Identification, Characteristics and Mechanism of 1-Deoxy-N-acetylglucosamine from Deep-Sea Virgibacillus dokdonensis MCCC 1A00493
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structure Identification of the Antibacterial Substance
2.2. Antimicrobial Bioassay
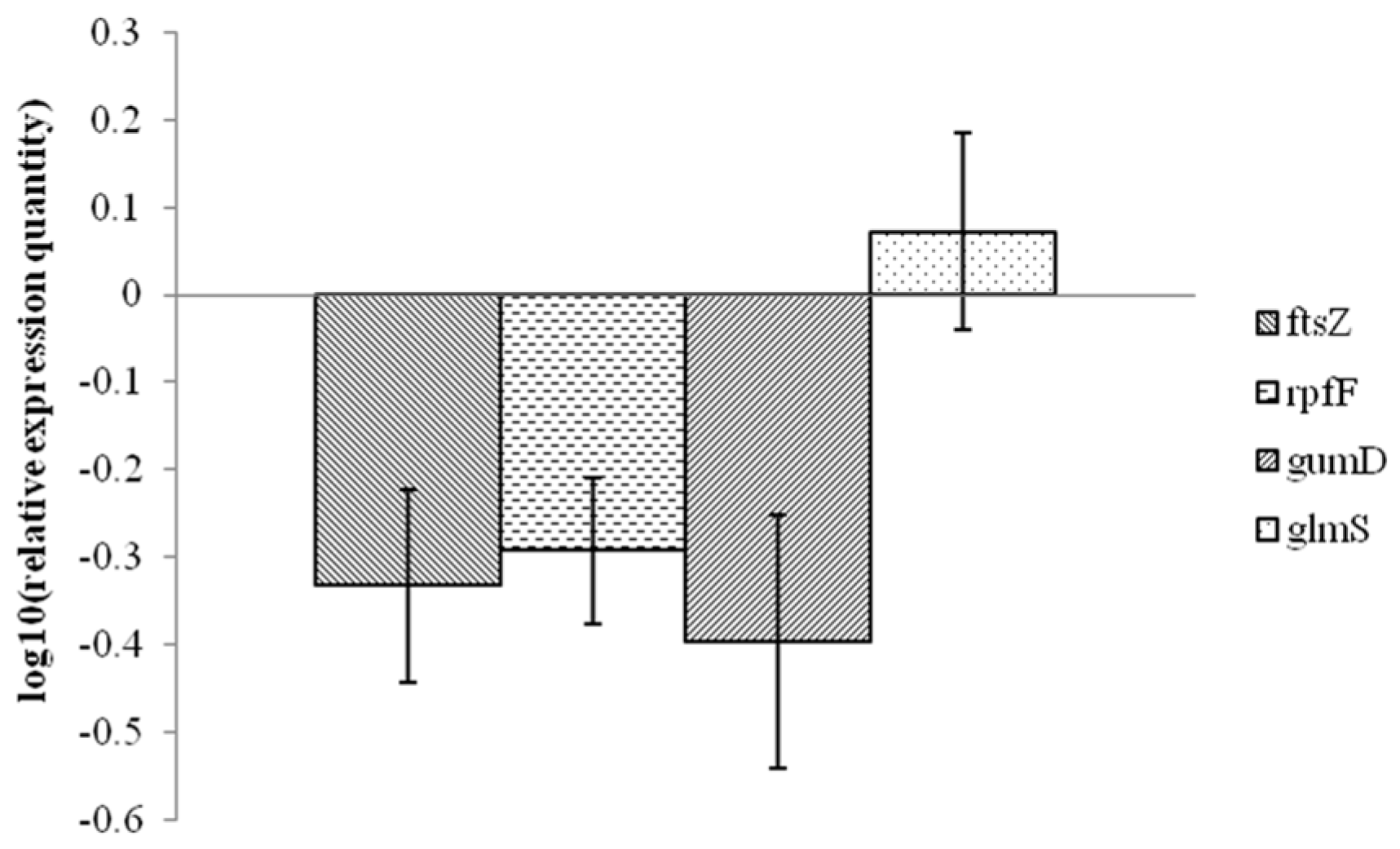
2.3. Analysis of Xanthomonas Potential Target Gene Expression after Exposure to 1-DGlcNAc
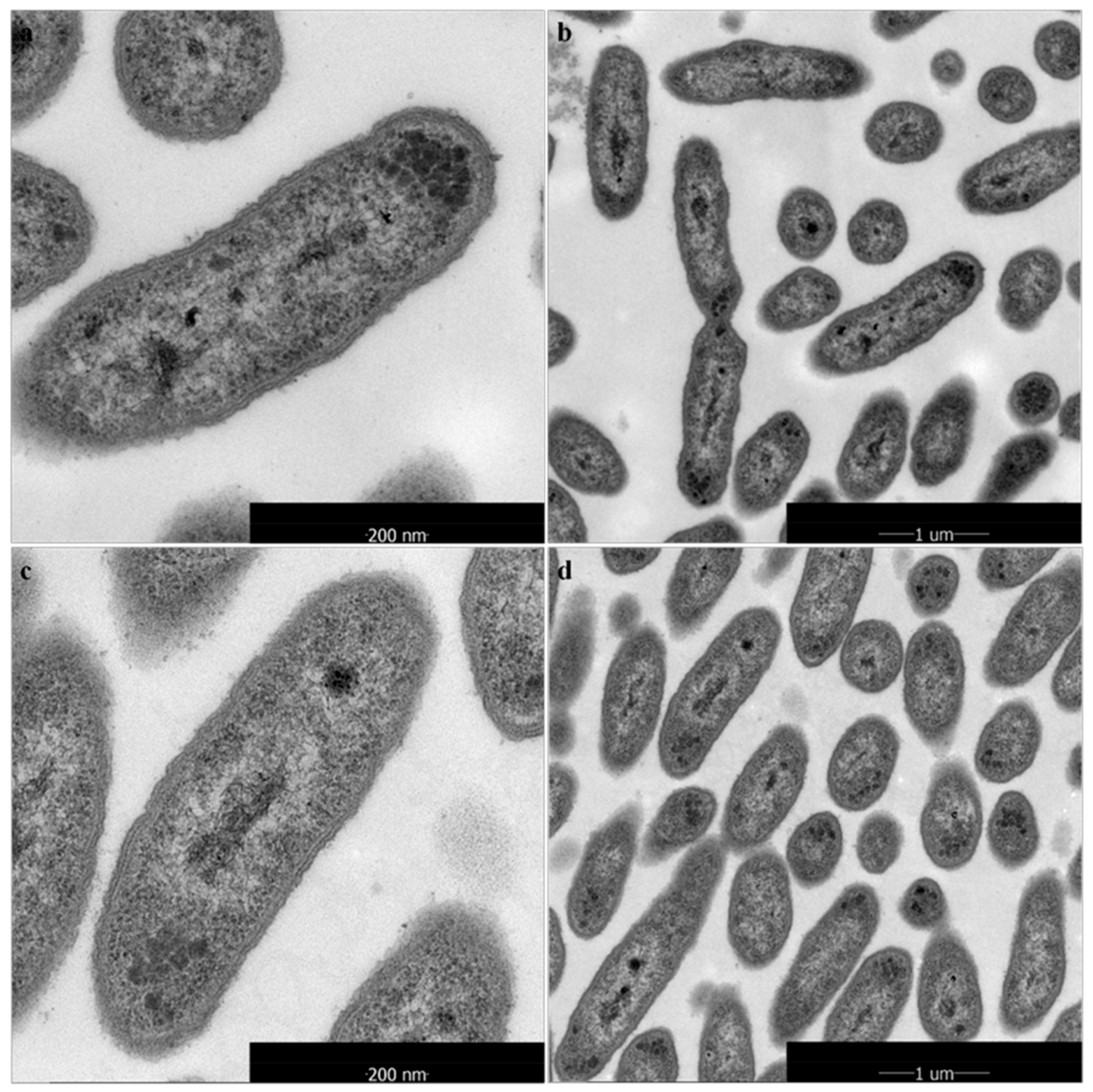
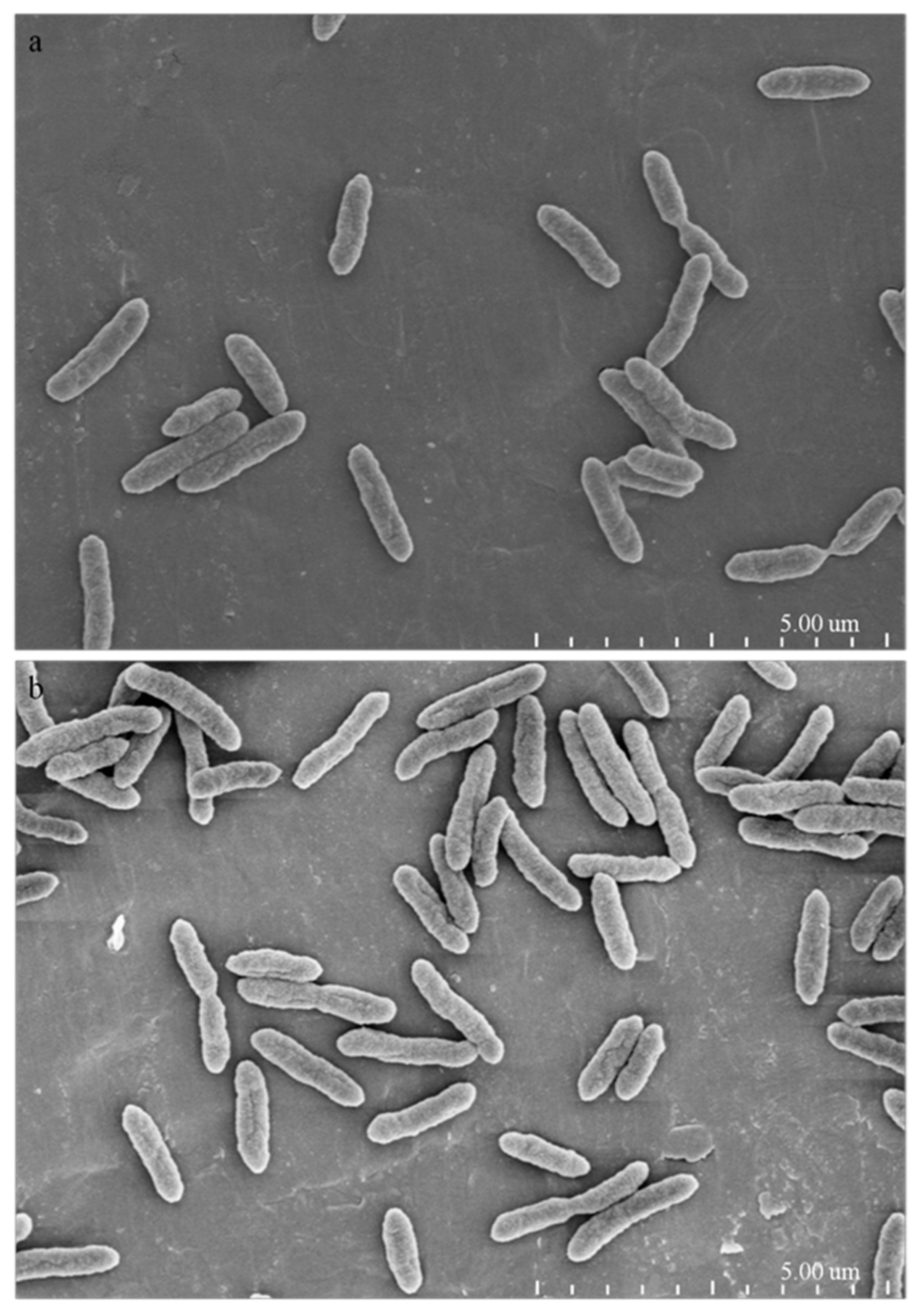
2.4. Morphological and Ultrastructural Changes of Xanthomonas Cells in the Presence of 1-DGlcNAc
2.5. Prediction of 1-DGlcNAc Potential Target Proteins
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Pathogens and Chemicals
3.2. Strain isolation and Fermentation
3.3. Extraction and Isolation of the Active Substance
3.4. Spectroscopic and NMR Analysis
3.5. Theoretical Calculation
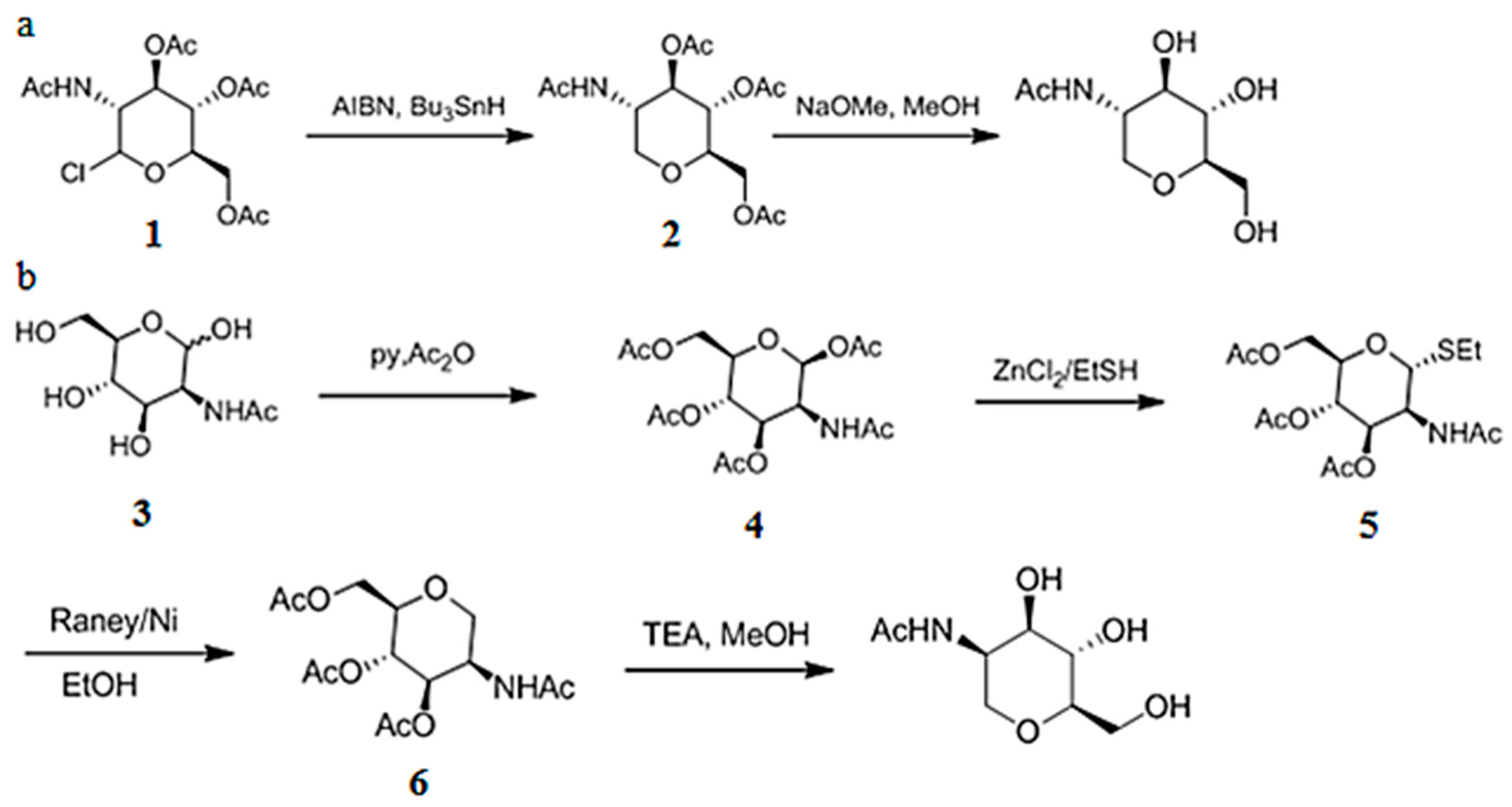
3.6. Chemical Synthesis of 1-DGlcNAc and Its Diastereomer 2-Acetamido-1,5-anhydro-2-deoxy-d-mannitol
3.7. In Vitro Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of 1-DGlcNAc
3.8. Electron Microscopy Studies
3.9. Quantitative Real Time-PCR Analysis
3.10. PharmMapper Server
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tagami, Y.; Mizukami, T. Historical review of the researches on bacterial blight of rice caused by Xanthomonas oryzae (Uyede and Ishiyama) Dowson. Spec. Rep. Plant Dis. Insect Pests Forecast. Serv. 1962, 10, 1–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjan, R.K.; Bimla, R.; Jha, P.K. In Vitro screening of plant extract to control bacterial leaf blight of rice disease caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Environ. Ecol. 2017, 35, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, H.P.T.; Ho, T.H.; Lee, I.; Tran, H.T.; Sur, B.