Metal–Organic Frameworks as Active Materials in Electronic Sensor Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. MOF-Based Gas Sensors
2.1. Impedance Sensors
2.2. Chemicapacitive Sensors
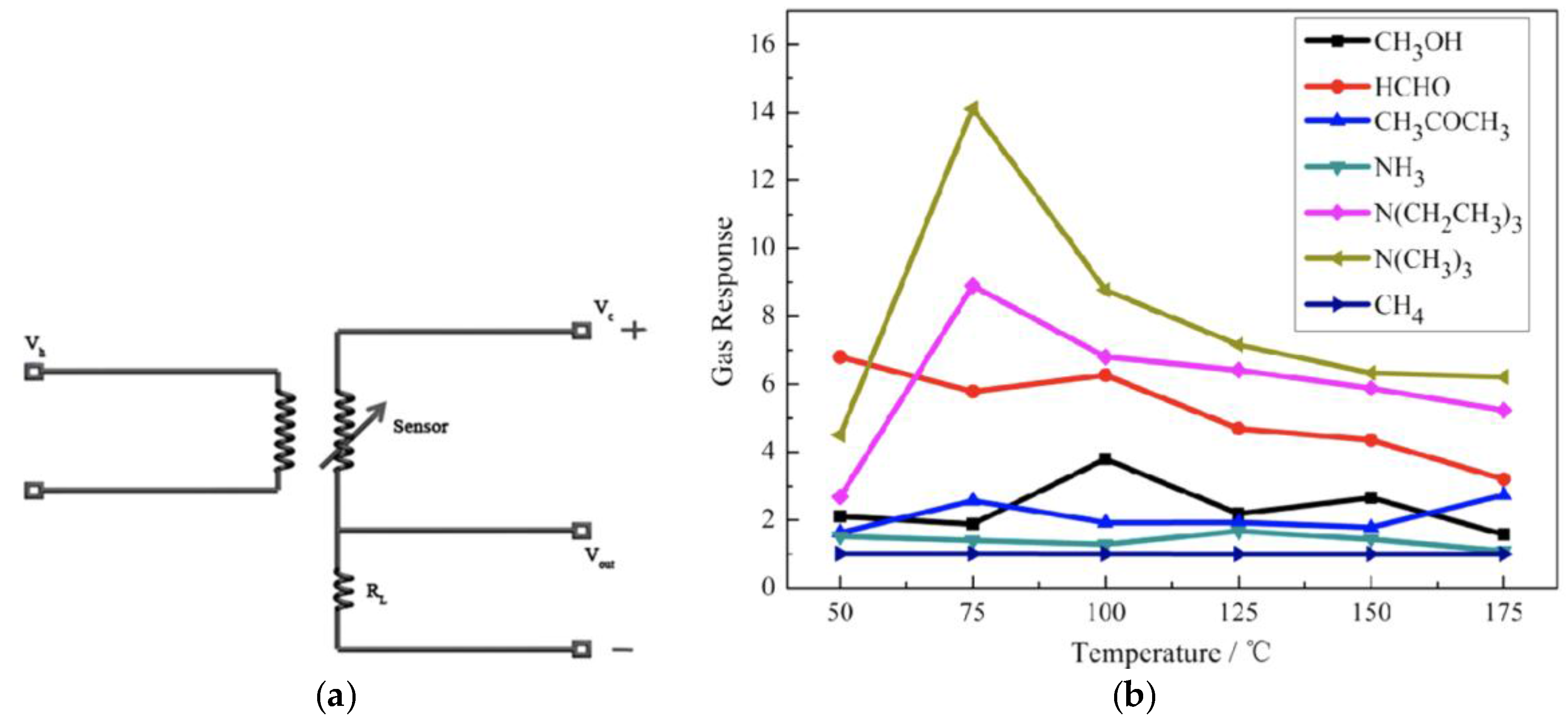
2.3. Chemiresistive Sensors
2.4. Kelvin Probe and Field Effect Transistor Sensors
3. MOF-Based Ion Sensors and Biosensors
4. Outlook
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kreno, L.E.; Leong, K.; Farha, O.K.; Allendorf, M.; Van Duyne, R.P.; Hupp, J.T. Metal–Organic Framework Materials as Chemical Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1105–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wales, D.J.; Grand, J.; Ting, V.P.; Burke, R.D.; Edler, K.J.; Bowen, C.R.; Mintova, S.; Burrows, A.D. Gas sensing using porous materials for automotive applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4290–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, F.-Y.; Chen, D.; Wu, M.-K.; Han, L.; Jiang, H.-L. Chemical Sensors Based on Metal-Organic Frameworks. ChemPlusChem 2016, 81, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allendorf, M.D.; Schwartzberg, A.; Stavila, V.; Talin, A.A. A Roadmap to Implementing Metal-Organic Frameworks in Electronic Devices: Challenges and Critical Directions. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 11372–11388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavila, V.; Talin, A.A.; Allendorf, M.D. MOF-based electronic and opto-electronic devices. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5994–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shustova, N.B.; Cozzolino, A.F.; Reineke, S.; Baldo, M.; Dincă, M. Selective Turn-On Ammonia Sensing Enabled by High-Temperature Fluorescence in Metal–Organic Frameworks with Open Metal Sites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13326–13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Yang, Y.; Zapata, F.; Lin, G.; Qian, G.; Lobkovsky, E.B. Luminescent Open Metal Sites within a Metal–Organic Framework for Sensing Small Molecules. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 1693–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Zapata, F.; Qian, G.; Lobkovsky, E.B. A Luminescent Microporous Metal−Organic Framework for the Recognition and Sensing of Anions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6718–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allendorf, M.D.; Bauer, C.A.; Bhakta, R.K.; Houk, R.J.T. Luminescent metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Ma, L.; deKrafft, K.E.; Jin, A.; Lin, W. Porous Phosphorescent Coordination Polymers for Oxygen Sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 922–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, D.; Hu, Z.; Li, J. Luminescent metal–organic frameworks as explosive sensors. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 10668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allendorf, M.D.; Houk, R.J.T.; Andruszkiewicz, L.; Talin, A.A.; Pikarsky, J.; Choudhury, A.; Gall, K.A.; Hesketh, P.J. Stress-Induced Chemical Detection Using Flexible Metal−Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14404–14405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biemmi, E.; Darga, A.; Stock, N.; Bein, T. Direct growth of Cu3(BTC)2(H2O)3·xH2O thin films on modified QCM-gold electrodes—Water sorption isotherms. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 114, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameloot, R.; Stappers, L.; Fransaer, J.; Alaerts, L.; Sels, B.F.; De Vos, D.E. Patterned Growth of Metal-Organic Framework Coatings by Electrochemical Synthesis. