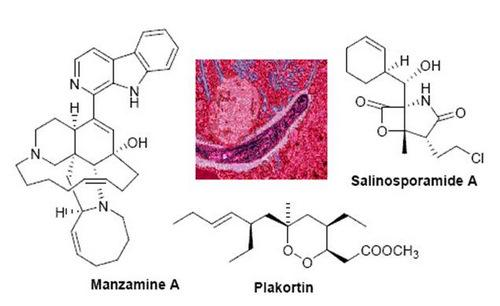
Marine Antimalarials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
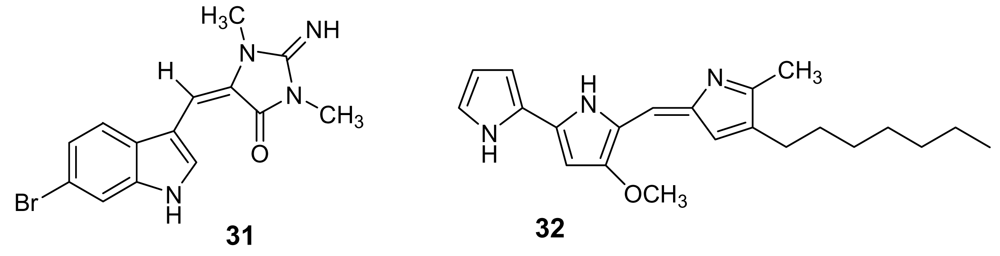
2. Isonitrile-containing derivatives and their analogues
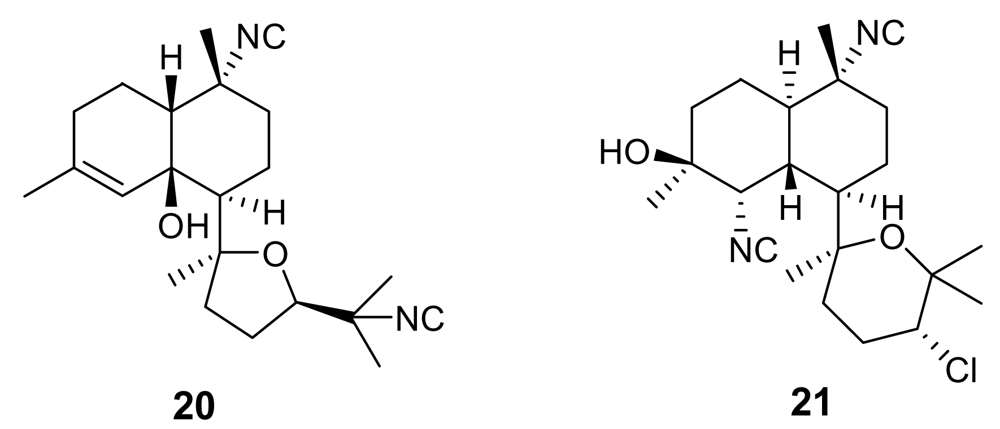
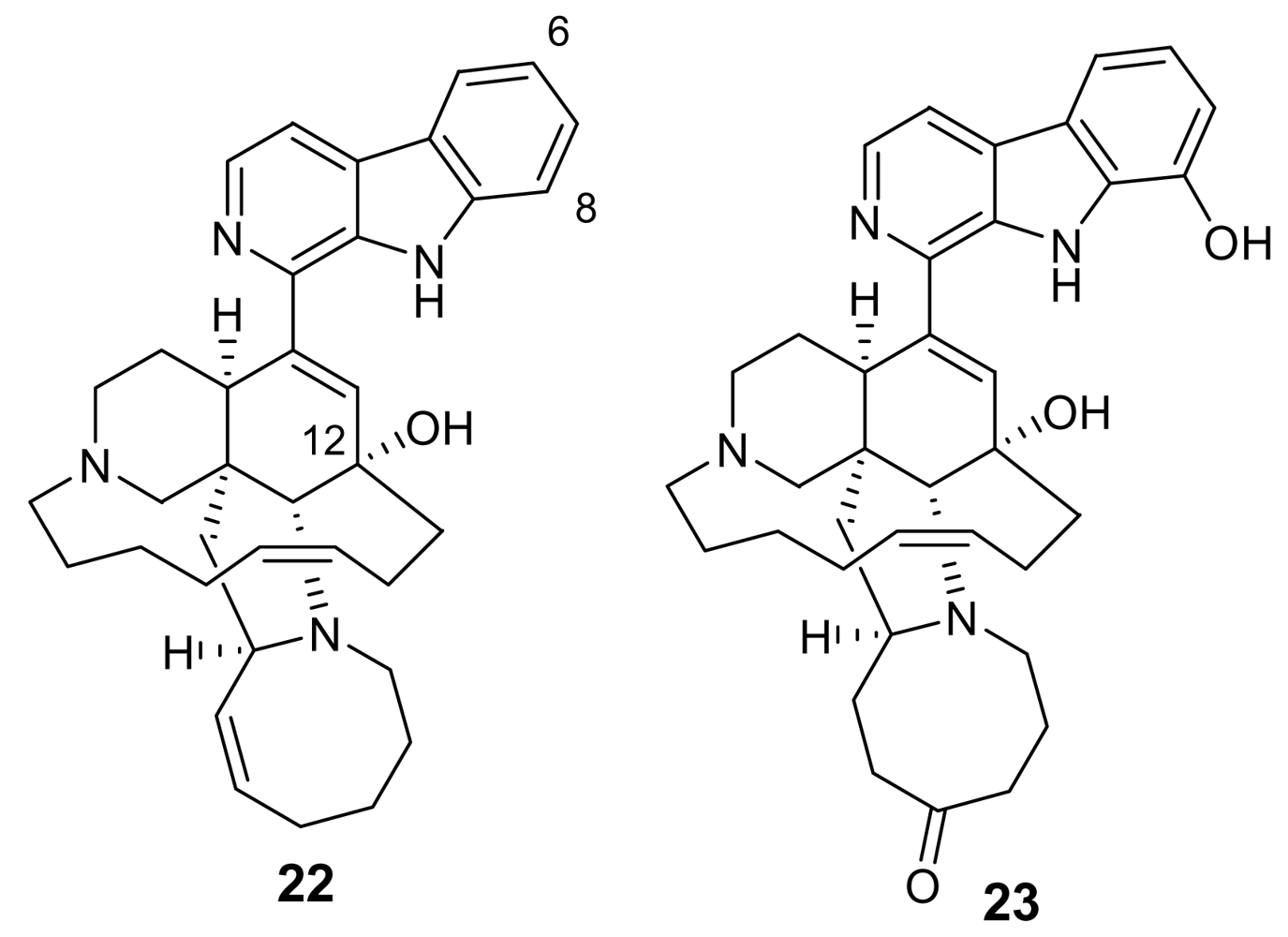
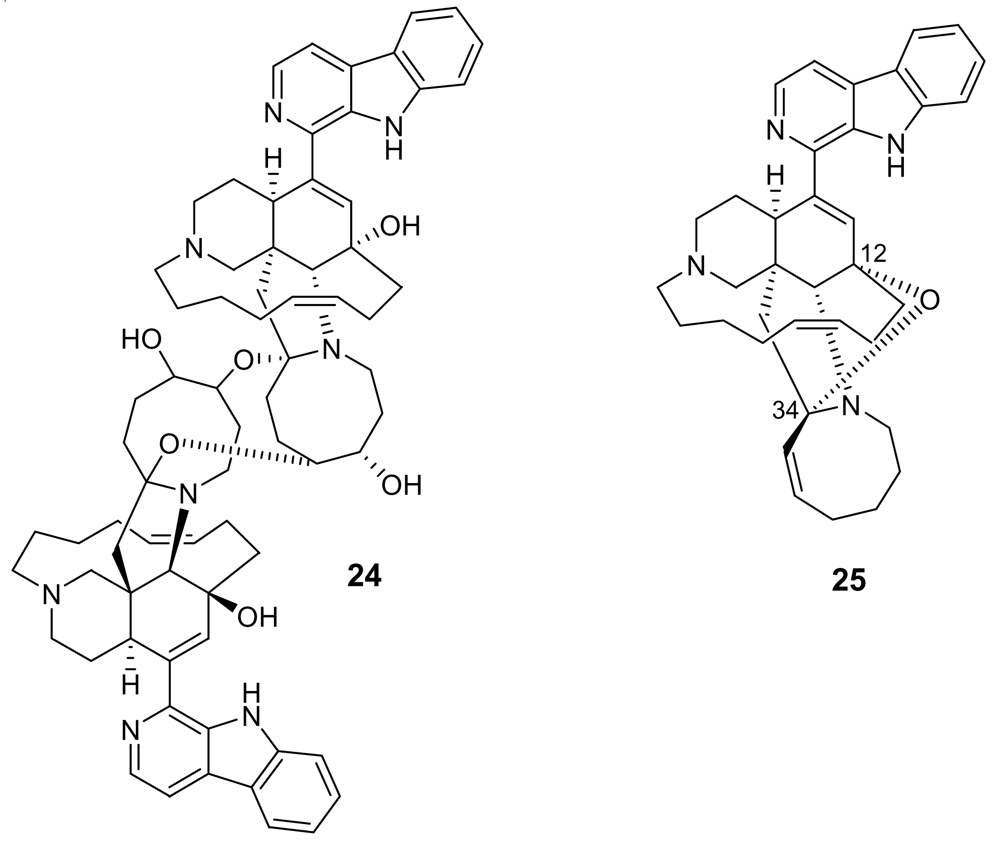
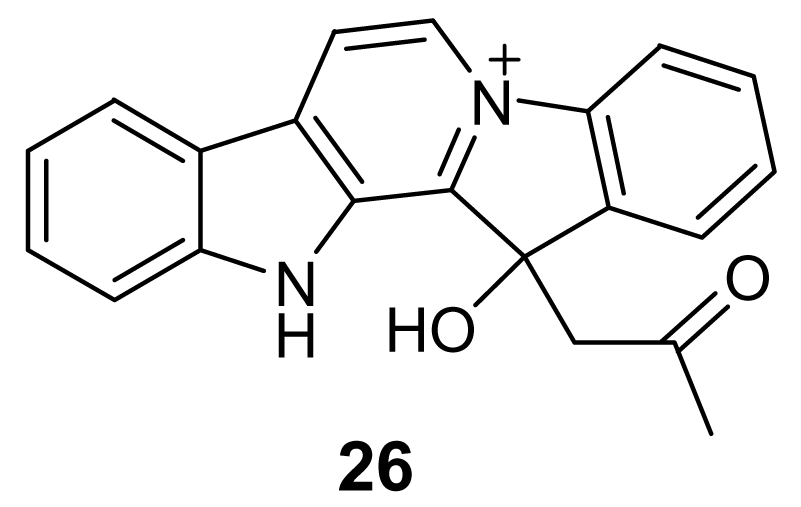
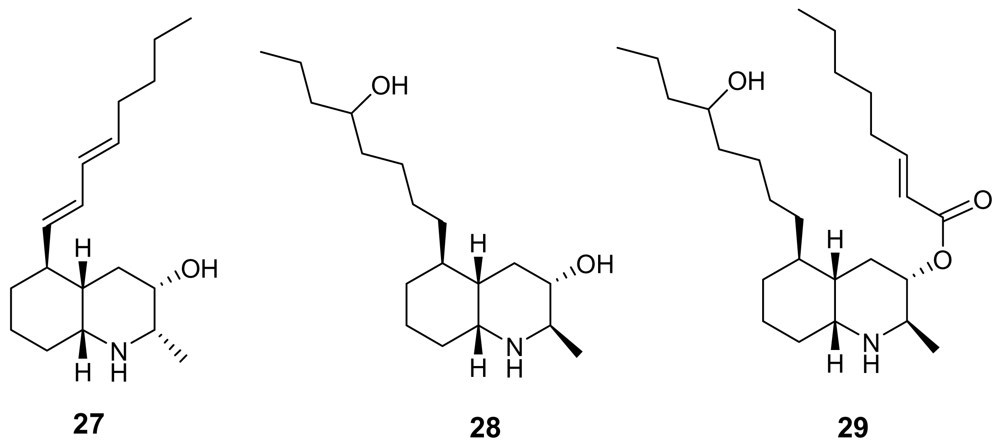
3. Alkaloids
4. Endoperoxides
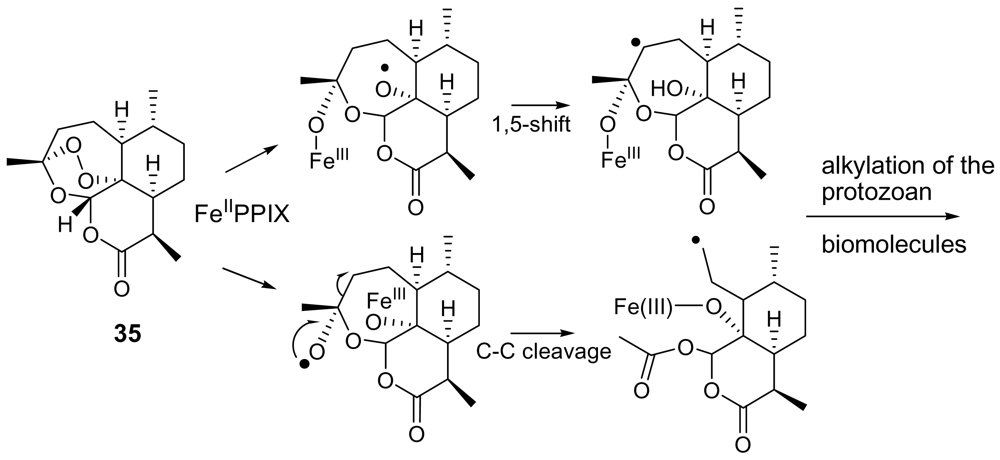
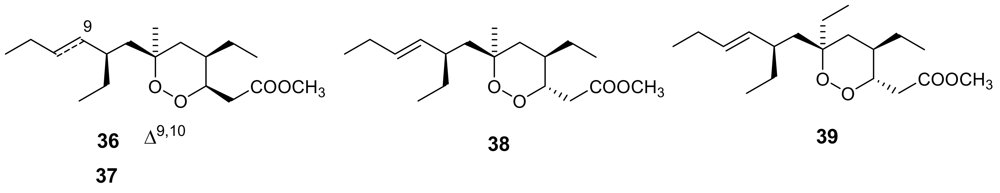
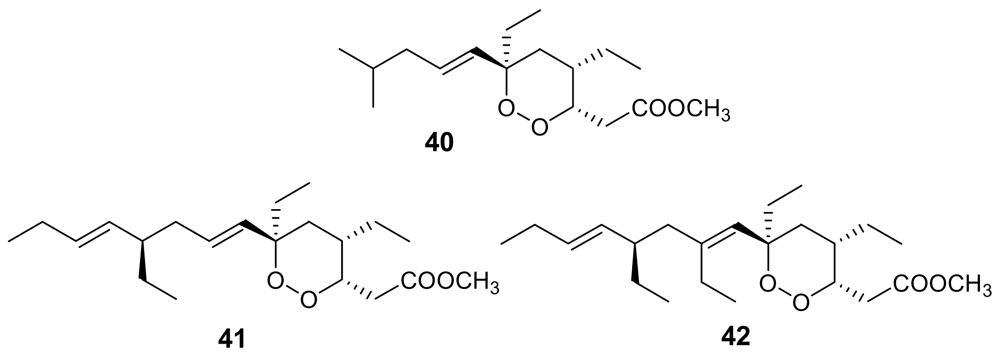
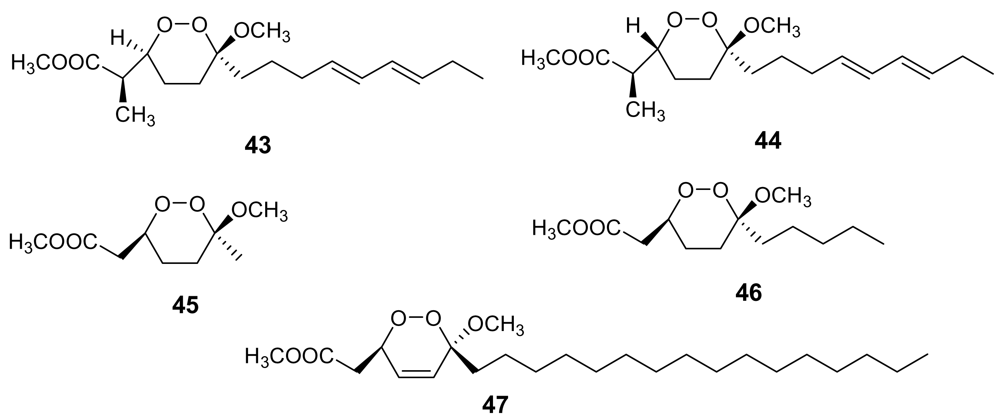
4.1. Polyketides
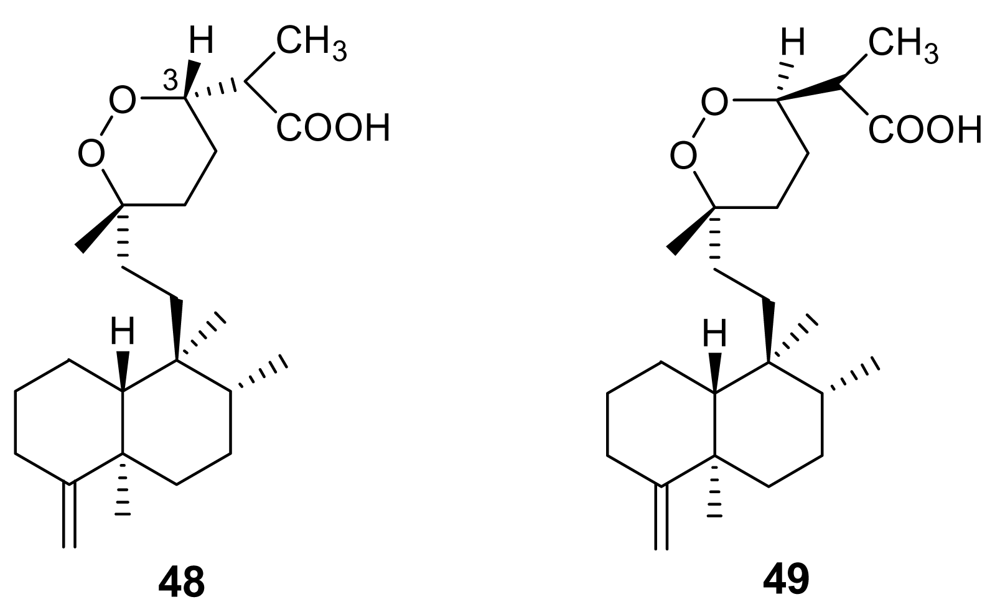
4.2. Terpenoids
5. Miscellaneous Compounds
5.1. Quinones and Phenols
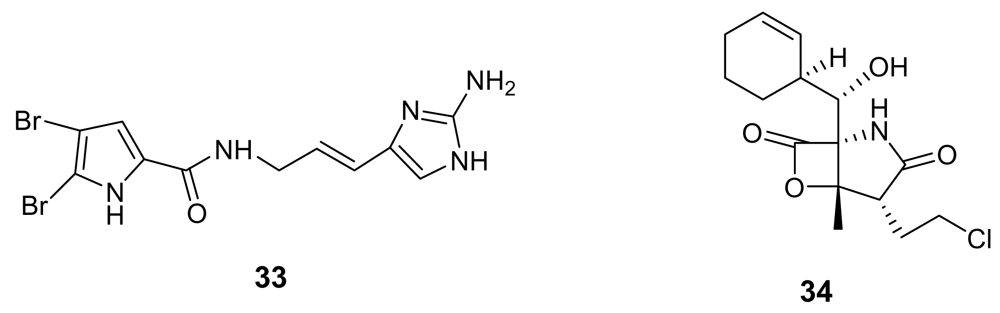
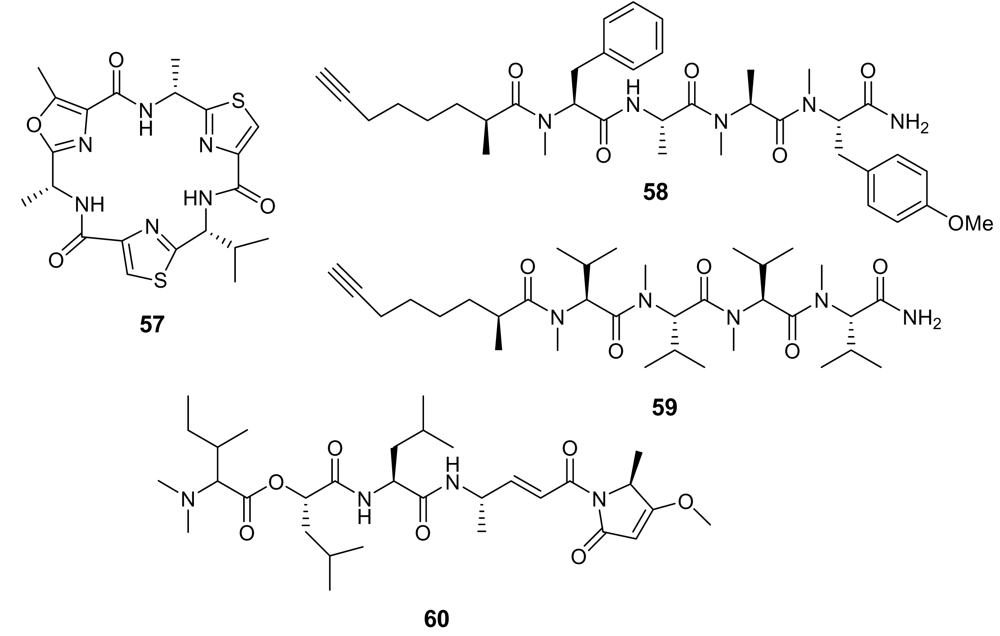
5.2. Peptides
6. Conclusions
References and Notes
- Data taken from Malaria Foundation International. http://www.malaria.org and linked sites accessed on April 6, 2009.
- Available online: http://www.who.int accessed on April 6, 2009.
- Collins, WE; Barnwell, JW. A hopeful beginning for malaria vaccines. N Engl J Med 2008, 359, 2599–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, MJ; Hall, N; Fung, E; White, O; Berriman, M; Hyman, RW; Calton, JM; Pain, A; Nelson, KE; Bowman, S. Genome sequence of the human malaria parasite. Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 2002, 419, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefford, CW. Why artemisinin and certain synthetic peroxides are potent antimalarials. Implications for the mode of action. Curr Med Chem 2001, 15, 1803–1826. [Google Scholar]
- Klayman, DL. Qinghaosu (artemisinin): an antimalarial drug from China. Science 1985, 228, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernan, VS. McClintock, JB, Baker, BJ, Eds.; Marine Chemical Ecology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 567–592. [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel, U. Natural products from marine microorganisms. Chem Bio Chem 2002, 3, 1151–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, CE; Magarvey, NA; Sherman, DH. Merging the potential of microbial genetics with biological and chemical diversity: an even brighter future for marine natural product drug discovery. Nat Prod Rep 2004, 21, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, I; Guella, G; Defant, A. Synthesis of marine natural products with antimalarial activity. Mini-Rev Med Chem 2008, 8, 1265–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattorusso, E; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Atta-ur-Rahman, Ed.; Studies in Natural Products Chemistry, vol 32, Bioactive Natural Products (Part L); Elsevier Pub: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 169–207. [Google Scholar]
