Extraction and Identification of Phlorotannins from the Brown Alga, Sargassum fusiforme (Harvey) Setchell
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
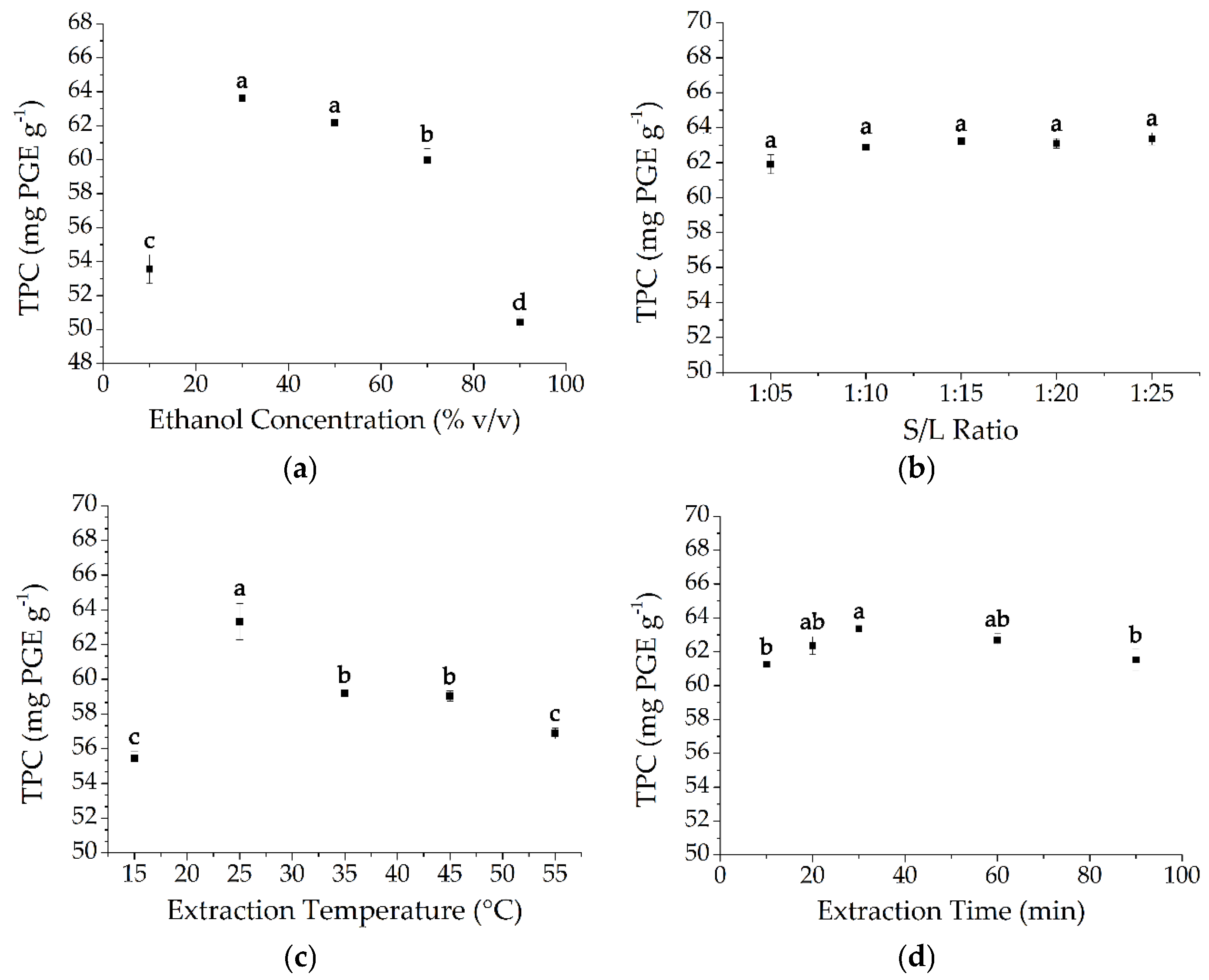
2.1. Determination of Extraction Parameters
2.1.1. Effect of Solvent Concentration
2.1.2. Effect of Solid/Liquid Ratio
2.1.3. Effect of Extraction Temperature
2.1.4. Effect of Extraction Time
2.2. Total Phlorotannin Content (TPC) and Antioxidative Activity of 30% Ethanol Extract and Its Solvent Fractions
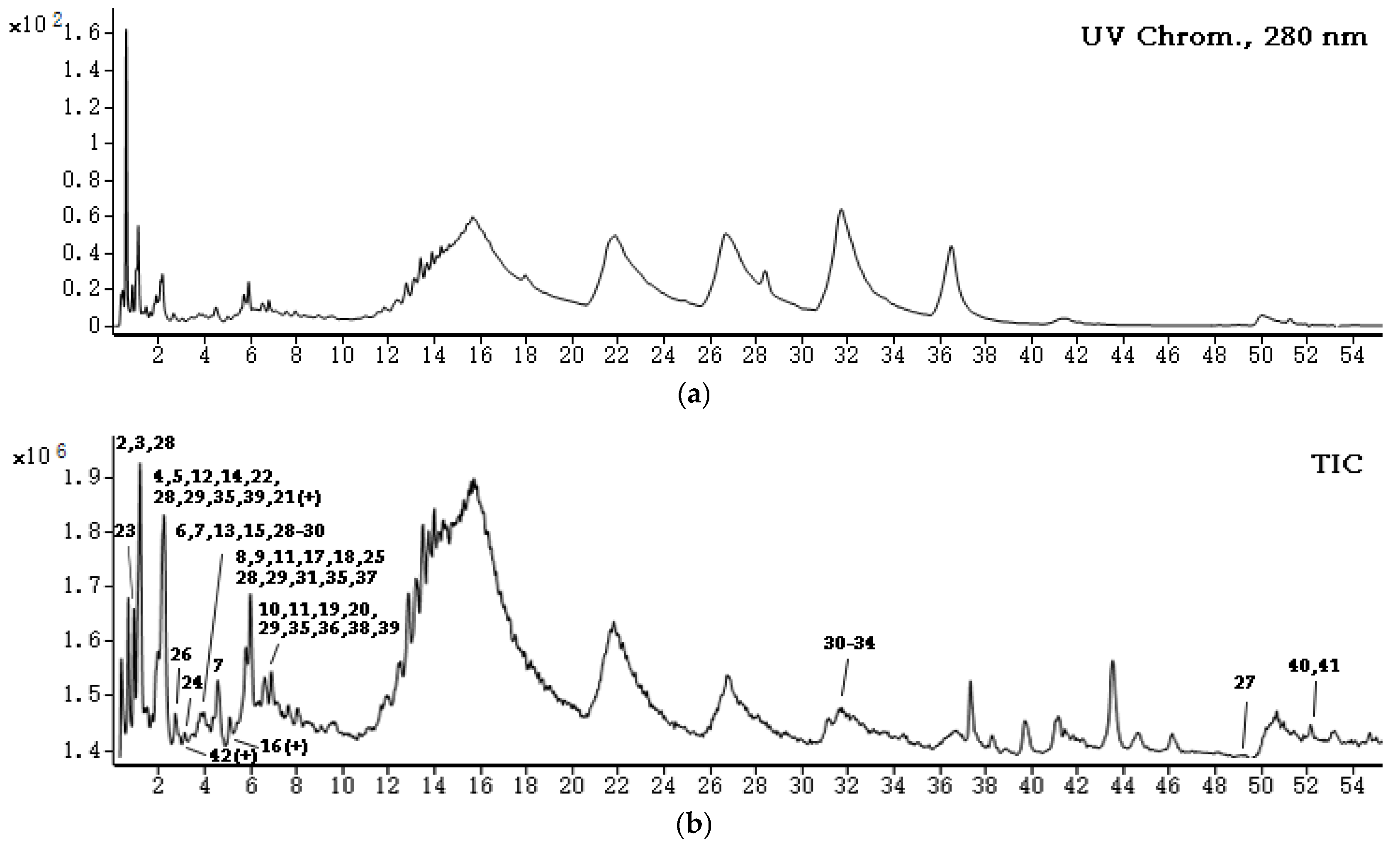
2.3. UHPLC-QQQ-MS and MS/MS Profiling of the Phlorotannin-Enriched Fraction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples and Chemicals
3.2. Determination of Total Phlorotannin Content (TPC)
3.3. Determination of Extraction Parameters
3.3.1. Initial Extraction Method
3.3.2. Single Factor Experimental Design
3.4. Preparation of Seaweed Extracts and Fractions
3.5. Antioxidative Activity Assay
3.5.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity (DRSA)
3.5.2. Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP)
3.6. UHPLC-QQQ-MS of Phlorotannin-Enriched Fractions
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.; Jonsdottir, R.; Liu, H.; Gu, L.; Kristinsson, H.G.; Raghavan, S.; Olafsdottir, G. Antioxidant capacities of phlorotannins extracted from the brown algae Fucus vesiculosus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5874–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyton, A.; Pezoa-Conte, R.; Barriga, A.; Buschmann, A.H.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Mikkola, J.P.; Lienqueo, M.E. Identification and efficient extraction method of phlorotannins from the brown seaweed Macrocystis pyrifera using an orthogonal experimental design. Algal Res. 2016, 16, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meslet-Cladiere, L.; Delage, L.; Leroux, C.J.; Goulitquer, S.; Leblanc, C.; Creis, E.; Gall, E.A.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Czjzek, M.; Potin, P. Structure/function analysis of a type iii polyketide synthase in the brown alga Ectocarpus siliculosus reveals a biochemical pathway in phlorotannin monomer biosynthesis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 3089–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, L.; Sanchez-Camargo, A.P.; Garcia-Canas, V.; Tanniou, A.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Russo, M.; Rastrelli, L.; Cifuentes, A.; Herrero, M.; Ibanez, E. Anti-proliferative activity and chemical characterization by comprehensive two-dimensional liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry of phlorotannins from the brown macroalga Sargassum muticum collected on North-Atlantic coasts. