New Aromatic Bisabolane Derivatives with Lipid-Reducing Activity from the Marine Sponge Myrmekioderma sp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
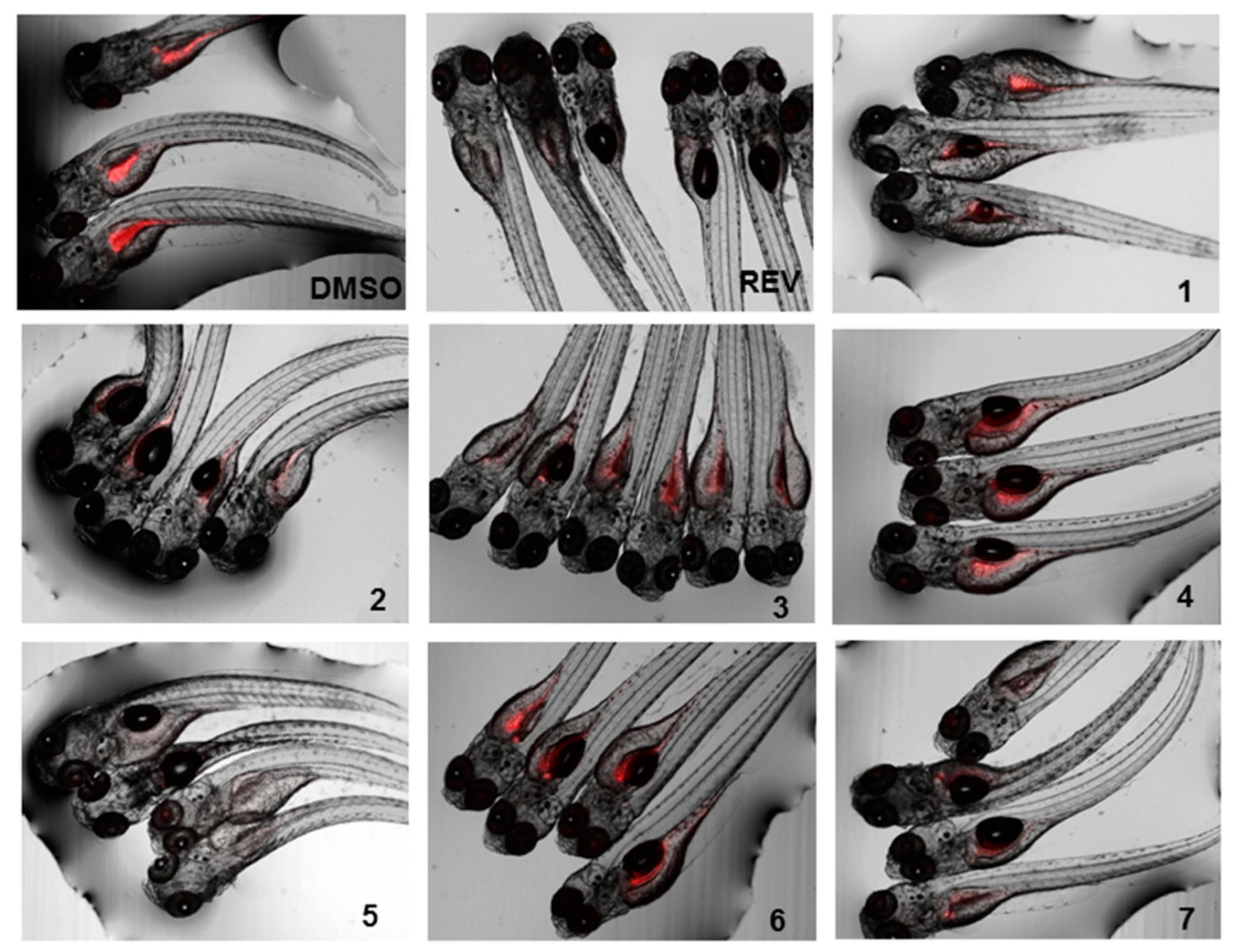
2. Results and Discussion
Isolation and Structure Elucidation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experiments
3.2. Biological Sample
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Biological Activities
3.4.1. Cytotoxicity
3.4.2. Zebrafish Nile Red Fat Metabolism Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haefner, B. Drugs from the deep: Marine natural products as drug candidates. Drug Discov. Today 2003, 8, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 8–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 235–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mehbub, M.F.; Lei, J.; Franco, C.; Zhang, W. Marine sponge derived natural products between 2001 and 2010: Trends and opportunities for discovery of bioactives. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4539–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, B.J.M.; de Groot, A. Occurrence, biological activity and synthesis of drimane sesquiterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 449–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, D.-Q.; Liu, H.-L.; Chen, S.-H.; Mollo, E.; Gavagnin, M.; Li, J.; Li, X.-W.; Guo, Y.-W. 5-Alkylpyrrole-2-carboxaldehyde derivatives from the Chinese sponge Mycale lissochela and their PTP1B inhibitory activities. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 1190–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.L.; Tinto, W.F.; McLean, S.; Reynolds, W.F.; Yu, M. Bisabolane Sesquiterpenes from Barbadian Pseudopterogorgia spp. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 1116–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.; Wu, W.-M.; Yu, H.-Y.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Tian, T.; Ruan, H.-L. Bisabolane-Type Sesquiterpenoids from the Whole Plant of Parasenecio rubescens. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yegdaneh, A.; Putchakarn, S.; Yuenyongsawad, S.; Ghannadi, A.; Plubrukarn, A. 3-Oxoabolene and 1-Oxocurcuphenol, Aromatic Bisabolanes from the Sponge Myrmekioderma sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1355–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.E.; Pomponi, S.A.; McConnell, O.J.; Kohmoto, S.; McCarthy, P.J. (+)-Curcuphenol and (+)-Curcudiol, Sesquiterpene Phenols from Shallow and Deep Water Collections of the Marine Sponge Didiscus flavus. J. Nat. Prod. 1987, 50, 976–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta-Yahya, P.P.; Ouellet, M.; Chan, R.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Keasling, J.D.; Lee, T.S. Identification and microbial production of a terpene-based advanced biofuel. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hurt, R.T.; Kulisek, C.; Buchanan, L.A.; McClave, S.A. The Obesity Epidemic: Challenges, Health Initiatives, and Implications for Gastroenterologists. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 6, 780–792. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. Natural Products with Anti-obesity Effects and Different Mechanisms of Action. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 9571–9585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Tao, N.; Wang, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, M. Marine-derived bioactive compounds with anti-obesity effect: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 372–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Preto, M.; Vasconcelos, V.; Urbatzka, R. Obesity: The Metabolic Disease, Advances on Drug Discovery and Natural Product Research. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 2577–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noinart, J.; Buttachon, S.; Dethoup, T.; Gales, L.; Pereira, J.A.; Urbatzka, R.; Freitas, S.; Lee, M.; Silva, A.M.S.; Pinto, M.M.M.; et al. A New Ergosterol Analog, a New Bis-Anthraquinone and Anti-Obesity Activity of Anthraquinones from the Marine Sponge-Associated Fungus Talaromyces stipitatus KUFA 0207. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, N.G.; Pavkov-Keller, T.; Richter, N.; Wiltschi, B.; Gruber, K.; Kroutil, W. Biocatalytic Friedel–Crafts Acylation and Fries Reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7615–7619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capon, R.; Ghisalberti, E.; Jefferies, P. New aromatic sesquiterpenes from a Halichondria sp. Aust. J. Chem. 1982, 35, 2583–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arihara, S.; Umeyama, A.; Bando, S.; Imoto, S.; Ono, M.; Yoshikawa, K. Three New Sesquiterpenes from the Black Heartwood of Cryptomeria japonica. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, B.; Subbaraju, G.; Rao, C.; Trimurtulu, G. Two New Oxigenated Lobanes from a Soft Coral of Lobophytum species of the Andaman and Nicobar Coasts. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, C.; El-Gamal, A.; Chiang, C.; Chu, C.; Wang, S.; Dai, C. New Cytotoxic Xenia Diterpenoids from the Formosan Soft Coral Xenia umbellata. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1882–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishara, A.; Rudi, A.; Goldberg, I.; Benayahu, Y.; Kashman, Y. Novaxenicins A–D and xeniolides I–K, seven new diterpenes from the soft coral Xenia novaebrittanniae. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 12092–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davyt, D.; Fernandez, R.; Suescun, L.; Mombru, A.W.; Saldana, J.; Dominguez, L.; Fujii, M.T.; Manta, E. Bisabolanes from the red alga Laurencia scoparia. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, Q.A.; Shao, C.L.; She, Z.G.; Lin, Y.C. Five Sesquiterpenoids from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp Isolated from a Gorgonian Dichotella gemmacea. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, D.; Menkis, A.; Olson, Å.; Stenlid, J.; Broberg, A.; Karlsson, M. Biosynthesis of fomannoxin in the root rotting pathogen Heterobasidion occidentale. Phytochemistry 2012, 84, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prompanya, C.; Dethoup, T.; Gales, L.; Lee, M.; Pereira, J.A.C.; Silva, A.M.S.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Kijjoa, A. New Polyketides and New Benzoic Acid Derivatives from the Marine Sponge-Associated Fungus Neosartorya quadricincta KUFA 0081. Mar Drugs 2016, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, C.; Kehraus, S.; Prudêncio, M.; König, M.K. Marilones A–C, phthalides from the sponge-derived fungus Stachylidium sp. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2011, 7, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Maddah, F.; Eguereva, E.; Kehraus, S.; König, G.M. Biosynthetic studies of novel polyketides from the marine sponge-derived fungus Stachylidium sp. 293K04. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 2747–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbatzka, R.; Freitas, S.; Palmeira, A.; Almeida, T.; Moreira, J.; Azevedo, C.; Afonso, C.; Correia-da-Silva, M.; Sousa, E.; Pinto, M.; et al. Lipid reducing activity and toxicity profiles of a library of polyphenol derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 151, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Rosa, F.; Ribeiro, T.; Hernandez-Bautista, R.; Bonaldo, M.; Goncalves Silva, N.; Eiriksson, F.; Thorsteinsdottir, M.; Ussar, S.; Urbatzka, R. Identification of Cyanobacterial Strains with Potential for the Treatment of Obesity-Related Co-Morbidities by Bioactivity, Toxicity Evaluation and Metabolite Profiling. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.S.; Alimov, A.P.; Rilo, H.L.; Jandacek, R.J.; Woollett, L.A.; Penberthy, W.T. A high throughput live transparent animal bioassay to identify non-toxic small molecules or genes that regulate vertebrate fat metabolism for obesity drug development. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skehan, P.; Storeng, R.; Scudiero, D.; Monks, A.; McMahon, J.; Vistica, D.; Warren, J.T.; Bokesch, H.; Kenney, S.; Boyd, M.R. New Colorimetric Cytotoxicity Assay for Anticancer-Drug Screening. JNCI 1990, 82, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, R.H. The NCI60 human tumour cell line anticancer drug screen. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ImageJ. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/index.html (accessed on 7 September 2018).





