Gas–Solid Two-Phase Flow Pattern Identification Based on Artificial Neural Network and Electrostatic Sensor Array
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. ESA and ANN
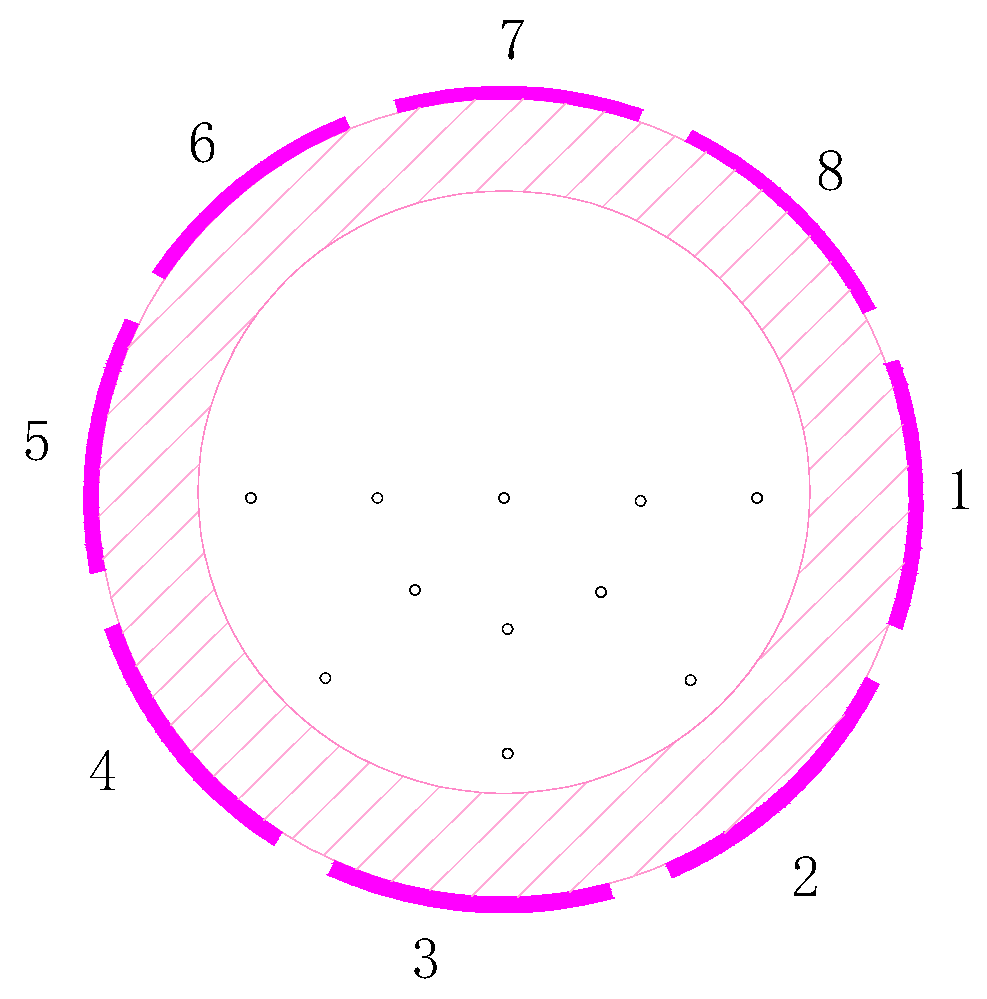
2.1. Structure and Working Principle of ESA