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1428, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, M.S.; Smyth, T.J.; Rai, D.K.; Soler-Vila, A.; Croft, A.K.; Brunton, N. Enrichment of polyphenol contents and antioxidant activities of Irish brown macroalgae using food-friendly techniques based on polarity and molecular size. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steevensz, A.J.; Mackinnon, S.L.; Hankinson, R.; Craft, C.; Connan, S.; Stengel, D.B.; Melanson, J.E. Profiling phlorotannins in brown macroalgae by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2012, 23, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubia, M.; Fabre, M.S.; Kerjean, V.; Lann, K.L.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Fauchon, M.; Deslandes, E. Antioxidant and antitumoural activities of some phaeophyta from brittany coasts. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Kondo, S.; Segawa, S.; Lin, Y.C.; Toyohara, H.; Ito, H.; Konoki, K.; Cho, Y.; Uchida, T. Isolation and structural determination of two novel phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome Okamura, and their radical scavenging activities. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, M.S.; Soler-Vila, A.; Rai, D.K.; Croft, A.K.; Brunton, N.P.; Smyth, T.J. UPLC-MS profiling of low molecular weight phlorotannin polymers in Ascophyllum nodosum, Pelvetia canaliculata and Fucus spiralis. Metabolomics 2013, 10, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffernan, N.; Brunton, N.P.; FitzGerald, R.J.; Smyth, T.J. Profiling of the molecular weight and structural isomer abundance of macroalgae-derived phlorotannins. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 509–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiger, V.; Horiguchi, T.; Yoshida, T.; Coleman, A.W.; Masuda, M. Phylogenetic relationships within the genus sargassum (fucales, phaeophyceae), inferred from its-2 nrdna, with an emphasis on the taxonomic subdivision of the genus. Phycol. Res. 2003, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.Y.; Wang, B.; Yu, C.-G.; Qu, Y.-L.; Su, C.L. Evaluation of antioxidant activities of five selected brown seaweeds from China. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 2557–2565. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.R.; Ali, M.Y.; Woo, M.-H.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory potential of the edible brown alga Hizikia fusiformis. J. Food Biochem. 2015, 39, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, Y.; Kinoshita, Y.; Abe, M.; Murase, N.; Tanaka, R.; Matsushita, T.; Usui, M.; Hanaoka, K.-I.; Miyata, M. Suppressive effects of the diethyl ether fraction from a brown alga Sargassum fusiforme on allergic and inflammatory reactions. Fish. Sci. 2016, 82, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shafay, S.M.; Ali, S.S.; El-Sheekh, M.M. Antimicrobial activity of some seaweeds species from red sea, against multidrug resistant bacteria. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2016, 42, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paskaleva, E.E.; Lin, X.; Duus, K.; McSharry, J.J.; Veille, J.C.; Thornber, C.; Liu, Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Canki, M. Sargassum fusiforme fraction is a potent and specific inhibitor of HIV-1 fusion and reverse transcriptase. Virol. J. 2008, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahmoune, F.; Nayak, B.; Moussi, K.; Remini, H.; Madani, K. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of polyphenols from Myrtus communis L. leaves. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghitescu, R.E.; Volf, I.; Carausu, C.; Buhlmann, A.M.; Gilca, I.A.; Popa, V.I. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of polyphenols from spruce wood bark. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 22, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boi, V.N.; Cuong, D.X.; Khanh Vinh, P.T. Effects of extraction conditions over the phlorotannin content and antioxidant activity of extract from brown algae Sargassum serratum (Nguyen Huu Dai 2004). Free Radic. Antioxid. 2017, 7, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cujic, N.; Savikin, K.; Jankovic, T.; Pljevljakusic, D.; Zdunic, G.; Ibric, S. Optimization of polyphenols extraction from dried chokeberry using maceration as traditional technique. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, S.; Liao, M. Optimization of ultrasonic extraction of phenolic compounds from Euryale ferox seed shells using response surface methodology. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 49, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Luo, Z.; Tao, B.; Chen, C. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction and purification of phenolic compounds from sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) rinds. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.A.; Jung, H.J.; Jeong, H.Y.; Kwon, H.J.; Ali, M.Y.; Choi, J.S. Phlorotannins isolated from the edible brown alga Ecklonia stolonifera exert anti-adipogenic activity on 3T3-L1 adipocytes by downregulating C/EBPα and PPARγ. Fitoterapia 2014, 92, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glombitza, K.W.; Pauli, K. Fucols and phlorethols from the brown alga Scytothamnus australis Hook. et Harv. (Chnoosporaceae). Bot. Mar. 2003, 46, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, J.H.; Castaneda, H.G. Preparation and chromatographic analysis of phlorotannins. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2013, 51, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanniou, A.; Leon, E.S.; Vandanjon, L.; Ibanez, E.; Mendiola, J.A.; Cerantola, S.; Kervarec, N.; La Barre, S.; Marchal, L.