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.G.; Ahn, Y.J.; Cha, S.S.; Kang, L.W. Crystal structures of peptide deformylase from rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in complex with substrate peptides, actinonin, and fragment chemical compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7307–7314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.M.; Park, Y.J.; Park, D.S.; Kang, H.W.; Kim, J.G.; Song, E.S.; Park, I.C.; Yoon, U.H.; Hahn, J.H.; Koo, B.S.; et al. The genome sequence of Xanthomonas oryzae pathovar oryzae KACC10331, the bacterial blight pathogen of rice. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochiai, H.; Inoue, Y.; Takeya, M.; Sasaki, A.; Kaku, H. Genome sequence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae suggests contribution of large numbers of effector genes and insertion sequences to its race diversity. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2005, 39, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzberg, S.L.; Sommer, D.D.; Schatz, M.C.; Phillippy, A.M.; Rabinowicz, P.D.; Tsuge, S.; Furutani, A.; Ochiai, H.; Delcher, A.L.; Kelley, D.; et al. Genome sequence and rapid evolution of the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99A. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Rashidul, I.M.; Hirata, H.; Tsuyumu, S. KdgR, an IClR family transcriptional regulator, inhibits virulence mainly by repression of hrp genes in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 6674–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, K.; Yang, B.; Tian, D.S.; Wu, L.F.; Wang, D.J.; Sreekala, C.; Yang, F.; Chu, Z.Q.; Wang, G.L.; White, F.F.; et al. R gene expression induced by a type-III effector triggers disease resistance in rice. Nature 2005, 435, 