- Cafieri, F; Fattorusso, E; Magno, S; Santacroce, C; Sica, D. Isolation and structure of axisonitrile 1 and axisothiocyanate 1, two unusual sesquiterpenoids from the marine sponge Axinella cannabina. Tetrahedron 1973, 29, 4259–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, E; Magno, S; Mayol, L; Santacroce, C; Sica, D. Isolation and structure of axisonitrile 2. New sesquiterpenoid isonitrile from the sponge Axinella cannabina. Tetrahedron 1974, 30, 3911–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, E; Magno, S; Mayol, L; Santacroce, C; Sica, D. New sesquiterpenoids from the sponge Axinella cannabina. Tetrahedron 1975, 31, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Blasio, B; Fattorusso, E; Magno, S; Mayol, L; Pedone, C; Santacroce, C; Sica, D. Axisonitrile-3, axisothiocyanate-3 and axamide-3. Sesquiterpenes with a novel spiro[4,5]decane skeleton from the sponge Axinella cannabina. Tetrahedron 1976, 32, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y-L; Dhanasekaran, M; Sha, C-K. Total Syntheses of Axamide-1 and Axisonitrile-1 via 6-Exo-dig Radical Cyclization. J Org Chem 2009, 74, 2033–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angerhofer, CK; Pezzuto, JM; Koenig, GM; Wright, AD; Sticher, O. Antimalarial activity of sesquiterpenes from the marine sponge Acanthella klethra. J Nat Prod 1992, 55, 1787–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, GM; Wright, AD; Angerhofer, CK. Novel Potent Antimalarial diterpene isocyanates, isothiocyanates, and isonitriles from the tropical marine sponge Cymbastela hooperi. J Org Chem 1996, 61, 3259–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, AD; Lang-Unnasch, N. Diterpene Formamides from the Tropical Marine Sponge Cymbastela hooperi and Their Antimalarial Activity in Vitro. J Nat Prod 2009, 72, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaoka, H; Shimomura, M; Kimura, H; Yamada, Y; Kim, HS; Wataya, Y. Antimalarial activity of kalihinol A and new relative diterpenoids from the Okinawan sponge, Acanthella sp. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 13467–13474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, RD; Gregg, FK; Slown, CD; Wood, JL. Total synthesis of (±)- kalihinol C. Org Lett 2004, 6, 1123–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, AD; Wang, H; Gurrath, M; Koenig, GM; Kocak, G; Neumann, G; Loria, P; Foley, M; Tilley, L. Inhibition of Heme Detoxification Processes Underlies the Antimalarial Activity of Terpene Isonitrile Compounds from Marine Sponges. J Med Chem 2001, 44, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, R; Higa, T; Jefford, CW; Bernardinelli, G. Manzamine A, a novel antitumor alkaloid from a sponge. J Am Chem Soc 1986, 108, 6404–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J; Rao, Karumanchi V; Choo, YM; Hamann, MT. Fattorusso, E, Taglialatela-Scafati, O, Eds.; Modern Alkaloids; Wiley-VCH Pub: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 189–232. [Google Scholar]
