Gas Sensors Based on Electrospun Nanofibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sensors
2.1. Acoustic Wave Gas Sensors
2.2. Resistive Gas Sensors
2.3. Photoelectric Gas Sensors
2.4. Optical Gas Sensors
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Kong, J.; Franklin, N.; Zhou, C.; Chapline, M.; Peng, S.; Cho, K.; Dai, H. Nanotube molecular wires as chemical sensors. Science 2000, 287, 622–625. [Google Scholar]
- Gopel, W.; Schierbaum, K. SnO2 sensors current status and future prospects. Sensor Actuator B-Chem 1995, 26, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, Y.; Seno, Y.; Masuoka, Y.; Yamashita, K. Nitrogen oxides sensing characteristics of Zn2SnO4 thin film. Sensor Actuator B-Chem 1998, 49, 248–252. [Google Scholar]
- Slater, J.; Watt, E.; Freeman, N.; May, I.; Weir, D. Gas and vapor detection with poly(pyrrole) gas sensors. Analyst 1992, 117, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Slater, J.; Paynter, J.; Watt, E. Multilayer conducting polymer gas sensor arrays for olfactory sensing. Analyst 1993, 118, 379–384. [Google Scholar]
- Schierbaum, K.; Weimar, U.; Gopel, W. Comparison of ceramic, thick-film and thin-film chemical sensors based upon SnO2. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 1992, 7, 709–716. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, N.; Chwierogh, B.; Ginwalla, A.; Patton, B.; Akbar, S.; Dutta, P. Composite n-p semiconducting titanium oxides as gas sensors. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 2001, 79, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Varghese, O.; Kichambre, P.; Gong, D.; Ong, K.; Dickey, E.; Grimes, C. Gas sensing characteristics of multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 2001, 81, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Lukaszewicz, J. Carbon materials for chemical sensors: a review. Sens. Lett 2006, 4, 53–98. [Google Scholar]
- Lonergan, M.; Severin, E.; Doleman, B.; Beaber, S.; Grubb, R.; Lewis, N. Array-based vapor sensing using chemically sensitive, carbon black-polymer resistor. Chem. Mater 1996, 8, 2298–2312. [Google Scholar]
- Unde, S.; Ganu, J.; Radhakrishnan, S. Conducting polymer-based chemical sensor: characteristics and evaluation of polyaniline composite films. Adv. Funct. Mater 1996, 6, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Gopel, W. Supramolecular and polymeric structures for gas sensors. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 1995, 24, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Han, S.; Huh, J.; Lee, D. Nitrogen oxides-sensing characteristics of WO3-based nanocrystalline thick film gas sensor. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 1999, 60, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Zhou, H.; Jin, Z.; Savinell, R.; Liu, C. Application of nano-crystalline porous tin oxide thin film for CO sensing. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 1998, 52, 188–194. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, Z. Gas sensing properties of nano-ZnO prepared by arc plasma method. Nanostruct. Mater 1997, 8, 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumiya, M.; Shin, W.; Izu, N.; Murayama, N. Nano-structured thin-film Pt catalyst for thermoelectric hydrogen gas sensor. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 2003, 93, 309–315. [Google Scholar]
- Reneker, D.; Chun, I. Nanometer diameter fibers of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216–223. [Google Scholar]
- Doshi, J.; Reneker, D. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrost 1995, 35, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, H.; Chun, I.; Reneker, D. Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymer 1999, 40, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar]
- Reneker, D.; Yarin, A.; Fong, H.; Koombhongse, S. Bending instability of electrically charged liquid jets of polymer solutions in electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys 2000, 87, 4531–4547. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, Y.; Hohman, M.; Brenner, M.; Rutledge, G. Experimental characterization of electrospinning: the electrically forced jet and instabilities. Polymer 2001, 42, 9955–9967. [Google Scholar]
- Deitzel, J.M.; Kleinmeyer, J.; Harris, D.; Beck Tan, N.C. The effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun nanofibers and textiles. Polymer 2001, 42, 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Dejuan, L.; Delamora, J. Charge and size distributions of electrospray drops. J. Colloid Interface Sci 1997, 186, 280–293. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Pui, D. Experimental investigation of scaling laws for electrospraying: dielectric constant effect. Aerosol Sci. Tech 1997, 27, 367–380. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, B.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.; Choi, K. Preparation and characterization of nanoscaled poly(vinyl alcohol) fibers via electrospinning. Fiber. Polym 2002, 3, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- McCann, J.; Marquez, M.; Xia, Y. Highly porous fibers by electrospinning into a cryogenic liquid. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2006, 128, 1436–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, B.; Li, C.; Miyauchi, Y.; Kuwaki, O.; Shiratori, S. Formation of novel 2D polymer nanowebs via electrospinning. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3685–3691. [Google Scholar]
