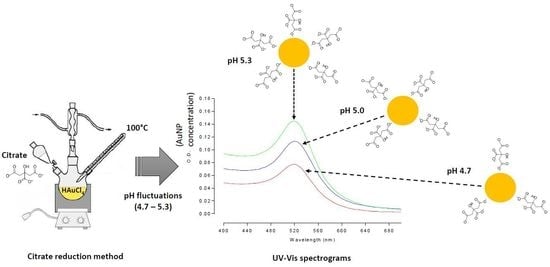
Slight pH Fluctuations in the Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis Process Influence the Performance of the Citrate Reduction Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs)
2.2. AuNP Concentration
2.3. Electron Microscopy Analysis
2.4. Surface Charge Characterization (pZ)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. pH Effect on the Concentration
3.2. AuNPs Characterization
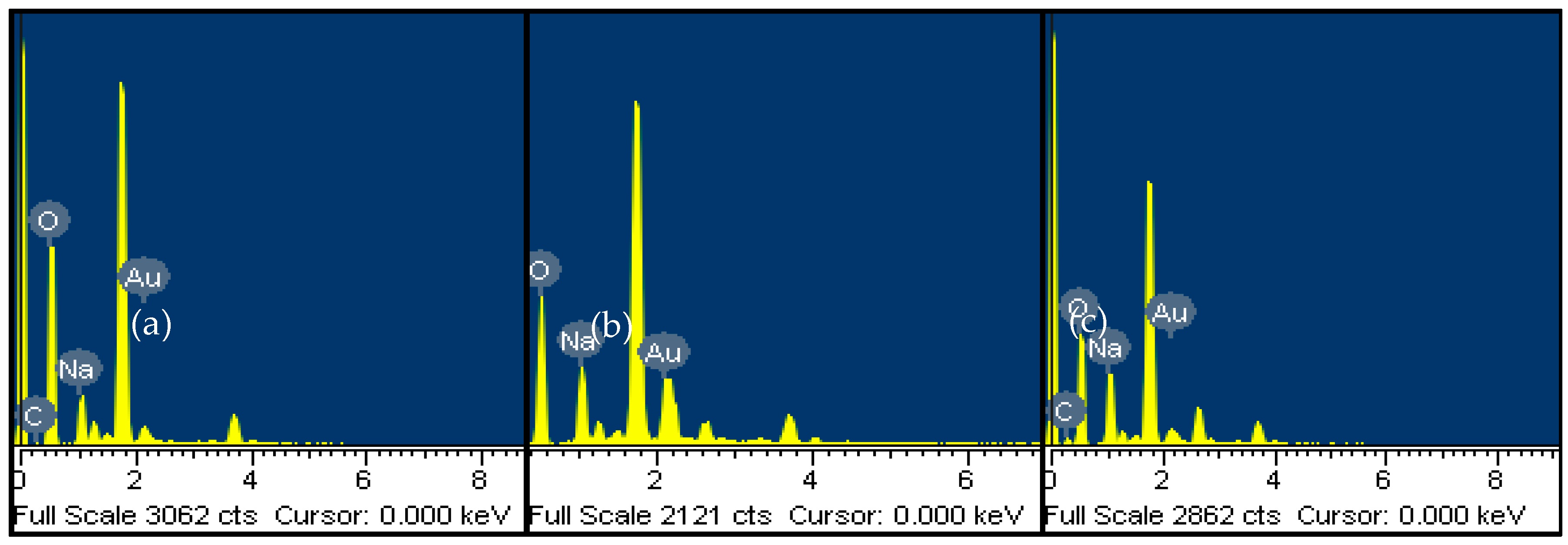
3.3. Surface Charge Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saha, K.; Agasti, S.S.; Kim, C.; Li, X.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2739–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, S.H.; Azzazy, H.M. Gold nanoparticles for molecular diagnostics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2009, 9, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhter, S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Ahmad, F.J.; Storm, G.; Kok, R.J. Gold nanoparticles in theranostic oncology: Current state-of-the-art. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 1225–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Oh, N.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.; Pack, C.G.; Park, J.H.; Park, Y. Label-free high-resolution 3-D imaging of gold nanoparticles inside live cells using optical diffraction tomography. Methods 2017, 136, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Tan, W. Aptamer-conjugated gold nanoparticles for bioanalysis. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, M.; Panneer Selvam, A.; Craven, J.E.; Prasad, S. Antibody-conjugated gold nanoparticle-based immunosensor for ultra-sensitive detection of troponin-T. J. Lab. Autom. 2014, 19, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amendola, V.; Pilot, R.; Frasconi, M.; Marago, O.M.; Iati, M.A. Surface plasmon resonance in gold nanoparticles: A review. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 203002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.L.; Coronado, E.; Zhao, L.L.; Schatz, G.C. The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: The influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, E.; Pradhan, N. Metal-induced aggregation of valine capped gold nanoparticles: An efficient and rapid approach for colorimetric detection of Pb2+ ions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, I.A.; Lee, S.J.; Jurng, J.; Gu, M.B. A novel colorimetric aptasensor using gold nanoparticle for a highly sensitive and specific detection of oxytetracycline. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1644–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xie, G.; Chen, J.; Lu, A.; Li, C.; Fu, H.; Ma, Z.; Wang, J. Rapid visual detection of aflatoxin B1 by label-free aptasensor using unmodified gold nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Y. Colorimetric sensor array based on gold nanoparticles with diverse surface charges for microorganisms identification. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10639–10643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Li, N.; Astruc, D. State of the art in gold nanoparticle synthesis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 638–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Ding, B. UV irradiation induced formation of Au nanoparticles at room temperature: The case of pH values. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 301, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Park, H.G.; Choi, S.H. γ-Irradiation-induced preparation of Ag and Au nanoparticles and their characterizations. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 105, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrolhosseini, A.R.; Abdul Rashid, S.; Zakaria, A. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles dispersed in palm oil using laser ablation technique. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 6496390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth process in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frens, G. Controlled nucleation for regulation of particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Santhanam, V. Monodisperse sub-10 nm gold nanoparticles by reversing the order of addition in Turkevich method—The role of chloroauric acid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husanua, E.; Chiappea, C.; Bernardinia, A.; Cappello, V.; Gemmi, M. Synthesis of colloidal Ag nanoparticles with citrate based ionic liquids as reducing and capping agents. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 538, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimling, J.; Maier, M.; Okenve, B.; Kotaidis, V.; Ballot, H.; Plech, A. Turkevich method for gold nanoparticle synthesis revisited. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 15700–15707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patungwasa, W.; Hodak, J. pH tunable morphology of the gold nanoparticles produced by citrate reduction. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 108, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Song, X.; Li, J.; Bai, Y.; Yang, W.; Peng, X. Size control of gold nanocrystals in citrate reduction: The third role of citrate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 13939–13948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, D.; Wan, G.; Xu, J.; Hou, W. Facile synthesis of concentrated gold nanoparticles with low size-distribution in water: Temperature and pH controls. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manimegalai, S.; Sridharan, T.; Rameshpathy, M.; Devi Rajeswari, V. Recent trends and methodologies in gold nanoparticle synthesis-a prospective review on drug delivery aspect. OpenNano 2017, 2, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Weston, A.; Brown, P. HPLC and CE: Principles and Practice; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Maye, M.; Han, L.; Kariuki, N.; Ly, N.; Chan, W.; Luo, J.; Zhong, C. Gold and alloy nanoparticles in solution and thin film assembly: Spectrophotometric determination of molar absorptivity. Anal. Chem. Acta 2003, 496, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasband, W. ImageJ. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 17 March 2018).
- Al-Johani, H.; Abou-Hamad, E.; Jedidi, A.; Widdifield, C.M.; Viger-Gravel, J.; Sangaru, S.S.; Gajan, D.; Anjum, D.H.; Ould-Chikh, S.; Hedhili, M.N.; et al. The structure and binding mode of citrate in the stabilization of gold nanoparticles. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, H.; Kushwaha, A.; Kumar, A.; Aslam, M. A Facile pH controlled citrate-based reduction method for gold nanoparticle synthesis at room temperature. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Shumaker-Parry, J.S. Structural study of citrate layers on gold nanoparticles: Role of intermolecular interactions in stabilizing nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1907–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, S.; Barcaro, G.; Sementa, L.; Carravetta, V.; Ågren, H. Characterization of the adsorption dynamics of trisodium citrate on gold in water solution. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 49655–49663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, W.; Han, S.; Shin, W.; Kim, Y. Adsorption of carboxylic acids on gold by anodic reaction. Langmuir 2003, 19, 4211–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, N.D.; Harvey, S.; Idesis, F.A.; Murphy, C.J. Understanding the seed-mediated growth of gold nanorods through a fractional factorial design of experiments. Langmuir 2016, 33, 1891–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| pH | Zeta Potential Mean (mV) | Peak 1 (mV) | Peak 2 (mV) | Peak 3 (mV) | Concentration (nM) | Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.7 | −42.2 ± 35.1 | −58.5 ± 15.2 | −26.7 ± 8.2 | 16.8 ± 7.1 | 1.29 ± 0.09 | 13.92 ± 1.45 |
| 5.0 | −44.9 ± 5.1 | −44.9 ± 5.1 | 1.88 ± 0.03 | 14.94 ± 1.53 | ||
| 5.3 | −45.7 ± 7.6 | −45.7 ± 7.6 | 2.40 ± 0.12 | 15.50 ± 1.51 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Contreras-Trigo, B.; Díaz-García, V.; Guzmán-Gutierrez, E.; Sanhueza, I.; Coelho, P.; Godoy, S.E.; Torres, S.; Oyarzún, P. Slight pH Fluctuations in the Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis Process Influence the Performance of the Citrate Reduction Method. Sensors 2018, 18, 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072246
Contreras-Trigo B, Díaz-García V, Guzmán-Gutierrez E, Sanhueza I, Coelho P, Godoy SE, Torres S, Oyarzún P. Slight pH Fluctuations in the Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis Process Influence the Performance of the Citrate Reduction Method. Sensors. 2018; 18(7):2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072246
Chicago/Turabian StyleContreras-Trigo, Braulio, Víctor Díaz-García, Enrique Guzmán-Gutierrez, Ignacio Sanhueza, Pablo Coelho, Sebastián E. Godoy, Sergio Torres, and Patricio Oyarzún. 2018. "Slight pH Fluctuations in the Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis Process Influence the Performance of the Citrate Reduction Method" Sensors 18, no. 7: 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072246
APA StyleContreras-Trigo, B., Díaz-García, V., Guzmán-Gutierrez, E., Sanhueza, I., Coelho, P., Godoy, S. E., Torres, S., & Oyarzún, P. (2018). Slight pH Fluctuations in the Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis Process Influence the Performance of the Citrate Reduction Method. Sensors, 18(7), 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072246