-5g-tech-28-ghz (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- InterDigital. InterDigital, Imec and Peraso Demonstrate World’s First WiGig-Based Millimeter Wave Mesh Backhaul System. Available online: http://ir.interdigital.com/releasedetail.cfm?releaseid=827608 (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- NEC Corporation. NEC launches New Millimeter Wave Radio for 5G Backhauling. Available online: http://www.nec.com/en/press/201602/global_20160210_01.html (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). Small Cell Enhancements for E-UTRA and E-UTRAN; Higher Layer Aspects; 3GPP Technical Report 36.842, v12.0.0; 3GPP: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nokia Networks White Paper, LTE-Advanced Carrier Aggregation Optimization. Available online: http://networks.nokia.com/sites/default/files/document/nokia_carrier_aggregation_white_paper.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2016).
- Lauridsen, M.; Wang, H.; Mogensen, P. LTE UE Energy Saving by Applying Carrier Aggregation in a HetNet scenario. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 77th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Dresden, Germany, 2–5 June 2013.
- Mohamed, E.M.; Sakaguchi, K.; Sampei, S. Delayed offloading using cloud cooperated millimeter wave gates. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 25th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communication (PIMRC), Washington, DC, USA, 2–5 September 2014; pp. 1852–1856.
- 4G Americas White Paper, LTE Aggregation & Unlicensed Spectrum, 2015. Available online: http://www.4gamericas.org/ (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- Burbidge, R. Liaison from 3GPP on LWA and LWP; IEEE doc. 802.11-16/351r0; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Francois, R. ITU-R Administrative Circular CA/226. In Proceedings of the First Session of the Conference Preparatory Meeting for WRC-19 (CPM19-1), Geneva, Switzerland, 30 November–1 December 2015.
- 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); User Equipment (UE) Radio Transmission and Reception (Release 13); 3GPP Technical Specification 36.101, v13.3.0; 3GPP: Sofia Antipolis, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, S.K.; Xia, P.; Garcia, A.V. 60 GHz Technology for Gbps WLAN and WPAN; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro, C. 802.11 NG60 SG Proposed PAR; IEEE doc, 802.11-14/1151r8; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Intel Product Brief, Intel® Tri-Band Wireless-AC 17265. Available online: http://www.intel.com/ (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). Architecture Enhancement for Non-3GPP Access; 3GPP Technical Specification 23.402, v13.5.0; 3GPP: Sofia Antipolis, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE Standards Association. IEEE Standard for Information Technology—Telecommunications and Information Exchange between Systems–Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Specific Requirements—Part 3: CSMA/CD Access Method and Physical Layer Specifications Amendment 3: Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) Power via the Media Dependent Interface (MDI) Enhancements; 802.3at-2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). Access to the 3GPP Evolved Packet Core (EPC) via Non-3GPP Access Networks; 3GPP Technical specification 24.302, Stage 3, v13.5.0; 3rd Generation Parnership Project (3GPP): Sofia Antipolis, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). Access Network Discovery and Selection Function (ANDSF) management object (MO); 3GPP Technical specification 24.312; v13.2.0; 3rd Generation Parnership Project (3GPP): Sofia Antipolis, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Thomas, M.; Li, M.; Xia, J.; Giannelli, C. Mobile Wireless Middleware, Operating Systems, and Applications; Springer Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.C.; Patel, M.; Sabella, D.; Sprecher, N.; Young, V. Mobile Edge Computing—A Key Technology towards 5G, 1st ed.; ETSI White Paper, no. 11; European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI): Sophia Antipolis, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Nanba, S. LTE/WiGig RAN-level interworking architecture for 5G millimeter-wave heterogeneous networks. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2015, E98-B, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Encinar, J.A. Reflectarray Antennas; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Rappaport, S.; Heath, R.W.; Andrew, N.; Rangan, S. MIMO for Millimeter-wave Wireless Communications: Beamforming, Spatial Multiplexing, or Both? IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltsev, A.; Sadri, A.; Pudeyev, A.; Bolotin, I.; Davydov, A.; Morozov, G.; Weiler, R.J. Partially Adaptive Arrays application for MU-MIMO mode in a MmWave Small Cells. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 26th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Hong Kong, China, 30 August–2 September 2015.
- Fernandes, C.A. Shaped dielectric lenses for wireless millimeter-wave communications. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 1999, 41, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karttunen, A.; Ala-Laurinaho, J.; Sauleau, R.; Räisänen, A.V. A Study of Extended Hemispherical Lenses for a High-Gain Beam-Steering Antenna. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Barcelona, Spain, 12–16 April 2010.
- Artemenko, A.; Maltsev, A.; Mozharovskiy, A.; Maselennikov, R.; Sevastyanov, A.; Ssorin, V. Millimeter-wave electronically steerable integrated lens antennas for WLAN/WPAN applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 1665–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). Open Radio Equipment Interface (ORI): Requirements for Open Radio Equipment Interface (ORI); Release 4; ETSI: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). Open Radio Equipment Interface (ORI): Interface Specification. Par 1: Low Layers (Release 4); ETSI: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Open vSwitch Website. Available online: http://openvswitch.org/ (accessed on 30 May 2016).
- Iperf. Available online: https://iperf.fr/ (accessed on 17 August 2016).
- MiWEBA Proof of Concept. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qTPv13c7n34 (accessed on 8 July 2016).
- Tran, G.K.; Shimodaira, H.; Rezagah, R.; Sakaguchi, K.; Araki, K. Dynamic cell activation and user association for green 5G heterogeneous cellular networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 26th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), London, UK, 30 August–2 September 2015.
- Tran, G.K.; Shimodaira, H.; Rezagah, R.; Sakaguchi, K.; Araki, K. Practical evaluation of on-demand smallcell on/off based on traffic model for 5G cellular networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE WCNC 2016, Doha, Qatar, 3–6 April 2016.