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V. Green improved processes to extract bioactive phenolic compounds from brown macroalgae using Sargassum muticum as model. Talanta 2013, 104, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Surget, G.; Roberto, V.P.; Le Lann, K.; Mira, S.; Guérard, F.; Laizé, V.; Poupart, N.; Cancela, M.L.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V. Marine green macroalgae: A source of natural compounds with mineralogenic and antioxidant activities. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Lann, K.; Surget, G.; Couteau, C.; Coiffard, L.; Cérantola, S.; Gaillard, F.; Larnicol, M.; Zubia, M.; Guérard, F.; Poupart, N.; et al. Sunscreen, antioxidant, and bactericide capacities of phlorotannins from the brown macroalga Halidrys siliquosa. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 3547–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Yoon, N.Y.; Jung, W.K.; Jeon, Y.J.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, Y.M. α-Glucosidase- and α-amylase-inhibitory activities of phlorotannins from Eisenia bicyclis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2084–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Kang, K.; Jeon, J.S.; Jho, E.H.; Kim, C.Y.; Nho, C.W.; Um, B.H. Isolation of phlorotannins from Eisenia bicyclis and their hepatoprotective effect against oxidative stress induced by tert-butyl hyperoxide. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 165, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, T.H.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, C.G.; Park, N.H. Antioxidant activity of various solvent fractions from edible brown alga, Eisenia bicyclis and its active compounds. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, C679–C684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwangi, H.M.; Van Der Westhuizen, J.; Marnewick, J.; Mabusela, W.T.; Kabanda, M.M.; Ebenso, E.E. Isolation, identification and radical scavenging activity of phlorotannin derivatives from brown algae, Ecklonia maxima: An experimental and theoretical study. Free Radic. Antioxid. 2013, 3, S1–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardhana, N.; Kim, K.-N.; Lee, K.-W.; Kim, S.-H.; Ha, J.-H.; Song, C.B.; Lee, J.-B.; Jeon, Y.-J. Optimisation of hydrophilic antioxidant extraction from Hizikia fusiformis by integrating treatments of enzymes, heat and pH control. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardhana, N.; Lee, K.W.; Jeon, Y.J. Radical scavenging potential of hydrophilic phlorotannins of Hizikia fusiformis. Algae 2005, 20, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Q.; Lu, H.Y.; Li, Y.P.; Liu, Y. Antioxidative activities of phlorotannins with different molecular weight extracted from Sargassum fusiforme. Mar. Sci. 2013, 37, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.L.; Gao, H.