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponciano, G.; Yoshikawa, M.; Lee, J.L.; Ronald, P.C.; Whalen, M.C. Pathogenesis-related gene expression in rice is correlated with developmentally controlled Xa21-mediated resistance against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2006, 69, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.B.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, D.; Chen, L.; Webster, J.; Fang, A.C. Gene prioritization of resistant rice gene against Xanthomas oryzae pv. oryzae by using text mining technologies. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 853043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.T.; Wang, S.P. Rice versus Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae: A unique pathosystem. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2013, 16, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hop, D.; Phuong Hoa, P.T.; Quang, N.D.; Ton, P.H.; Ha, T.H.; Van Hung, N.; Van, N.T.; Van Hai, T.; Kim Quy, N.T.; Anh Dao, N.T.; et al. Biological control of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae causing rice bacterial blight disease by Streptomyces toxytricini VN08-A-12, isolated from soil and leaf-litter samples in Vietnam. Biocontrol Sci. 2014, 19, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jambhulkar, P.P.; Sharma, P. Development of bioformulation and delivery system of Pseudomonas fluorescens against bacterial leaf blight of rice (Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae). J. Environ. Biol. 2014, 35, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chung, E.J.; Hossain, M.T.; Khan, A.; Kim, K.H.; Jeon, C.O.; Chung, Y.R. Bacillus oryzicola sp. nov., an endophytic bacterium isolated from the roots of rice with antimicrobial, plant growth promoting and systemic resistance inducing activities