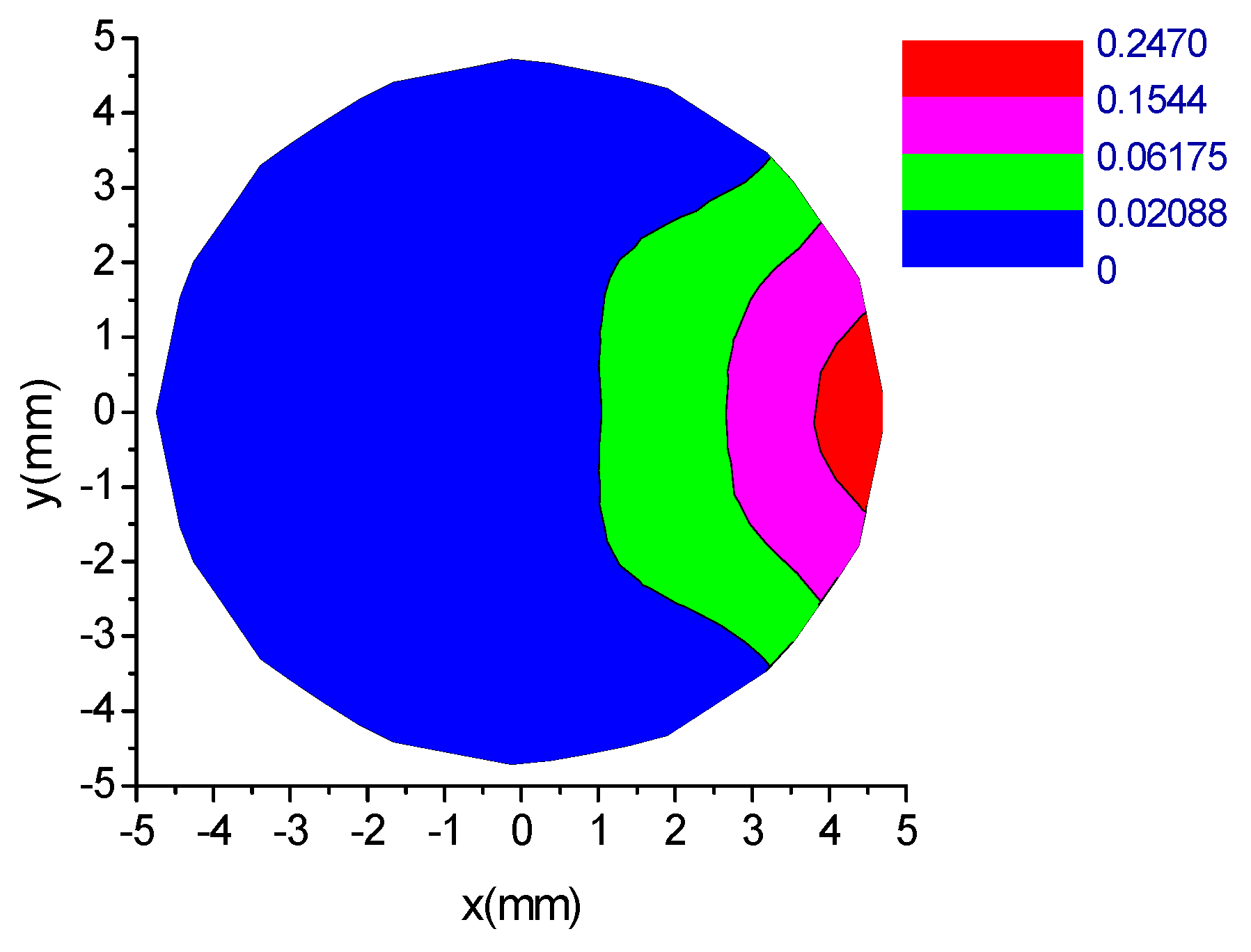
2.2. Computational Modelling of ESA
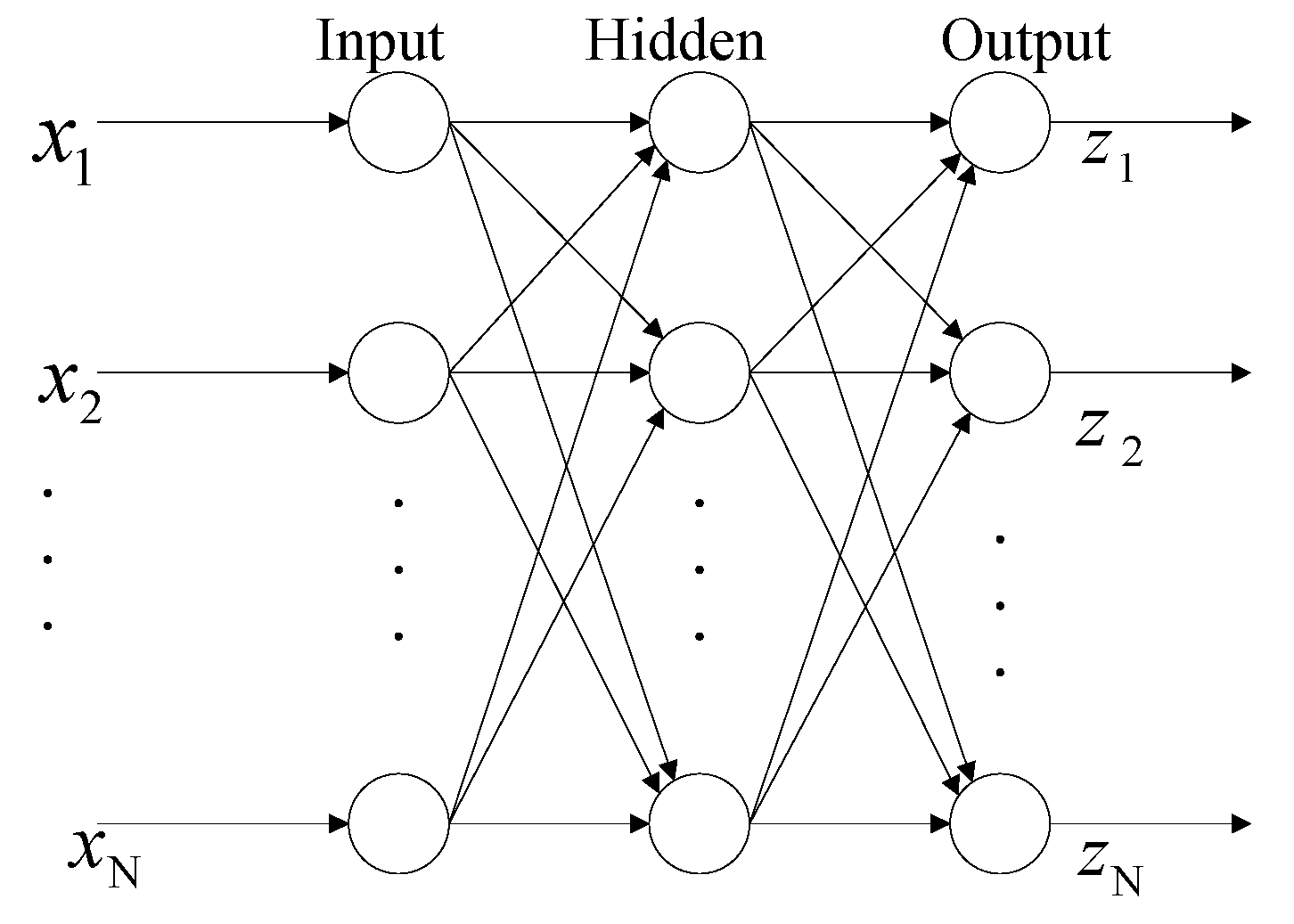
2.3. ANN
