Classifier Level Fusion of Accelerometer and sEMG Signals for Automatic Fitness Activity Diarization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.2. Classification
2.3. Results
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naranjo-Hernández, D.; Roa, L.M.; Reina-Tosina, J.; Estudillo-Valderrama, M.A. SoM: A Smart Sensor for Human Activity Monitoring and Assisted Healthy Ageing. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 3177–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Martin, D.; Samà, A.; Perez-Lopez, C.; Català, A.; Cabestany, J.; Rodriguez-Molinero, A. SVM-based posture identification with a single waist-located triaxial accelerometer. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 7203–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannini, A.; Intille, S.S.; Rosenberger, M.; Sabatini, A.M.; Haskell, W. Activity recognition using a single accelerometer placed at the wrist or ankle. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 2193–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Huitzil, C.; Nuno-Maganda, M. Robust smartphone-based human activity recognition using a tri-axial accelerometer. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 6th Latin American Symposium on Circuits Systems (LASCAS), Montevideo, Uruguay, 24–27 February 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Biagetti, G.; Crippa, P.; Falaschetti, L.; Orcioni, S.; Turchetti, C. An Efficient Technique for Real-Time Human Activity Classification Using Accelerometer Data. In Intelligent Decision Technologies 2016, Proceedings of the 8th KES International Conference on Intelligent Decision Technologies—Part I, Puerto de la Cruz, Spain, 15–17 June 2016; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 425–434. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Lee, Y.K.; Lee, S.; Kim, T.S. Human Activity Recognition via an Accelerometer-Enabled-Smartphone Using Kernel Discriminant Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2010 5th International Conference on Future Information Technology, Busan, Korea, 21–23 May 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dernbach, S.; Das, B.; Krishnan, N.C.; Thomas, B.L.; Cook, D.J. Simple and Complex Activity Recognition through Smart Phones. In Proceedings of the 2012 8th International Conference on Intelligent Environments, Guanajuato, Mexico, 26–29 June 2012; pp. 214–221. [Google Scholar]
- Anguita, D.; Ghio, A.; Oneto, L.; Parra, X.; Reyes-Ortiz, J.L. Energy Efficient Smartphone-Based Activity Recognition using Fixed-Point Arithmetic. J. Univ. Comput. Sci. 2013, 19, 1295–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Bayat, A.; Pomplun, M.; Tran, D.A. A study on human activity recognition using accelerometer data from smartphones. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 34, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; He, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Ayoola, I. Identifying typical physical activity on smartphone with varying positions and orientations. BioMed. Eng. Online 2015, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantelopoulos, A.; Bourbakis, N. A survey on wearable biosensor systems for health monitoring. In Proceeding of the 2008 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–25 August 2008; pp. 4887–4890. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, T.Y.; Echeimberg, J.O.; Pompeu, J.E.; Lucareli, P.R.G.; Garbelotti, S.; Gimenes, R.; Apolinário, A. Root mean square value of the electromyographic signal in the isometric torque of the quadriceps, hamstrings and brachial biceps muscles in female subjects. J. Appl. Res. 2010, 10, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.M.; Liu, S.H.; Wu, X.H. A wireless sEMG recording system and its application to muscle fatigue detection. Sensors 2012, 12, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Koo, K.H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Spatiotemporal analysis of EMG signals for muscle rehabilitation monitoring system. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 2nd Global Conference on Consumer Electronics, Tokyo, Japan, 1–4 October 2013; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Biagetti, G.; Crippa, P.; Falaschetti, L.; Orcioni, S.; Turchetti, C. A Rule Based Framework for Smart Training Using sEMG Signal. In Intelligent Decision Technologies; Neves-Silva, R., Jain, L.C., Howlett, R.J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Biagetti, G.; Crippa, P.; Curzi, A.; Orcioni, S.; Turchetti, C. Analysis of the EMG Signal During Cyclic Movements Using Multicomponent AM-FM Decomposition. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2015, 19, 1672–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagetti, G.; Crippa, P.; Orcioni, S.; Turchetti, C. Surface EMG Fatigue Analysis by Means of Homomorphic Deconvolution. In Mobile Networks for Biometric Data Analysis; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 173–188. [Google Scholar]
- Biagetti, G.; Crippa, P.; Orcioni, S.; Turchetti, C. Homomorphic Deconvolution for MUAP Estimation from Surface EMG Signals. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2017, 21, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagetti, G.; Crippa, P.; Falaschetti, L.; Orcioni, S.; Turchetti, C. Wireless surface electromyograph and electrocardiograph system on 802.15.4. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2016, 62, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawab, S.H.; Roy, S.H.; Luca, C.J.D. Functional activity monitoring from wearable sensor data. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–5 September 2004; pp. 979–982. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.H.; Cheng, M.S.; Chang, S.S.; Moore, J.; Luca, G.D.; Nawab, S.H.; Luca, C.J.D. A Combined sEMG and Accelerometer System for Monitoring Functional Activity in Stroke. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2009, 17, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.H.; Yang, J.H.; Lantz, V.; Wang, K.Q. Hand Gesture Recognition and Virtual Game Control Based on 3D Accelerometer and EMG Sensors. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, Sanibel Island, FL, USA, 8–11 February 2009; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 401–406. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemzadeh, H.; Jafari, R.; Prabhakaran, B. A Body Sensor Network With Electromyogram and Inertial Sensors: Multimodal Interpretation of Muscular Activities. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Lantz, V.; Wang, K.; Yang, J. A Framework for Hand Gesture Recognition Based on Accelerometer and EMG Sensors. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A 2011, 41, 1064–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spulber, I.; Georgiou, P.; Eftekhar, A.; Toumazou, C.; Duffell, L.; Bergmann, J.; McGregor, A.; Mehta, T.; Hernandez, M.; Burdett, A. Frequency analysis of wireless accelerometer and EMG sensors data: Towards discrimination of normal and asymmetric walking pattern. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Seoul, Korea, 20–23 May 2012; pp. 2645–2648. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Chen, R.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X. Electromyography-Based Locomotion Pattern Recognition and Personal Positioning Toward Improved Context-Awareness Applications. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2013, 43, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gong, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, X.; Chen, X. Motor function evaluation of hemiplegic upper-extremities using data fusion from wearable inertial and surface EMG sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faundez-Zanuy, M. Data fusion in biometrics. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2005, 20, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanedo, F. A review of data fusion techniques. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 704504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, I.; Garcia, N.; Pombo, N.; Flórez-Revuelta, F. From data acquisition to data fusion: A comprehensive review and a roadmap for the identification of activities of daily living using mobile devices. Sensors 2016, 16, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapata, J.; Duque, C.; Rojas-Idarraga, Y.; Gonzalez, M.; Guzmán, J.; Becerra Botero, M. Data fusion applied to biometric identification—A review. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2017, 735, 721–733. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Ji, W.; Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Weng, J.; Deng, S.; Gao, S.; Yuan, C.A. Review on mining data from multiple data sources. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2018, 109, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Chen, L.; Wu, X.; Guo, H.; Chen, G. Hierarchical Complex Activity Representation and Recognition Using Topic Model and Classifier Level Fusion. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagetti, G.; Crippa, P.; Falaschetti, L.; Orcioni, S.; Turchetti, C. A portable wireless sEMG and inertial acquisition system for human activity monitoring. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2017, 10209, 608–620. [Google Scholar]
- Biagetti, G.; Crippa, P.; Falaschetti, L.; Orcioni, S.; Turchetti, C. Human Activity Monitoring System Based on Wearable sEMG and Accelerometer Wireless Sensor Nodes. BioMed. Eng. Online 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Hermens, H.J.; Freriks, B. European recommendations for surface electromyography [CDROM]. Roessingh Res. Dev. 1999, 8, 13–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J.R. Induction of decision trees. Mach. Learn. 1986, 1, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinberger, K.Q.; Saul, L.K. Distance metric learning for large margin nearest neighbor classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2009, 10, 207–244. [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga, K. Introduction to Statistical Pattern Recognition; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
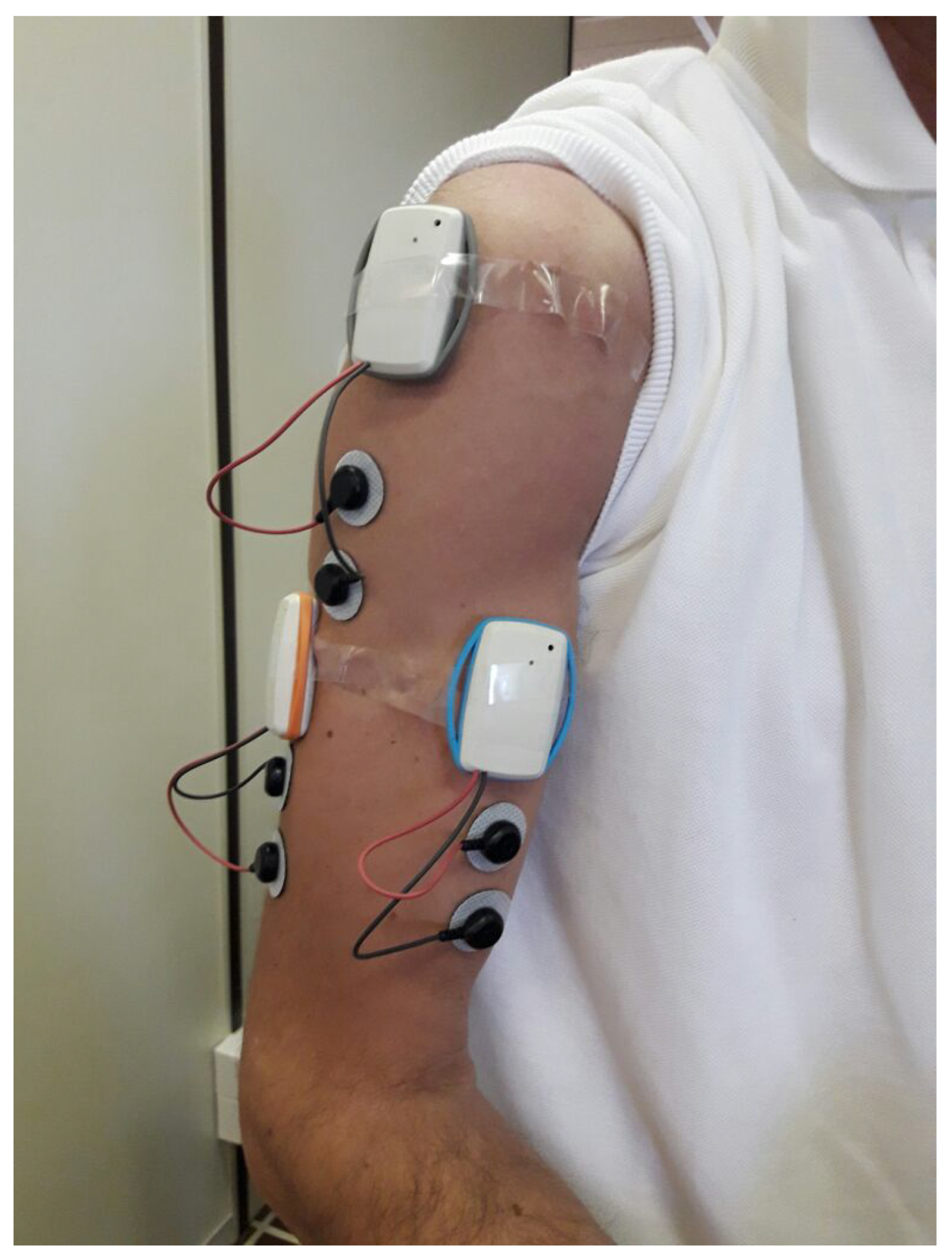

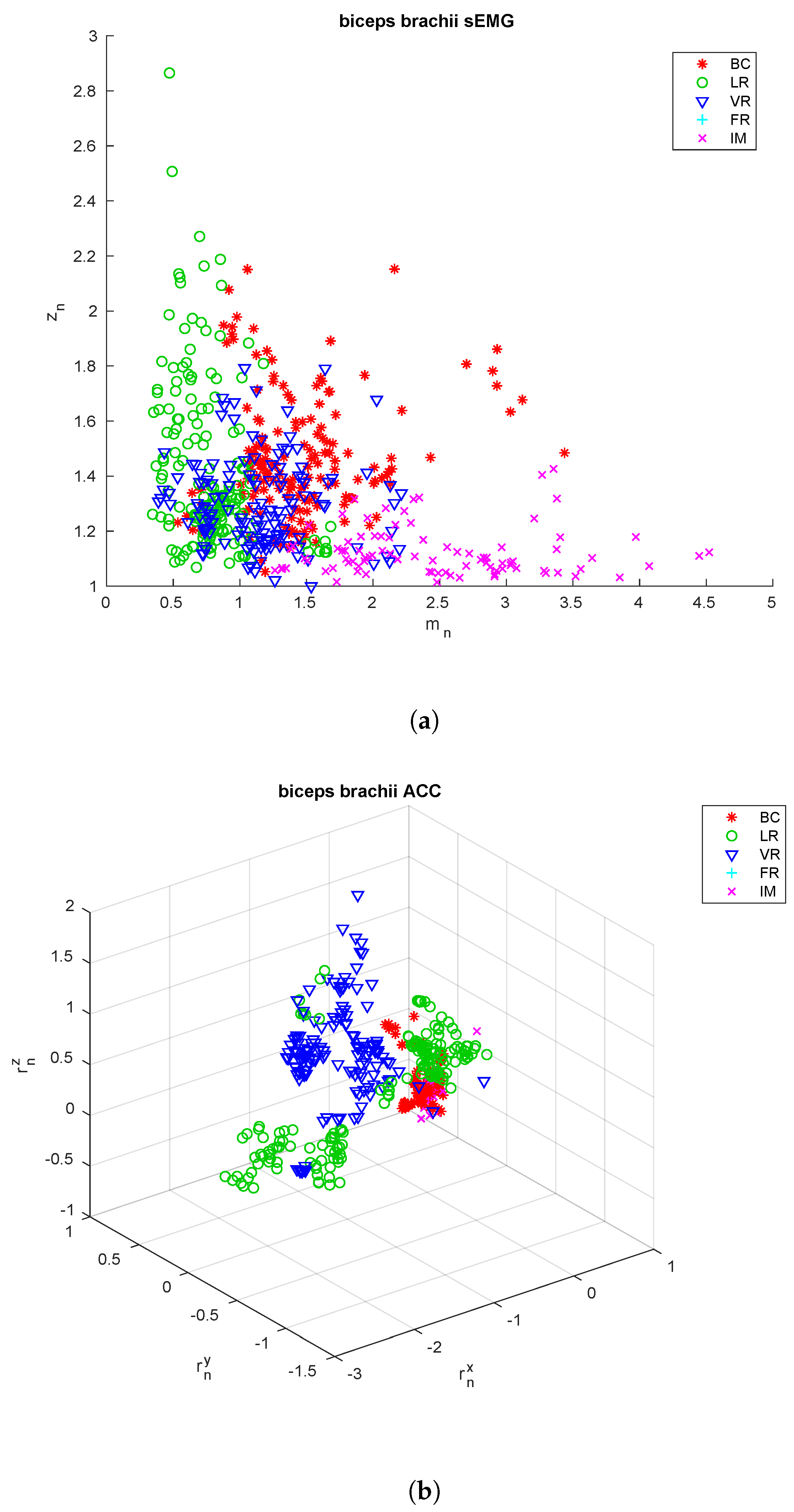

