Glyphosate, Hard Water and Nephrotoxic Metals: Are They the Culprits Behind the Epidemic of Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology in Sri Lanka?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology (CKDu) in Sri Lanka
- (1)
- No past history of, or current treatment for diabetes mellitus or chronic and/or severe hypertension, snake bites, urological disease of known etiology or glomerulonephritis.
- (2)
- Normal glycosylated hemoglobin levels (HbA1C ˂ 6.5%).
- (3)
- Blood pressure ˂160/100 mmHg untreated or ˂140/90 mmHg on up to two antihypertensive agents.
1.2. CKDu and Ground Water Hardness

- (a)
- The number of villagers who complain that the ground water hardness in CKDu endemic area has increased steadily over the last two decades.
- (b)
- Certain shallow wells (2–5 m), which were previously been used for drinking purposes are now abandoned due to high hardness and bad taste.
- (c)
- There are a few natural springs located in the CKDu endemic area where water is not hard. People who consume water from these sources have been determined to be free from the disease.
- (d)
- Individuals who drink treated water from large water supply schemes (especially in the two cities of Anuradhapura and Polonnaruwa), while living in the same endemic areas, do not have the disease.
- (e)
- In the adjoining farming areas of the Northern Province of Sri Lanka, where the ground water hardness level is known to also be hard or very hard, there have not been any significant number of CKDu cases reported.
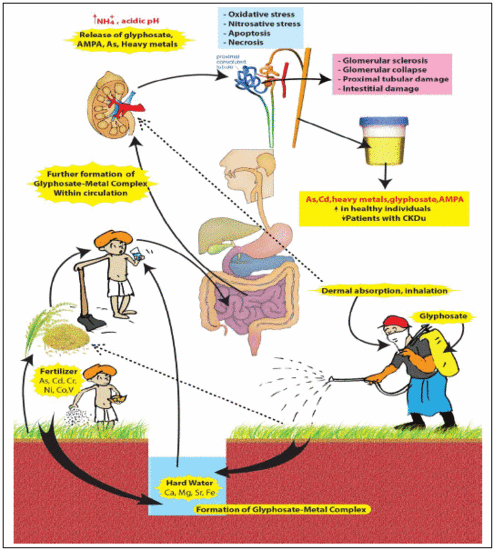
2. Compound X
- (a)
- A compound made of recently (2–3 decades) introduced chemicals to the CKDu endemic area.
- (b)
- Ability to form stable complexes with hard water.
- (c)
- Ability to capture and retain arsenic and nephrotoxic metals and act as a “carrier” in delivering these toxins to the kidney.
- (d)
- Possible multiple routes of exposure: ingestion, dermal and respiratory absorption.
- (e)
- Not having a significant first pass effect when complexed with hard water.
- (f)
- Presenting difficulties in identification when using conventional analytical methods.
| Rank | Pesticide | kg or L Approved for Import |
|---|---|---|
| 01 | Glyphosate (acid equivalent) | 5,295,082 |
| 02 | Propanil | 995,310 |
| 03 | MCPA | 686,375 |
| 04 | Mancozeb | 671,504 |
| 05 | Chlorpyrifos | 420,008 |
| 06 | Carbofuran | 299,000 |
| 07 | Diazinon | 196,735 |
| 08 | Profenofos | 140,768 |
| 09 | Carbosulfan | 107,000 |
| 10 | Pretilachlor + Pyribenzoxim | 102,297 |
2.1. Glyphosate


2.2. Glyphosate-metal Complex (GMC)

- (a)
- [Glyphosate/AMPA + Ca/Mg/Fe/Sr ] complex in drinking water.
- (b)
- [Glyphosate/AMPA + Cd/Cr/Ni/Co/Pb/Vanadium (V) or As] complex in food.
- (c)
- [Glyphosate/AMPA coming from dermal/ respiratory route] + low amount of [metals/As] from water and foods, here the complex is formed within circulation.