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Tao, F.; Ge, L.M.; Mu, H.L. Study for antioxidant activity of extracts from Sargassum fusiforme. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 11, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, T.; Nagayama, K.; Sugiura, S.; Makino, S.; Ueda, M.; Tamaru, Y. Analysis on composition and antioxidative properties of phlorotannins isolated from Japanese Eisenia and Ecklonia species. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 2510–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glombitza, K.W.; Schmidt, A. Trihydroxyphlorethols from the brown alga Carpophyllum angustifolium. Phytochemistry 1999, 51, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parys, S.; Kehraus, S.; Krick, A.; Glombitza, K.W.; Carmeli, S.; Klimo, K.; Gerhauser, C.; Konig, G.M. In vitro chemopreventive potential of fucophlorethols from the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus L. By anti-oxidant activity and inhibition of selected cytochrome P450 enzymes. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, Y.B.; Jeong, H.J.; Yoon, S.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, S.J.; Rho, M.C.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, W.S. Influenza virus neuraminidase inhibitory activity of phlorotannins from the edible brown alga Ecklonia cava. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6467–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glombitza, K.W. Pseudofuhalols from the brown alga Sargassum spinuligerum. Phytochemistry 1997, 46, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keusgen, M.; Glombitza, K.W. Phlorotannins from the brown alga Sargassum spinuligerum. Planta Med. 1991, 57, A20–A21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glombitza, K.W.; Keusgen, M. Fuhalols and deshydroxyfuhalols from the brown alga Sargassum spinuligerum. Phytochemistry 1995, 38, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glombitza, K.W.; Li, S.M. Hydroxyphlorethols from the brown alga Carpophyllum maschalocarpum. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 2741–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glombitza, K.W.; Hauperich, S.; Keusgen, M. Phlorotannins from the brown algae Cystophora torulosa and Sargassum spinuligerum. Nat. Toxins 1997, 5, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.M.; Glombitza, K.W. Carmalols and phlorethofuhalols from the brown alga Carpophyllum maschalocarpum. Phytochmtistry 1991, 30, 3417–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, M.; Kageyama, N.; Nakahara, K.; Miki, W. Phlorotannins as radical scavengers from the extract of Sargassum ringgoldianum. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.M.; Glombitza, K.W. Phlorotannins from the brown alga Landsburgia quercifolia (Hook. fil. et Harv.) harv. Bot. Mar. 1991, 34, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Jégou, C.; Cérantola, S.; Guérard, F.; Lann, K.L. Phlorotannins in Sargassaceae species from Brittany (France): Interesting molecules for ecophysiological and valorisation purposes. Adv. Bot. Res. 2014, 71, 379–412. [Google Scholar]