- Yousaf, M; El Sayed, KA; Rao, KV; Lim, CW; Hu, J; Kelly, M; Franzblau, SG; Zhang, F; Peraud, O; Hill, RT; Hamann, MT. 12,34-Oxamanzamines, novel biocatalytic and natural products from manzamine producing Indo-Pacific sponges. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 7397–7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypych, JC; Nguyen, TM; Nuhant, P; Benechie, M; Marazano, C. Further Insight from Model Experiments into a Possible Scenario Concerning the Origin of Manzamine Alkaloids. Angew Chem Intl Ed 2008, 47, 5418–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, KKH; Holmes, MJ; Higa, T; Hamann, MT; Kara, UAK. In vivo antimalarial activity of the .beta.-carboline alkaloid manzamine A. Antimicrob Agent Chemother 2000, 44, 1645–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, KV; Donia, MS; Peng, J; Garcia-Palomero, E; Alonso, D; Martinez, A; Medina, M; Franzblau, SG; Tekwani, BL; Khan, SI; Wayhuono, S; Willett, KL; Hamann, MT. Manzamine B and E and Ircinal A Related Alkaloids from an Indonesian Acanthostrongylophora Sponge and Their Activity against Infectious, Tropical Parasitic, and Alzheimer’s Diseases. J Nat Prod 2006, 69, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sayed, KA; Kelly, M; Kara, UAK; Ang, KKH; Katsuyama, I; Dunbar, DC; Khan, AA; Hamann, MT. New manzamine alkaloids with potent activity against infectious diseases. J Am Chem Soc 2001, 123, 1804–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousaf, M; El Sayed, KA; Rao, KV; Lim, CW; Hu, J; Kelly, M; Franzblau, SG; Zhang, F; Peraud, O; Hill, RT; Hamann, MT. 12,34-Oxamanzamines, novel biocatalytic and natural products from manzamine producing Indo-Pacific sponges. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 7397–7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilabin, AG; Kasanah, N; Tekwani, BL; Hamann, MT. Kinetic Studies and Bioactivity of Potential Manzamine Prodrugs. J Nat Prod 2008, 71, 1218–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousaf, M; Hammond, NL; Peng, J; Wayhuono, S; McIntosh, KA; Charman, WN; Mayer, AMS; Hamann, MT. New manzamine alkaloids from an Indo-Pacific sponge. Pharmacokinetics, oral availability, and the significant activity of several manzamines against HIV-I, AIDS opportunistic infections, and inflammatory diseases. J Med Chem 2004, 47, 3512–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, KV; Santarsiero, BD; Mesecar, AD; Schinazi, RF; Tekwani, BL; Hamann, MT. New manzamine alkaloids with activity against infectious and tropical parasitic diseases from an Indonesian sponge. J Nat Prod 2003, 66, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamann, MT; Alonso, D; Martin-Aparicio, E; Fuertes, A; Perez-Puerto, J; Castro, A; Morales, S; Navarro, ML; del Monte-Millan, M; Medina, M; Pennaka, H; Balaiah, A; Peng, J; Cook, J; Wahyuono, S; Martinez, A. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3) Inhibitory Activity and Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) Studies of the Manzamine Alkaloids. Potential for Alzheimer’s Disease. J Nat Prod 2007, 70, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, JD; Axten, JM. The first total syntheses of ircinol A, ircinal A, and manzamines A and D. J Am Chem Soc 1998, 120, 6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, SF; Humphrey, JM; Ali, A; Hillier, MC. Enantioselective total syntheses of ircinal A and related manzamine alkaloids. J Am Chem Soc 1999, 121, 866–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, J; Liao, Y; Ali, A; Rein, T; Wong, Y-L; Chen, H-J; Courtney, AK; Martin, SF. Enantioselective total syntheses of manzamine A and related alkaloids. J Am Chem Soc 2002, 124, 8584–8592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, G; Koeng, GM; Wright, AD; Kaminsky, R. A New Bioactive Sesterterpene and Antiplasmodial Alkaloids from the Marine Sponge Hyrtios cf erecta. J. Nat. Prod 2000, 63, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffan, B. Lepadin A, a decahydroquinoline alkaloid from the tunicate Clavelina lepadiformis. Tetrahedron 1991, 42, 8729–8732. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, AD; Goclik, E; Koenig, GM; Kaminsky, RJ; Lepadins, DF. Antiplasmodial and Antitrypanosomal Decahydroquinoline Derivatives from the Tropical Marine Tunicate Didemnum sp. J Med Chem 2002, 45, 3067–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuneki, H; You, Y; Toyooka, N; Sasaoka, T; Nemoto, H; Dani, JA; Kimura, I. Marine alkaloids (−)-pictamine and (−)-lepadin B block neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biol Pharm Bull 2005, 28, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G; Hsung, RP; Slafer, BW; Sagamanova, IK. Total Synthesis of (+)-Lepadin F. Org Lett 2008, 10, 4991–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourany-Lefoll, E; Pais, M; Sevenet, T; Guittet, E; Montagnac, A; Fontaine, C; Guenard, D; Adeline, MT; Debitus, C. Phloeodictines A and B: new antibacterial and cytotoxic bicyclic amidinium salts from the new caledonian sponge, Phloeodictyon sp. J Org Chem 1992, 57, 3832–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, I; Guella, G; Sauvain, M; Debitus, C; Duigou, A; Ausseil, F; Menou, J; Pietra, F. New 1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrimidinium alkaloids (phloeodictynes) from the New Caledonian shallow-water haplosclerid sponge Oceanapia fistulosa. Structural elucidation from mainly LC-tandem-MS-soft-ionization techniques and discovery of antiplasmodial activity. Org Biomol Chem 2004, 2, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubert, BJ; Snider, BB. Synthesis of (±)-Phloeodictine A1. Org Lett 2003, 5, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tymiak, AA; Rinehart, KL. Constituents of morphologically similar sponges. Aplysina and Smenospongia species. Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J; Schetz, JA; Kelly, M; Peng, J; Ang, KKH; Flotow, H; Leong, CY; Ng, SB; Buss, AD; Wilkins, SP; Hamann, MT. New antiinfective and human 5-HT2 receptor binding natural and semisynthetic compounds from the Jamaican sponge Smenospongia aurea. J Nat Prod 2002, 65, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazaro, JEH; Nitcheu, J; Predicala, RZ; Mangalindan, GC; Nesslany, F; Marzin, D; Concepcion, GP; Diquet, B. Heptyl prodigiosin, a bacterial metabolite, is antimalarial in vivo and non-mutagenic in vitro. J Nat Tox 2002, 11, 367–377. [Google Scholar]
- Forenza, S; Minale, L; Riccio, R; Fattorusso, E. New bromopyrrole derivatives from the sponge Agelas oroides. J Chem Soc: Chem Commun 1971, 18, 1129–30. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, A; Fattorusso, E; Menna, M; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Fattorusso, E, Taglialatela-Scafati, O, Eds.; Modern Alkaloids Structure, Isolation, Synthesis and Biology; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; pp. 271–304. [Google Scholar]
- Tasdemir, D; Topaloglu, B; Perozzo, R; Brun, R; O’Neill, R; Carballeira, NM; Zhang, X; Tonge, PJ; Linden, A; Rueedi, P. Marine natural products from the Turkish sponge Agelas oroides that inhibit the enoyl reductases from Plasmodium falciparum, Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Escherichia coli. Bioorg Med Chem 2007, 15, 6834–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feling, RH; Buchanan, GO; Mincer, TJ; Kauffman, CA; Jensen, PR; Fenical, W. Salinosporamide A: a highly cytotoxic proteasome inhibitor from a novel microbial source, a marine bacterium of the new genus Salinispora. Angew Chem Int Ed 2003, 42, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudhomme, J; McDaniel, E; Ponts, N; Bertani, S; Fenical, W; Jensen, P; Le Roch, K. Marine Actinomycetes: A New Source of Compounds against the Human Malaria Parasite. PLoS One 2008, 3, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T; Sugiyama, K; Arima, S; Harigaya, Y; Nagamitsu, T; Omura, S. Total Synthesis of Salinosporamide. A Org Lett 2008, 10, 4239–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K; Midori, M; Kawano, K; Ishihara, J; Hatakeyama, S. Entry to heterocycles based on indium-catalyzed Conia-ene reactions: asymmetric synthesis of (−)-salinosporamide A. Angew Chem, Int Ed 2008, 47, 6244–6246. [Google Scholar]