in rice. Plant Pathol. J. 2015, 31, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravil, A.V.; Musthafal, K.S.; Jegathammball, G.; Kathiresan, K.; Pandian, S.K. Screening and evaluation of probiotics as a biocontrol agent against pathogenic Vibrios in marine aquaculture. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tresa Remya, A.T.; Devanand, P.K.; Ponnapakkam, A.L. Marine drugs from sponge-microbe association—A review. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1417–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Schinke, C.; Martins, T.; Queiroz, S.C.N.; Melo, I.S.; Reyes, F.G.R. Antibacterial compounds from marine bacteria, 2010–2015. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- William, H.G.; Amanda, M.F. Drug discovery from marine microbes. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 800–806. [Google Scholar]
- Heyndrickx, M.; Lebbe, L.; Kersters, K.; De Vos, P.; Forsyth, G.; Logan, N.A. Virgibacillus: A new genus to accommodate Bacillus pantothenticus (Proom and Knight 1950). Emended description of Virgibacillus pantothenticus. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essghaier, B.; Fardeau, M.L.; Cayol, J.L.; Hajlaoui, M.R.; Boudabous, A.; Jijakli, H.; Sadfi-Zouaoui, N. Biological control of grey mould in strawberry fruits by halophilic bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broxterman, H.J.G.; van der Marel, G.A.; van Boom, J.H. Synthesis of 2-acetamido-1,5-anhydro-2-deoxy-d-mannose as potential inhibitors of sialic acid biosynthesis. J. Carbohyd. Chem. 1991, 10, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, L.; Taha, M.I. Reaction of 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-d-glucose with ethanethiol and hydrochloric acid. J. Chem. Soc. 1956, 