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 2580–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zybaylo, O.; Shekhah, O.; Wang, H.; Tafipolsky, M.; Schmid, R.; Johannsmann, D.; Wöll, C. A novel method to measure diffusion coefficients in porous metal–organic frameworks. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 8092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Campbell, M.G.; Dincă, M. Electrically Conductive Porous Metal-Organic Frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 3566–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobek, M.; Kim, J.-H.; Bechelany, M.; Vallicari, C.; Julbe, A.; Kim, S.S. MOF-Based Membrane Encapsulated ZnO Nanowires for Enhanced Gas Sensor Selectivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8323–8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.S.; Tang, W.X.; Wang, G.E.; Nath, B.; Xu, G. MOF Thin Film-Coated Metal Oxide Nanowire Array: Significantly Improved Chemiresistor Sensor Performance. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5229–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achmann, S.; Hagen, G.; Kita, J.; Malkowsky, I.M.; Kiener, C.; Moos, R. Metal-Organic Frameworks for Sensing Applications in the Gas Phase. Sensors 2009, 9, 1574–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cong, H.; Fu, B.; Wen, S.; Ruan, S. A novel humidity sensor based on NH2-MIL-125(Ti) metal organic framework with high responsiveness. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.S.; Zeinali, S.; Sheikhi, M.H. Fabrication of capacitive sensor based on Cu-BTC (MOF-199) nanoporous film for detection of ethanol and methanol vapors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 230, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassine, O.; Shekhah, O.; Assen, A.H.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Salama, K.N.; Eddaoudi, M. H2S Sensors: Fumarate-Based fcu-MOF Thin Film Grown on a Capacitive Interdigitated Electrode. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 16111–16115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, S.; Soccol, D.; Gravesteijn, D.J.; Kapteijn, F.; Sudhölter, E.J.R.; Gascon, J.; de Smet, L.C.P.M. Polymer–Metal Organic Framework Composite Films as Affinity Layer for Capacitive Sensor Devices. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnorr, J.M.; Swager, T.M. Emerging Applications of Carbon Nanotubes. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, J.F.; Liu, S.F.; Azzarelli, J.M.; Weis, J.G.; Rochat, S.; Mirica, K.A.; Ravnsbæk, J.B.; Swager, T.M. Nanowire Chemical/Biological Sensors: Status and a Roadmap for the Future. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 1266–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.-X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework as Formaldehyde Gas Sensor. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 5411–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.-X.; Fu, H.-R.; Lin, R.; Tan, Y.-X.; Zhang, J. Highly Selective and Sensitive Trimethylamine Gas Sensor Based on Cobalt Imidazolate Framework Material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22871–22875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hmadeh, M.; Lu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Gándara, F.; Furukawa, H.; Wan, S.; Augustyn, V.; Chang, R.; Liao, L.; Zhou, F.; et al. New Porous Crystals of Extended Metal-Catecholates. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 3511–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambe, T.; Sakamoto, R.; Hoshiko, K.; Takada, K.; Miyachi, M.; Ryu, J.