| Abbreviation | Term | Abbreviation | Term |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3GPP | 3rd generation partnership | IMS | IP multimedia subsystem |
| AAA | Authentication, authorization and accounting | IP | Internet protocol |
| ANDSF | Access network discovery and selection function | LTE | Long-Term Evolution |
| AP | Access point | MME | Mobility management entity |
| eNB | Evolved Node-B | PDN | Packet data network |
| EPC | Evolved packet core | S-GW | Serving gateway |
| ePDG | Evolved packet data gateway | TWAG | Trusted wireless access gateway |
| GW | Gateway | UE | User equipment |
| HSS | Home subscriber server | WLAN | Wireless local area network |

| Abbreviation | Term | Abbreviation | Term |
|---|---|---|---|
| LWA | LTE-WLAN aggregation | MAC | Medium access control |
| LWAAP | LWA adaptation protocol | PDCP | Packet data convergence protocol |
| LWIP | LTE-WLAN radio level integration with IPsec tunnel | PHY | Physical |
| LWIPEP | LWIP endpoint | RLC | Radio link control |
| LWIP-SeGW | LWIP security gateway | SDU | Service data unit |











| MCS Index | PHY Mode | Modulation | Coding Rate | PHY Data Rate (Mbps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SC | π/2-BPSK | 1/2 | 385 |
| 6 | SC | π/2-QPSK | 1/2 | 1540 |
| 9 | SC | π/2-QPSK | 13/16 | 2502.5 |
| 10 | SC | π/2-16QAM | 1/2 | 3080 |
| 12 | SC | π/2-16QAM | 5/8 | 4620 |
| 13 | OFDM | SQPSK | 1/2 | 693.00 |
| 15 | OFDM | QPSK | 1/2 | 1386.00 |
| 18 | OFDM | 16QAM | 1/2 | 2772.00 |
| 22 | OFDM | 64QAM | 5/8 | 5197.50 |
| 24 | OFDM | 64QAM | 13/16 | 6756.75 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okasaka, S.; Weiler, R.J.; Keusgen, W.; Pudeyev, A.; Maltsev, A.; Karls, I.; Sakaguchi, K. Proof-of-Concept of a Millimeter-Wave Integrated Heterogeneous Network for 5G Cellular. Sensors 2016, 16, 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091362
Okasaka S, Weiler RJ, Keusgen W, Pudeyev A, Maltsev A, Karls I, Sakaguchi K. Proof-of-Concept of a Millimeter-Wave Integrated Heterogeneous Network for 5G Cellular. Sensors. 2016; 16(9):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091362
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkasaka, Shozo, Richard J. Weiler, Wilhelm Keusgen, Andrey Pudeyev, Alexander Maltsev, Ingolf Karls, and Kei Sakaguchi. 2016. "Proof-of-Concept of a Millimeter-Wave Integrated Heterogeneous Network for 5G Cellular" Sensors 16, no. 9: 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091362
APA StyleOkasaka, S., Weiler, R. J., Keusgen, W., Pudeyev, A., Maltsev, A., Karls, I., & Sakaguchi, K. (2016). Proof-of-Concept of a Millimeter-Wave Integrated Heterogeneous Network for 5G Cellular. Sensors, 16(9), 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091362