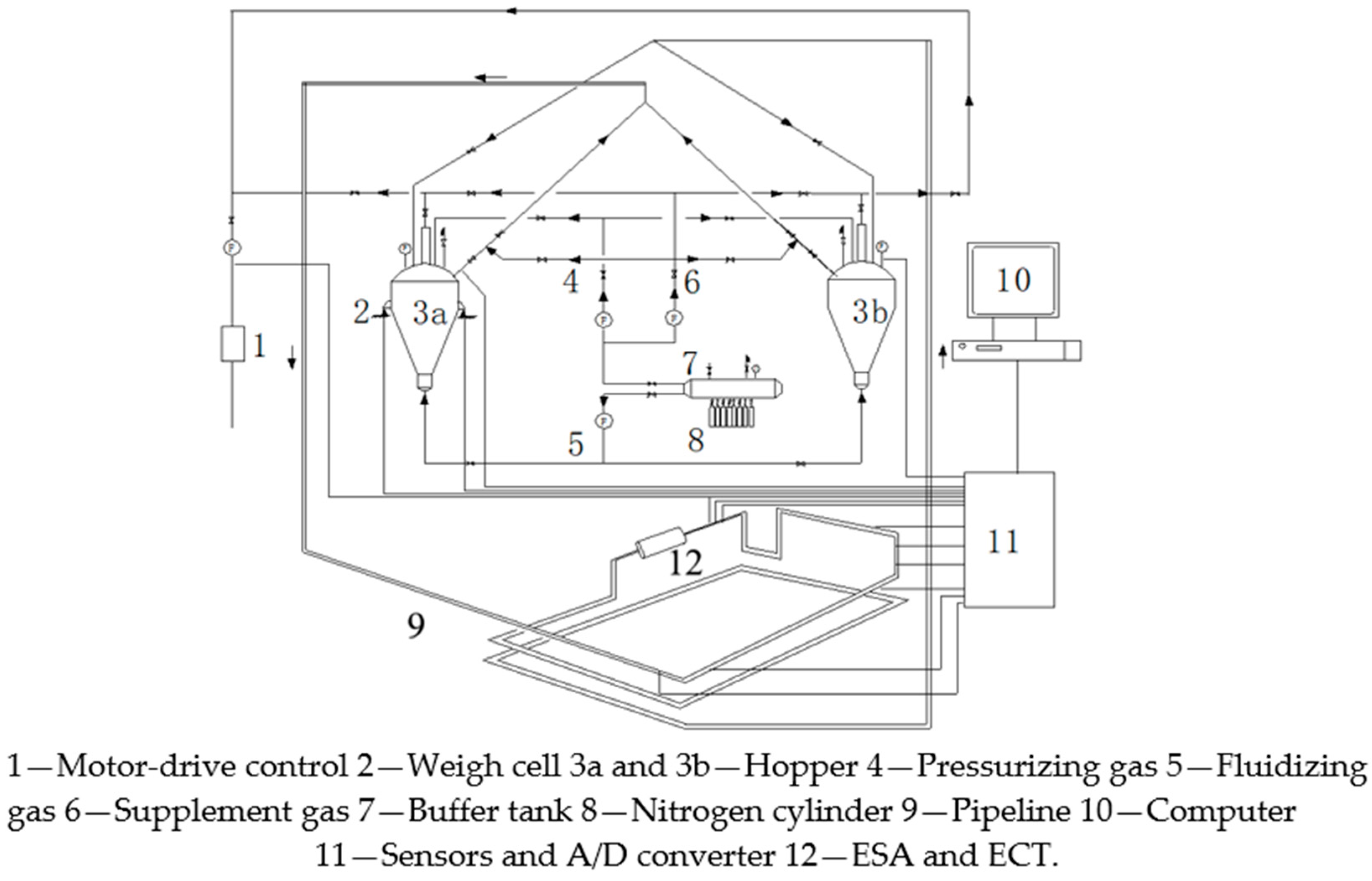
3. Experimental Setup
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Flow Patterns
