Cytotoxic Anthranilic Acid Derivatives from Deep Sea Sediment-Derived Fungus Penicillium paneum SD-44
Abstract
:1. Introduction
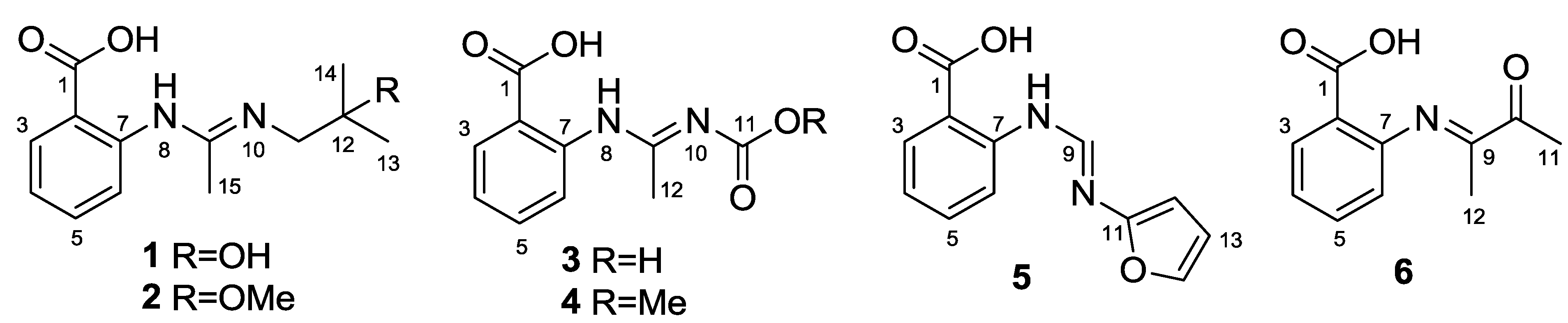
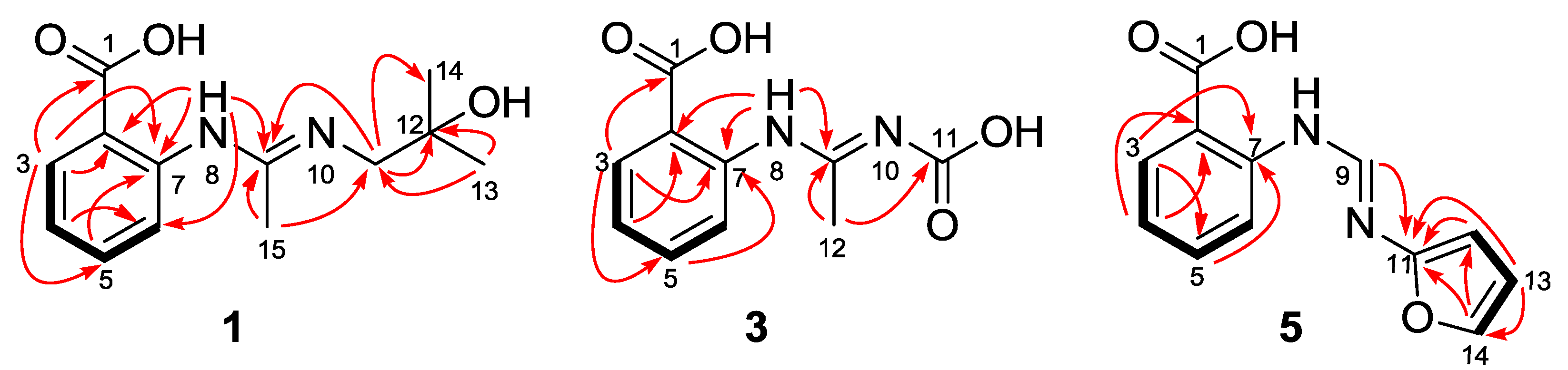
2. Results and Discussion
Structure Elucidation of the New Compounds
| No. | 1 a | 2 b | 3 c | 4 b | 5 b | 6 b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 7.97 dd (7.9, 0.8) | 7.89 dd (8.0, 1.3) | 7.89 d (7.9) | 7.98 d (7.7) | 7.92 d (7.8) | 7.99 dd (7.9, 1.2) |
| 4 | 6.76 br t (7.9) | 6.70 br t (8.0) | 6.94 t (7.4) | 6.93 t (7.5) | 6.77 t (7.5) | 6.94 td (8.0, 0.9) |
| 5 | 7.45 td ( 8.2, 1.0) | 7.38 td (8.5, 1.4) | 7.55 t (7.4) | 7.48 t (7.5) | 7.42 t (7.5) | 7.46 td (8.0, 1.5) |
| 6 | 7.50 br d (8.2) | 7.58 br d (8.5) | 7.81 d (8.4) | 7.80 d (8.4) | 7.66 br d (8.5) | 7.76 br d (8.4) |
| 8 | 10.63 s | - | 11.36 s | - | - | |
| 9 | 7.82 s | |||||
| 11 | 2.53 s | 2.53 s | 2.47 s | |||
| 12 | 2.04 s | 2.14 s | 6.63 d (3.1) | 2.01 s | ||
| 13 | 1.35 s | 1.23 s | 6.50 dd (2.8, 1.7) | |||
| 14 | 1.35 s | 1.23 s | 7.55 br s | |||
| 15 | 2.00 s | 1.97 s | ||||
| OMe | 3.27 s |
| No. | 1 a | 2 b | 3 c | 4 b | 5 b | 6 b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 172.9 s | 172.3 s d | 170.4 s | 172.7 s | 172.2 s | 173.3 s d |
| 2 | 108.4 s | 111.1 s | 112.4 s | 112.1 s | 112.2 s | 117.6 s |
| 3 | 131.8 d | 132.5 d | 131.6 d | 132.6 d | 132.5 d | 132.7 d |
| 4 | 117.5 d | 117.9 d | 120.2 d | 121.0 d | 118.7 d | 121.3 d |
| 5 | 135.7 d | 135.2 d | 135.0 d | 135.0 d | 135.1 d | 134.2 d |
| 6 | 113.1 d | 114.1 d | 114.3 d | 115.0 d | 114.4 d | 114.5 d |
| 7 | 148.3 s | 149.7 s | 146.4 s | 147.5 s | 148.7 s | 146.8 s |
| 9 | 148.4 s | 147.9 s | 136.5 s | 135.4 s | 131.5 d | 143.4 s |
| 10 | 199.3 s | |||||
| 11 | 49.7 t | 48.7 t | 166.2 s | 167.4 s | 152.3 s | 8.5 q |
| 12 | 70.8 s | 76.8 s | 11.4 q | 11.4 q | 110.8 d | 24.2 q |
| 13 | 29.4 q | 25.6 q | 112.7 d | |||
| 14 | 29.4 q | 25.6 q | 144.5 d | |||
| 15 | 17.9 q | 17.3 q | ||||
| OMe | 49.0 q | 52.7 q |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.2. Fungal Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Cytotoxic Assay
3.5. Antimicrobial Assays
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rateb, M.E.; Ebel, R. Secondary metabolites of fungi from marine habitats. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 290–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 196–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 165–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Hu, W.P.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 170–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, X.M.; Meng, L.; Li, C.S.; Gao, S.S.; Shang, Z.; Proksch, P.; Huang, C.G.; Wang, B.G. Nigerapyrones A–H, α-pyrone derivatives from the marine mangrove-derived endophytic fungus Aspergillus niger MA-132. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1787–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.S.; Li, X.M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.S.; Cui, C.M.; Wang, B.G. Comazaphilones A–F, azaphilone derivatives from the marine sediment-derived fungus Penicillium commune QSD-17. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.Y.; Li, X.M.; Li, C.S.; Shang, Z.; Wang, B.G. Cristatumins A–D, new indole alkaloids from the marine-derived endophytic fungus Eurotium cristatum EN-220. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 4650–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.F.; Li, X.M.; Meng, L.; Cui, C.M.; Gao, S.S.; Li, C.S.; Huang, C.G.; Wang, B.G. Asperolides A–C, tetranorlabdane diterpenoids from the marine alga-derived endophytic fungus Aspergillus wentii EN-48. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.M.; Shang, Z.; Li, C.S.; Ji, N.Y.; Wang, B.G. Meroterpenoid and diphenyl ether derivatives from Penicillium sp. MA-37, a fungus isolated from marine mangrove rhizospheric soil. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1888–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.Y.; Li, X.M.; Li, C.S.; Gao, S.S.; Shang, Z.; Wang, B.G. Triazoles and other N-containing metabolites from the marine-derived endophytic fungus Penicillium chrysogenum EN-118. Helv. Chim. Acta 2013, 96, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; An, C.Y.; Li, X.M.; Gao, S.S.; Cui, C.M.; Sun, H.F.; Wang, B.G. Triazole and dihydroimidazole alkaloids from the marine sediment-derived fungus Penicillium paneum SD-44. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1331–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Mitu, L.; Latif, S.; Mahmood, I.N.; Zaman, S.S.; Fatima, S. Antibacterial Co (II), Ni (II), Cu (II) and Zn (II) complexes with biacetyl-derived Schiff bases. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2010, 75, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekata, M.; Seto, H.; Tamura, G. The selective inhibitors against sv40-transformed cells. 4, isolation of ortho-acetylbenzene-amidinocarboxylic acid, a new metabolite of Gibberella saubinetii. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1982, 46, 1711–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Nawaz, S.A.; Afza, N.; Malik, A.; Fatima, I.; Khan, S.B.; Ahmad, M.; Choudhary, M.I. Isolation of onosmins A and B, lipoxygenase inhibitors from Onosma hispida. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-El-Wafa, S.M.; El-Behairy, M.A.; Issa, R.M.; Saleh, A.A. On the formation of Mn (II) antranilic acid anilide complexes, structural elucidation by TGA, IR, electronic, EPR spectra and potentiometric studies. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 1988, 10, 464–469. [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxcity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Burtamani, S.K.S.; Fatope, M.O.; Marwah, R.G.; Onifade, A.K.; Al-Saidi, S.H. Chemical composition, antibacterial and antifungal activities of the essential oil of Haplophyllum tuberculatum from Oman. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 96, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeckh, V.; Brakhage, A.A. Fungal secondary metabolites-strategies to activate silent gene clusters. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2011, 48, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherlach, K.; Hertweck, C. Triggering cryptic natural product biosynthesis in microorganisms. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, V.; Sanglier, J.J.; DiTullio, D.; Braccili, S.; Bonner, P.; Waters, J.; Hughes, D.; Zhang, L. Diversifying microbial natural products for drug discovery. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 62, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, H.B.; Bethe, B.; Hofs, R.; Zeeck, A. Big effects from small changes: Possible ways to explore nature’s chemical diversity. Chembiochem 2002, 3, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagata, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yamada, T.; Doi, M.; Minoura, K.; Ohishi, H.; Yamori, T.; Numata, A. Variation in cytostatic constituents of a sponge-derived Gymnascella dankaliensis by manipulating the carbon source. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranagama, P.A.; Wijeratne, E.M.K.; Gunatilaka, A.A.L. Uncovering biosynthetic potential of plant-associated fungi: Effect of culture conditions on metabolite production by Paraphaeosphaeria quadriseptata and Chaetomium chiWersii. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.-S.; Li, X.-M.; Gao, S.-S.; Lu, Y.-H.; Wang, B.-G. Cytotoxic Anthranilic Acid Derivatives from Deep Sea Sediment-Derived Fungus Penicillium paneum SD-44. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3068-3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11083068
Li C-S, Li X-M, Gao S-S, Lu Y-H, Wang B-G. Cytotoxic Anthranilic Acid Derivatives from Deep Sea Sediment-Derived Fungus Penicillium paneum SD-44. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(8):3068-3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11083068
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chun-Shun, Xiao-Ming Li, Shu-Shan Gao, Yan-Hua Lu, and Bin-Gui Wang. 2013. "Cytotoxic Anthranilic Acid Derivatives from Deep Sea Sediment-Derived Fungus Penicillium paneum SD-44" Marine Drugs 11, no. 8: 3068-3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11083068





