Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation Based on Deep Q-Network in V2V Communications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
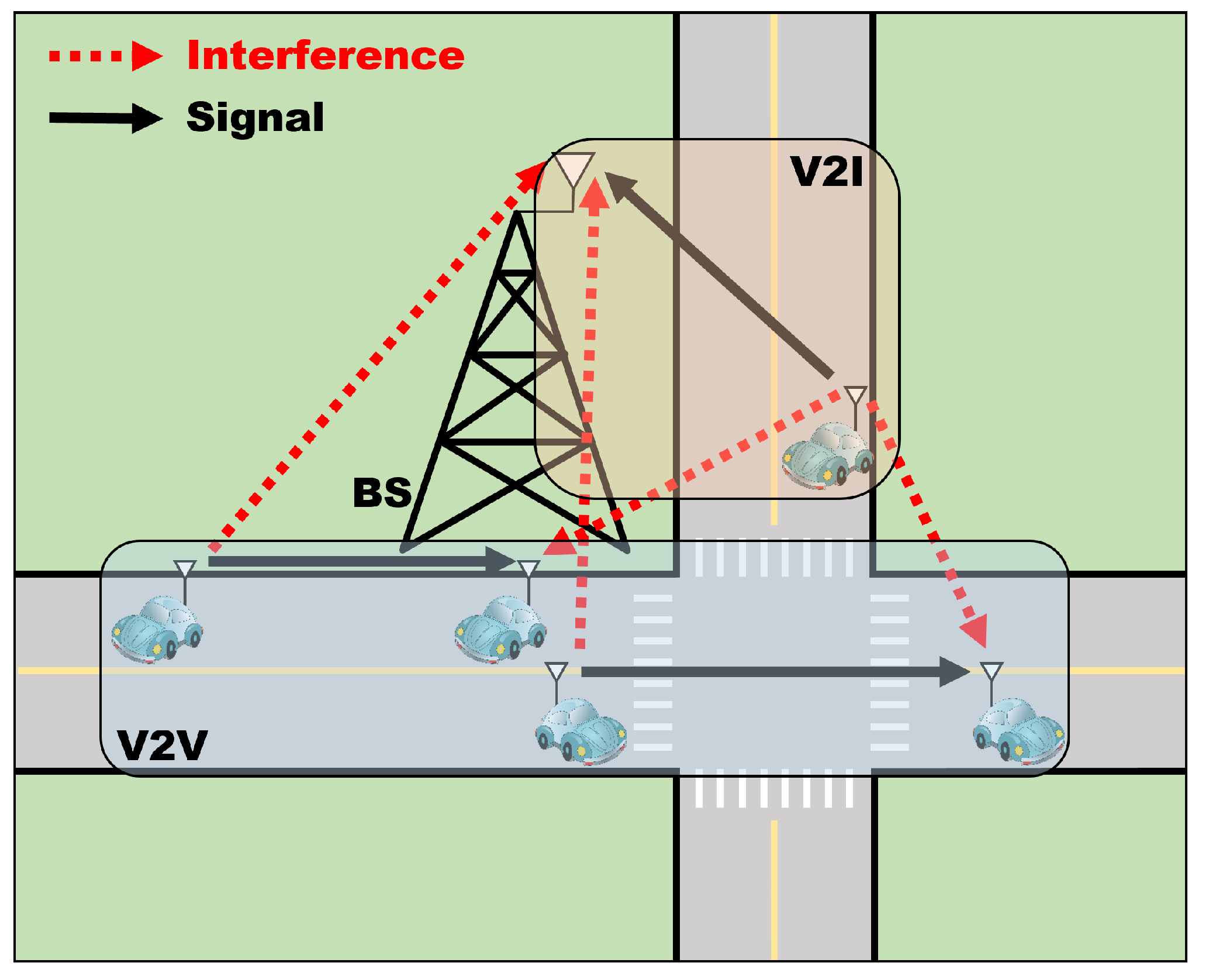
3. System Model
4. Deep Q-Network for Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation
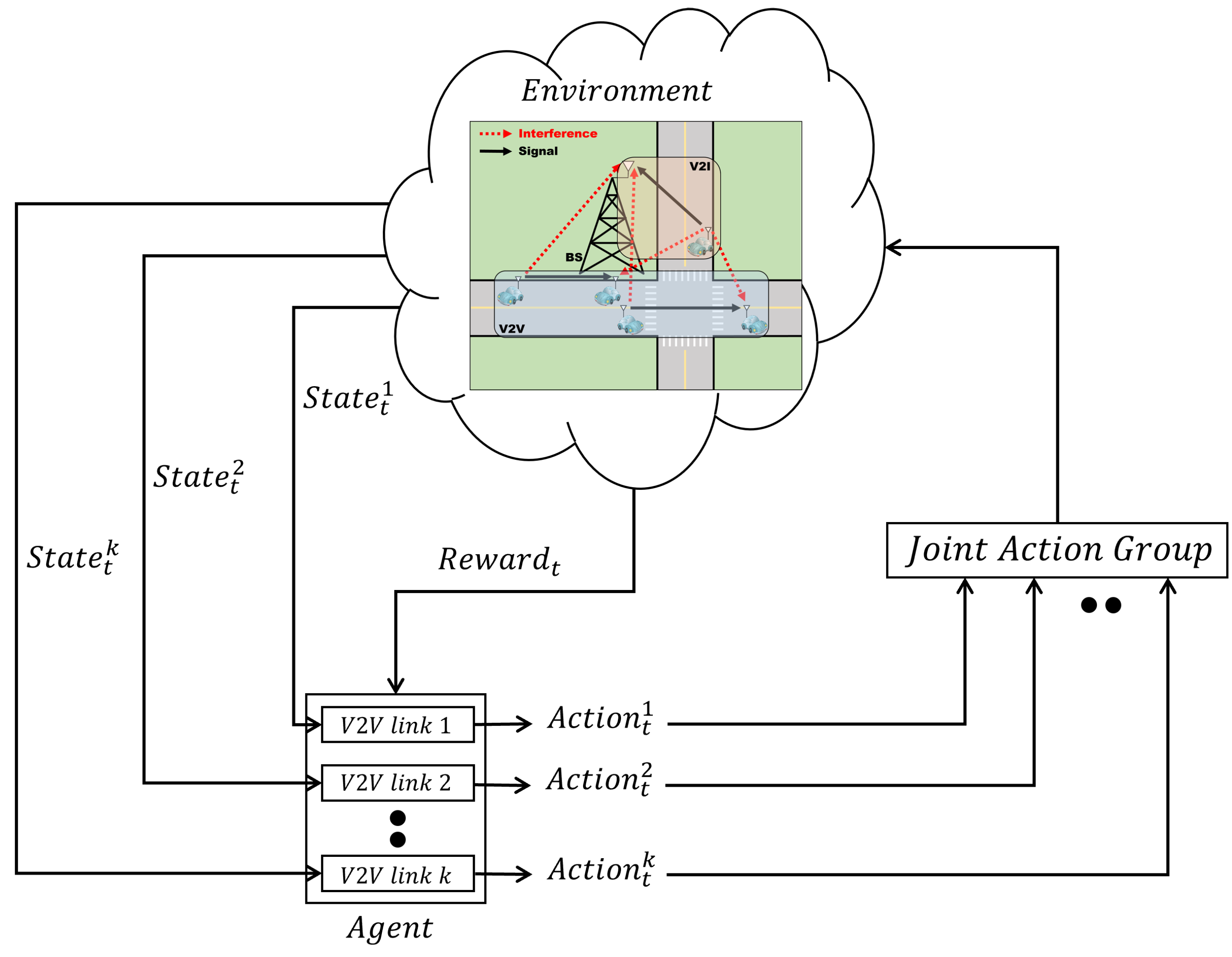
4.1. Reinforcement Learning
- 1.
- State space: We use the following state, similar to the unicast scenario of [11].where is the CSI of V2I links at time t; is the interference power to the link at time ; is the instantaneous CSI of the corresponding V2V link at time t; is the information of RBs selected by surrounding vehicles at time ; is the time remaining to satisfy the latency constraints at time t; and is the remaining data to be received from the transmitter of the V2V link at time t. , , , and are vectors containing the state information of the corresponding RBs, and and are scalar values that are the time remaining to satisfy the latency constraints and the remaining data, respectively. Therefore, the dimension of the state space is given by .
- 2.
- Action space: The action determines the transmit power and the allocation of RBs. Hence, the dimensions of the action space are given by , where is the number of transmit power levels in the V2V link and is the number of RBs.
- 3.
- Reward: We formulate the following reward function taking two penalties into account, the transmission time and the power consumption:where is the maximum tolerable latency, and therefore, means the transmission time. Moreover, is the maximum transmit power in the V2V link. and represent the weight for the sum rate of the V2I links and the sum rate of the V2V links, respectively. and represent the weight of the penalty according to an increase in the transmission time and the penalty according to an increase in the transmit power, respectively. As the sum rate of the V2I or V2V links increases, a positive factor is added. However, as the transmission time or power consumption increases, a negative factor is added.