- Theron, A.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L. Electrostatic field-assisted alignment of electrospun nanofibers. Nanotechnology 2001, 12, 384–390. [Google Scholar]
- Kameoka, J.; Orth, R.; Yang, Y.; Czaplewski, D.; Mathers, R.; Coates, G.; Craighead, H. A scanning tip electrospinning source for deposition of oriented nanofibers. Nanotechnology 2003, 14, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, B.; Kim, H.; Kim, C.; Khil, M.; Park, S. Morphology and crystalline phase study of electrospun TiO2-SiO2 nanofibers. Nanotechnology 2003, 14, 532–537. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C.; Kim, H.; Gong, J.; Lee, D. A novel method for making silica nanofibers by using electrospun fibers of polyvinyl alcohol/silica composite as precursor. Nanotechnology 2002, 13, 635–637. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, B.; Kim, C.; Kim, H.; Seo, M.; Park, S. Titanium dioxide nanofibers prepared by using electrospinning method. Fiber. Polym 2004, 5, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Hajra, M.; Mehta, K.; Chase, G. Effects of humidity, temperature, and nanofibers on drop coalescence in glass fiber media. Sep. Purif. Technol 2003, 30, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wnek, G.; Carr, M.; Simpson, D.; Bowlin, G. Electrospinning of nanofiber fibrinogen structures. Nano Lett 2003, 3, 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Kenawy, E.; Bowlin, G.; Mansfield, K.; Layman, J.; Simpson, D.; Sanders, E.; Wnek, G. Release of tetracycline hydrochloride from electrospun poly(ethylene-co-vinylacetate), poly(lactic acid), and a blend. J. Control. Release 2002, 81, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Dersch, R.; Steinhart, M.; Boudriot, U.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Nanoprocessing of polymers: applications in medicine, sensors, catalysis, photonics. Polym. Advan. Technol 2005, 16, 276–282. [Google Scholar]