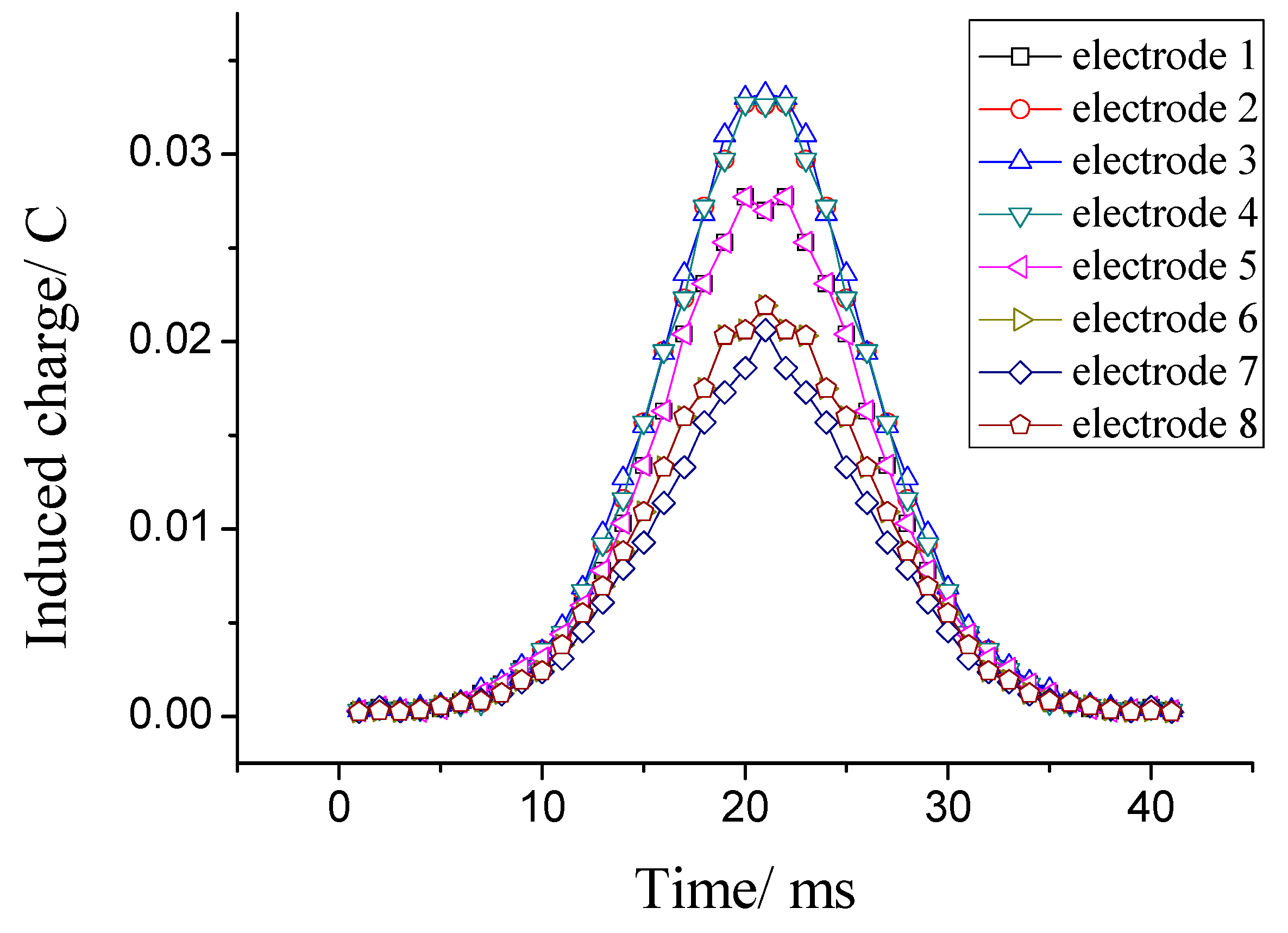
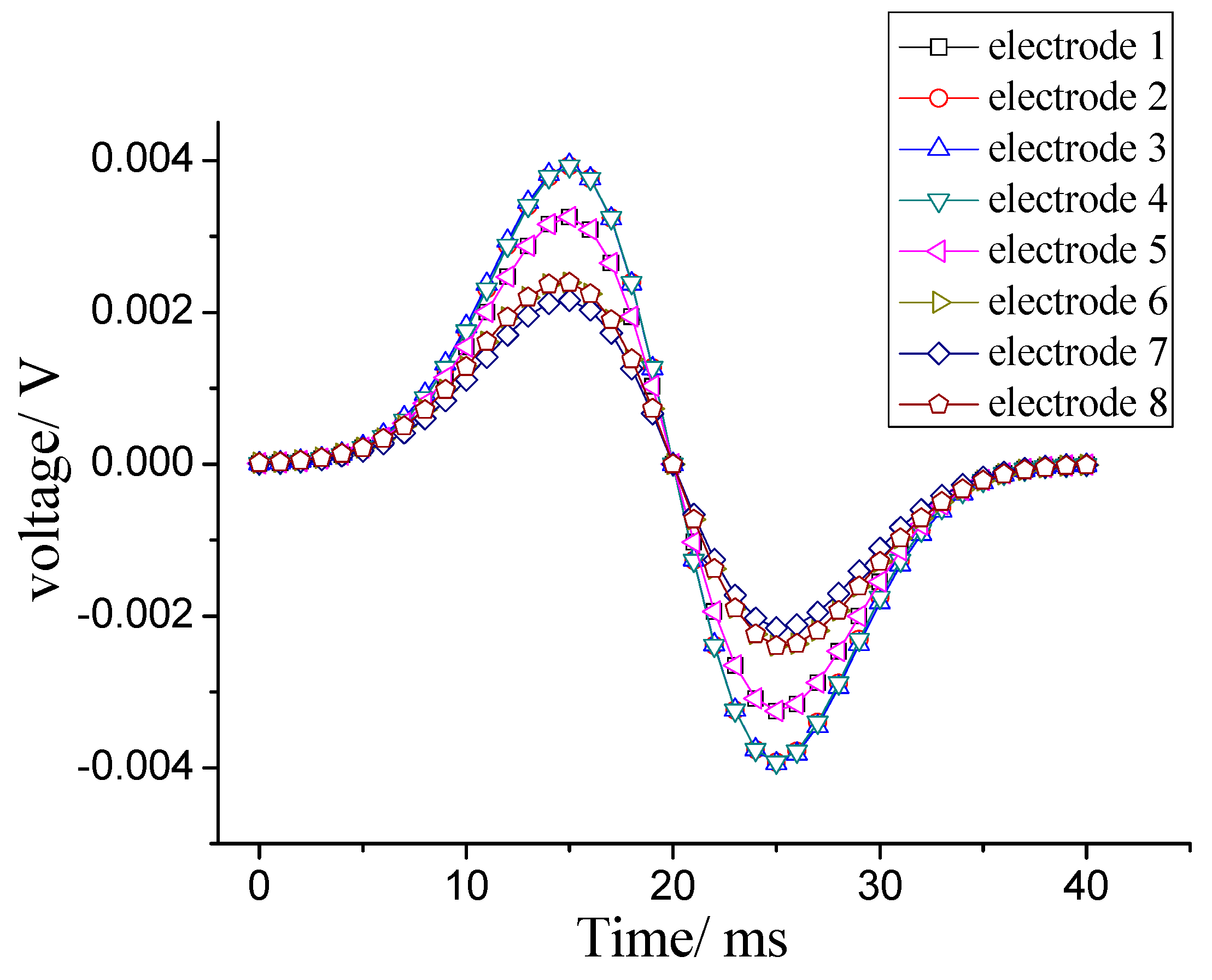
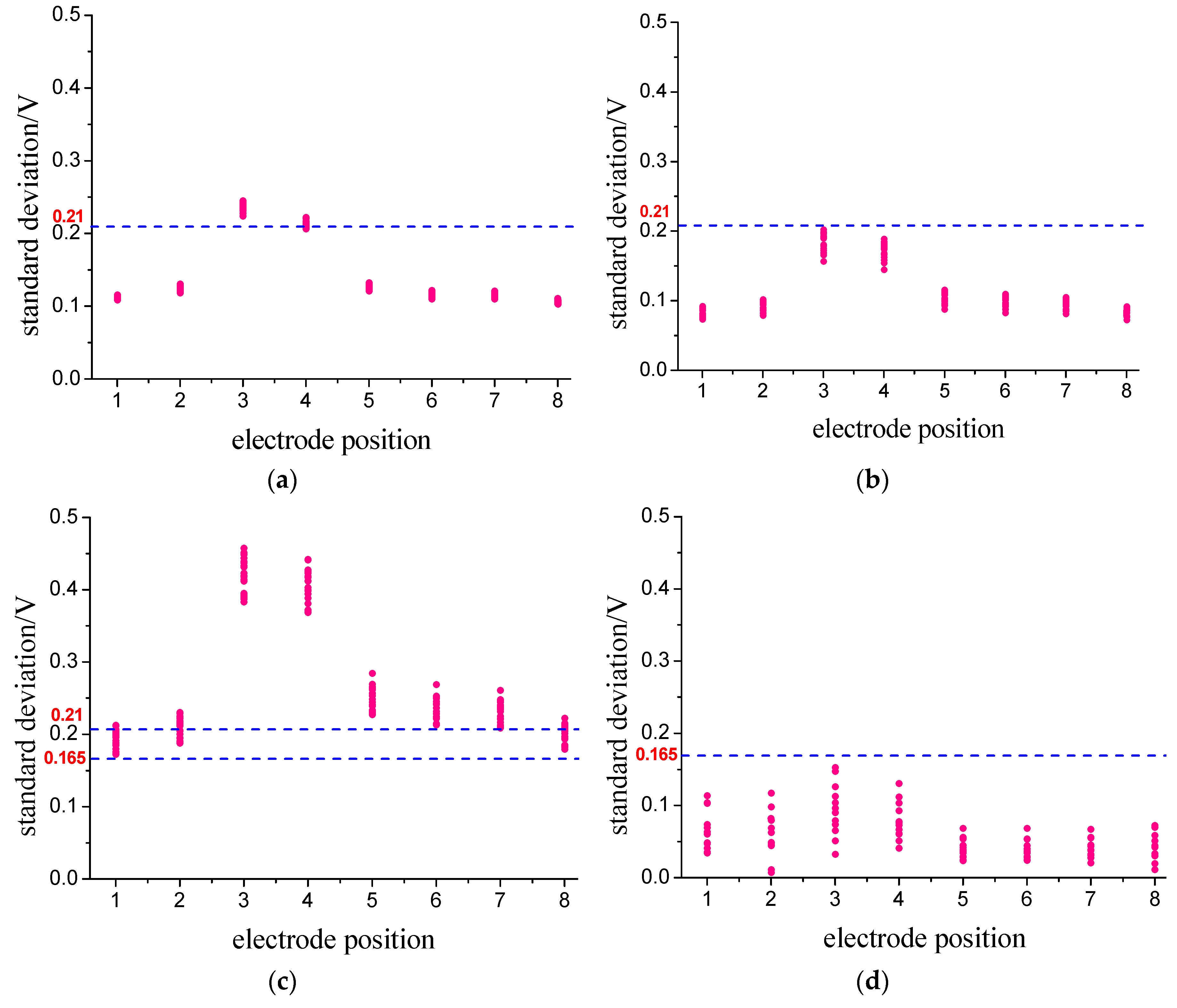
4.2. System Identification
- the average values of eight output signals’ amplitudes, [A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8];
- the standard deviation of eight output signals’ amplitudes, [S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8].