| Position | Compound 3 | Compound 4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, Type | δH, mult (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH, mult (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 147.5, C | 146.4, C | ||
| 2 | 118.8, CH | 6.68, s | 112.5, CH | 6.87, s |
| 3 | 125.4, C | 123.9, C | ||
| 4 | 147.0, C | 150.4, C | ||
| 5 | 117.2, CH | 6.50, s | 110.0, CH | 6.64, s |
| 6 | 124.2, C | 130.4, C | ||
| 7 | 148.0, C | 48.1, C | ||
| 8 | 76.7, CH | 4.40, dd (8.6, 5.4) | 37.4, CH2 | 2.42, dd (14.1, 7.9) 2.58, dd (14.1, 8.3) |
| 9 | 34.3, CH2 | α 2.30, m β 2.15, m | 117.2, CH | 4.85, dddd (9.7, 5.5, 2.8, 1.4) |
| 10 | 118.8, CH | 5.06, m | 136.5, C | |
| 11 | 136.9, C | 18.0, CH3 | 1.56, s | |
| 12 | 26.1, CH3 | 1.71, s | 25.8, CH3 | 1.60, s |
| 13 | 18.1, CH3 | 1.53, s | 23.5, CH3 | 1.44, s |
| 14 | 15.8, CH3 | 2.20, s | 16.2, CH3 | 2.26, s |
| 15 | 120.3, CH2 | α 5.43, d (1.3) β 5.24, d (1.6) | 180.8, C | |
| OH-1 | 8.02, br s | |||
| OH-4 | 4.48, br s | 4.65, br s | ||
| OH-8 | 3.27, br s | |||
| Position | Compound 6 | Compound 7 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, Type | δH, mult (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH, mult (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 149.5, C | 146.7, C | ||
| 2 | 118.9, CH | 6.63, s | 116.9, CH | 6.70, s |
| 3 | 124.5, C | 125.1, C | ||
| 4 | 146.7, C | 148.1, C | ||
| 5 | 114.2, CH | 6.48, s | 110.3, CH | 6.62, s |
| 6 | 126.0, C | 132.1, C | ||
| 7 | 82.4, C | 122.0, C | ||
| 8 | 39.8, CH2 | 1.84, m | 118.7, C | 5.36, dd (3.8, 1.5) |
| 9 | 22.8, CH2 | α 2.00, m β 1.89, m | 75.6, CH | 4.51, ddt (8.3, 3.9, 1.5) |
| 10 | 123.9, CH | 5.04, t (6.6, 6.5) | 63.8, CH | 3.06, d (8.3) |
| 11 | 132.0, C | 57.7, C | ||
| 12 | 17.7, CH3 | 1.51, m | 25.1, CH3 | 1.33, s |
| 13 | 25.8, CH3 | 1.65, s | 19.4, CH3 | 1.35, s |
| 14 | 15.6, CH3 | 2.18, s | 15.9, CH3 | 2.19, s |
| 15 | 22.4, CH3 | 1.55, s | 18.3, CH3 | 2.01, t (1.5) |
| 16 | 50.5, OCH3 | 3.21, s | ||
| OH-1 | 8.28, br s | |||
| OH-4 | 8.28, br s | 3.49, br s | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, M.; Coello, L.; Urbatzka, R.; Pérez, M.; Thorsteinsdottir, M. New Aromatic Bisabolane Derivatives with Lipid-Reducing Activity from the Marine Sponge Myrmekioderma sp. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060375
Costa M, Coello L, Urbatzka R, Pérez M, Thorsteinsdottir M. New Aromatic Bisabolane Derivatives with Lipid-Reducing Activity from the Marine Sponge Myrmekioderma sp. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(6):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060375
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Margarida, Laura Coello, Ralph Urbatzka, Marta Pérez, and Margret Thorsteinsdottir. 2019. "New Aromatic Bisabolane Derivatives with Lipid-Reducing Activity from the Marine Sponge Myrmekioderma sp." Marine Drugs 17, no. 6: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060375