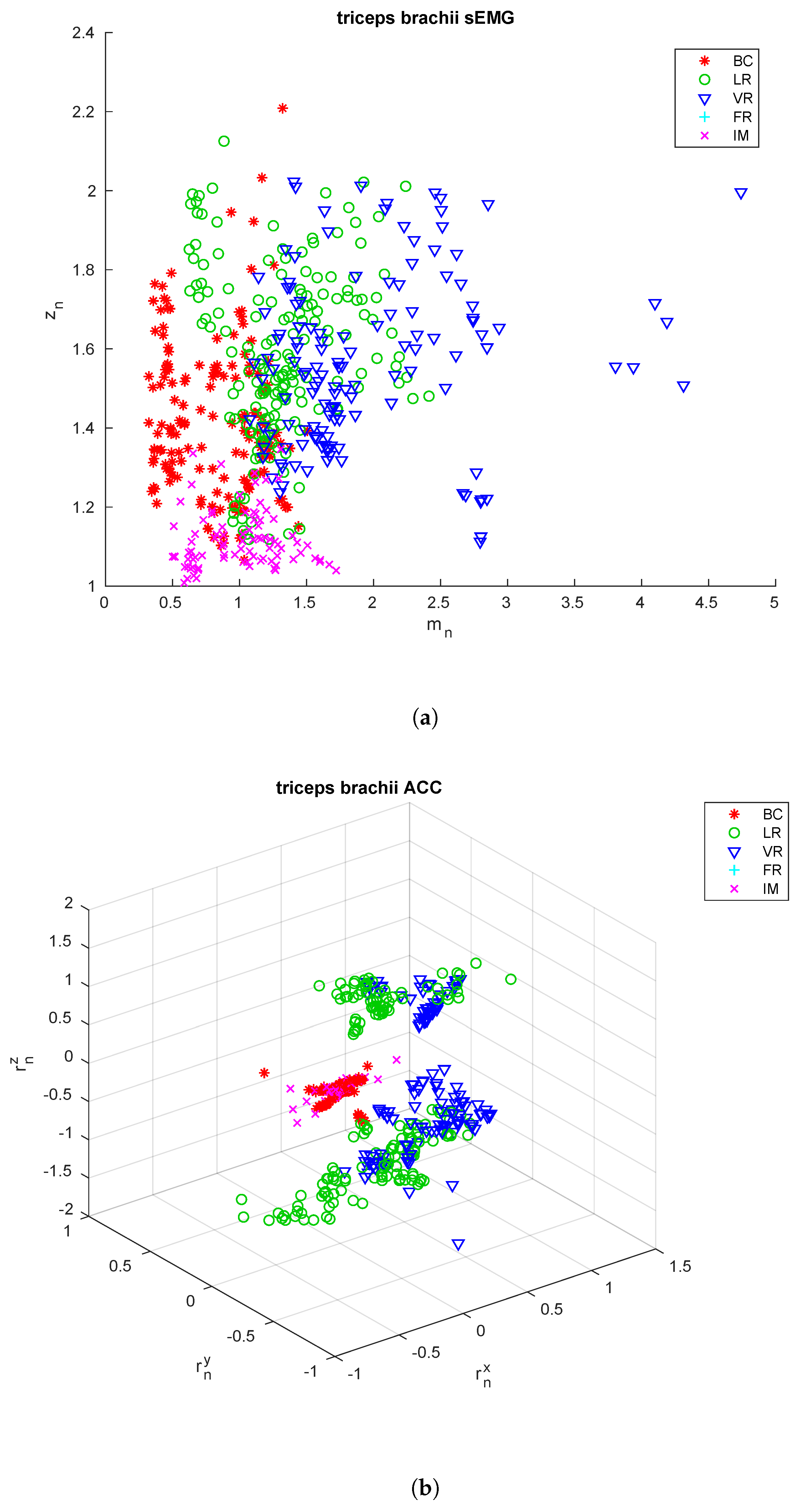

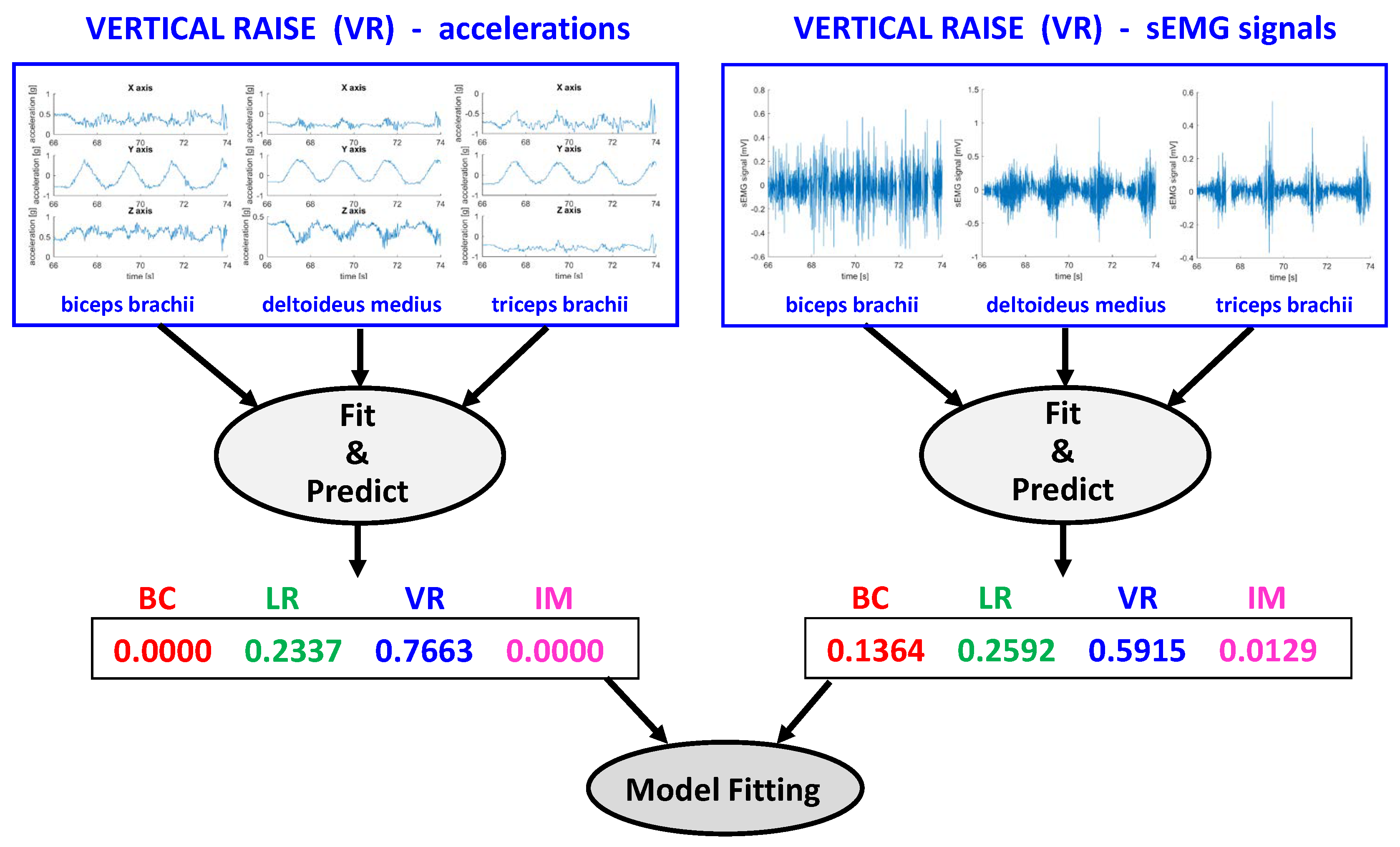
| Subject | Gender | Weight | BC | LR | VR | FR | IM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 3 kg | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | M | 3 kg | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| 3 | M | 3 kg | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | M | 3 kg | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 5 | M | 3 kg | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 6 | M | 3 kg | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | M | 3 kg | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 8 | M | 3 kg | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 9 | F | 1 kg | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 10 | M | 3 kg | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Subject | BC | LR | VR | FR | IM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 67 (18) | 74 (20) | 65 (17) | 68 (18) | 50 (13) |
| 2 | 54 (14) | 51 (13) | 36 (10) | 47 (13) | 40 (11) |
| 3 | 74 (19) | 72 (19) | 35 ( 9) | 0 ( 0) | 3 ( 0) |
| 4 | 41 (11) | 65 (17) | 62 (16) | 49 (13) | 37 ( 9) |
| 5 | 69 (18) | 61 (16) | 59 (16) | 71 (19) | 28 (08) |
| 6 | 32 ( 8) | 28 ( 7) | 29 ( 8) | 27 ( 7) | 23 ( 6) |
| 7 | 87 (23) | 99 (26) | 71 (18) | 83 (22) | 65 (17) |
| 8 | 90 (23) | 93 (24) | 56 (15) | 96 (24) | 51 (13) |
| 9 | 52 (14) | 59 (16) | 51 (14) | 53 (14) | 25 ( 7) |
| 10 | 59 (15) | 60 (16) | 57 (15) | 58 (15) | 24 ( 6) |
| Total | 625 (163) | 662 (174) | 521 (138) | 552 (145) | 346 (90) |
| 1st Stage | No Fusion | 2nd Stage Classifier | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | EMG | SVMp | SVMg | SVMl | Tree | KNN | LDA | |||
| SVMp | 73.5 48.1–96.0 | 75.3 43.9–99.2 | 80.3 57.5–98.0 | 61.2 41.5–78.7 | 80.6 57.5–98.0 | 70.0 45.0–96.0 | 71.4 46.3–87.5 | 82.1 59.4–100 | ||
| SVMg | 59.6 40.2–73.8 | 48.3 32.1–61.1 | 53.8 36.5–68.3 | 28.1 16.8–35.5 | 47.5 31.0–71.3 | 39.5 20.6–63.0 | 63.9 49.1–78.7 | 36.3 8.6–49.7 | ||
