Physicochemical Characteristics and Anticoagulant Activities of the Polysaccharides from Sea Cucumber Pattalus mollis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
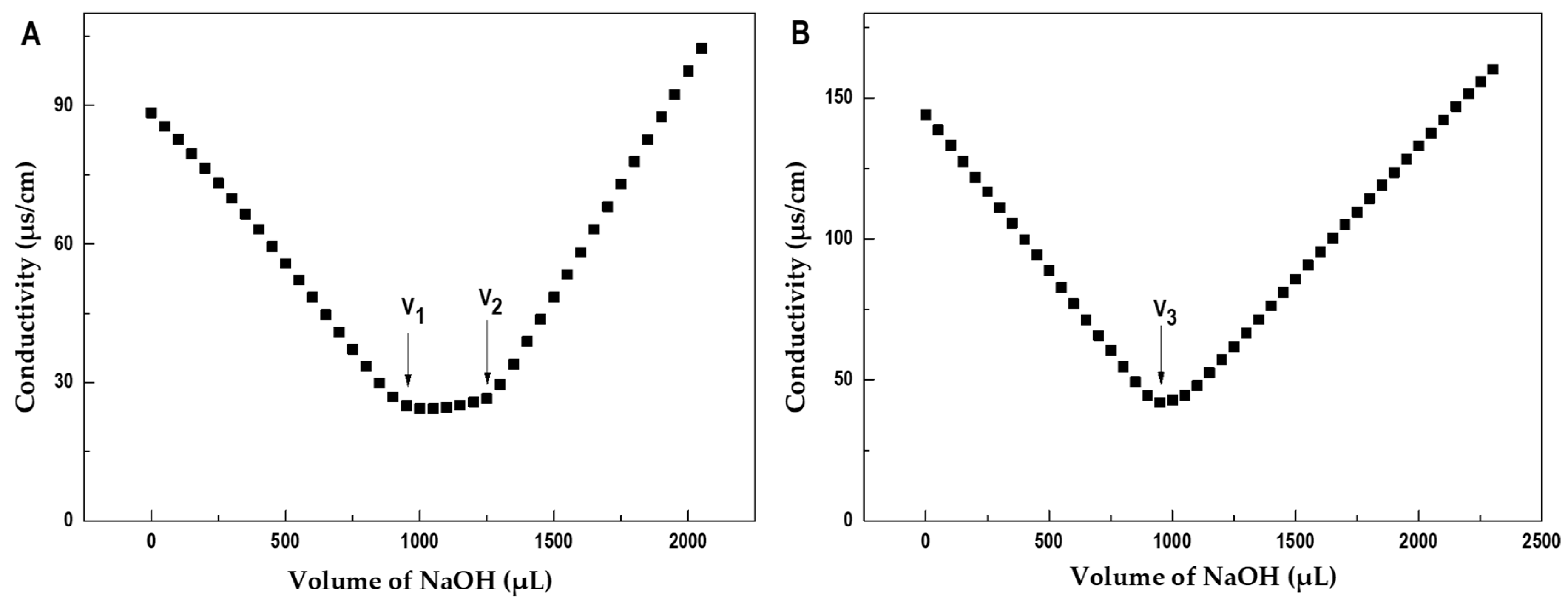
2.1. Isolation and Purification of Polysaccharides from P. mollis
2.2. Physicochemical Analysis
2.3. NMR Analysis
2.4. Anticoagulant Activity Evaluation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Isolation and Purification of Polysaccharides
3.3. Analysis of Physicochemical Properties
3.4. FT-IR and NMR Spectroscopic Analysis
3.5. Preparation of dPmFG-I – -III and PmFS-I – -III
3.6. Anticoagulant Activity Assays
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bordbar, S.; Anwar, F.; Saari, N. High-value components and bioactivities from sea cucumbers for functional foods-A review. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1761–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomin, V.H. Holothurian fucosylated chondroitin sulfate. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.G.; Xue, C.H.; Yin, L.; Tang, Q.J.; Yu, G.L.; Chai, W.G. Comparison of structures and anticoagulant activities of fucosylated chondroitin sulfates from different sea cucumbers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.H.; Jiang, T.F.; Lv, Z.H. Novel branch patterns and anticoagulant activity of glycosaminoglycan from sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.N.; Mou, R.R.; Zhang, Z.D.; Gao, N.; Lin, L.S.; Li, Z.; Wu, M.Y.; Zhao, J.H. Structural analysis and anticoagulant activities of three highly regular fucan sulfates as novel intrinsic factor Xase inhibitors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariya, Y.; Mulloy, B.; Imai, K.; Tominaga, A.; Kaneko, T.; Asari, A.; Suzuki, K.; Masuda, H.; Kyogashima, M.; Ishii, T. Isolation and partial characterization of fucan sulfates from the body wall of sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus and their ability to inhibit osteoclastogenesis. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Wu, M.Y.; Zheng, C.B.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, J.H.; Zheng, Y.T. The depolymerized fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from sea cucumber potently inhibits HIV replication via interfering with virus entry. Carbohydr. Res. 2013, 380, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.Y.; Wen, D.D.; Gao, N.; Xiao, C.; Yang, L.; Xu, L.; Lian, W.; Peng, W.L.; Jiang, J.M.; Zhao, J.H. Anticoagulant and antithrombotic evaluation of native fucosylated chondroitin sulfates and their derivatives as selective inhibitors of intrinsic factor Xase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 92, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsig, L.; Wang, L.; Cavalcante, M.C.; Cardilo-Reis, L.; Ferreira, P.L.; Mourão, P.A.; Esko, J.D.; Pavão, M.S. Selectin blocking activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan from sea cucumber. Effect on tumor metastasis and neutrophil recruitment. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14984–14991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.Y.; Wu, M.Y.; Xiao, C.; Yang, L.; Zhou, L.T.; Gao, N.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.C.; Liu, J.K.; et al. Discovery of an intrinsic tenase complex inhibitor: Pure nonasaccharide from fucosylated glycosaminoglycan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2015, 112, 8284–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.H.; Zhou, L.T.; Gao, N.