- Glombitza, K.W.; Gerstberger, G. Phlorotannins with dibenzodioxin structural elements from the brown alga Eisenia arborea. Phyrochemurry 1985, 24, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glombitza, K.W.; Keusgen, M. Phlorethols, fuhalols and their derivatives from the brown alga Sargassum spinuligerum. Phytochemistry 1995, 38, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailler, B.; Glombitza, K.W. Phlorethols and fucophlorethols from the brown alga Cystophora retroflexa. Phytochemistry 1999, 50, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glombitza, K.W.; Forster, M.; Farnham, W.F. Polyhydroxyphenyl ethers from brown alga Sargassum muticum (Yendo) Fensholt. Bot. Mar. 1982, 25, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanniou, A.; Vandanjon, L.; Incera, M.; Serrano Leon, E.; Husa, V.; Le Grand, J.; Nicolas, J.L.; Poupart, N.; Kervarec, N.; Engelen, A.; et al. Assessment of the spatial variability of phenolic contents and associated bioactivities in the invasive alga Sargassum muticum sampled along its european range from norway to portugal. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 26, 1215–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glombitza, K.W.; Keusgen, M.; Hauperich, S. Fucophlorethols from the brown algae Sargassum spinuligerum and Cystophora torulosa. Phytochemistry 1997, 46, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Ishimaru, K.; Kawaguchi, S.; Yoshikawa, H.; Hama, Y. Antioxidant activities of phlorotannins isolated from Japanese Laminariaceae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 20, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Yan, X.; Fang, G.; Chen, Y.; Lou, G. Antioxidative properties of high molecular weight polyphenols from brown seaweed. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 1999, 5, 494–499. [Google Scholar]

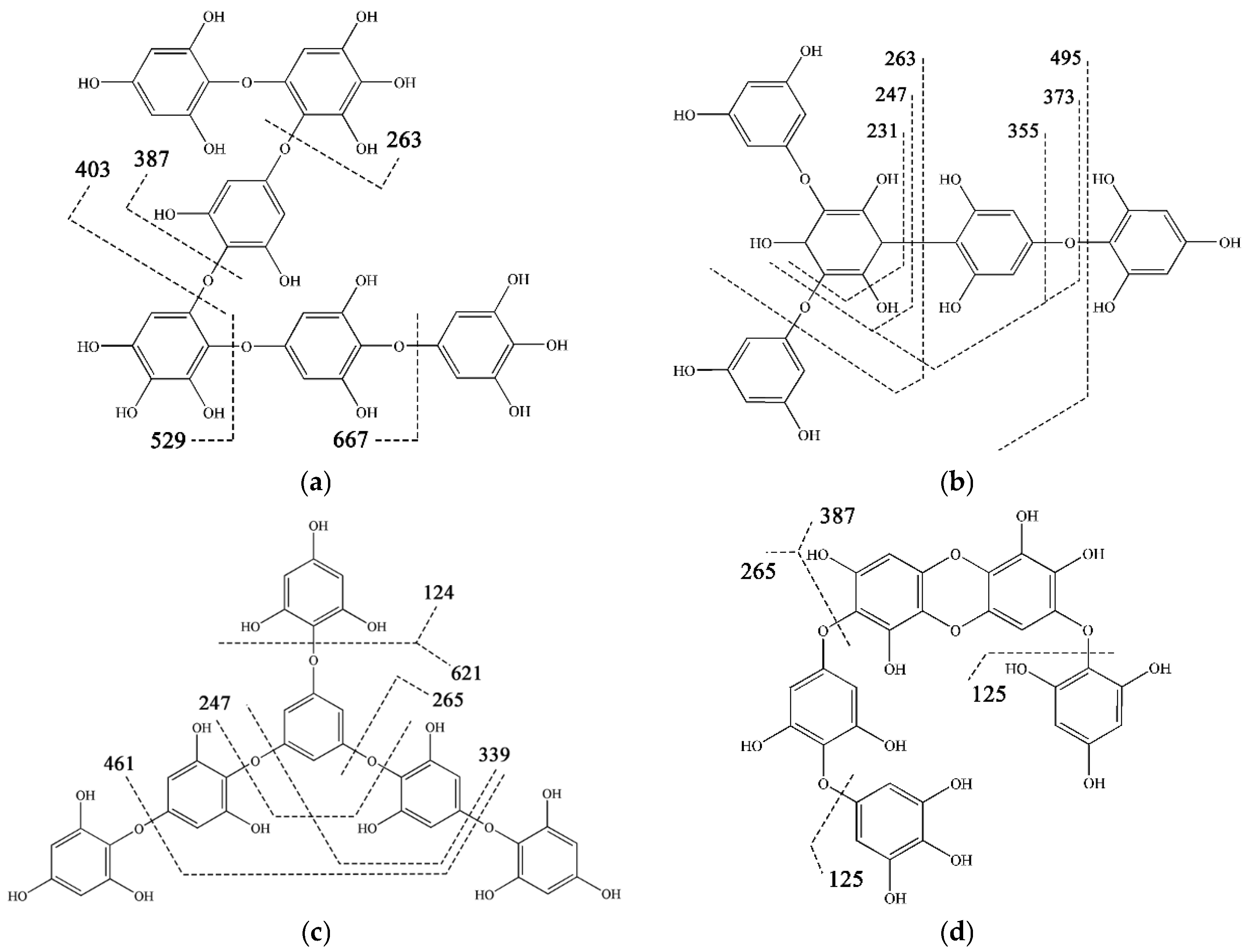
| Categories | No. | DP 1 | ESI | Measured Mass (m/z) | MS/MS Fragments Detected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuhalols | |||||
| 1 | 2-(1) | (−) | 265 | 111, 123, 125, 139, 141, 247 | |
| 2 | 3-(1) | (−) | 389 | 123, 125, 139, 245, 263, 265, 353 | |
| 3 | 4-(2) | (−) | 529 | 123, 139, 245, 263, 389, 403 | |
| 4 | 5-(2) | (−) | 653 | 139, 245, 263, 387, 389, 513, 527 | |
| 5 | 6-(3) | (−) | 793 | 139, 263, 387, 389, 403, 529, 667 | |
| 6 | 7-(3) | (−) | 917 | 373, 387, 527, 653, 785 | |
| 7 | 8-(4) | (−) | 1057 | 262, 527, 543, 793, 917 | |