-H.; Sasaki, S.; Kim, J.; Nakazato, K.; Takata, M.; et al. π-Conjugated Nickel Bis(dithiolene) Complex Nanosheet. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2462–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheberla, D.; Sun, L.; Blood-Forsythe, M.A.; Er, S.; Wade, C.R.; Brozek, C.K.; Aspuru-Guzik, A.; Dincă, M. High Electrical Conductivity in Ni3(2,3,6,7,10,11-hexaiminotriphenylene)2, a Semiconducting Metal–Organic Graphene Analogue. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 8859–8862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, M.G.; Sheberla, D.; Liu, S.F.; Swager, T.M.; Dincă, M. Cu3(hexaiminotriphenylene)2: An Electrically Conductive 2D Metal-Organic Framework for Chemiresistive Sensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 4349–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, M.G.; Liu, S.F.; Swager, T.M.; Dincă, M. Chemiresistive Sensor Arrays from Conductive 2D Metal–Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13780–13783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.K.; Jensen, K.E.; Pivak, P.A.; Mirica, K.A. Direct Self-Assembly of Conductive Nanorods of Metal–Organic Frameworks into Chemiresistive Devices on Shrinkable Polymer Films. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 5264–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.; Brown, R.B. Chemical sensors with integrated electronics. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janata, J. Thirty Years of CHEMFETs—A Personal View. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 1831–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, T.; Banerjee, R. High Charge Carrier Mobility in Two Dimensional Indium (III) Isophthalic Acid Based Frameworks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. A Phys. Sci. 2014, 84, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Huang, J.; Zang, Y.; He, J.; Xu, G. Porous Field-Effect Transistors Based on a Semiconductive Metal–Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1360–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohle, R.; Tawil, A.; Davydovskaya, P.; Fleischer, M. Metal Organic Frameworks as Promising High Surface Area Material for Work Function Gas Sensors. Procedia Eng. 2011, 25, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydovskaya, P.; Pohle, R.; Tawil, A.; Fleischer, M. Work function based gas sensing with Cu-BTC metal-organic framework for selective aldehyde detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 187, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydovskaya, P.; Pentyala, V.; Yurchenko, O.; Hussein, L.; Pohle, R.; Urban, G.A. Work function based sensing of alkanes and alcohols with benzene tricarboxylate linked metal organic frameworks. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentyala, V.; Davydovskaya, P.; Ade, M.; Pohle, R.; Urban, G. Metal–organic frameworks for alcohol gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stassen, I.; Bueken, B.; Reinsch, H.; Oudenhoven, J.F.M.; Wouters, D.; Hajek, J.; Van Speybroeck, V.; Stock, N.; Vereecken, P.M.; Van Schaijk, R.; et al. Towards metal–organic framework based field effect chemical sensors: UiO-66-NH2 for nerve agent detection. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 5827–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xie, J.; Ge, H.; Hu, X. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes and metal–organic framework nanocomposites as novel hybrid electrode materials for the determination of nano-molar levels of lead in a lab-on-valve format. Analyst 2013, 138, 5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wei, C.; Pang, H. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-67 Rhombic Dodecahedral Microcrystals with Porous {110} Facets As a New Electrocatalyst for Sensing Glutathione. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 32, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Jiang, Q.; Yu, P.; Yang, L.; Mao, L. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for in Vivo Electrochemical Measurements. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7550–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.-J.; Zhuo, Y.; Chai, Y.-Q.; Yuan, R. Ce-based metal-organic frameworks and DNAzyme-assisted recycling as dual signal amplifiers for sensitive electrochemical detection of lipopolysaccharide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 83, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miner, E.M.; Fukushima, T.; Sheberla, D.; Sun, L.; Surendranath, Y.; Dincă, M. Electrochemical oxygen reduction catalysed by Ni3(hexaiminotriphenylene)2. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, J.; He, C.-T.; Yin, H.; An, P.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.; Gao, C.; Zhang, L.; et al. Ultrathin metal–organic framework nanosheets for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Pan, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M. Gas Adsorption Effects on the Electronic Properties of Two-Dimensional Nickel Bis(dithiolene) Complex. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 3846–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, C.; Mandal, B.; Sarkar, P. Bis(dithioline)-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks with Superior Electronic and Magnetic Properties: Spin Frustration to Spintronics and Gas Sensing. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 28307–28319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, J.A.; Wilmer, C.E. Computational Design of Metal–Organic Framework Arrays for Gas Sensing: Influence of Array Size and Composition on Sensor Performance. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 6033–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, K.J.; Léonard, F.; Stavila, V.; Foster, M.E.; Spataru, C.D.; Jones, R.E.; Foley, B.M.; Hopkins, P.E.; Allendorf, M.D.; Talin, A.A. Thin Film Thermoelectric Metal–Organic Framework with High Seebeck Coefficient and Low Thermal Conductivity. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3453–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheberla, D.; Bachman, J.C.; Elias, J.S.; Sun, C.-J.; Shao-Horn, Y.; Dincă, M. Conductive MOF electrodes for stable supercapacitors with high areal capacitance. Nat. Mater. 2016, 16, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campbell, M.G.; Dincă, M. Metal–Organic Frameworks as Active Materials in Electronic Sensor Devices. Sensors 2017, 17, 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051108
Campbell MG, Dincă M. Metal–Organic Frameworks as Active Materials in Electronic Sensor Devices. Sensors. 2017; 17(5):1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051108
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampbell, Michael G., and Mircea Dincă. 2017. "Metal–Organic Frameworks as Active Materials in Electronic Sensor Devices" Sensors 17, no. 5: 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051108
APA StyleCampbell, M. G., & Dincă, M. (2017). Metal–Organic Frameworks as Active Materials in Electronic Sensor Devices. Sensors, 17(5), 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051108