2042–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.H.; Yao, X.Y.; Duan, M.; Luo, Y.F.; Liu, B.; Qi, P.Y.; Sun, M.; Ruan, L.F. Two overlapping two-component systems in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae contribute to full fitness in rice by regulating virulence factors expression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabe, Y.; Sakata, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Kurata, K.; Yoshimatsu, H.; Ueda, K. Differential mechanisms of feeding modulation induced by amino sugars in rats. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1988, 188, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Yoshimatsu, H.; Kurokawa, M.; Oohara, A.; Sakata, T. Aminoglucose-induced feeding suppression is regulated by hypothalamic neuronal histamine in rats. Brain Res. 1993, 631, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garay, A.S. Molecular chirality of life and intrinsic chirality of matter. Nature 1978, 271, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.M.; Selinger, J. Cosmic chirality. Science 1998, 282, 880–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Sonti, R.V. rpfF mutants of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae are deficient for virulence and growth under low iron conditions. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2002, 15, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, G.L.; Zhou, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.C.; Song, Z.W.; Wang, S.Y.; Fan, J.Q.; Hu, B.S.; Venturi, V.; Liu, F.Q. Proteomic analysis reveals novel extracellular virulence-associated proteins and functions regulated by the diffusible signal factor (DSF) in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 3327–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, I.C.; Regasini, L.O.; Petronio, M.S.; Silva, D.H.S.; Bolzani, V.D.S.; Belasque, J.; Sacramento, L.V.S.; Ferreira, H. Antibacterial