| 8 | 9-(4) | (−) | 1181 | ||
| 9 | 10-(5) | (−) | 1321 | ||
| 10 | 11-(5) | (−) | 1445 | ||
| 11 | 12-(6) | (−) | 1585 | ||
| 12 | 4-(1) | (−) | 513 | 246, 265, 373, 389 | |
| 13 | 5-(1) | (−) | 637 | 123, 247, 265, 373, 388, 511 | |
| 14 | 6-(1) | (−) | 761 | 140, 261, 263, 355, 387, 389, 512, 621, 635 | |
| 15 | 6-(2) | (−) | 777 | 124, 245, 387, 389, 402, 513, 636 | |
| 16 | 7-(1) | (+) | 887 | ||
| 17 | 7-(2) | (−) | 901 | 262, 387, 511, 513, 527, 635, 637 | |
| 18 | 8-(3) | (−) | 1041 | 245, 263, 387, 389, 511, 513, 527, 621, 653, 777, 901 | |
| 19 | 9-(3) | (−) | 1165 | ||
| 20 | 10-(4) | (−) | 1305 | ||
| Phlorethols/Fucols/Fucophlorethols | |||||
| 21 | 2 | (+) | 251 | 93, 109, 123, 139, 233 | |
| 22 | 5 | (−) | 621 | 139, 231, 247, 263, 355, 373, 495 | |
| 23 | 6 | (−) | 745 | 124, 247, 265, 339, 461, 621, 727 | |
| 24 | 8 | (−) | 993 | ||
| 25 | 9 | (−) | 1117 | ||
| 26 | 10 | (−) | 1241 | ||
| 27 | 11 | (−) | 1365 | ||
| Eckols | |||||
| Carmalol Derivatives | 28 | 2-(1) | (−) | 263 | 111, 219, 245 |
| 29 | 3-(1) | (−) | 387 | 123, 245, 262, 329 | |
| 30 | 4-(1) | (−) | 511 | ||
| 31 | 5-(1) | (−) | 635 | ||
| 32 | 6-(1) | (−) | 759 | ||
| 33 | 7-(1) | (−) | 883 | ||
| 34 | 8-(1) | (−) | 1007 | ||
| 35 | 4-(2) | (−) | 527 | 123, 233, 261, 263, 139, 403 | |
| 36 | 5-(2) | (−) | 651 | 125, 265, 244, 387, 632 | |
| 37 | 6-(3) | (−) | 791 | 261, 356, 385, 747 | |
| 38 | 7-(3) | (−) | 915 | 263, 387, 652, 681, 791 | |
| 39 | 8-(4) | (−) | 1055 | ||
| Eckol | 40 | 3 | (−) | 371 | 121, 140, 229, 246, 317, 335 |
| Dieckol | 41 | 6 | (−) | 741 | 389, 600 |
| Dioxinodehydroeckol | 42 | 3 | (+) | 371 | 121, 236, 248, 267, 335, 353 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Fu, X.; Duan, D.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Gao, X. Extraction and Identification of Phlorotannins from the Brown Alga, Sargassum fusiforme (Harvey) Setchell. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15020049
Li Y, Fu X, Duan D, Liu X, Xu J, Gao X. Extraction and Identification of Phlorotannins from the Brown Alga, Sargassum fusiforme (Harvey) Setchell. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(2):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15020049
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yajing, Xiaoting Fu, Delin Duan, Xiaoyong Liu, Jiachao Xu, and Xin Gao. 2017. "Extraction and Identification of Phlorotannins from the Brown Alga, Sargassum fusiforme (Harvey) Setchell" Marine Drugs 15, no. 2: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15020049
APA StyleLi, Y., Fu, X., Duan, D., Liu, X., Xu, J., & Gao, X. (2017). Extraction and Identification of Phlorotannins from the Brown Alga, Sargassum fusiforme (Harvey) Setchell. Marine Drugs, 15(2), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15020049