- Klayman, DL; Lin, AJ; Acton, N; Scovill, JP; Hoch, JM; Milhous, WK; Theoharides, AD; Dobek, AS. Isolation of artemisinin (qinghaosu) from Artemisia annua growing in the United States. J Nat Prod 1984, 47, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, MA; Chong, WKM; Jennings-White, C. Stereoselective total synthesis of (+)-artemisinin, the antimalarial constituent of Artemisia annua L. J Am Chem Soc 1992, 114, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein-Ludwig, U; Webb, RJ; Van Goethem, IDA; East, JM; Lee, AG; Kimura, M; O’Neill, PM; Bray, PG; Ward, SA; Krishna, S. Artemisinins target the SERCA of Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 2003, 424, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgs, MD; Faulkner, DJ. Plakortin, an antibiotic from Plakortis halichondrioides. J Org Chem 1978, 43, 3454–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafieri, F; Fattorusso, E; Taglialatela-Scafati, O; Ianaro, A. Metabolites from the sponge Plakortis simplex. Determination of absolute stereochemistry of plakortin. Isolation and stereostructure of three plakortin related compounds. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 7045–7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnuolo, C; Fattorusso, E; Romano, A; Taglialatela-Scafati, O; Basilico, N; Parapini, S; Taramelli, D. Antimalarial polyketide cycloperoxides from the marine sponge Plakortis simplex. Eur J Org Chem 2005, 5077–5083. [Google Scholar]
- Fattorusso, E; Parapini, S; Campagnuolo, C; Basilico, N; Taglialatela-Scafati, O; Taramelli, D. Activity against Plasmodium falciparum of cycloperoxide compounds obtained from the sponge Plakortis simplex. J Antimicrob Chemother 2002, 50, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattorusso, C; Campiani, G; Catalanotti, B; Persico, M; Basilico, N; Parapini, S; Taramelli, D; Campagnuolo, C; Fattorusso, E; Romano, A; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Endoperoxide Derivatives from Marine Organisms: 1,2-Dioxanes of the Plakortin Family as Novel Antimalarial Agents. J Med Chem 2006, 49, 7088–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroche, M; Imperatore, C; Grozdanov, L; Costantino, V; Mangoni, A; Hentschel, U; Fattorusso, E. Cellular localization of secondary metabolites isolated from the Caribbean sponge Plakortis simplex. Marine Biol 2006, 151, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J; Gao, H; Kelly, M; Hamann, MT; Plakortides, K-N. four new cyclic peroxides from an undescribed Jamaican sponge Plakortis sp. (Homosclerophorida, Plakinidae). Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 9379–9383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, MDS; Garzon, SP; Rodriguez, AD. Plakortides M and N, bioactive polyketide endoperoxides from the Caribbean marine sponge Plakortis halichondrioides. J Nat Prod 2003, 66, 655–661, In this paper plakortides O and P were named plakortides M and N, respectively, but their names were later corrected. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M; Kondo, K; Kitagawa, I. Antifungal peroxyketal acids from an Okinawan marine sponge of Plakortis sp. Chem Pharm Bull 1993, 41, 1324–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, N; Kawanishi, M; Itagaki, S; Horii, T; Kobayashi, M. New readily accessible peroxides with high antimalarial potency. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2002, 12, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, N; Kawanishi, M; Mostaqul, HM; Li, J; Itagaki, S; Horii, T; Kobayashi, M. New anti-malarial peroxides with In vivo potency derived from spongean metabolites. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2003, 13, 4081–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinoa, E; Kho, E; Manes, LV; Crews, P. Heterocycles from the marine sponge Xestospongia sp. J Org Chem 1986, 51, 4260–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, KA; Dunbar, DC; Goins, DK; Cordova, CR; Perry, TL; Wesson, KJ; Sanders, SC; Janus, SA; Hamann, MT. The marine environment: A resource for prototype antimalarial agents. J Nat Toxins 1996, 5, 261–285. [Google Scholar]
- El Sayed, KA; Hamann, MT; Hashish, NE; Shier, WT; Kelly, M; Khan, AA. Antimalarial, antiviral, and antitoxoplasmosis norsesterterpene peroxide acids from the Red Sea sponge Diacarnus erythraeanus. J Nat Prod 2001, 64, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ambrosio, M; Guerriero, A; Debitus, C; Waikedre, J; Pietra, F. Relative contributions to antitumoral activity of lipophilic vs. polar reactive moieties in marine terpenoids. Tetrahedron Lett 1997, 38, 6285–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosio, M; Guerriero, A; Deharo, E; Debitus, C; Munoz, V; Pietra, F. New types of potentially antimalarial agents. Epidioxy-substituted norditerpene and norsesterterpenes from the marine sponge Diacarnus levii. Helv Chim Acta 1998, 81, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H; Kobayashi, J; Kobayashi, M; Ohizumi, Y; Hirata, Y. Physiologically active marine natural products from Porifera. VII. Xestoquinone. A novel cardiotonic marine natural product isolated from the Okinawan sea sponge Xestospongia sapra. Chem Lett 1985, 6, 713–16. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, D; Jullian, V; Parenty, A; Knibiehler, M; Dorin, D; Schmitt, S; Lozach, O; Lebouvier, N; Frostin, M; Alby, F; Maurel, S; Doerig, C; Meijer, L; Sauvain, M. Antimalarial potential of xestoquinone, a protein kinase inhibitor isolated from a Vanuatu marine sponge Xestospongia sp. Bioorg Med Chem 2006, 14, 4477–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goclik, E; Konig, GM; Wright, AD; Kaminsky, R. Pelorol from the tropical marine sponge Dactylospongia elegans. J Nat Prod 2000, 63, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desoubzdanne, D; Marcourt, L; Raux, R; Chevalley, S; Dorin, D; Doerig, C; Valentin, A; Ausseil, F; Debitus, C. Alisiaquinones and Alisiaquinol, Dual Inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum Enzyme Targets from a New Caledonian Deep Water Sponge. J Nat Prod 2008. [Google Scholar]