activity of alkyl gallates against Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciechowski, M.; Milewski, S.; Mazerski, J.; Borowski, E. Glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase, a novel target for antifungal agents. Molecular modelling studies in drug design. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2005, 52, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buttner, D.; Bonas, U. Regulation and secretion of Xanthomonas virulence factors. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Y.; Wang, J.; Zeigler, R.S. The 3,000 rice genomes project: New opportunities and challenges for future rice research. GigaScience. 2014, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.B.; Zheng, A.M.; Liu, H.L.; Yu, H.Y.; Wu, X.Y.; Xiao, C.N.; Dai, H.; Hao, F.H.; Zhang, L.M.; Wang, Y.L.; et al. Identification of three novel polyphenolic compounds, origanine A-C, with unique skeleton from Origanum vulgare L. using the hyphenated LC-DAD-SPE-NMR/MS methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruhn, T.; Schaumloffel, A.; Hemberger, Y.; Bringmann, G. SpecDis: Quantifying the comparison of calculated and experimental electronic circular dichroism spectra. Chirality 2013, 25, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, H.J.; Douglas, H.G. Screening methods for determining antibiotic activity of higher plants. J. Bacteriol. 1948, 55, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Wu, H.; Chen, L.; Yu, X.; Borriss, R.; Gao, X. Difficidin and bacilysin from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 have antibacterial activity against Xanthomonas oryzae rice pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.F.; Ouyang, S.S.; Yu, B.