- Onozuka, K.; Ding, B.; Tsuge, Y.; Naka, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Sugi, S.; Ohno, S.; Yoshikawa, M.; Shiratori, S. Electrospinning processed nanofibrous TiO2 membranes for photovoltaic applications. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.; Lee, Y.; Joo, C.; Lee, S.; Park, J.; Han, K. Electrospun PVDF nanofiber web as polymer electrolyte or separator. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 50, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Composites Sci. Technol 2000, 287, 622–625. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of nanofibers: reinventing the wheel? Advan. Mater 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J. Electrospinning: a fascinating method for the preparation of ultrathin fibers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2007, 46, 5670–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, P.; Ding, B. Applications of electropun fibers. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol 2008, 2, 169–182. [Google Scholar]
- Syritski, V.; Reut, J.; Opik, A.; Idla, K. Environmental QCM sensors coated with polypyrrole. Synthetic Meth 1999, 102, 1326–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Muratsugu, M; Ohta, F.; Miya, Y.; Hosokawa, T.; Kurosawa, S.; Kamo, N.; Ikeda, H. Quartz crystal microbalance for the detection of microgram quantities of human serum albumin: relationship between the frequency change and the mass of protein adsorbed. Anal. Chem 1993, 65, 2933–2937. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, K.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, D.K.; Jung, S.B.; Chang, J.S.; Kwon, Y.S. Effect of pH on the properties of palmitic acid LB films for gas sensors. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 2001, 77, 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, M.; Nogueira, P.; Oliveira, J. Quantification of CO2, SO2, NH3, and H2S with a single coated piezoelectric quartz crystal. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 2000, 68, 218–222. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, B.; Kim, J.; Miyazaki, Y.; Shiratori, S. Electrospun nanofibrous membranes coated quartz crystal microbalance as gas sensor for NH3 detection. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 2004, 101, 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, B.; Yamazaki, M.; Shiratori, S. Electrospun fibrous polyacrylic acid membrane-based gas sensors. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 2005, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Shiratori, S. Fabrication of nanoporous and hetero structure thin film via a layer-by-layer self assembly method for a gas sensor. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 2004, 102, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, B.; Kikuchi, M.; Li, C.; Shiratori, S. Electrospun nanofibrous polyelectrolytes membranes as high sensitive coatings for QCM-based gas sensors. In Nanotechnology at the Leading Edge; Dirote, E.V., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, USA, 2006; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Stutzmann, N.; Friend, R.; Sirringhaus, H. Self-aligned, vertical-channel, polymer field-effect transistors. Science 2003, 299, 1881–1884. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Kameoka, J.; Czaplewski, D.; Craighead, H. Polymeric nanowire chemical sensor. Nano Lett 2004, 4, 671–675. [Google Scholar]
- Manesh, K.; Gopalan, A.; Lee, K.; Santhosh, P.; Song, K.; Lee, D. Fabrication of functional nanofibrous ammonia sensor. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol 2007, 6, 513–518. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Gong, J.; Fan, B.; Su, Z.; Qu, L. Polyaniline nanotubes prepared using fiber mats membrane as the template and their gas-response behavior. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 8215–8222. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, M. Gas sensing properties of a composite composed of electrospun poly(methyl methacrylate) nanofibers and in situ polymerized polyaniline. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 2008, 133, 644–649. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, N.; Ramos, I.; Rojas, R.; Wang, P.; Johnson, A., Jr. Electric response of isolated electrospun polyaniline nanofibers to vapors of aliphatic alcohols. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 2008, 129, 621–627. [Google Scholar]
- Aussawasathien, D.; Sahasithiwat, S.; Menbangpung, L. Electrospun camphorsulfonic acid doped poly(o-toluidine)-polystyrene composite fibers: chemical vapor sensing. Synth. Met 2008, 158, 259–263. [Google Scholar]
- Lala, N.; Thavasi, V.; Ramakrishna, S. Preparation of surface adsorbed and impregnated multi-walled carbon nanotube/nylon-6 nanofiber composites and investigation of their gas sensing ability. Sensors 2009, 9, 86–101. [Google Scholar]
- Kessick, R.; Tepper, G. Electrospun polymer composite fiber arrays for the detection and identification of volatile organic compounds. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 2006, 117, 205–210. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazoe, N. Toward innovations of gas sensor technology. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 2005, 108, 2–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kolmakov, A.