2.3. The Nephrotoxicity of Glyphosate-metal/As (GMA) Lattice
2.4. Compound X-elusiveness of Detection by Standard Tests
2.5. Lack of a Significant First Pass Effect
3. CKDu Elsewhere

4. Glyphosate as “Compound-X”—Available Evidence and Areas for Further Research
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jayasumana, M.A.; Paranagama, P.A.; Dahanayake, K.S.; Wijewardena, K.C.; Amarasinghe, M.D.; Fonseka, S.I. Possible link of chronic arsenic toxicity to chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in Sri Lanka. JNSR 2013, 3, 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Jayatilake, N.; Mendis, S.; Maheepala, P.; Mehta, F.R.; CKDu National Research Project Team. Chronic kidney disease of uncertain aetiology: Prevalence and causative factors in a developing country. BMC Nephrology 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government Medical Officer’s Association of Sri Lanka Press Release. Available online: http://www.lakbima.lk/oldpapers/daliylakbima/2013/November/last_13_11_13/main.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2013).
- Athuraliya, N.T.; Abeysekera, T.D.; Amerasinghe, P.H.; Kumarasiri, R.; Bandara, P.; Karunaratne, U.; Milton, A.H.; Jones, A.L. Uncertain etiologies of proteinuric-chronic kidney disease in rural Sri Lanka. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health. Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology; Circular no 01-10/2009; Ministry of Health: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nanayakkara, S.; Komiya, T.; Ratnatunga, N.; Senevirathna, S.T.; Harada, K.H.; Hitomi, T.; Gobe, G.; Muso, E.; Abeysekera, T.; Koizumi, A. Tubulointerstitial damage as the major pathological lesion in endemic chronic kidney disease among farmers in North Central Province of Sri Lanka. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2012, 17, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasumana, M.A. Sri Lankan Agricultural Nephropathy. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Chronic Kidney Disease of Nontraditional Causes, San Salvador, El Salvador, 25–27 November 2012.
- Nanayakkara, S.; Senevirathna, S.T.; Karunaratne, U.; Chandrajith, R.; Harada, K.H.; Hitomi, T.; Watanabe, T.; Abeysekera, T.; Aturaliya, T.N.; Koizumi, A. Evidence of tubular damage in the very early stage of chronic kidney disease of uncertain etiology in the North Central Province of Sri Lanka: A cross-sectional study. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2012, 17, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrajith, R.; Nanayakkara, S.; Itai, K.; Aturaliya, T.N.; Dissanayake, C.B.; Abeysekera, T.; Harada, K.; Watanabe, T.; Koizumi, A. Chronic kidney diseases of uncertain etiology (CKDue) in Sri Lanka: Geographic distribution and environmental implications. Environ. Geochem. Health 2011, 33, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanigasuriya, K.P.; Peiris-John, R.J.; Wickremasinghe, R.; Hittarage, A. Chronic renal failure in North Central Province of Sri Lanka: An environmentally induced disease. Trans. Roy. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 101, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanigasuriya, K.P.; Peiris-John, R.J.; Wickremasinghe, R. Chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology in Sri Lanka: Is cadmium a likely cause? BMC Nephrology 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris-John, R.J.; Wanigasuriya, J.K.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; Dissanayake, W.P.; Hittarage, A. Exposure to acetylcholinesterase-inhibiting pesticides and chronic renal failure. Ceylon Med. J. 2006, 51, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Hardness in Drinking Water, Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Water Hardness Classification of the United States Geological Survey. Available online: https://water.usgs.gov/owq/hardness-alkalinity.html (accessed on 10 December 2013).
- Jayasumana, M.A.; Paranagama, P.A.; Amarasinghe, M.D.; Fonseka, S.I. Sri Lankan Agricultural Nephropathy and High Ground Water Hardness-possible Link. In Proceedings of the 1st International Research Workshop on the Mesoamerican Epidemic of Nephropathy, San Jose, Costa Rica, 28–30 November 2012; pp. 195–197.
- Jayasumana, M.A.; Paranagama, P.A.; Amarasinghe, M.D.; Fonseka, S.I. Is Hard Water an Etiological Factor for Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Origin? In Proceedings of the 1st International Research Workshop on the Mesoamerican Epidemic of Nephropathy, San Jose, Costa Rica, 28–30 November 2012; pp. 91–99.