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L.Y.; Shang, F.N.; Wu, M.Y.; Zhao, J.H. Oligosaccharides from depolymerized fucosylated glycosaminoglycan: Structures and minimum size for intrinsic factor Xase complex inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 14089–14099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, P.A.; Bastos, I.G. Highly acidic glycans from sea cucumbers. Isolation and fractionation of fucose-rich sulfated polysaccharides from the body wall of Ludwigothurea grisea. Eur. J. Biochem. 1987, 166, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariya, Y.; Watabe, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Yoshida, K. Occurrence of chondroitin sulfate E in glycosaminoglycan isolated from the body wall of sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus. J Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 5081–5085. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vieira, R.P.; Pedrosa, C.; Mourão, P.A. Extensive heterogeneity of proteoglycans bearing fucose-branched chondroitin sulfate extracted from the connective tissue of sea cucumber. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 2254–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.I.; Minami, Y.; Nemoto, H.; Numata, K.; Yamanaka, E. Structure of DHG, a depolymerized glycosaminoglycan from sea cucumber, Stichopus japonicus. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 4959–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariya, Y.; Watabe, S.; Kyogashima, M.; Ishihara, M.; Ishii, T. Structure of fucose branches in the glycosaminoglycan from the body wall of the sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus. Carbohydr. Res. 1997, 297, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariya, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Ochiai, Y.; Murata, K. Glycosaminoglycan from the body wall of the sea cucumber Stichopus japonicas. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1990, 95, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzman, R.L.; Jeanloz, R.W. Acid polysaccharides from invertebrate connective tissue: phylogenetic aspects. Science 1969, 166, 758–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtkamp, A.D.; Kelly, S.; Ulber, R.; Lang, S. Fucoidans and fucoidanases-focus on techniques for molecular structure elucidation and modification of marine polysaccharides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomin, V.H.; Mourão, P.A.S. Structure, biology, evolution, and medical importance of sulfated fucans and galactans. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevolot, L.; Mulloy, B.; Ratiskol, J.; Foucault, A.; Colliec-Jouault, S. A disaccharide repeat unit is the major structure in fucoidans from two species of brown algae. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 330, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.S.; Mulloy, B.; Mourão, P.A.S. Structure and anticoagulant activity of sulfated fucans: comparison between the regular, repetitive and linear fucans from echinoderms with the more heterogeneous and branched polymers from brown algae. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 7656–7667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Ge, L.; Xue, C.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y. Structural study of fucoidan from sea cucumber Acaudina molpadioides: a fucoidan containing novel tetra-fucose repeating unit. Food Chem. 2014, 142, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.Y.; Xu, L.; Zhao, L.Y.; Xiao, C.; Gao, N.; Luo, L.