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Moskovits, M. Detection of CO and O2 using tin oxide nanowire sensors. Advan. Mater 2003, 15, 997–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I.; Rothschild, A.; Lee, B.; Kim, D.; Jo, S.; Tuller, H. Ultrasensitive chemiresistors based on electrospun TiO2 nanofibers. Nano Lett 2006, 6, 2009–2013. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, O.; Rothschild, A.; Zussman, E. Processing-microstructure-properties correlation of ultrasensitive gas sensors produced by electrospinning. Chem. Mater 2009, 21, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, C.; MacDiarmid, A.; Wei, Y. Highly sensitive and stable humidity nanosensors based on LiCl doped TiO2 electrospun nanofibers. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2008, 130, 5036–5037. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ramos, I.; Santiago-Aviles, J. Detection of moisture and methanol gas using a single electrospun tin oxide nanofiber. IEEE Sens. J 2007, 7, 1347–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Li, J.; Miao, Z.; Huang, F. Fabrication and ethanol-sensing properties of micro gas sensor based on electrospun SnO2 nanofibers. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem 2008, 132. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.; Tao, X.; Wang, R. Room temperature gas sensing properties of SnO2/multiwall-carbon-nanotube composite nanofibers. Appl. Phys. Lett 2007, 91, 133110. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Ji, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, X.; Gouma, P.; Dudley, M. Fabrication and characterization of polycrystalline WO3 nanofibers and their application for ammonia sensing. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 23777–23782. [Google Scholar]
- Sahner, K.; Gouma, P.; Moos, R. Electrodeposited and sol-gel precipitated p-type SrTi1−xFexO3−δ semiconductors for gas sensing. Sensors 2007, 7, 1871–1886. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Xie, T.; Peng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D. Fabrication and photoelectric oxygen sensing characteristics of electrospun Co doped ZnO nanofibers. Appl. Phys. A-Mat. Sci. Process 2007, 89, 427–430. [Google Scholar]
- Luoh, R.; Hahn, H.T. Electrospun nanocomposite fiber mats as gas sensors. Composites. Sci. Technol 2006, 66, 2436–2441. [Google Scholar]
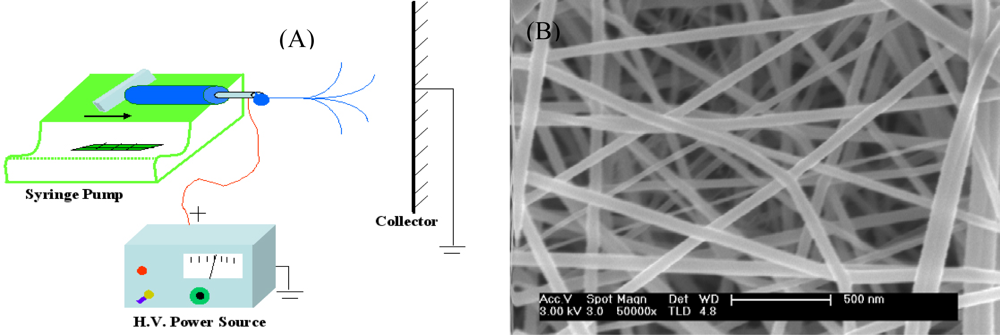

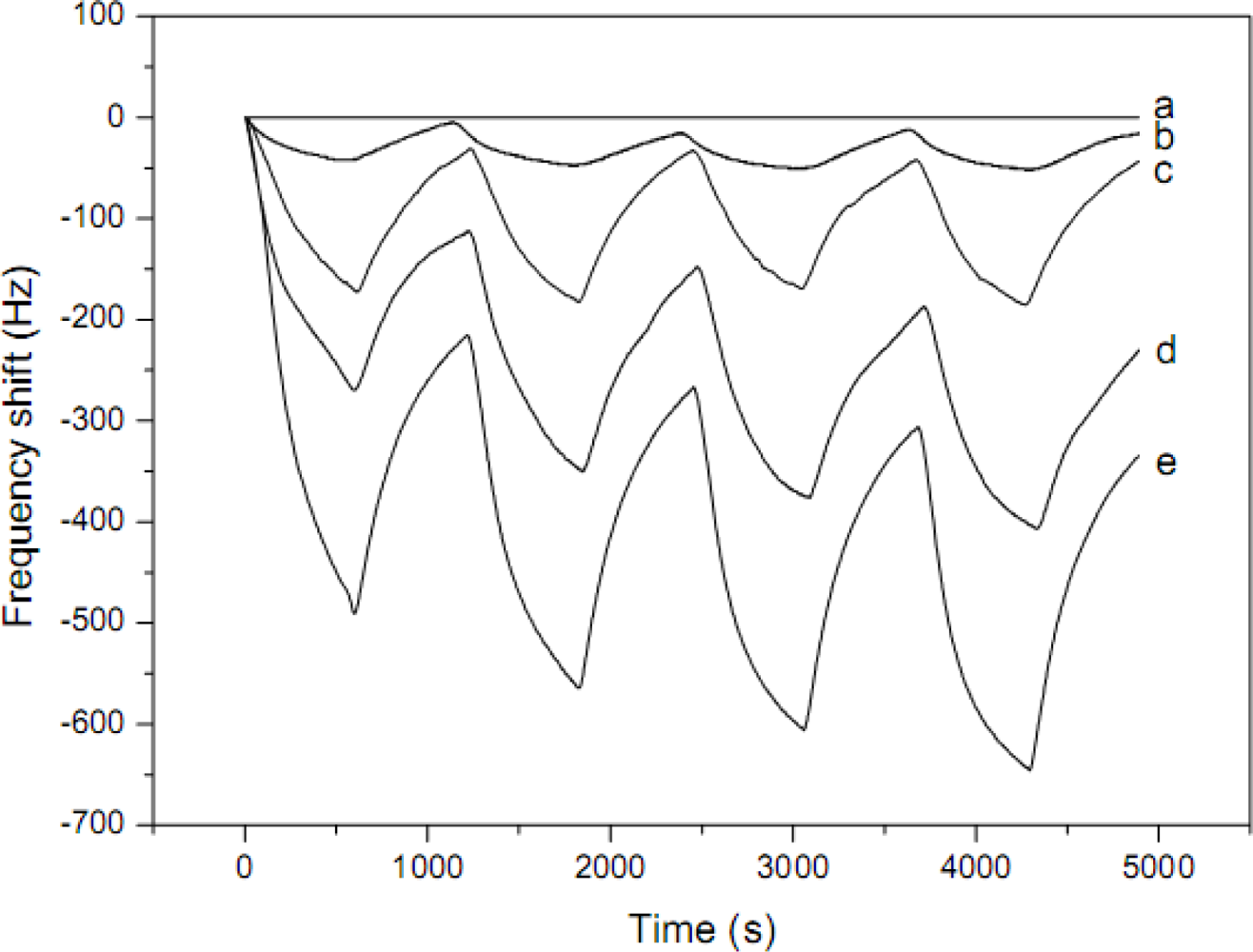
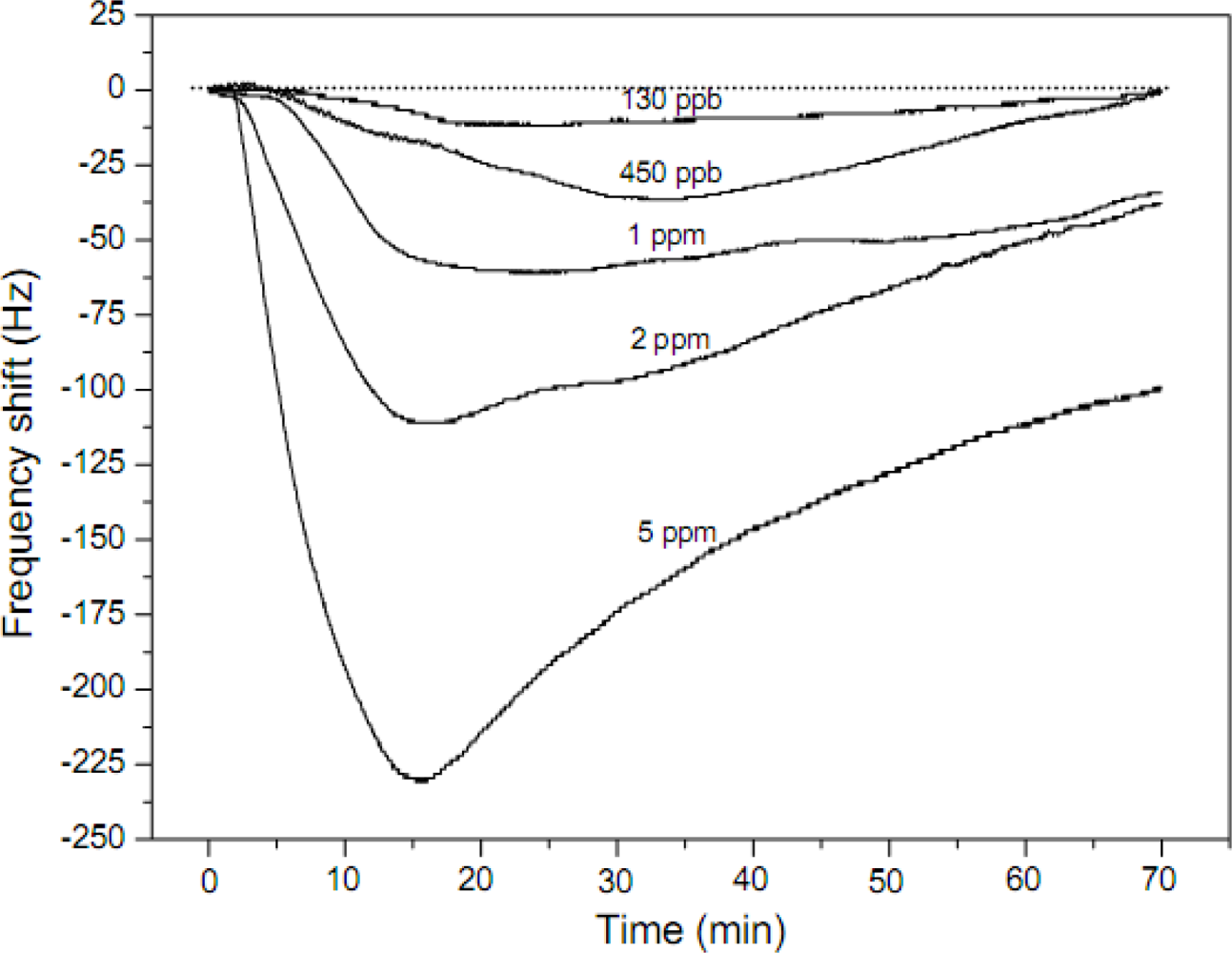

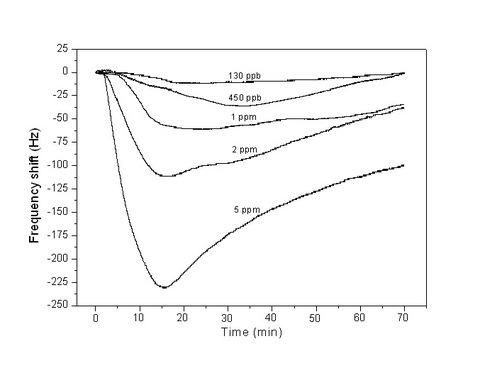