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cong, X.L.; Guo, X.L.; Cong, X.; Liu, K.; Sun, X.L. Flow pattern characteristics in vertical dense-phase pneumatic conveying of pulverized coal using Electrical Capacitance Tomography. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 15268–15275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Y.; Zhou, B.; Xu, C.L.; Wang, S.M. Thick-wall electrical capacitance tomography and its application in dense-phase pneumatic conveying under high pressure. Image Process. 2011, 5, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, J. Potential measurement in ECT system. J. Electrost. 2009, 67, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, E.; Salgado, R.; Ohishi, T.; Mastelari, N. Performance comparison of artificial neural networks and expert systems applied to flow pattern identification in vertical ascendant gas–liquid flows. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2010, 36, 738–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Moustafa, E.; Abdelsalam, A. Artificial neural network application for multiphase flow patterns detection: A new approach. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 145, 548–564. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Pratihar, D.; Maiti, B.; Das, P. Identification of flow regimes using conductivity probe signals and neural networks for counter-current gas–liquid two-phase flow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 84, 417–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.F.; Xu, C.L.; Wang, S.M. Flow characterization of high-pressure dense-phase pneumatic conveying of coal powder using multi-scale signal analysis. Particuology 2018, 36, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, S. Velocity measurement of pneumatically conveyed solid particles using an electrostatic sensor. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.L.; Wang, S.M.; Yan, Y. The spatial filtering method for solid particle velocity measurement based on an electrostatic sensor. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2013, 62, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liang, C.; Zhou, B.; Wang, S. HHT analysis of electrostatic fluctuation signals in dense phase pneumatic conveying of pulverized coal at high pressure. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.L.; Li, J.; Gao, H.M.; Wang, S.M. Investigations into sensing characteristics of electrostatic sensor arrays through computational modelling and practical experimentation. J. Electrost. 2012, 70, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.F.; Kong, M.; Xu, C.L.; Liang, C.; Wang, S.M. Flow Characterization of Dense-Phase Pneumatic Conveying System of Pulverized Coal through Electrostatic Sensor Arrays. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fu, F.F.; Li, S.; Xu, C.L.; Wang, S.M. Velocity characterization of dense phase pneumatically conveyed solid particles in horizontal pipeline through an integrated electrostatic sensor. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2015, 76, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H. Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall-Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Demuth, H.; Beale, M.; Hagan, M. Neural Network Toolbox 6: Users Guide; The Mathwork Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2008; Volume 21, pp. 1225–1233. [Google Scholar]






| Material | Mean Size/μm | Density/kg·m−3 | Resistivity/(Ω·m) | Moisture Content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lignite | 208.5 | 1350 | 2.3 × 1012 | 10.39 |
| Flow Pattern | Total Transportation Differential Pressure/MPa | Carrier Gas | Solid Mass Flow Rate/kg·s | Gas Velocity/m·s−1 | Ratio of Solid‒Gas Mass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fully suspended flow | 1.00 | CO2 | 0.264 | 8.284 | 5.8 |
| Stratified flow | 0.75 | CO2 | 0.218 | 6.815 | 6.2 |
| Dune flow | 0.50 | N2 | 0.192 | 4.757 | 15.7 |
| Slug flow | 0.33 | N2 | 0.128 | 4.029 | 12.8 |
| Correct Classification | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter/Pattern | SF | LF | DDF | DF |
| [A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8] | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| [S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8] | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, F.-f.; Li, J. Gas–Solid Two-Phase Flow Pattern Identification Based on Artificial Neural Network and Electrostatic Sensor Array. Sensors 2018, 18, 3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103522
Fu F-f, Li J. Gas–Solid Two-Phase Flow Pattern Identification Based on Artificial Neural Network and Electrostatic Sensor Array. Sensors. 2018; 18(10):3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103522
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Fei-fei, and Jian Li. 2018. "Gas–Solid Two-Phase Flow Pattern Identification Based on Artificial Neural Network and Electrostatic Sensor Array" Sensors 18, no. 10: 3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103522
APA StyleFu, F.-f., & Li, J. (2018). Gas–Solid Two-Phase Flow Pattern Identification Based on Artificial Neural Network and Electrostatic Sensor Array. Sensors, 18(10), 3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103522




