Ultrafast and Energy-saving Synthesis of Nitrogen and Chlorine Co-doped Carbon Nanodots via Neutralization Heat for Selective Detection of Cr(VI) in Aqueous Phase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Nitrogen/Chlorine Dual-Doped Carbon Nanodots (N,Cl-CDs)
2.3. Characterization of the As-Synthesized N,Cl-CDs
2.4. Determination of Cr(VI)
2.5. Real Sample Analysis
2.6. MTT Assay
3. Results and Discussion
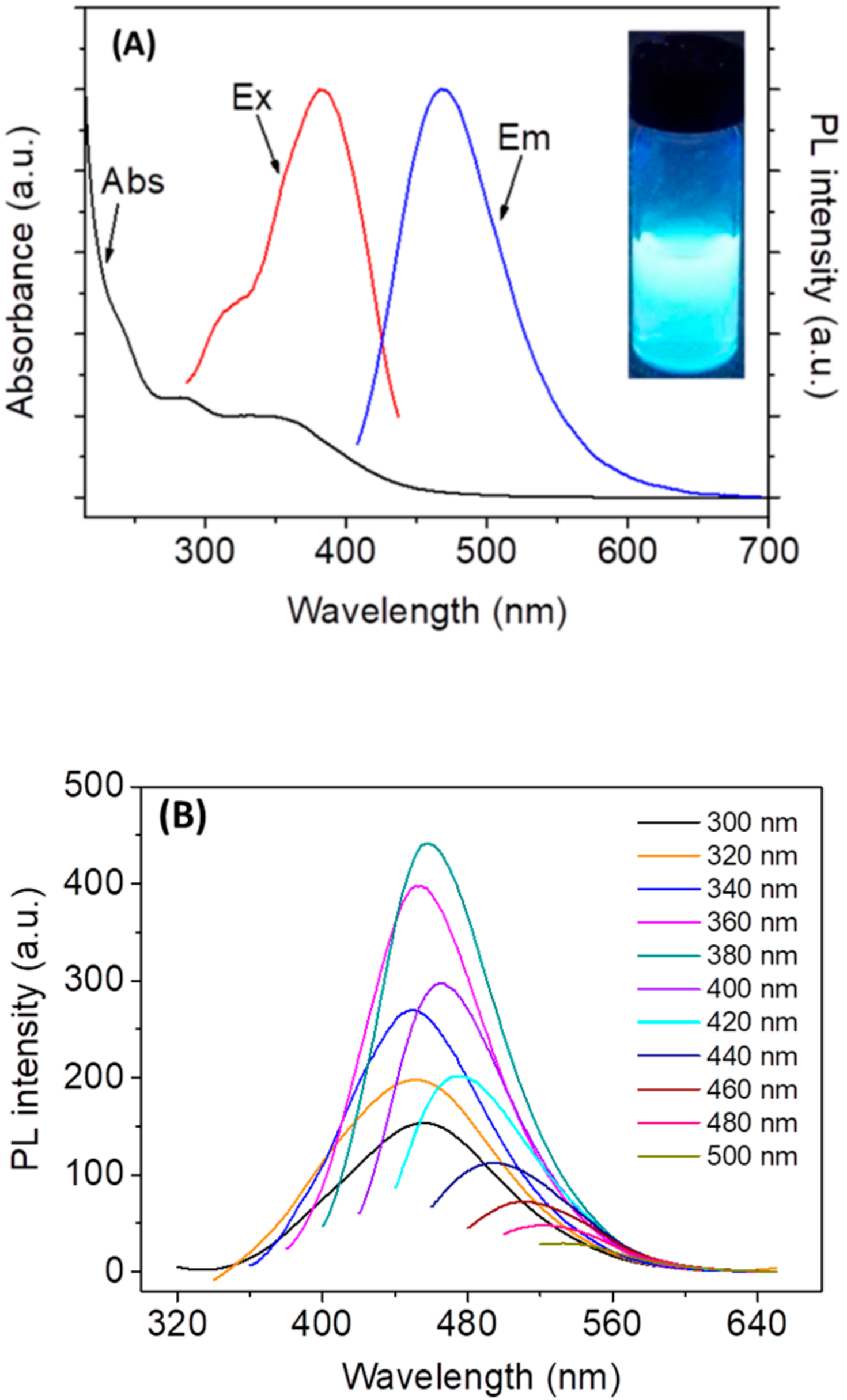
3.1. Characterization of N,Cl-CDs
3.2. Optimization of the Experimental Conditions for Cr(VI) Detection
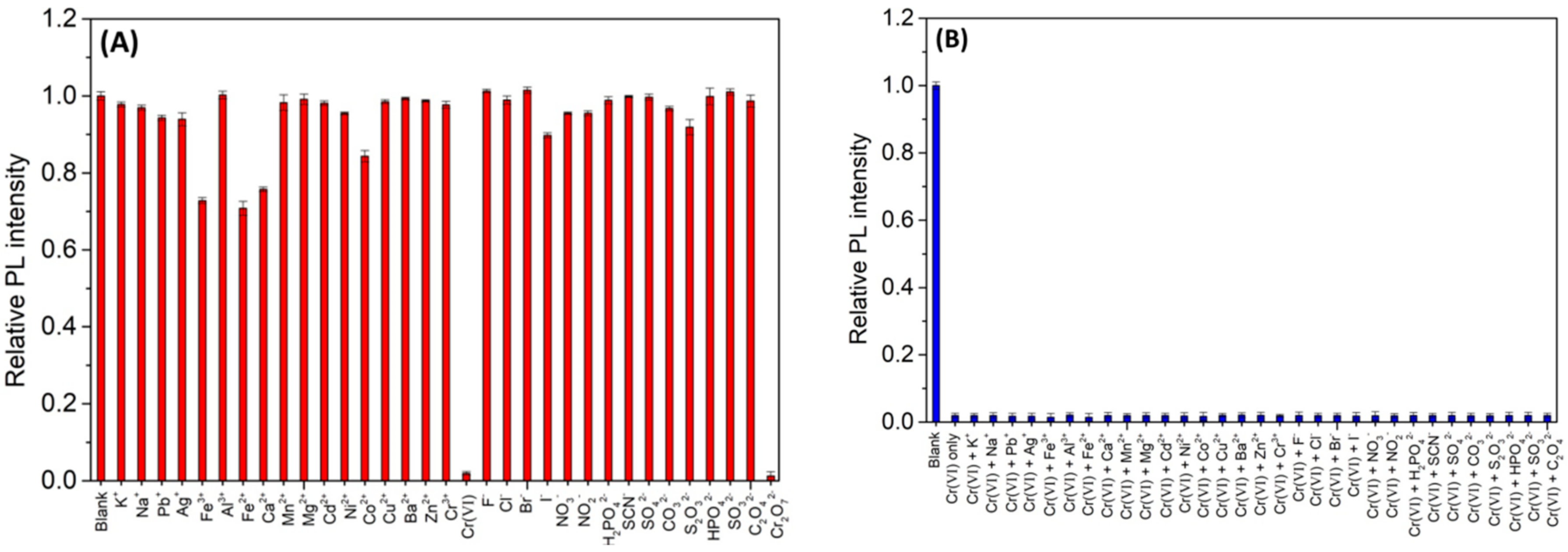
3.3. Selectivity of N,Cl-CDs to Various Ions
3.4. Effects of Competition Ions
3.5. Dependence of the Fluorescence of N,Cl-CDs on the Cr(VI) Concentration
3.6. Discussion of the Reaction Mechanism
3.7. Real Samples Analysis
3.8. Cytotoxicity of the N,Cl-CDs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, J.J.; Zhong, Z.F.; Rong, M.Z.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.D.; Zhang, M.Q. An easy approach of preparing strongly luminescent carbon dots and their polymer based composites for enhancing solar cell efficiency. Carbon 2014, 70, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-T.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, F.; Luo, P.G.; Cao, L.; Meziani, M.J.; Liu, J.-H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; et al. Carbon Dots as Nontoxic and High-Performance Fluorescence Imaging Agents. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 18110–18114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Ding, C.; Zhu, A.; Tian, Y. Carbon-Dot-Based Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Imaging and Biosensing of Superoxide Anion in Live Cells. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7071–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, H.M.R.; Duarte, A.J.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G. Optical fiber sensor for Hg(II) based on carbon dots. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ge, H.; Tian, G.; Cao, N.; Li, Y. A fluorescent turn-off/on method based on carbon dots as fluorescent probes for the sensitive determination of Pb2+ and pyrophosphate in an aqueous solution. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Haddad, R.E.; Fan, H.; Sun, Z. Formation mechanism and optimization of highly luminescent N-doped graphene quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, B. Highly Photoluminescent Carbon Dots for Multicolor Patterning, Sensors, and Bioimaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3953–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, C.; Bai, T.; Li, W.; Dai, L.; Liu, W. Highly luminescent carbon nanodots by microwave-assisted pyrolysis. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7955–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Huang, J.; Cai, Z.; Choi, M.M.F. Boron and nitrogen co-doped carbon dots as a sensitive fluorescent probe for the detection of curcumin. Luminescence 2018, 33, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Paau, M.C.; Zhang, Y.; Chan, W.; Gong, X.; Zhang, L.; Choi, M.M.F. Capillary electrophoretic study of amine/carboxylic acid-functionalized carbon nanodots. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1304, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, G.; Xie, A.; Li, J.; Su, T.; Pan, X.; Dong, W. Large Emission Red-Shift of Carbon Dots by Fluorine Doping and Their Applications for Red Cell Imaging and Sensitive Intracellular Ag+ Detection. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 26558–26565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Shuang, S.; Choi, M.M.F.; Dong, C. Phosphorus and Nitrogen Dual-Doped Hollow Carbon Dot as a Nanocarrier for Doxorubicin Delivery and Biological Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11288–11297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, B.; Su, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, M.; Liu, R.; Zhao, S. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Co-Doped Carbon Nanodots as a Novel Fluorescent Probe for Highly Sensitive Detection of Fe3+ in Human Serum and Living Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10717–10725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Brückner, C.; Lei, Y. One-pot and ultrafast synthesis of nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon dots possessing bright dual wavelength fluorescence emission. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 17278–17282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Fu, J.; Fu, X.; Gan, W.; Hao, H. Rapid synthesis of N, S co-doped carbon dots and their application for Fe3+ ion detection. J. Nanopart. Res. 2018, 20, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, D.; Zhuo, K.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Simple and green synthesis of nitrogen-, sulfur-, and phosphorus-co-doped carbon dots with tunable luminescence properties and sensing application. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 54060–54065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Duan, W.; Song, W.; Liu, J.; Ren, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, D.; Chen, H. Red Emission B, N, S-co-Doped Carbon Dots for Colorimetric and Fluorescent Dual Mode Detection of Fe3+ Ions in Complex Biological Fluids and Living Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 12663–12672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ruan, F.; Lv, T.; Liu, Y.; Deng, D.; Zhao, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, S. One step synthesis of Al/N co-doped carbon nanoparticles with enhanced photoluminescence. J. Lumin. 2015, 158, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.-H.; Feng, L. Rapid detection of Cr(VI) ions based on cobalt(II)-doped carbon dots. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Pan, X.; Han, Z.; Dong, W. One-Step Synthesis of Nitrogen and Chlorine Co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Detection of Fe3+. Nano 2017, 12, 1750135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Xie, Z.; Qu, D.; Li, D.; Du, P.; Jing, X.; Sun, Z. On–Off–On Fluorescent Carbon Dot Nanosensor for Recognition of Chromium(VI) and Ascorbic Acid Based on the Inner Filter Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 13242–13247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Jia, R.; Chen, Z. Core-shell Cu@Au nanoparticles as an optical probe for ultrasensitive detection of chromium(VI) via an etching effect. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3817–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwastowska, J.; Skwara, W.; Sterlińska, E.; Pszonicki, L. Speciation of chromium in mineral waters and salinas by solid-phase extraction and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2005, 66, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arancibia, V.; Valderrama, M.; Silva, K.; Tapia, T. Determination of chromium in urine samples by complexation-supercritical fluid extraction and liquid or gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 785, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer Pressman, M.A.; Aldstadt, J.H. A comparative study of diffusion samplers for the determination of hexavalent chromium by sequential injection spectrophotometry. Microchem. J. 2003, 74, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-J.; Du, X.-M.; Wang, M.; Wang, T.-C.; Ou-Yang, H.; Wang, B.; Zhu, M.-T.; Wang, Y.; Jia, G.; Feng, W.-Y. Using ion-pair reversed-phase HPLC ICP-MS to simultaneously determine Cr(III) and Cr(VI) in urine of chromate workers. Talanta 2010, 81, 1856–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, P.; Sarkar, S.; Soni, S.K.; Kumar, D. Label-free colorimetric detection of Cr(VI) in aqueous systems based on flower shaped silver nanoparticles. Polyhedron 2016, 120, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shuang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, C. An “on-off-on” fluorescent nanoprobe for recognition of chromium(VI) and ascorbic acid based on phosphorus/nitrogen dual-doped carbon quantum dot. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 968, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, C.; Liu, J.; Zheng, J. Ammonium citrate derived carbon quantum dot as on-off-on fluorescent sensor for detection of chromium(VI) and sulfites. Mater. Lett. 2017, 191, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Hong, Y.; Feng, H.; Li, S.F.Y. An efficient “off–on” carbon nanoparticle-based fluorescent sensor for recognition of chromium(VI) and ascorbic acid based on the inner filter effect. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2979–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lin, Y.; Tan, H.; Luo, M.; Dai, S.; Lu, H.; Huang, Z. One-pot synthesis of N-doped carbon dots by pyrolyzing the gel composed of ethanolamine and 1-carboxyethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride and their selective fluorescence sensing for Cr(VI) ions. Analyst 2018, 143, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Shang, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Cai, Y. Highly fluorescent N, S-co-doped carbon dots and their potential applications as antioxidants and sensitive probes for Cr (VI) detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 248, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Jia, L.; Yu, J.-S. Ethanol in aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution: Hydrothermal synthesis of highly photoluminescent carbon dots as multifunctional nanosensors. Carbon 2015, 93, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; He, B.; Huang, J. Amphibious fluorescent carbon dots: One-step green synthesis and application for light-emitting polymer nanocomposites. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8078–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Park, J.; Kim, H.; Singha, K.; Kim, W.J. Transfection and intracellular trafficking properties of carbon dot-gold nanoparticle molecular assembly conjugated with PEI-pDNA. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7168–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-C.; Chen, Y.-N.; Hsu, P.-C.; Shih, C.-C.; Chang, H.-T. Photoluminescent organosilane-functionalized carbon dots as temperature probes. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 1639–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Cui, J.; Zheng, M.; Hu, C.; Tan, S.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y. One-step synthesis of amino-functionalized fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by hydrothermal carbonization of chitosan. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, T.-Y.; Wang, C.-I.; Chang, H.-T. Photoluminescent C-dots@RGO for sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Talanta 2013, 115, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, A.; Shakir, M. An inner filter effect based Schiff base chemosensor for recognition of Cr(VI) and ascorbic acid in water matrices. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dong, L.; Yu, S.-H. A selective sensor for cyanide ion (CN−) based on the inner filter effect of metal nanoparticles with photoluminescent carbon dots as the fluorophore. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.; Bhatt, M.; Kumar, A.; Vyas, G.; Gajaria, T.; Paul, P. Green route for synthesis of multifunctional fluorescent carbon dots from Tulsi leaves and its application as Cr(VI) sensors, bio-imaging and patterning agents. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 167, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Nan, Q.; Yang, J.; Yang, R. Bright carbon dots via inner filter effect for the sensitive determination of the purine metabolic disorder in human fluids. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 203, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.; Qiu, F. Environmentally friendly cleaner water-soluble fluorescent carbon dots coated with chitosan: Synthesis and its application for sensitivity determination of Cr(VI) ions. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2018, 15, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Qiao, Y. One-pot synthesis of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots and its application for sensor and multicolor cellular imaging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 485, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, L.; Peng, J.; Peng, H.; Liu, S.; Xiao, H.; Liu, D.; Pan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; He, Y. Fluorescent carbon dots for the sensitive detection of Cr(VI) in aqueous media and their application in test papers. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 95469–95475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; He, Y.; Ge, Y.; Song, G. One-pot synthesis of boron and nitrogen co-doped carbon dots as the fluorescence probe for dopamine based on the redox reaction between Cr(VI) and dopamine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | Cr(VI) (µM) | Added (µM) | Found (µM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | N.D. | 5 | 4.92 | 98.38 | 0.41 |
