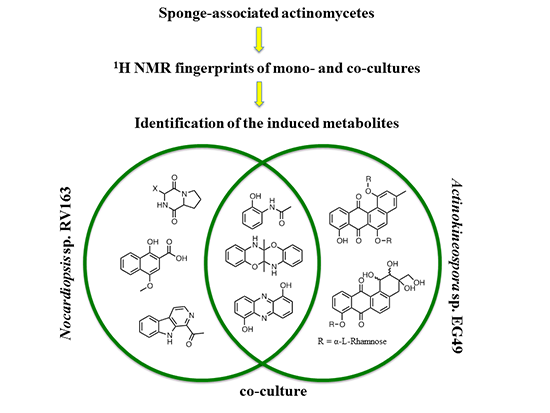
Production of Induced Secondary Metabolites by a Co-Culture of Sponge-Associated Actinomycetes, Actinokineospora sp. EG49 and Nocardiopsis sp. RV163
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Monoculture Chemical Profiles
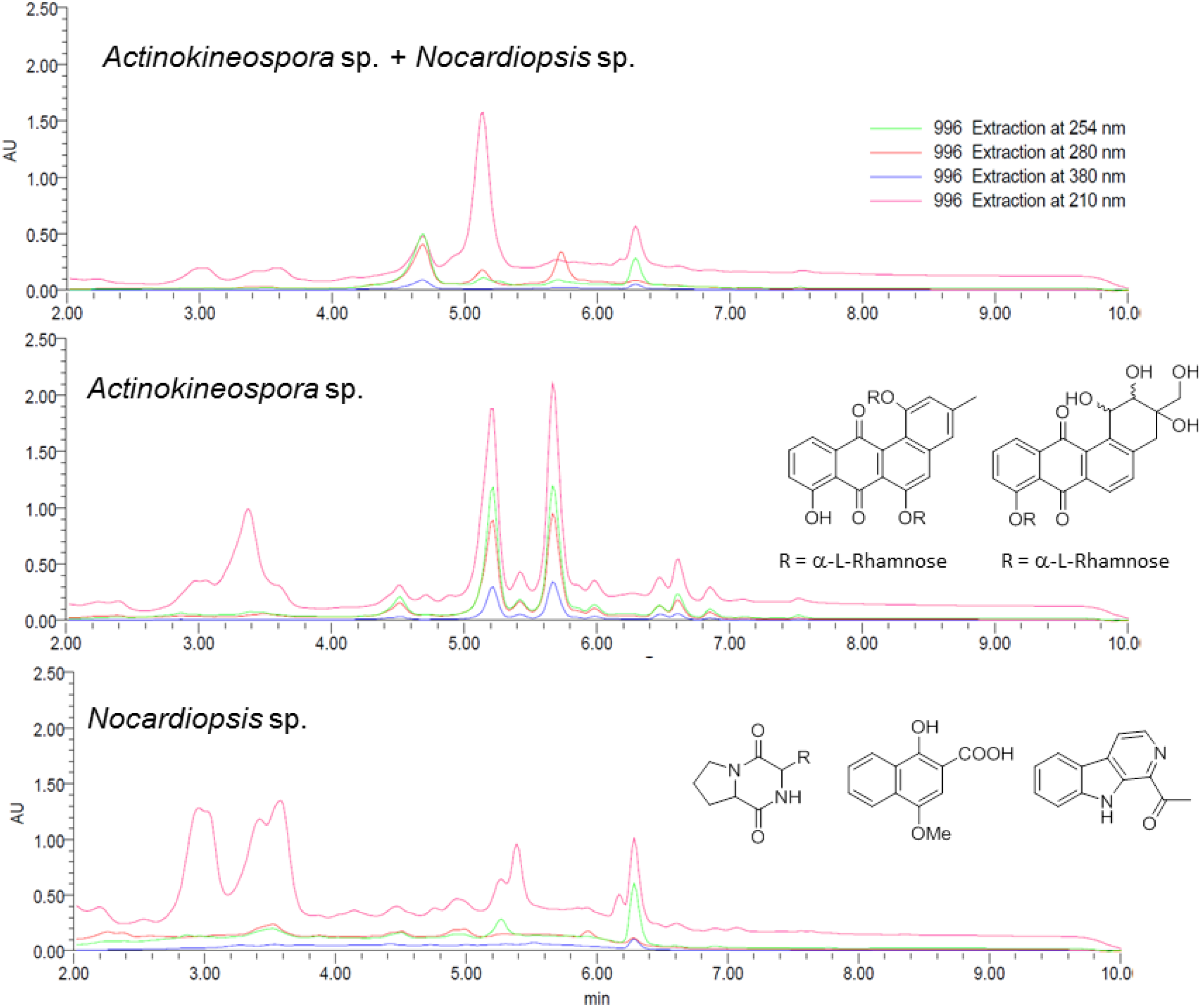

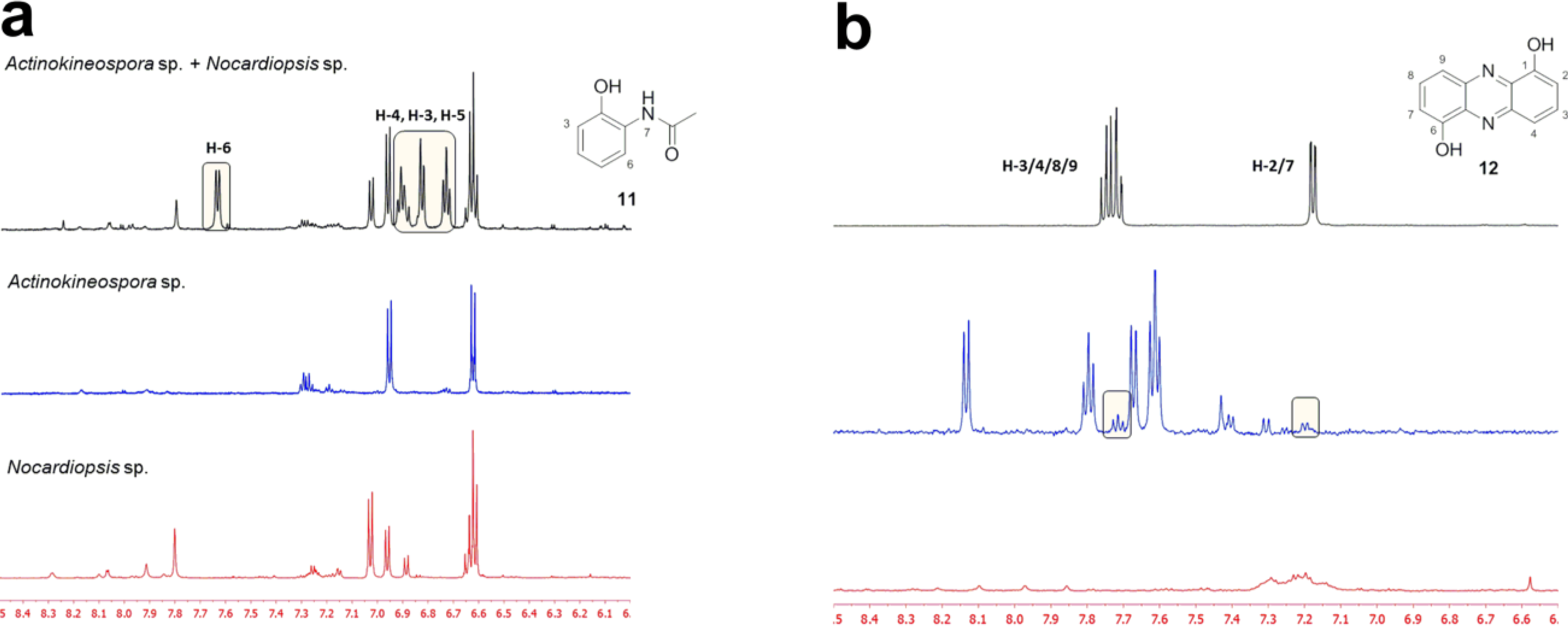
2.2. Co-Culture Chemical Profile
2.3. Anti-Infective Activity of Induced Metabolites
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Microbial Fermentation and Extracts Preparation
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.3.1. General Chromatographic Procedures for Large-Scale Isolation and Fingerprinting Work
3.3.2. Actinokineospora sp. EG49
3.3.3. Nocardiopsis sp. RV163
3.3.4. Actinokineospora sp. EG49 and Nocardiopsis sp. RV163 Co-Culture
3.4. Bioactivity Testing
3.4.1. Antibacterial Activity
3.4.2. Anti-Trypanosomal Activity
- Y1
- mean of the duplicate determination of the first measured cell density that is less than half the average of the growth control divided by the average of control growth.