- El Sayed, KA; Yousaf, M; Hamann, MT; Avery, MA; Kelly, M; Wipf, P. Microbial and Chemical Transformation Studies of the Bioactive Marine Sesquiterpenes (S)-(+)-Curcuphenol and -Curcudiol Isolated from a Deep Reef Collection of the Jamaican Sponge Didiscus oxeata. J Nat Prod 2002, 65, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasu, SS; Yeung, BKS; Hamann, MT; Scheuer, PJ; Kelly-Borges, M; Goins, K. Puupehenone-related metabolites from two Hawaiian sponges, Hyrtios spp. J Org Chem 1995, 60, 7290–7292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linington, RG; Gonzalez, J; Urena, L-D; Romero, LI; Ortega-Barria, E; Gerwick, WH. Venturamides A and B: Antimalarial Constituents of the Panamanian Marine Cyanobacterium Oscillatoria sp. J Nat Prod 2007, 70, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhail, KL; Correa, J; Linington, RG; Gonzalez, J; Ortega-Barria, E; Capson, TL; Gerwick, WH. Antimalarial Linear Lipopeptides from a Panamanian Strain of the Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J Nat Prod 2007, 70, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linington, RG; Clark, BR; Trimble, EE; Almanza, A; Urena, L-D; Kyle, DE; Gerwick, WH. Antimalarial peptides from marine cyanobacteria: Isolation and structural elucidation of gallinamide A. J Nat Prod 2009, 72, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, M; Meujo, DAF; Kevin, D; Hamann, MT; Anderson, M; Hill, RT. A new antimalarial polyether from a marine Streptomyces sp. H668. Tetrahedron Lett 2008, 49, 6282–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otoguro, K; Ishiyama, A; Ui, H; Kobayashi, M; Manabe, C; Yan, G; Takahashi, Y; Tanaka, H; Yamada, H; Omura, S. In vitro and in vivo antimalarial activities of the monoglycoside polyether antibiotic, K-41 against drug resistant strains of Plasmodia. J Antibiot 2002, 55, 832–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
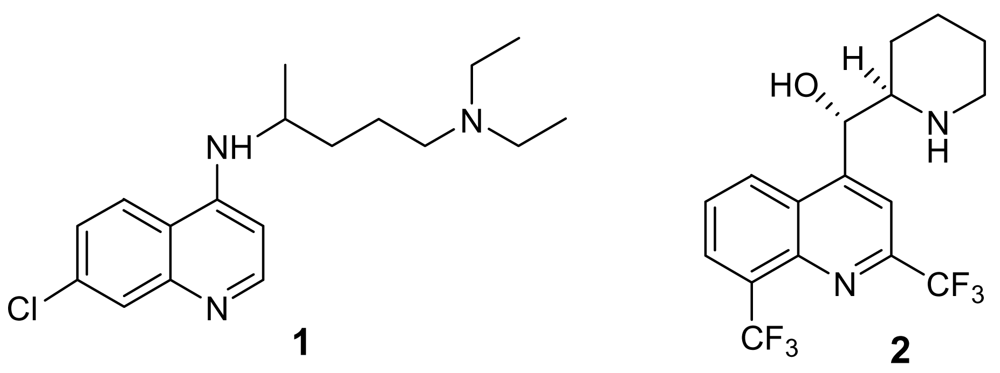
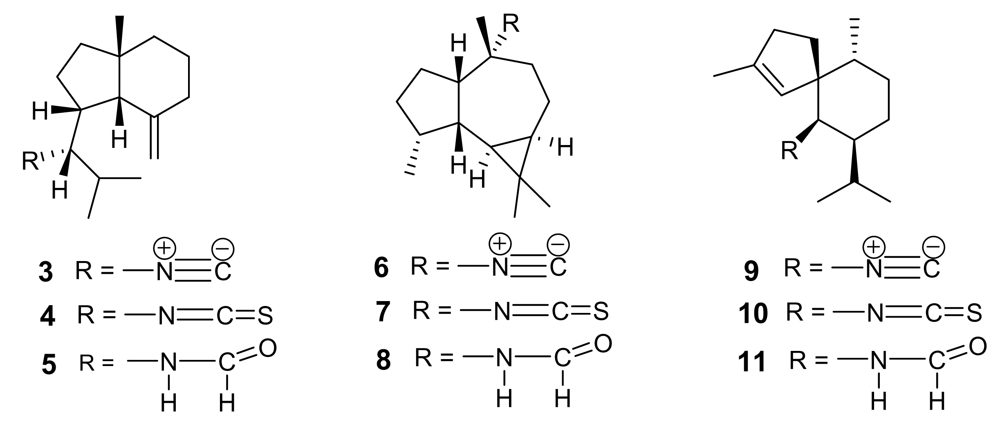
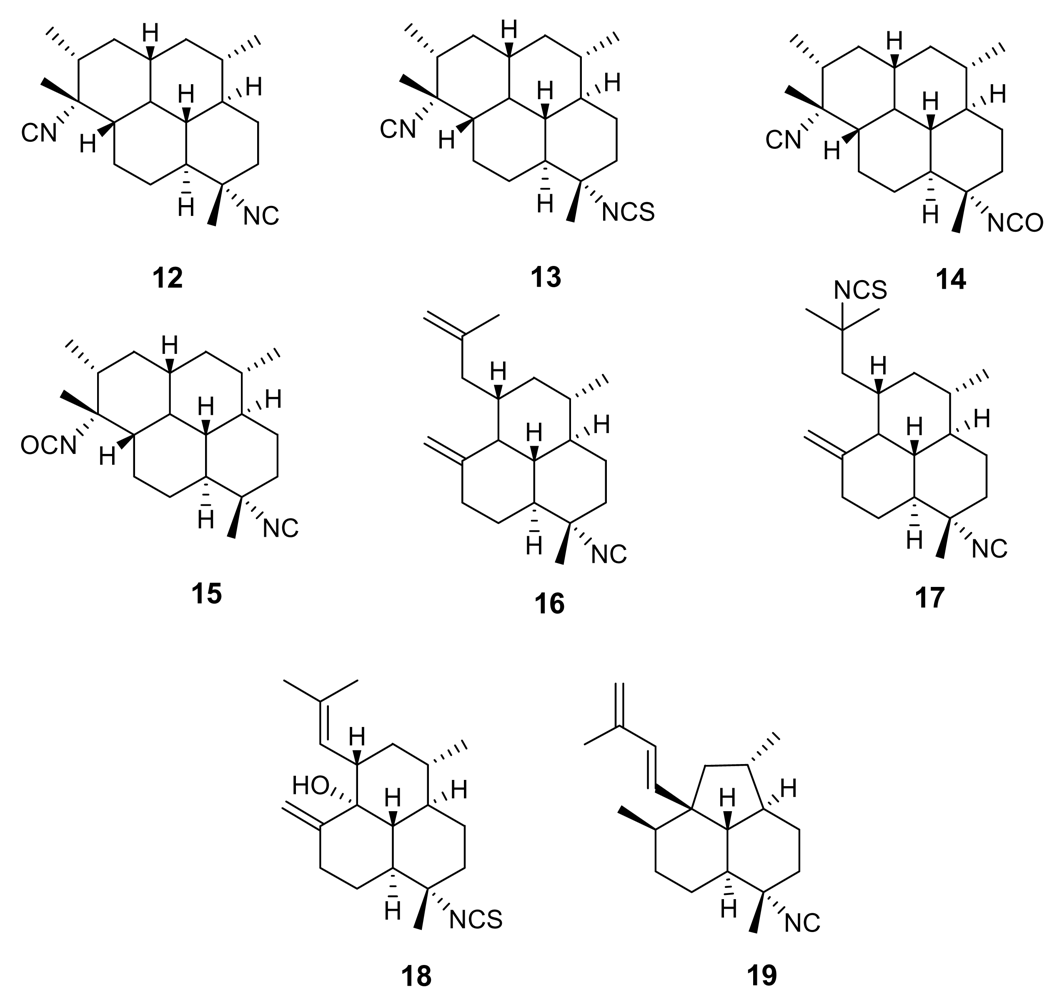


© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Marine Antimalarials. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 130-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7020130
Fattorusso E, Taglialatela-Scafati O. Marine Antimalarials. Marine Drugs. 2009; 7(2):130-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7020130
Chicago/Turabian StyleFattorusso, Ernesto, and Orazio Taglialatela-Scafati. 2009. "Marine Antimalarials" Marine Drugs 7, no. 2: 130-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7020130
APA StyleFattorusso, E., & Taglialatela-Scafati, O. (2009). Marine Antimalarials. Marine Drugs, 7(2), 130-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7020130