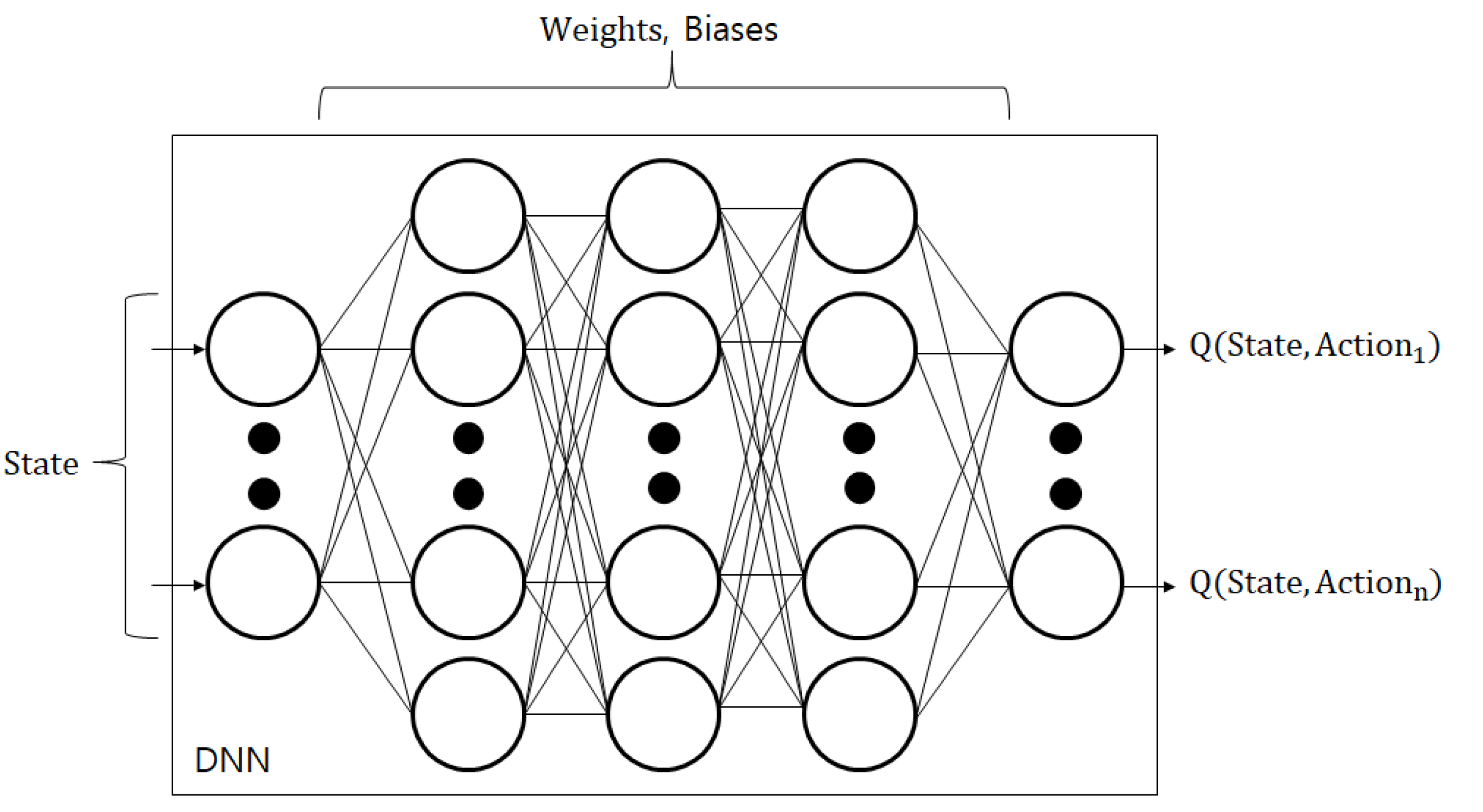
4.2. Deep Q-Network
4.3. Training and Testing Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: Training algorithm |
|
| Algorithm 2: Testing algorithm |
|
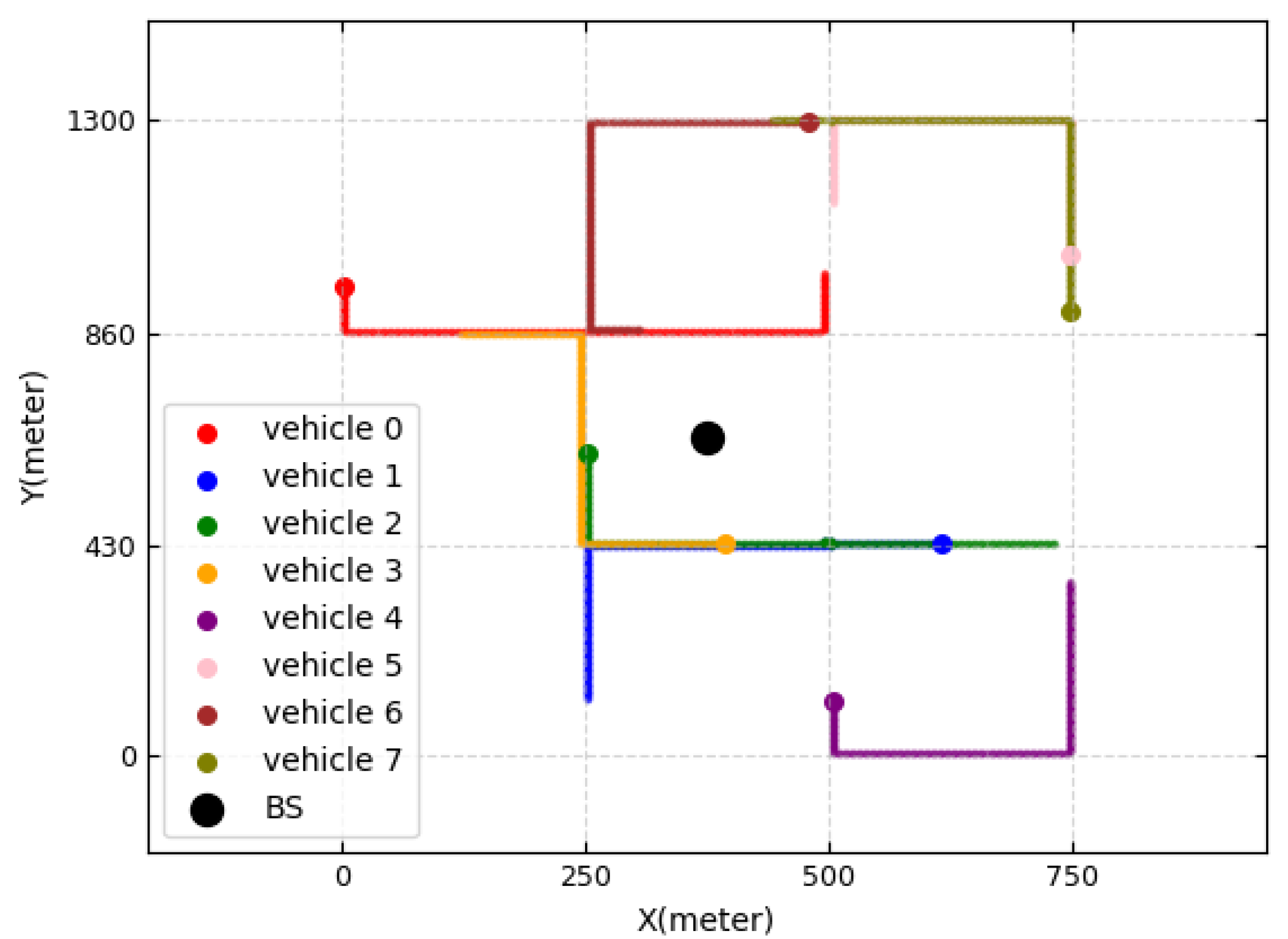
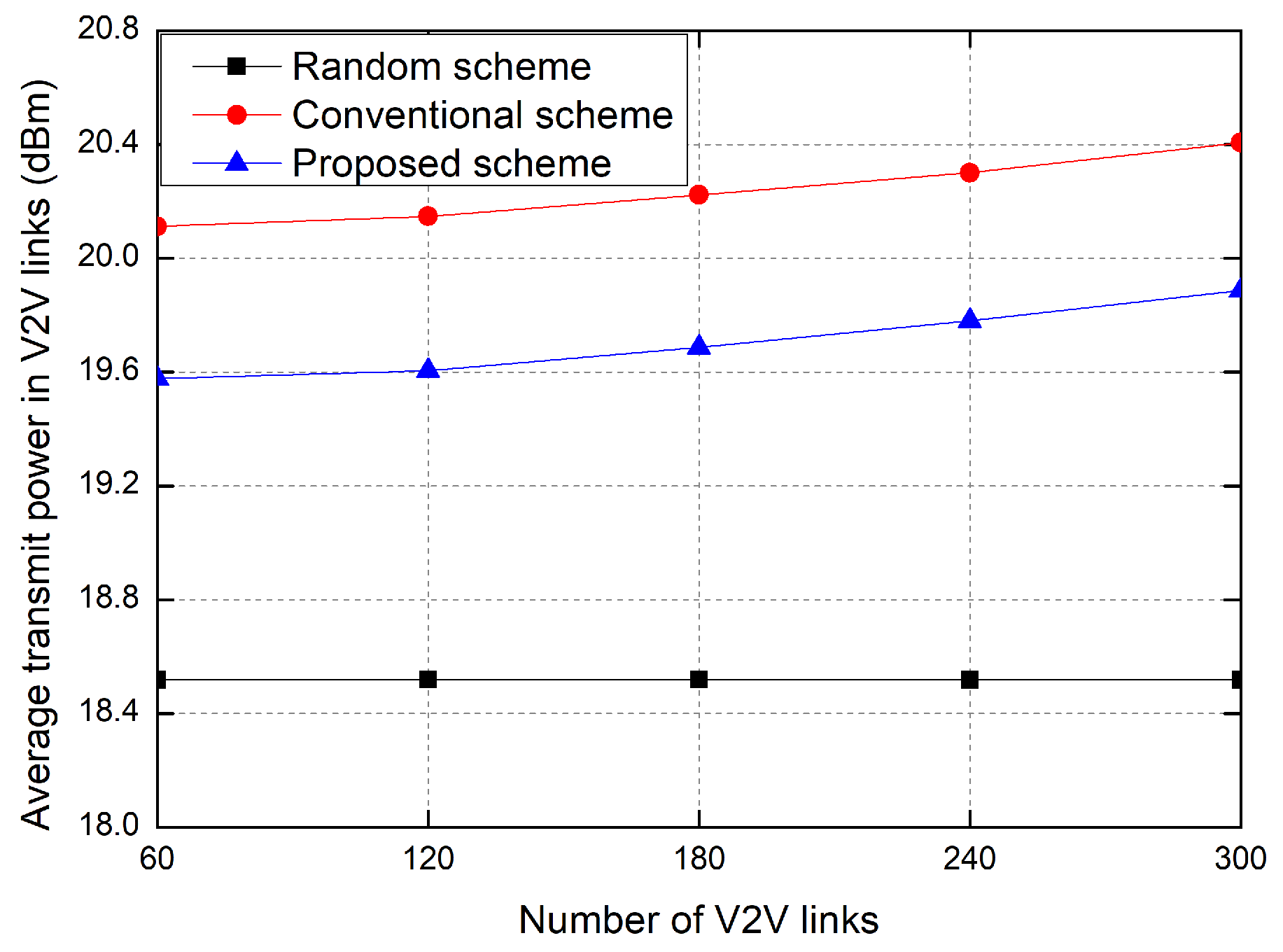
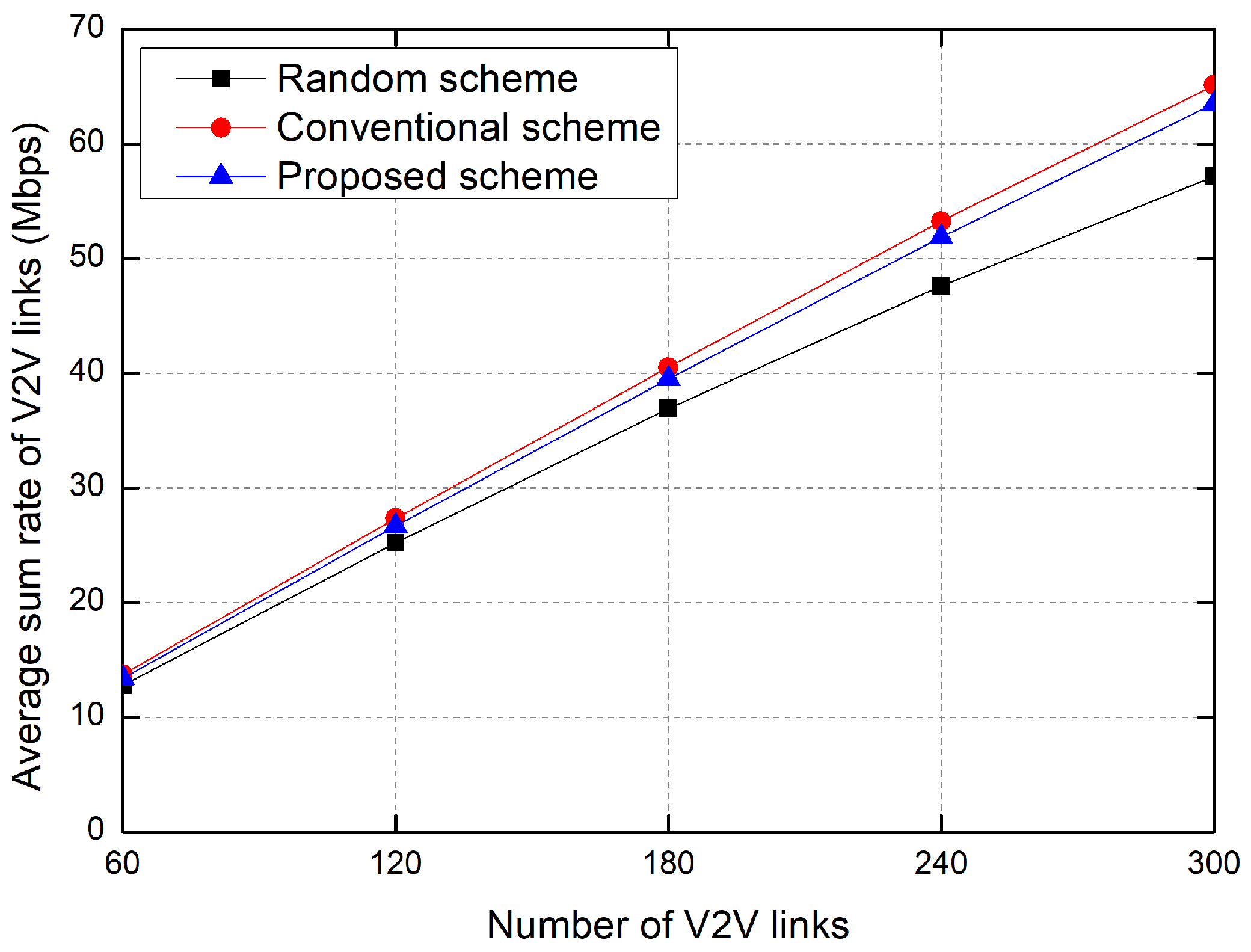
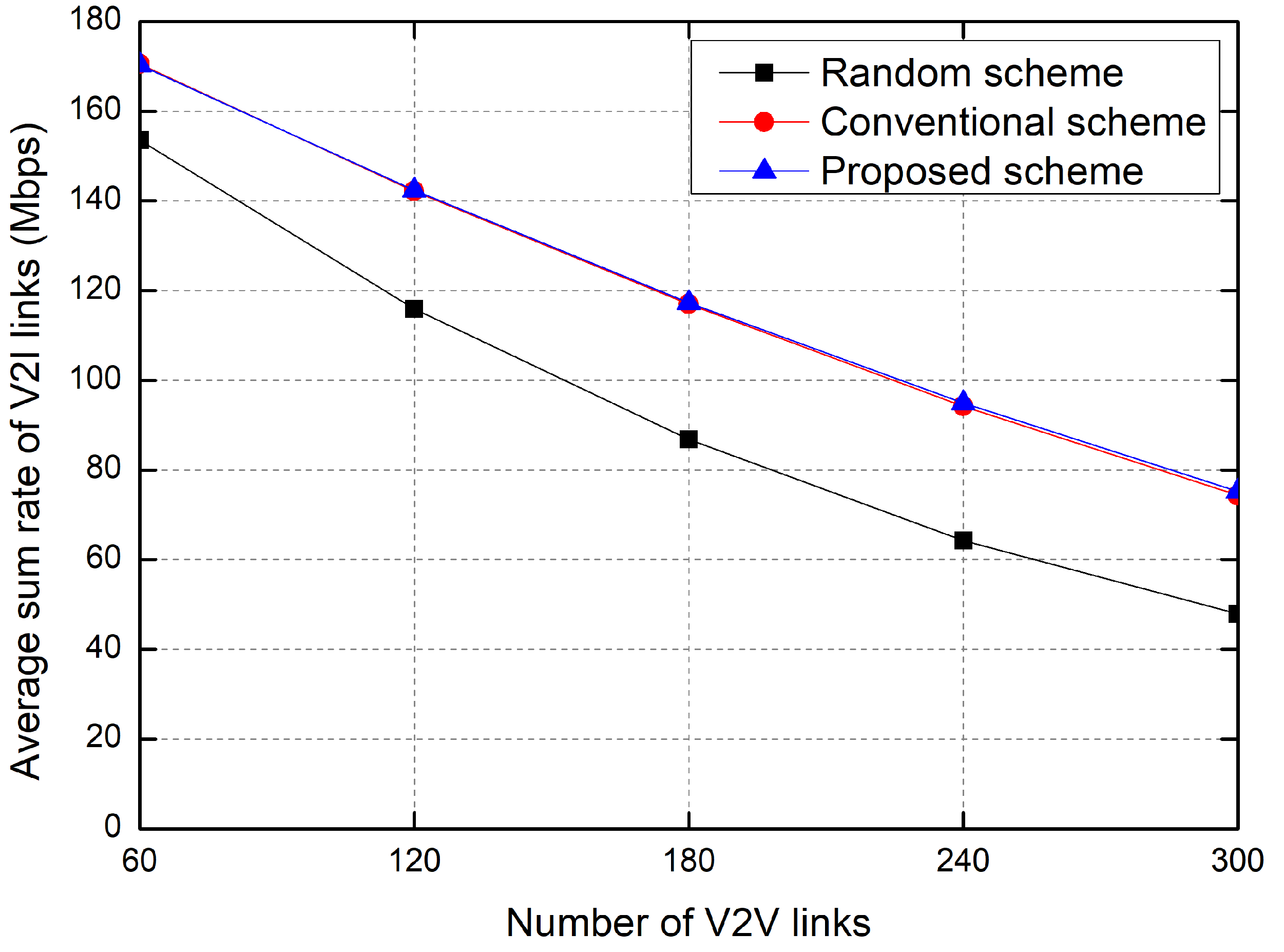
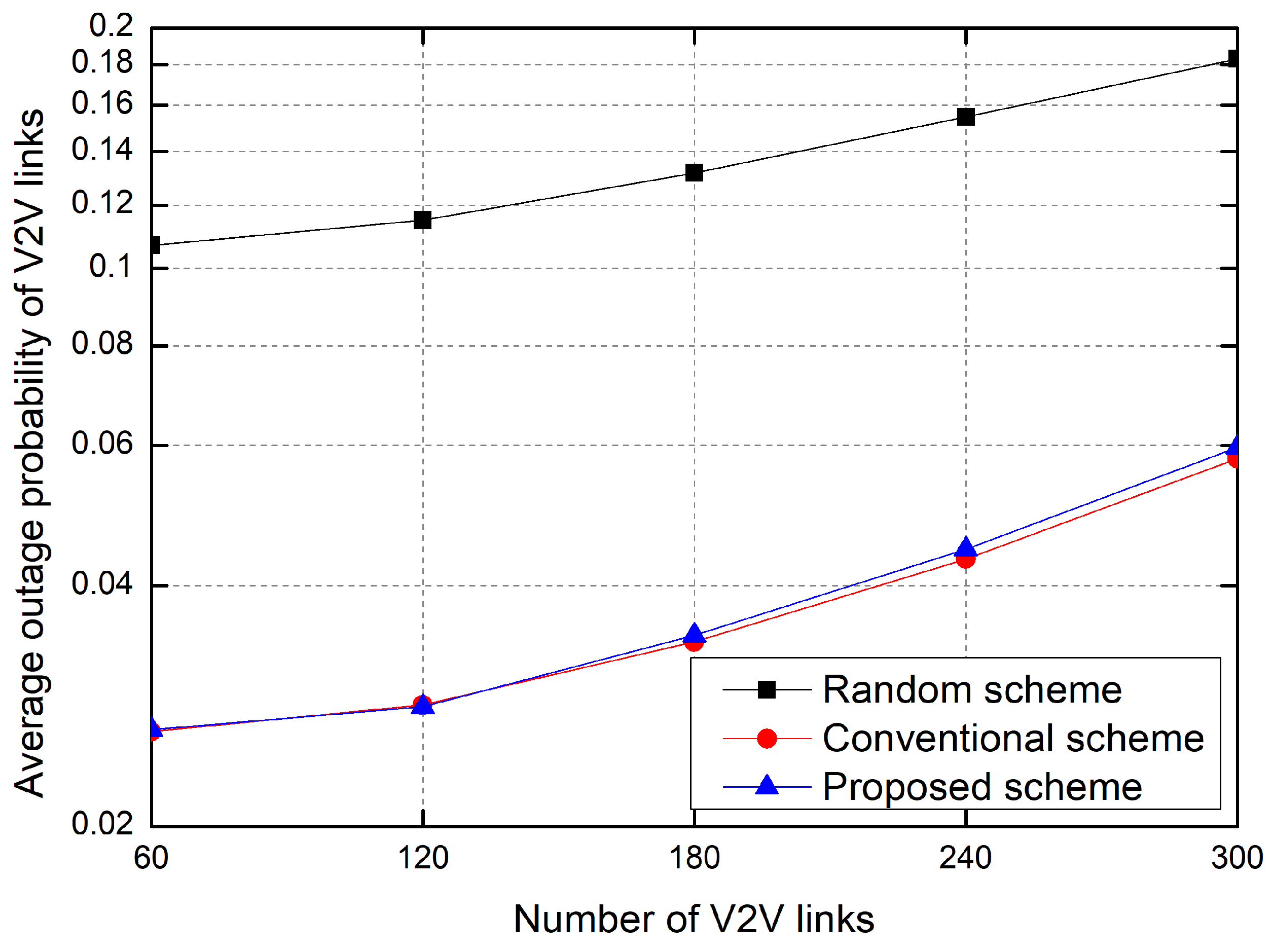
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia, M.H.C.; Molina-Galan, A.; Boban, M.; Gozalvez, J.; Coll-Perales, B.; Şahin, T.; Kousaridas, A. A tutorial on 5G NR V2X communications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1972–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Masegosa, R.; Gozalvez, J. LTE-V for sidelink 5G V2X vehicular communications: A new 5G technology for short-range vehicle-to-everything communications. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2017, 12, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, S.Y.; Deng, D.J.; Lin, C.C.; Tsai, H.L.; Chen, T.; Guo, C.; Cheng, S.M. 3GPP NR sidelink transmissions toward 5G V2X. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 35368–35382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.; So, J. One-bit signaling-based interference management for MIMO V2V sidelink. ICT Express 2022, 8, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Shan, H.; Song, M.; Zhuang, W.; Xiang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yu, X. A joint design of platoon communication and control based on LTE-V2V. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 15893–15907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Ye, H.; Yu, G.; Li, G.Y. Deep-learning-based wireless resource allocation with application to vehicular networks. Proc. IEEE 2020, 108, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, L.; Ye, H.; Li, G.Y.; Juang, B.H.F. Resource allocation based on graph neural networks in vehicular communications. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Taipei, Taiwan, 7–11 December 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Zhuang, W. Energy-efficient cross-layer resource allocation for heterogeneous wireless access. IEEE Tran. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 4819–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Gamage, A.T.; Zhuang, W.; Shen, X.; Serpedin, E.; Qaraqe, K. Uplink decentralized joint bandwidth and power allocation for energy-efficient operation in a heterogeneous wireless medium. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2015, 63, 1483–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, B.; Chen, C.; Xue, L.; Guan, X.; Wu, F. Cross-layer scheduling for OFDMA-based cognitive radio systems with delay and security constraints. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 5919–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Li, G.Y.; Juang, B.H.F. Deep reinforcement learning based resource allocation for V2V communications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 3163–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadauria, S.; Shabbir, Z.; Roth-Mandutz, E.; Fischer, G. QoS based deep reinforcement learning for V2X resource allocation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Black Sea Conference on Communications and Networking (BlackSeaCom), Odessa, Ukraine, 26–29 May 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Zhu, D.; Chronopoulos, A.T. Power allocation With energy efficiency optimization in cellular D2D-based V2X communication network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 21, 4947–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Ye, H.; Li, G.Y. Spectrum sharing in vehicular networks based on multi-agent reinforcement learning. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2019, 37, 2282–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, P.; Shan, H.; Wang, M.; Xiang, Z.; Zhu, Z. Multi-agent RL enables decentralized spectrum access in vehicular networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 10750–10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymani, D.M.; Ravichandran, L.; Gholami, M.R.; Del Galdo, G.; Harounabadi, M. Energy-efficient autonomous resource selection for power-saving users in NR V2X. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 32nd Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Helsinki, Finland, 13–16 September 2021; pp. 972–978. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Hou, Y.; Tao, X.; Zhu, M. Energy-efficient power control and resource allocation for V2V communication. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lorincz, J.; Matijevic, T.; Petrovic, G. On interdependence among transmit and consumed power of macro base station technologies. Comput. Commun. 2014, 50, 10–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorincz, J.; Capone, A.; Begušić, D. Heuristic algorithms for optimization of energy consumption in wireless access networks. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2011, 5, 626–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorincz, J.; Bogarelli, M.; Capone, A.; Begušić, D. Heuristic approach for optimized energy savings in wireless Access Networks. In Proceedings of the 18thInternational Conference on Software, Telecommunications and Computer Networks, Dalmatia, Croatia, 23–25 September 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W. Graph-based deep learning for communication networks: A survey. Comput. Commun. 2022, 185, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.; Tonchev, K.; Poulkov, V.; Manolova, A.; Neshov, N.N. Graph-based resource allocation for integrated space and terrestrial communications. Sensors 2022, 22, 5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L. Learning-based resource allocation in heterogeneous ultradense network. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 20229–20242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Qin, H.; Song, B.; Han, B.; Du, X.; Guizani, M. A graph convolutional network-based deep reinforcement learning approach for resource allocation in a cognitive radio network. Sensors 2020, 20, 5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatabani, L.E.; Ali, E.S.; Mokhtar, R.A.; Saeed, R.A.; Alhumyani, H.; Hasan, M.K. Deep and reinforcement learning technologies on internet of vehicle (IoV) applications: Current issues and future trends. J. Adv. Transp. 