Further Investigation of the Mediterranean Sponge Axinella polypoides: Isolation of a New Cyclonucleoside and a New Betaine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
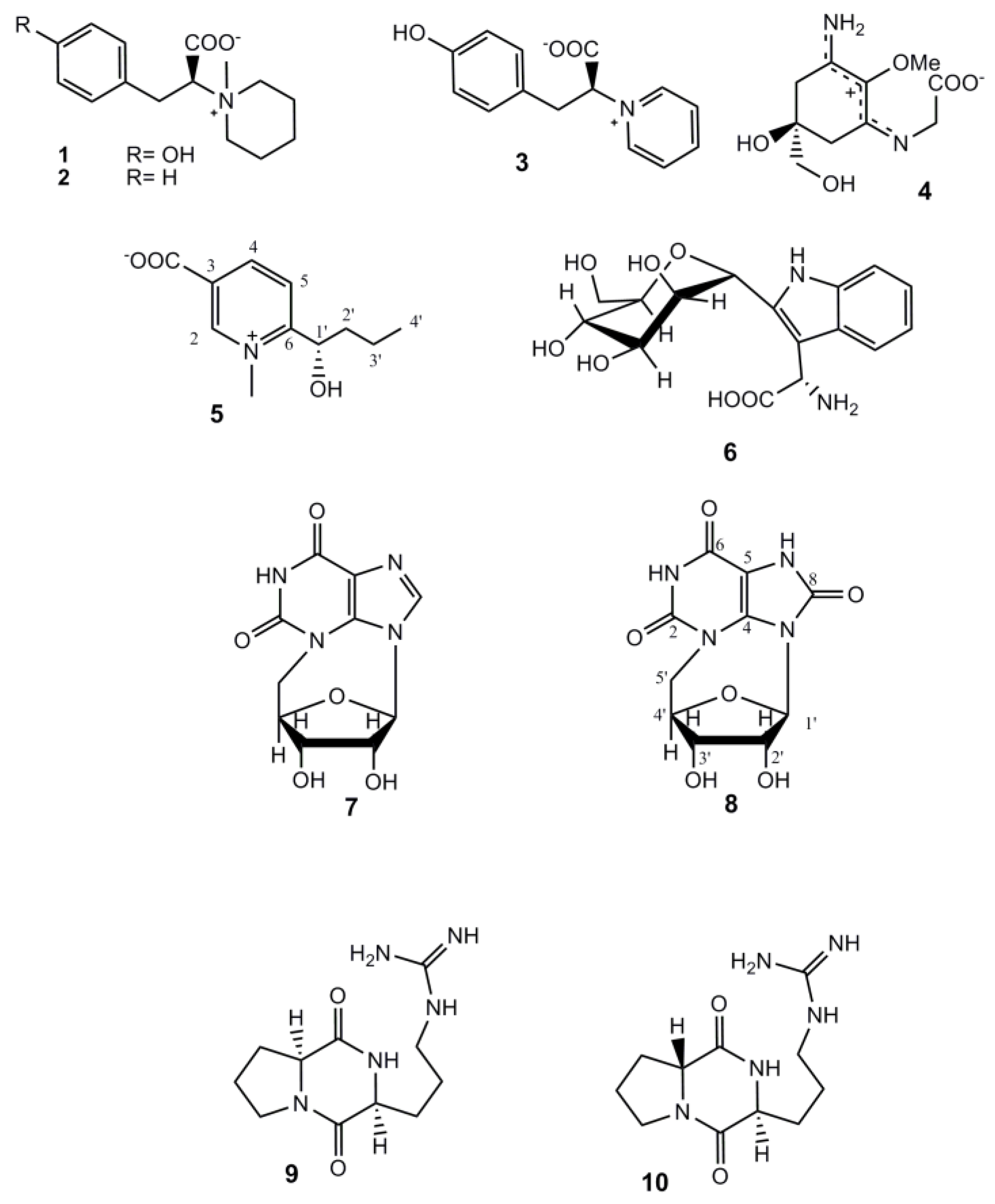
2. Results and Discussion
| Position | δH (mult., J in Hz) | δC | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-NMe | 4.38 (s) | 46.1 | 2, 6 |
| 2 | 9.10 (bs) | 148.7 | 1-NMe, 4, 6, COO- |
| 3 | - | 137.8 | - |
| 4 | 8.84 (bd, 8.2) | 146.3 | 2, 6, COO−Na+ |
| 5 | 8.19 (d, 8.2) | 126.6 | 3, 6, 1′ |
| 6 | - | 163.0 | - |
| 1′ | 5.13 (dd, 3.3, 9.0) | 69.3 | 6, 2′ |
| 2′ | 1.72 (m) | 38.9 | 6, 1′, 3′, 4′ |
| 1.81(m) | |||
| 3′ | 1.54 (m) | 19.9 | 1′, 2′, 4′ |
| 1.63 (m) | |||
| 4′ | 1.00 (t, 7.5) | 14.0 | 2′, 3′ |
| –COO- | - | 167.0 | - |
 ) of S-5 model vs. experimental curve (
) of S-5 model vs. experimental curve (  ) of compound 5.