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y.B.; Gong, J.Y.; Zheng, S.S.; Li, Z.H.; Li, H.L.; Jiang, H.L. PharmMapper Server: A web server for potential drug target identification via pharmacophore mapping approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Shen, Y.H.; Wang, S.W.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, W.L.; Liu, X.F.; Lai, L.H.; Pei, J.F.; Li, H.L. PharmMapper 2017 update: A web server for potential drug target identification with a comprehensive target pharmacophore database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
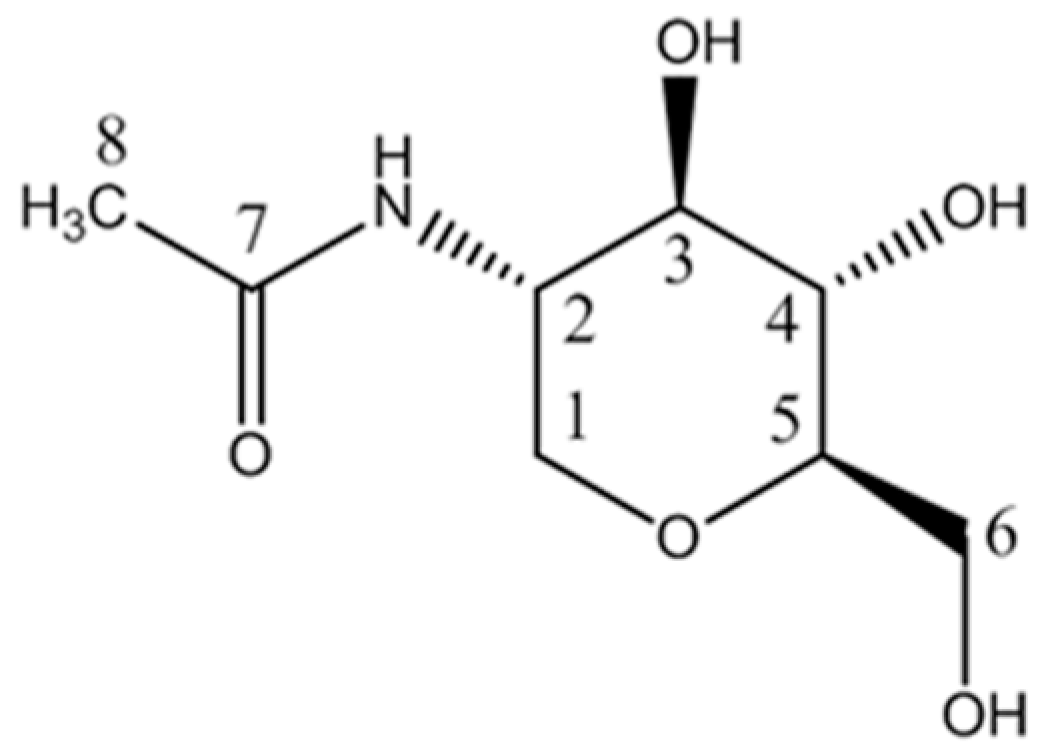
| No. | 1H | Group | Multiplicity (J-Value) | 13C | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.13 | C1H | t (11.0) | 69.2 | C2, C3, C5 |
| 3.90 | C1H’ | dd (11.0, 5.2) | 69.2 | C2, C3, C4, C5 | |
| 2 | 3.81 | C2H | ddd(11.0, 10.1, 5.2) | 53.2 | C1, C3, C4, C7 |
| 3 | 3.41 | C3H | dd (10.1, 8.6) | 77.0 | C1, C2, C4, C5 |
| 4 | 3.28 | C4H | dd (9.7, 8.6) | 72.6 | C2, C3, C5, C6 |
| 5 | 3.19 | C5H | ddd (9,7, 6.0, 2.2) | 82.7 | C1, C3, C4, C6 |
| 6 | 3.63 | C6H | dd (11.9, 6.0) | 63.2 | C4, C5 |
| 3.84 | C6H’ | dd (11.9, 2.2) | 63.2 | C4, C5 | |
| 7 | - | COCH3 | - | 174.2 | - |
| 8 | 1.97 | COCH3 | s | 22.9 | C1, C2, C3, C7 |
| Pathogenic Bacteria | Antibacterial Effect | |
|---|---|---|
| 1-DGlcNAc | 2-Acetamido-1,5-anhydro-2-deoxy-d-mannitol | |
| Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99A | + | - |
| Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae PXOΔ00069 | + | - |
| Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris str.8004 | - | - |
| Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola RS105 | - | - |
| Escherichia coli | - | - |
| Staphylococcus aureus | - | - |
| Salmonella typhimurium | - | - |
| Pseudomonas solanacearum | - | - |