| N.D. | 10 | 9.94 | 99.36 | 0.17 | |
| N.D. | 20 | 20.77 | 103.89 | 0.55 | |
| N.D. | 30 | 30.86 | 102.88 | 0.54 | |
| Rain water | N.D. | 5 | 4.86 | 97.19 | 0.12 |
| N.D. | 10 | 9.81 | 98.11 | 0.25 | |
| N.D. | 20 | 19.40 | 97.01 | 0.73 | |
| N.D. | 30 | 30.06 | 100.20 | 0.82 | |
| River water Sample A | N.D. | 5 | 4.92 | 98.31 | 0.28 |
| N.D. | 10 | 9.82 | 98.15 | 0.15 | |
| N.D. | 20 | 20.29 | 101.45 | 0.29 | |
| N.D. | 30 | 29.32 | 97.72 | 0.57 | |
| River water Sample B | N.D. | 5 | 4.93 | 98.57 | 0.16 |
| N.D. | 10 | 9.95 | 99.55 | 0.29 | |
| N.D. | 20 | 19.66 | 98.31 | 0.35 | |
| N.D. | 30 | 30.18 | 100.59 | 0.38 |
| Methods | Fabrication Method | Linear Range | LOD | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This work | Neutralization heat; 2 min | 3‒40 µM | 0.28 µM | Water | |
| CDs | Hydrothermal; 200 °C, 4 h | 1.6‒50 µM | 1.6 µM | Water | [42] |
| Chitosan-CDs | Hydrothermal; 180 °C, 13 h | 0‒600 µM | 13.8 µM (0.72 mg/L) | Water; soil | [44] |
| Co(II)-doped CDs | Hydrothermal; 180 °C, 4 h | 5‒125 µM | 1.17 µM | Water; fish | [19] |
| N,S-doped CDs | Hydrothermal; 160 °C, 6 h | 1‒80 µM | 0.86 µM | NA | [45] |
| P-doped CDs | Microwave Heating; NA | 1‒400 µM | 0.24 µM | Water | [46] |
| P,N-doped CDs | Neutralization heat; NA | 1.5‒30 µM | 0.023 µM | NA | [28] |
| N,B-doped CDs | Hydrothermal; 180 °C, 4 h | 1.39–260 µM | 0.28 µM | NA | [47] |
| N-doped CDs | Hydrothermal; 220 °C, 4 h | 0‒50 µM | 0.01 µM | NA | [29] |
| N-doped CDs | Calcination; 400 °C, 20 min | 0.5‒160 µM | 0.15 µM | Water | [30] |
| N-doped CDs | Pyrolysis; 170 °C, 30 min | 0.01‒50 µM | NA | NA | [21] |
| N-doped CDs | Pyrolysis; 200–240 °C, 2 h | 0.2–2 and 2–40 μM | 0.018 and 0.25 μM | Water | [31] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Q.; Li, T.; Gao, L.; Gong, X.; Rao, S.; Fang, W.; Gu, R.; Yang, Z. Ultrafast and Energy-saving Synthesis of Nitrogen and Chlorine Co-doped Carbon Nanodots via Neutralization Heat for Selective Detection of Cr(VI) in Aqueous Phase. Sensors 2018, 18, 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103416
Hu Q, Li T, Gao L, Gong X, Rao S, Fang W, Gu R, Yang Z. Ultrafast and Energy-saving Synthesis of Nitrogen and Chlorine Co-doped Carbon Nanodots via Neutralization Heat for Selective Detection of Cr(VI) in Aqueous Phase. Sensors. 2018; 18(10):3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103416
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Qin, Tao Li, Lu Gao, Xiaojuan Gong, Shengqi Rao, Weiming Fang, Ruixia Gu, and Zhenquan Yang. 2018. "Ultrafast and Energy-saving Synthesis of Nitrogen and Chlorine Co-doped Carbon Nanodots via Neutralization Heat for Selective Detection of Cr(VI) in Aqueous Phase" Sensors 18, no. 10: 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103416
APA StyleHu, Q., Li, T., Gao, L., Gong, X., Rao, S., Fang, W., Gu, R., & Yang, Z. (2018). Ultrafast and Energy-saving Synthesis of Nitrogen and Chlorine Co-doped Carbon Nanodots via Neutralization Heat for Selective Detection of Cr(VI) in Aqueous Phase. Sensors, 18(10), 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103416