2022, 2022, 1947886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatabani, L.E.; Ali, E.S.; Saeed, R.A. Deep learning approaches for IoV applications and services. In Intelligent Technologies for Internet of Vehicles; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 253–291. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, E.S.; Hassan, M.B.; Saeed, R.A. Machine learning technologies on internet of vehicles. In Intelligent Technologies for Internet of Vehicles; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 225–252. [Google Scholar]
- Elfatih, N.M.; Hasan, M.K.; Kamal, Z.; Gupta, D.; Saeed, R.A.; Ali, E.S.; Hosain, M.S. Internet of vehicle’s resource management in 5G networks using AI technologies: Current status and trends. IET Commun. 2021, 16, 400–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.S.; Hasan, M.K.; Hassan, R.; Saeed, R.A.; Hassan, M.B.; Islam, S.; Nafi, N.S.; Bevinakoppa, S. Machine learning technologies for secure vehicular communication in internet of vehicles: Recent advances and applications. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 8868355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, N.; Yin, H. Integrated networking, caching, and computing for connected vehicles: A deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhu, C.; Wu, H.; Li, Q.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. Toward response time minimization considering energy consumption in caching-assisted vehicular edge computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 5051–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xiao, B.; Wang, W.; Yang, G.; Zhou, X.; Peng, Z. Real-time cache-aided route planning based on mobile edge computing. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2020, 27, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Wu, H. Joint optimization of task caching and computation offloading in vehicular edge computing. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2022, 15, 854–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.L.; Cui, T.; Gong, S.; He, W.; Jiang, X.; Jin, H.; Jin, J.; Kendall, G.; et al. Analytics and machine learning in vehicle routing research. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Niemegeers, I.G.; De Groot, S.M.H. Dynamic power allocation for cell-free massive MIMO: Deep reinforcement learning methods. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 102953–102965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Peng, M.; Yan, S.; Sun, Y. Deep-reinforcement-learning-based mode selection and resource allocation for cellular V2X communications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 6380–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, G.; Zhang, J. A deep Q-network based-resource allocation scheme for massive MIMO-NOMA. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 1544–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Jo, H.S.; Mun, C.; Yook, J.G. Deep reinforcement learning-based distributed congestion control in cellular V2X networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 2582–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Study LTE-Based V2X Services (Release 14), Document 3GPP TR 36.885 V14.0.0, 3rd Generation Partnership Project, June 2016. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/ftp/Specs/archive/36_series/36.885/36885-e00.zip (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Kyösti, P.; Meinilä, J.; Hentila, L.; Zhao, X.; Jämsä, T.; Schneider, C.; Narandzic, M.; Milojević, M.; Hong, A.; Ylitalo, J.; et al. WINNER II Channel Models. 02 2008, iST-4-027756 WINNER II D1.1.2 V1.2. Available online: http://www.ero.dk/93F2FC5C-0C4B-4E44-8931-00A5B05A331B (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Wang, C.-H.; Huang, K.-Y.; Yao, Y.; Chen, J.-C.; Shuai, H.-H.; Cheng, W.-H. Lightweight deep learning: An overview. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegari, M.; Ordonez, V.; Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Xnor-net: Imagenet classification using binary convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computing Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 525–542. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Road intersection size | m |
| Simulation area size | m |
| Absolute vehicle speed | 36 km/h |
| Vehicle drop and mobility model | Urban case of A.12 in 3GPP TR 36.885 [40] |