- X1
- concentration of the substance that belongs to the cell density of Y1.
- Y2
- mean of the duplicate determination of the first measured cell density that is greater than half the average of the growth control divided by the average of control growth.
- X2
- concentration of the substance that belongs to the cell density of Y2.
3.4.3. Anti-Leishmanial Activity
3.5. Structure Elucidation of Compounds 1–13
 = 0 (c 0.012, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε), 295 (3.61), 235 (3.77), 208 (4.36) nm; 1H, 13C NMR data in DMSO-d6 in good agreement with published values; 1H-NMR (pyridine-d5, 600 MHz) δ (J in Hz) 1.75 (s, 2CH3), 6.80 (t, 7.6, H-3/9), 6.90 (t, 7.6, H-2/8), 6.98 (d, 2H, H-4/10), 7.03 (d, 2H, H-1/7), 8.00 (s, 2NH); 13C NMR (pyridine-d5, 125 MHz) 22.2 (2CH3), 83.5 (C-5a/11a), 115.5 (C-1/7), 117.6 (C-4/10), 120.2 (C-3/9), 121.9 (C-2/8), 131.8 (C-6a/12a), 143.5 (C-4a/10a), LRESIMS m/z 269.3 [M + H]+.
= 0 (c 0.012, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε), 295 (3.61), 235 (3.77), 208 (4.36) nm; 1H, 13C NMR data in DMSO-d6 in good agreement with published values; 1H-NMR (pyridine-d5, 600 MHz) δ (J in Hz) 1.75 (s, 2CH3), 6.80 (t, 7.6, H-3/9), 6.90 (t, 7.6, H-2/8), 6.98 (d, 2H, H-4/10), 7.03 (d, 2H, H-1/7), 8.00 (s, 2NH); 13C NMR (pyridine-d5, 125 MHz) 22.2 (2CH3), 83.5 (C-5a/11a), 115.5 (C-1/7), 117.6 (C-4/10), 120.2 (C-3/9), 121.9 (C-2/8), 131.8 (C-6a/12a), 143.5 (C-4a/10a), LRESIMS m/z 269.3 [M + H]+.4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feling, R.H.; Buchanan, G.O.; Mincer, T.J.; Kauffman, C.A.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Salinosporamide A: a highly cytotoxic proteasome inhibitor from a novel microbial source, a marine bacterium of the new genus Salinospora. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 355–357. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, C.C.; Prieto-Davo, A.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. The marinopyrroles, antibiotics of an unprecedented structure class from a marine Streptomyces sp. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenical, W.; Jensen, P.R.; Palladino, M.A.; Lam, K.S.; Lloyd, G.K.; Potts, B.C. Discovery and development of the anticancer agent salinosporamide A (NPI-0052). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2175–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfender, J.L.; Marti, G.; Queiroz, E.F. Advances in techniques for profiling crude extracts and for the rapid identification of natural products: dereplication, quality control and metabolomics. Curr. Org. Chem. 2010, 14, 1808–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.P.; Lin, W.H.; Wray, V.; Lai, D.W.; Proksch, P. Induced production of depsipeptides by co-culturing Fusarium tricinctum and Fusarium begoniae. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 2492–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nett, M.; Ikeda, H.; Moore, B.S. Genomic basis for natural product biosynthetic diversity in the actinomycetes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 1362–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.M.; Behnken, S.; Hertweck, C. Genomics-inspired discovery of natural products. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, E.K.; Moore, C.M.; Krastel, P.; Petersen, F. Natural products as catalysts for innovation: a pharmaceutical industry perspective. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.M.; Chang, S.L.; Oakley, B.R.; Wang, C.C. Recent advances in awakening silent biosynthetic gene clusters and linking orphan clusters to natural products in microorganisms. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherlach, K.; Hertweck, C. Triggering cryptic natural product biosynthesis in microorganisms. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeckh, V.; Scherlach, K.; Nutzmann, H.W.; Shelest, E.; Schmidt-Heck, W.; Schuemann, J.; Martin, K.; Hertweck, C.; Brakhage, A.A. Intimate bacterial–fungal interaction triggers biosynthesis of archetypal polyketides in Aspergillus nidulans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14558–14563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuck, K.M.; Shipley, S.; Newman, D.J. Induced production of N-formyl alkaloids from Aspergillus fumigatus by co-culture with Streptomyces peucetius. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, R.K. Mixed fermentation for natural product drug discovery. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 83, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueto, M.; Jensen, P.R.; Kauffman, C.; Fenical, W.; Lobkovsky, E.; Clardy, J. Pestalone, a new antibiotic produced by a marine fungus in response to bacterial challenge. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1444–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.C.; Jensen, P.R.; Kauffman, C.A.; Fenical, W. Libertellenones A–D: Induction of cytotoxic diterpenoid biosynthesis by marine microbial competition. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 5267–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.-C.; Kauffman, C.A.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Induced production of emericellamides A and B from the marine-derived fungus Emericella sp. in competing co-culture. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisdiyanti, P.; Otoguro, M.; Ratnakomala, S.; Lestari, Y.; Hastuti, R.D.; Triana, E.; Katsuhiko, A.; Widyastuti, Y. Actinokineospora baliensis sp. nov., Actinokineospora cibodasensis sp. nov. and Actinokineospora cianjurensis sp. nov., isolated from soil and plant litter. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 2331–2335. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ming, H.; Nie, G.X.; Yang, L.L.; Tang, S.K.; Li, W.J. Actinokineospora soli sp. nov., a thermotolerant actinomycete isolated from soil, and emended description of the genus Actinokineospora. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1845–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Pimentel-Elardo, S.M.; Hanora, A.; Radwan, M.; Abou-El-Ela, S.H.; Ahmed, S.; Hentschel, U. Isolation, phylogenetic analysis and anti-infective activity screening of marine sponge-associated actinomycetes. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Cheng, C.; Viegelmann, C.; Zhang, T.; Grkovic, T.; Quinn, R.J.; Safwat, A.; Hentschel, U.; Edrada-Ebel, R. Dereplication strategies for targeted isolation of new anti-trypanosomal actinosporins A and B from a marine sponge associated-Actinokineospora sp. EG49. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1220–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engelhardt, K.; Degnes, K.F.; Kemmler, M.; Bredholt, H.; Fjaervik, E.; Klinkenberg, G.; Sletta, H.; Ellingsen, T.E.; Zotchev, S.B. Production of a new thiopeptide antibiotic, TP-1161, by a marine Nocardiopsis species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4969–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvin, J.; Shanmughapriya, S.; Gandhimathi, R.; Seghal Kiran, G.; Rajeetha Ravji, T.; Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Hema, T.A. Optimization and production of novel antimicrobial agents from sponge associated marine actinomycetes Nocardiopsis dassonvillei MAD08. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 83, 435–445. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Yan, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Feng, G.; Li, J. Nocardiopsis fildesensis sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 174–179. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.C.; Li, S.; Nam, S.J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C. Nocardiamides A and B, two cyclohexapeptides from the marine-derived actinomycete Nocardiopsis sp. Cnx037. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneemann, I.; Ohlendorf, B.; Zinecker, H.; Nagel, K.; Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F. Nocapyrones A–D, γ-pyrones from a Nocardiopsis strain isolated from the marine sponge Halichondria panicea. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1444–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.Y.; Williams, P.G.; Kwon, H.C.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Lucentamycins A–D, cytotoxic peptides from the marine-derived actinomycete Nocardiopsis lucentensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Q. Genome-based studies of marine microorganisms to maximize the diversity of natural products discovery for medical treatments. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2011, 2011, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Rateb, M.E.; Hallyburton, I.; Houssen, W.E.; Bull, A.T.; Goodfellow, M.; Santhanam, R.; Jaspars, M.; Ebel, R. Induction of diverse secondary metabolites in Aspergillus fumigatus by microbial co-culture. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 14444–14450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, H.B.; Kwon, H.C.; Lee, C.H.; Yang, H.O. Glionitrin A, an antibiotic-antitumor metabolite derived from competitive interaction between abandoned mine microbes. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, S.; Schumpp, O.; Bohni, N.; Monod, M.; Gindro, K.; Wolfender, J.L. De novo production of metabolites by fungal co-culture of Trichophyton rubrum and Bionectria ochroleuca. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidtz, F.J.; Vanderah, D.J.; Hollenbeak, K.H.; Enwall, C.E.L.; Gopichand, Y.; SenGupta, P.K.; Hossain, M.B.; Van der Helm, D. Metabolites from the marine sponge Tedania ignis. A new atisanediol and several known diketopiperazines. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 3941–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczeski, M.; Reed, A.R.; Crews, P. New and known diketopiperazines from the caribbean sponge, Calyx cf. Podatypa. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayatilake, G.S.; Thornton, M.P.; Leonard, A.C.; Grimwade, J.E.; Baker, B.J. Metabolites from an antarctic sponge-associated bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, A.J.; Russell, R.A. Studies in relation to biosynthesis-XLIV: Structural elucidations of brevianamides-B, -C, -D and -F. Tetrahedron 1972, 28, 2999–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen-ju, H.; Xiao-ling, L.; Qiang-zhi, X.; Xiao-yu, L.; Bing-hua, J. Isolation, identification and biological characterization of secondary metabolites produced by a marine Bacillus subtilis. Acad. J. Sec. Mil. Med. Univ. 2008, 29, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, B.M.; Diaz, C.E.; Quintana, N. Naphthohydroquinones and lignans from the roots of Plocama pendula, a canary island paleoendemism. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2010, 38, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, B.S.; Kamat, V.N.; Gawad, D.H. Some β-carboline alkaloids of Ailanthus malabarica DC. Heterocycles 1977, 7, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusecker, K.; Laatsch, H.; Helmke, E.; Weyland, H. Dihydrophencomycin methyl ester, a new phenazine derivative from a marine streptomycete. J. Antibiot. 1997, 50, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo Alonso, A.; Horcajada, R.; Groombridge, H.J.; Chudasama Née Mandalia, R.; Motevalli, M.; Utley, J.H.; Wyatt, P.B. Synthesis of phenazine derivatives for use as precursors to electrochemically generated bases. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 2832–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barluenga, J.; Aznar, F.; Liz, R.; Cabal, M.-P.; Cano, F.H.; Foces-Foces, C. Oxidative aminomercuration of 2-propyn-1-ols. Stereoselective syntheses and structures ofcis-[1,4]oxazino[3,2-b]-1,4-oxazine derivatives. Chem. Berichte 1986, 119, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrake, H.M.; Jamieson, C.; Burton, J.W. The changing faces of halogenated marine natural products: total synthesis of the reported structures of elatenyne and an enyne from Laurencia majuscula. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7199–7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfán, N.; Santillan, R.L.; Castillo, D.; Cruz, R.; Joseph-Nathan, P.; Daran, J.-C. Fused heterocycles derived from pseudoephedrine and ephedrine. Can. J. Chem. 1992, 70, 2764–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauer, E.; Grellmann, K.H. Photochemical dehydrogenation, ring contraction, and ring expansion of hydrogenated derivatives of benzoxazino-benzoxazine, quinoxalino-quinoxaline, and bibenzothiazole. Chem. Berichte 1990, 123, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, W.; Koella, J.C. A comparison of three methods of estimating EC50 in studies of drug resistance of malaria parasites. Acta Trop. 1993, 55, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte-Sucre, A.; Vicik, R.; Schultheis, M.; Schirmeister, T.; Moll, H. Aziridine-2,3-dicarboxylates, peptidomimetic cysteine protease inhibitors with antileishmanial activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2439–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Dashti, Y.; Grkovic, T.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Hentschel, U.; Quinn, R.J. Production of Induced Secondary Metabolites by a Co-Culture of Sponge-Associated Actinomycetes, Actinokineospora sp. EG49 and Nocardiopsis sp. RV163. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3046-3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12053046
Dashti Y, Grkovic T, Abdelmohsen UR, Hentschel U, Quinn RJ. Production of Induced Secondary Metabolites by a Co-Culture of Sponge-Associated Actinomycetes, Actinokineospora sp. EG49 and Nocardiopsis sp. RV163. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(5):3046-3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12053046
Chicago/Turabian StyleDashti, Yousef, Tanja Grkovic, Usama Ramadan Abdelmohsen, Ute Hentschel, and Ronald J. Quinn. 2014. "Production of Induced Secondary Metabolites by a Co-Culture of Sponge-Associated Actinomycetes, Actinokineospora sp. EG49 and Nocardiopsis sp. RV163" Marine Drugs 12, no. 5: 3046-3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12053046
APA StyleDashti, Y., Grkovic, T., Abdelmohsen, U. R., Hentschel, U., & Quinn, R. J. (2014). Production of Induced Secondary Metabolites by a Co-Culture of Sponge-Associated Actinomycetes, Actinokineospora sp. EG49 and Nocardiopsis sp. RV163. Marine Drugs, 12(5), 3046-3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12053046