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, L.Y.; Zhao, J.H. Structural analysis and anticoagulant activities of the novel sulfated fucan possessing a regular well-defined repeating unit from sea cucumber. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2063–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berteau, O.; Mulloy, B. Sulfated fucans, fresh perspectives: structures, functions, and biological properties of sulfated fucans and an overview of enzymes active toward this class of polysaccharide. Glycobiology 2003, 13, 29R–40R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomin, V.H. Review: An overview about the structure-function relationship of marine sulfated homopolysaccharides with regular chemical structures. Biopolymers 2009, 91, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomin, V.H. Sulfated glycans in inflammation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 92, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.J.; Cai, Y.; Yin, R.H.; Lin, L.S.; Li, Z.; Wu, M.Y.; Zhao, J.H. Structural analysis and anticoagulant activities of two sulfated polysaccharides from the sea cucumber Holothuria coluber. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wu, M.Y.; Xu, L.; Lian, W.; Xiang, J.Y.; Lu, F.; Gao, N.; Xiao, C.; Wang, S.M.; Zhao, J.H. Comparison of physicochemical characteristics and anticoagulant activities of polysaccharides from three sea cucumbers. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Luo, L.; Cai, Y.; Yang, W.J.; Lin, L.S.; Li, Z.; Gao, N.; Purcell, S.W.; Wu, M.Y.; Zhao, J.H. Structural elucidation and biological activity of a highly regular fucosylated glycosaminoglycan from the edible sea cucumber Stichopus herrmanni. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9315–9323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yang, W.J.; Yin, R.H.; Zhou, L.T.; Li, Z.; Wu, M.Y.; Zhao, J.H. An anticoagulant fucan sulfate with hexasaccharide repeating units from the sea cucumber Holothuria albiventer. Carbohydr. Res. 2018, 464, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, L.T.; He, Z.C.; Gao, N.; Shang, F.N.; Xu, J.P.; Li, Z.; Yang, Z.M.; Wu, M.Y.; Zhao, J.H. Structural analysis and biological activity of a highly regular glycosaminoglycan from Achatina fulica. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, R.P.; Mulloy, B.; Mourão, P.A.S. Structure of a fucose-branched chondroitin sulfate from sea cucumber. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 13530–13536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shang, F.N.; Gao, N.; Yin, R.H.; Lin, L.S.; Xiao, C.; Zhou, L.T.; Li, Z.; Purcell, S.W.; Wu, M.Y.; Zhao, J.H. Precise structures of fucosylated glycosaminoglycan and its oligosaccharides as novel intrinsic factor Xase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 148, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.Y.; Huang, R.; Wen, D.D.; Gao, N.; He, J.B.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J.H. Structure and effect of sulfated fucose branches on anticoagulant activity of the fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from sea cucumber Thelenata ananas. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Xu, S.M.; Zhao, J.H.; Kang, H.; Ding, H. Physicochemical characteristics and anticoagulant activities of low molecular weight fractions by free-radical depolymerization of a fucosylated chondroitin sulphate from sea cucumber Thelenata ananas. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Monosaccharide Compositions | SO3−/COO− (Molar Ratios) | SO3−/Fuc (Molar Ratios) | Mw (kDa) | Specific Rotations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GlcA | GalNAc | Fuc | Glc | |||||