) of compound 5.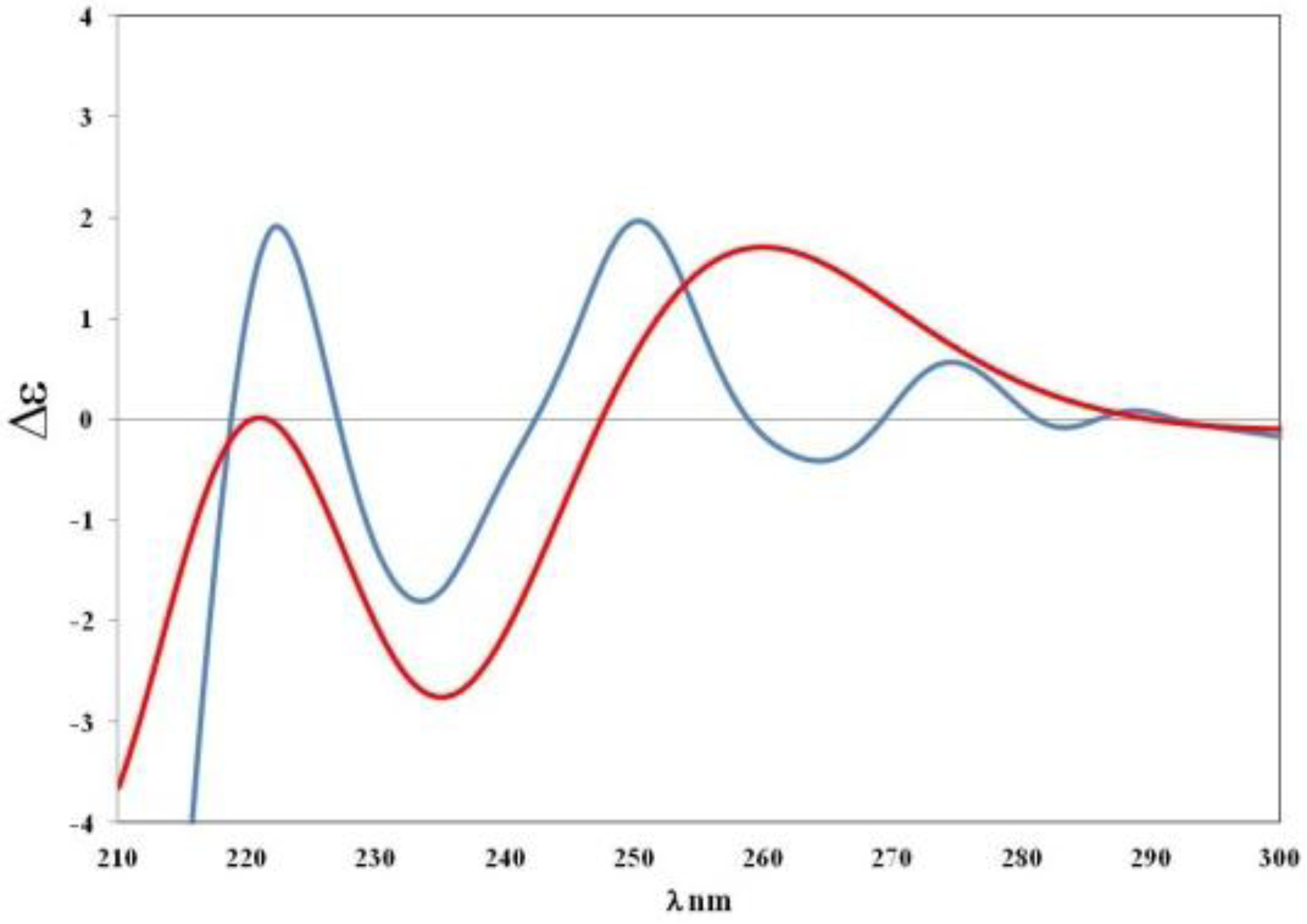
| Position | 7 | 8 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | HMBC a | |
| 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | 151.0 | - | 150.7 | - | - |
| 3 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 4 | 140.7 | - | 136.8 | - | - |
| 5 | 117.8 | - | 98.8 | - | - |
| 6 | 157.4 | - | 153.4 | - | - |
| 7 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 8 | 134.5 | 7.79 (s) | 149.6 | - | - |
| 9 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1′ | 92.5 | 6.15 (s) | 91.1 | 5.67 (s) | 4, 8, 2′, 3′, 4′ |
| 2′ | 75.8 | 3.87 (dd, 5.2, 5.0) | 75.0 | 3.90 (t, 5.3) | 1′, 4′ |
| 3′ | 70.1 | 4.20 (m) | 70.7 | 4.23 (m) | 5′ |
| 4′ | 83.7 | 4.55 (m) | 83.6 | 4.46 (m) | - |
| 5′a | 51.3 | 4.56 (m) | 52.3 | 4.51 (dd, 14.4, 2.4) | 2, 4, 3′, 4′ |
| 5′b | 51.3 | 3.71 (dd, 15.2, 3.2) | 52.3 | 3.72 (dd,14.4, 2.8) | 2, 4, 3′, 4′ |
| OH-2′ | - | 5.62 (d, 5.0) | - | 5.60 (d, 5.3) | - |
| OH-3′ | - | 5.62 (bs) | - | 5.35 (d, 7.1) | - |
| NH-1 | - | 11.2 | - | 11.3 | 5, 6 |
| NH-7 | - | - | - | 11.2 | 4, 5, 8 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Collection, Extraction and Isolation
3.3. Computational Details
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Supplementary Files
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
References
- Kelly, S.R.; Jensen, P.R.; Henkel, T.P.; Fenical, W.; Pawlik, J.R. Effects of Caribbean sponge extracts on bacterial attachment. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 31, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richelle-Maurer, E.; De Kluijver, M.J.; Feio, S.; Gaudencio, S.; Gaspar, H.; Gomez, R.; Tavares, R.; Van de Vyver, G.; Van Soest, R.W.M. Localization and ecological significance of oroidin and sceptrin in the Caribbean sponge Agelas conifera. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2003, 31, 1073–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, B.; Malgesini, B.; Piutti, C.; Quartieri, F.; Scolaro, A.; Papeo, G. A submarine journey: The pyrrole-imidazole alkaloids. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 705–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, G.; De Stefano, S.; Minale, L. Occurrence of hydroxyhydroquinone and 2-aminoimidazole in sponges. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 1974, 47, 895–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minale, L.; Sodano, G. Marine sterols. 19 Norstanols from the sponge Axinella polyoides. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1974, 15, 1888–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, M.; Minale, L.; Sodano, G. Metabolism in porifera-V,biosynthesis of 19-norstanols: Conversion of cholesterol into 19-norcholestanols by the sponge Axinella polypoides. Experientia 1975, 31, 758–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crist, B.V.; Djerassi, C. Minor and trace sterols in marine invertebrates 47. A re-investigation of the 19-nor stanols isolated from the sponge Axinella polypoides. Steroids 1983, 42, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, F.; Schulze, C.; Breloer, M.; Strupat, K.; Bretting, H. Amino acid sequence of the d-galactose binding lectin II from the sponge Axinella polypoides (Schmidt) and identification of the carbohydrate binding site in lectin II and related lectin I. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B 1998, 121, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabant, M.; Martin, M.; Moriou, C.; Ermolenko, L.; Guerineau, V.; Retailleau, P.; Thoison, O.