| SVMl | 64.3 41.2–93.9 | 81.4 49.5–99.0 | 79.1 43.9–99.2 | 58.5 38.1–70.3 | 81.8 49.0–100 | 78.5 45.5–99.2 | 79.6 45.9–100 | 82.6 50.0–100 | ||
| Tree | 62.2 36.2–89.3 | 71.9 42.9–91.2 | 66.0 37.8–96.9 | 63.3 39.4–83.5 | 65.8 39.4–96.9 | 65.4 43.2–86.9 | 66.1 40.4–83.6 | 64.4 38.7–92.1 | ||
| KNN | 75.1 42.5–91.8 | 74.6 45.9–96.1 | 80.6 63.2–97.5 | 77.6 48.0–93.0 | 75.9 46.2–90.8 | 75.1 42.5–91.8 | 79.9 59.8–97.5 | 30.8 26.0–36.0 | ||
| LDA | 66.6 40.7–88.0 | 77.7 49.5–100 | 76.5 48.4–99.0 | 74.1 40.8–97.1 | 80.2 51.0–99.2 | 77.6 50.5–98.8 | 78.4 59.7–98.4 | 80.4 52.5–99.2 | ||
| BC | LR | VR | IM | BC | LR | VR | IM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC | 143.6 | 0.4 | 6.6 | 12.4 | BC | 146.4 | 4.1 | 4.0 | 8.4 | |||
| LR | 1.0 | 140.2 | 32.8 | 0.0 | LR | 0.0 | 171.8 | 2.2 | 0.0 | |||
| VR | 1.0 | 36.1 | 100.9 | 0.0 | VR | 3.3 | 67.1 | 67.6 | 0.0 | |||
| IM | 8.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 82.0 | IM | 20.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 69.9 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biagetti, G.; Crippa, P.; Falaschetti, L.; Turchetti, C. Classifier Level Fusion of Accelerometer and sEMG Signals for Automatic Fitness Activity Diarization. Sensors 2018, 18, 2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092850
Biagetti G, Crippa P, Falaschetti L, Turchetti C. Classifier Level Fusion of Accelerometer and sEMG Signals for Automatic Fitness Activity Diarization. Sensors. 2018; 18(9):2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092850
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiagetti, Giorgio, Paolo Crippa, Laura Falaschetti, and Claudio Turchetti. 2018. "Classifier Level Fusion of Accelerometer and sEMG Signals for Automatic Fitness Activity Diarization" Sensors 18, no. 9: 2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092850
APA StyleBiagetti, G., Crippa, P., Falaschetti, L., & Turchetti, C. (2018). Classifier Level Fusion of Accelerometer and sEMG Signals for Automatic Fitness Activity Diarization. Sensors, 18(9), 2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092850