| PmFG | + | + | + | ˗ | 3.2 | / | 60.3 | −75.8° |
| PmFS | ˗ | ˗ | + | ˗ | / | 0.9 | 6.12 | −115.2° |
| PmNG-1 | ˗ | ˗ | ˗ | + | / | / | 275.6 | +172.4° |
| PmNG-2 | ˗ | ˗ | ˗ | + | / | / | 22.5 | +140.3 |
| Sugar Residues | Chemical Shifts a | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| U -4)-β-D-GlcA-(1- | H | 4.40 | 3.56 | 3.69 | 3.86 | 3.60 | -- | ||
| C | 107.1 | 78.2 | 80.0 | 79.2 | 82.0 | 178.1 | |||
| A -3)-β-D-GalNAc4S6S-(1- | H | 4.48 | 4.00 | 3.97 | 4.73 | 3.88 | 4.27/4.18 | -- | 1.98 |
| C | 102.8 | 54.5 | 76.7 | 79.1 | 74.8 | 70.2 | 178.1 | 25.6 | |
| I α-L-Fuc2S4S-(1- | H | 5.61 | 4.42 | 4.09 | 4.80 | 4.81 | 1.27 | ||
| C | 99.4 | 77.9 | 69.6 | 84.1 | 69.4 | 18.8 | |||
| II α-L-Fuc3S4S-(1- | H | 5.27 | 3.84 | 4.45 | 4.96 | 4.76 | 1.30 | ||
| C | 102.2 | 69.4 | 78.4 | 82.4 | 69.6 | 19.1 | |||
| III α-L-Fuc4S-(1- | H | 5.32 | 3.72 | 3.94 | 4.70 | 4.81 | 1.27 | ||
| C | 101.4 | 71.3 | 71.7 | 83.7 | 69.4 | 18.8 | |||
| Sugar Residues | Chemical Shifts a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| A | H | 5.17 | 4.43 | 4.14 | 3.92 | 4.44 | 1.33 |
| C | 99.3 | 75.6 | 67.1 | 82.7 | 68.5 | 16.2 | |
| B | H | 5.25 | 4.58 | 4.22 | 3.92 | 4.46 | 1.28 |
| C | 99.8 | 73.6 | 79.4 | 82.9 | 68.2 | 15.5 | |
| C | H | 5.22 | 4.43 | 4.16 | 3.96 | 4.38 | 1.35 |
| C | 98.8 | 75.6 | 67.0 | 82.7 | 68.4 | 15.9 | |
| D | H | 5.05 | 3.70 | 4.00 | 4.56 | 4.56 | 1.18 |
| C | 96.2 | 68.6 | 69.1 | 80.9 | 66.5 | 15.8 | |
| D’ | H | 5.02 | 3.66 | 4.32 | 3.81 | -- | -- |
| C | 96.2 | 68.6 | 69.1 | 80.9 | 66.5 | 15.8 | |
| Sample | Molecular Weight | APTT | Anti-FXase (IC50) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kDa) | (μg/mL) | (μM) | (ng/mL) | (nM) | |
| PmFG | 60.3 | 3.50 | 0.0580 | 13.7 | 0.227 |
| dPmFG-I | 12.8 | 6.24 | 0.488 | 14.0 | 1.09 |
| dPmFG-II | 6.97 | 7.97 | 1.14 | 17.6 | 2.53 |
| dPmFG-III | 3.71 | 19.3 | 5.20 | 126 | 34.0 |
| PmFS | 6.12 | 24.3 | 3.97 | 74.0 | 12.1 |
| PmFS-I | 8.64 | 22.7 | 2.63 | 87.9 | 10.2 |
| PmFS-II | 6.23 | 21.2 | 3.40 | 109 | 17.5 |
| PmFS-III | 5.06 | 22.5 | 4.45 | 99.2 | 19.6 |
| TaFS a | 61.2 | 21.7 | -- | 197 | -- |
| dTaFS a | 5.14 | 79.5 | -- | 745 | -- |
| LMWH | 3.50~5.50 | 11.6 | 2.11~3.31 | 59.0 | 10.7~16.9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, W.; Zhou, L.; Lin, L.; Cai, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhao, L.; Gao, N.; Yin, R.; Zhao, J. Physicochemical Characteristics and Anticoagulant Activities of the Polysaccharides from Sea Cucumber Pattalus mollis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040198
Zheng W, Zhou L, Lin L, Cai Y, Sun H, Zhao L, Gao N, Yin R, Zhao J. Physicochemical Characteristics and Anticoagulant Activities of the Polysaccharides from Sea Cucumber Pattalus mollis. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(4):198. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040198
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Wenqi, Lutan Zhou, Lisha Lin, Ying Cai, Huifang Sun, Longyan Zhao, Na Gao, Ronghua Yin, and Jinhua Zhao. 2019. "Physicochemical Characteristics and Anticoagulant Activities of the Polysaccharides from Sea Cucumber Pattalus mollis" Marine Drugs 17, no. 4: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040198
APA StyleZheng, W., Zhou, L., Lin, L., Cai, Y., Sun, H., Zhao, L., Gao, N., Yin, R., & Zhao, J. (2019). Physicochemical Characteristics and Anticoagulant Activities of the Polysaccharides from Sea Cucumber Pattalus mollis. Marine Drugs, 17(4), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040198