| V2V path loss model | WINNER + B1 Manhattan [41] |
| V2V shadowing | Log-normal with dB |
| V2I path loss model | 128.1 + 37.6 log(R), where R in kilometers |
| V2I shadowing | Log-normal with dB |
| V2V and V2I fast fading | Rayleigh fading |
| Noise power | dBm |
| Carrier frequency, | 2 GHz |
| Sub-carrier frequency | MHz |
| Number of V2I links, L | 20 |
| Number of V2V links, K, | [60, 120, 180, 240, 300] |
| Antenna height of eNode B type RSU | 25 m |
| Antenna gain of RSU | 8 dBi |
| Noise figure of RSU’s antenna | 5 dB |
| Antenna height of vehicles | m |
| Antenna gain of vehicles | 3 dBi |
| Noise figure of vehicle’s antenna | 9 dB |
| Latency constraints for V2V link | 100 ms |
| V2V payload size | 30 Mbits |
| Update time slot duration | 2 ms |
| Simulation time | 400 ms |
| transmit power level of V2V links | [5, 10, 23] dBm |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of neurons in the input layer | 82 |
| Number of neurons in each hidden layer | 500, 250, 120 |
| Number of neurons in the output layer | 60 |
| Reward discount factor | 0.99 |
| Hidden layer activation function | ReLU |
| Optimizer | RMSProp |
| Learning rate | 0.001 |
| Values of , , , and | 0.1, 0.9, 1, and 0.2, respectively |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, D.; So, J. Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation Based on Deep Q-Network in V2V Communications. Sensors 2023, 23, 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031295
Han D, So J. Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation Based on Deep Q-Network in V2V Communications. Sensors. 2023; 23(3):1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031295
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Donghee, and Jaewoo So. 2023. "Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation Based on Deep Q-Network in V2V Communications" Sensors 23, no. 3: 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031295
APA StyleHan, D., & So, J. (2023). Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation Based on Deep Q-Network in V2V Communications. Sensors, 23(3), 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031295