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Perez, T.; Al-Mourabit, A. Axiphenylalaninium and axityrosinium, modified amino acids from the Mediterranean marine sponge Axinella polypoides. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1875–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofsteenge, J.; Mueller, D.R.; de Beer, T.; Loeffler, A.; Richter, W.J.; Vliegenthart, J.F.G. New type of linkage between a carbohydrate and a protein: C-glycosylation of a specific tryptophan residue in human RNase Us. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 13524–13530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Trotter, N.S. N3,5′-cycloxanthosine, the first natural occurrence of a cyclonucleoside. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1689–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Lenis, L.A.; Jimenez, C.; Debitus, C.; Quiñoa, E.; Riguera, R. The occurrence of the human glycoconjugate C2-α-d-mannosylpyranosyl-l-tryptophan in marine ascidians. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 2765–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujino, I.; Yabe, K.; Sekikawa, I.; Hamanaka, N. Isolation and structure of a mycosporine from the red alga Chondrus yendoi. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 16, 1401–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Takano, S.; Uemura, D.; Hirata, Y. Isolation and structure of a new amino acid, palythine, from the zoanthid Palythoa tuberculos. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 26, 2299–2300. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.S.; Chen, C.S.; Chien, T.C.; Yeh, J.Y.; Kuo, C.C.; Talekar, R.S.; Chern, J.W. Nucleosides. IX. Synthesis of purine N3,5′-cyclonucleosides and N3,5′-Cyclo-2′,3′-seconucleosides via mitsunobu reaction as TIBO-like derivatives. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2004, 23, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broberg, A.; Kenne, L.; Pedersen, M. In situ identification of major metabolites in the red alga Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis using high-resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Planta 1998, 206, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, A.; Fattorusso, E.; Luciano, P.; Menna, M.; Vitalone, R. Polyaxibetaine, an amino acid derivative from the marine sponge Axinella polypoides. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumida, H.; Imamura, N.; Sano, H. A novel chitinase inhibitor from a marine bacterium, Pseudomonas sp. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergne, C.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Perez, T.; Martin, M.; Adeline, M.; Tran Huu Dau, E.; Al-Mourabit, A. Verpacamides A-D, a sequence of C11N5 diketopiperazines relating cyclo(Pro-Pro) to cyclo(Pro-Arg), from the marine sponge Axinella vaceleti: Possible biogenetic precursors of pyrrole-2-aminoimidazole alkaloid. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 2421–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, D.M.; Stephens, P.J. Determination of absolute configuration using density functional theory calculations of optical rotation and electronic circular dichroism: Chiral alkenes. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 6074–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, A.; Fattorusso, E.; Imperatore, C.; Luciano, P.; Menna, M.; Vitalone, R. Aplisulfamines, new sulfoxide-containing metabolites from an Aplidium tunicate: Absolute stereochemistry at chiral sulfur and carbon atoms assigned through an original combination of spectroscopic and computational methods. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrovic, A.G.; Navarro-Vazquez, A.; Alonso-Gomez, J.L. From relative to absolute configuration of complex natural products: Interplay between NMR, ECD, VCD, and ORD assisted by ab initio calculations. Curr. Org. Chem. 2010, 14, 1612–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R., Jr.; Montgomery, J.A.; Vreven, T.; Kudin, K.N.; Burant, J.C.; et al. Gaussian 03; Revision, B., Ed.; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Haber, M.; Carbone, M.; Mollo, E.; Gavagnin, M.; Ilan, M. Chemical defense against predators and bacterial fouling in the Mediterranean sponges Axinella polypoides and A. verrucosa. verrucosa. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 422, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, G.; De Stefano, S.; Minale, L.; Sodano, G. Metabolism in Porifera-III. Chemical patterns and classifications of the Desmospongiae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1975, 50B, 279–285. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, A.; D’Esposito, M.; Fattorusso, E.; Menna, M.; Muller, W.E.G.; Perovic-Ottstadt, S.; Schroder, H.C. Novel bioactive bromopyrrole alkaloids from the Mediterranean sponge Axinella verrucosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, M.; Carbone, M.; Ilan, M.; Gavagnin, M. Structure of debromo-carteramine A, a novel bromopyrrole alkaloid from the Mediterranean sponge Axinella verrucosa. Arkivoc 2010, 2, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Gazave, E.; Carteron, S.; Chenuil, A.; Richelle-Maurer, E.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Borchiellini, C. Polyphyly of the genus Axinella and of the family Axinellidae (Porifera: Demospongiaep). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 57, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Stoller, C.; Van Soest, R.W.M. Chemotaxonomy of Agelas (Porifera: Demospongiae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1992, 20, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Menna, M.; Aiello, A.; D'Aniello, F.; Fattorusso, E.; Imperatore, C.; Luciano, P.; Vitalone, R. Further Investigation of the Mediterranean Sponge Axinella polypoides: Isolation of a New Cyclonucleoside and a New Betaine. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2509-2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10112509
Menna M, Aiello A, D'Aniello F, Fattorusso E, Imperatore C, Luciano P, Vitalone R. Further Investigation of the Mediterranean Sponge Axinella polypoides: Isolation of a New Cyclonucleoside and a New Betaine. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(11):2509-2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10112509
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenna, Marialuisa, Anna Aiello, Filomena D'Aniello, Ernesto Fattorusso, Concetta Imperatore, Paolo Luciano, and Rocco Vitalone. 2012. "Further Investigation of the Mediterranean Sponge Axinella polypoides: Isolation of a New Cyclonucleoside and a New Betaine" Marine Drugs 10, no. 11: 2509-2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10112509
APA StyleMenna, M., Aiello, A., D'Aniello, F., Fattorusso, E., Imperatore, C., Luciano, P., & Vitalone, R. (2012). Further Investigation of the Mediterranean Sponge Axinella polypoides: Isolation of a New Cyclonucleoside and a New Betaine. Marine Drugs, 10(11), 2509-2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10112509