| Pseudomonas syringae | - | - |
| Rank | PDB ID | Normalized Fit Score | Target Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2C68 | 0.4792 | cell division protein kinase 2 |
| 64 | 1V0P | 0.3561 | cell division control protein 2 homolog |
| 235 | 1A4R | 0.2595 | cell division control protein 42 homolog |
| 239 | 1RQ2 | 0.258 | cell division protein ftsZ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, D.; Shao, Z.-Z.; Yu, Y.; Cai, M.-M.; Zheng, L.-Y.; Li, G.-Y.; Yu, Z.-N.; Yi, X.-F.; Zhang, J.-B.; Hao, F.-H. Identification, Characteristics and Mechanism of 1-Deoxy-N-acetylglucosamine from Deep-Sea Virgibacillus dokdonensis MCCC 1A00493. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020052
Huang D, Shao Z-Z, Yu Y, Cai M-M, Zheng L-Y, Li G-Y, Yu Z-N, Yi X-F, Zhang J-B, Hao F-H. Identification, Characteristics and Mechanism of 1-Deoxy-N-acetylglucosamine from Deep-Sea Virgibacillus dokdonensis MCCC 1A00493. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(2):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020052
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Dian, Zong-Ze Shao, Yi Yu, Min-Min Cai, Long-Yu Zheng, Guang-Yu Li, Zi-Niu Yu, Xian-Feng Yi, Ji-Bin Zhang, and Fu-Hua Hao. 2018. "Identification, Characteristics and Mechanism of 1-Deoxy-N-acetylglucosamine from Deep-Sea Virgibacillus dokdonensis MCCC 1A00493" Marine Drugs 16, no. 2: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020052
APA StyleHuang, D., Shao, Z.-Z., Yu, Y., Cai, M.-M., Zheng, L.-Y., Li, G.-Y., Yu, Z.-N., Yi, X.-F., Zhang, J.-B., & Hao, F.-H. (2018). Identification, Characteristics and Mechanism of 1-Deoxy-N-acetylglucosamine from Deep-Sea Virgibacillus dokdonensis MCCC 1A00493. Marine Drugs, 16(2), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020052