| Types | Materials | Array of fibers | Fiber diameter | Gases tested | Operating temperature (°C) | Detection limit | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acoustic wave | PAA-PVA | Nonwoven | 100–400 nm | NH3 | RT | 50 ppm | [47] | |
| PAA | Nonwoven | 1–7 μm | NH3 | RT | 130 ppb | [48] | ||
| PEI-PVA | Nonwoven | 100–600 nm | H2S | RT | 500 ppb | [50] | ||
| Resistive | HCSA-PANI/PEO | Single | 100–500 nm | NH3 | RT | 500 ppb | [52] | |
| PDPA-PMMA | Nonwoven | ∼400 nm | NH3 | RT | 1 ppm | [53] | ||
| PANI | Nonwoven | 0.3–1.5 μm | Amines | RT | 100 ppm | [54] | ||
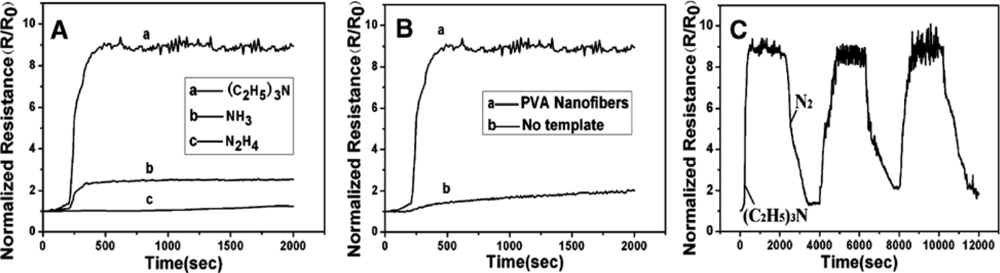
| PMMA-PANI | Nonwoven | 250–600 nm | (C2H5)3N | RT | 20 ppm | [55] | ||
| HCSA-PANI | Single | 20–150 nm | Alcohols | RT | No data | [56] | ||
| HCSA-POT/PS | Nonwoven | 0.2–1.9 μm | H2O | RT | No data | [57] | ||
| MWCNT/nylon | Nonwoven | 110–140 nm | VOCs | RT | No data | [58] | ||
| CB-PECH, | Oriented | ∼3 μm | CH3OH | RT | 1000 ppm | [59] | ||
| PEO, PIB, PVP | C5H10Cl2 | 5 ppm | ||||||
| C6H5CH3 | 250 ppm | |||||||
| C2HCl3 | 500 ppm | |||||||
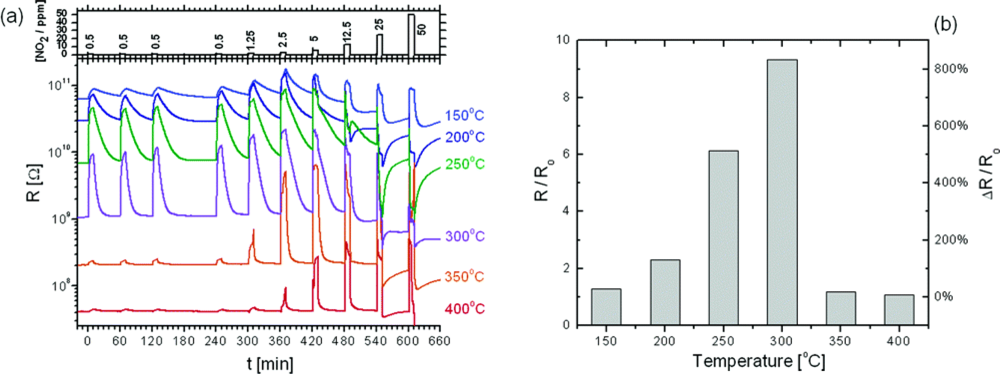
| TiO2 | Nonwoven | 200–500 nm | NO2 | 150–400 °C | 500 ppb | [62] | ||
| TiO2 | Nonwoven | 120–850 nm | CO, NO2 | 300–400 °C | 50 ppb | [63] | ||
| LiCl-TiO2 | Nonwoven | 150–260 nm | H2O | RT | 11% | [64] | ||
| SnO2 | Single | 700 nm | H2O | RT | No data | [65] | ||
| SnO2 | Nonwoven | ∼100 nm | C2H5OH | 330 °C | 10 ppb | [66] | ||
| MWCNT/SnO2 | Nonwoven | 300–800 nm | CO | RT | 47 ppm | [67] | ||
| WO3 | Nonwoven | 20–140 nm | NH3 | 350 °C | 50 ppm | [68] | ||
| SrTi0.8Fe0.2O3−δ | Nonwoven | ∼100 nm | CH3OH | 400 °C | 5 ppm | [69] | ||
| Photoelectric | Co-ZnO | Nonwoven | 50–400 nm | O2 | RT | 0.32 Torr | [70] | |
| Optical | Oxides-PAN | Nonwoven | 50–200 nm | CO2 | RT | 700 ppm | [71] | |
© 2009 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, B.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Sun, G. Gas Sensors Based on Electrospun Nanofibers. Sensors 2009, 9, 1609-1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/s90301609
Ding B, Wang M, Yu J, Sun G. Gas Sensors Based on Electrospun Nanofibers. Sensors. 2009; 9(3):1609-1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/s90301609
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Bin, Moran Wang, Jianyong Yu, and Gang Sun. 2009. "Gas Sensors Based on Electrospun Nanofibers" Sensors 9, no. 3: 1609-1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/s90301609
APA StyleDing, B., Wang, M., Yu, J., & Sun, G. (2009). Gas Sensors Based on Electrospun Nanofibers. Sensors, 9(3), 1609-1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/s90301609