- Baylis, A.D. Why glyphosate is a global herbicide: Strengths, weakness and prospects. Pest Manag. Sci. 2000, 56, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesticide Importation Data; Office of the Registrar of Pesticides: Gannoruwa, Sri Lanka, 2012.
- Aminomethylenephosphinic Acids, Salts Thereof, and Process for Their Production. Available online: http://www.google.com/patents/US3160632 (accessed on 10 December 2013).
- Aminophosphonate Herbicides. Available online: http://www.google.com/patents/US3455675 (accessed on 10 December 2013).
- Szekacs, A.; Darvas, B. Forty Years with Glyphosate. In Herbicides—Properties, Synthesis and Control of Weeds; Hasaneen, M.N., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 247–284. [Google Scholar]
- N-phosphonomethyl-glycine phytotoxicant compositions. Available online: http://www.google.com/patents/US3799758 (accessed on 10 December 2013).
- Franz, J.E.; Mao, M.K.; Sikorski, J.A. Glyphosate: A Unique Global Herbicide; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 521–527. [Google Scholar]
- Zwitterion Compounds. Available online: http://goldbook.iupac.org/Z06752.html (accessed on 10 December 2013).
- Bronstad, J.O.; Friestad, H.O. Behaviour of Glyphosate in the Aquatic Environment. In The Herbicide Glyphosate; Grossbard, E., Atkinson, D., Eds.; Butterworths: London, UK, 1985; p. 200. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, J.; Barry, G.; Kishore, G. The herbicide glyphosate. BioFactors 1989, 2, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Rueppel, M.L.; Brightwell, B.B.; Schaefer, J.; Marvel, J.T. Metabolism and degradation of glyphosphate in soil and water. J. Agr. Food Chem. 1977, 25, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attorney General of the State of New York. The Matter of Monsanto Company, Respondent. Assurance of Discontinuance Pursuant to Executive Law Chapter 63(15); Attorney General of the State of New York, Consumer Frauds and Protection Bureau, Environmental Protection Bureau: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Carlisle, S.M.; Trevors, J.T. Glyphosate in the environment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1988, 39, 409–420. [Google Scholar]
- Gimsing, A.L.; dos Santos, A.M. Glyphosate. In The Biogeochemistry of Chelating Agents; Nowack, B., van Briesen, J.M., Eds.; ACS Symposium Series: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 910, pp. 263–277. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlin, C.D.S. The Pesticide Manual: A World Compendium, 14th ed.; British Crop Protection Council: Hampshire, UK, 2006; pp. 545–548. [Google Scholar]
- Herbicide Handbook, 8th ed.; Vencill, W.K. (Ed.) Weed Science Society of America: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2002; pp. 231–234.
- Dick, R.E.; Quinn, J.P. Glyphosate-degrading isolates from environmental samples: Occurrence and pathways of degradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1995, 43, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, H.E.; Christensen, H.H.; Gottlieb-Petersen, C. Stability constants of copper(II), zinc, manganese(II), calcium, and magnesium complexes of N-(phosphonomethyl) glycine (glyphosate). Acta. Chem. Scand. 1978, 32, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Sumbramaniam, V.; Hoggard, P.E. Metal complexes of glyphosate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1988, 38, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberbach, P. Applying non-steady-state compartmental analysis to investigate the simultaneous degradation of soluble and sorbed glyphosate (N-(phosphonomethyl) glycine) in four soils. Pestic. Sci. 1998, 52, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, N.S.; Hilton, H.W. The adsorption and degradation of glyphosate in five Hawaiian sugarcane soils. Weed Res. 1977, 17, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereecken, H. Mobility and leaching of glyphosate: A review. Pest Manag. Sci. 2005, 61, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O.; Powles, S.B. Glyphosate: A once-in-a-century herbicide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, V.C.; de Geronimo, E.; Marino, D.; Primost, J.; Carriquiriborde, P.; Costa, J.L. Environmental fate of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in surface waters and soil of agricultural basins. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songa, E.A.; Waryo, T.; Jahed, N.; Baker, P.G.; Kgarebe, B.V.; Iwuoha, E.I. Electrochemical Nanobiosensor for Glyphosate Herbicide and Its Metabolite. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, C.L.; Meggitt, W.F.; Penner, D. Effect of diluents volume and calcium on glyphosate phytotoxicity. Weed Sci. 1978, 26, 476–479. [Google Scholar]
- Stahlman, P.W.; Philips, W.M. Inhibition of glyphosate phytotoxicity. Weed Sci. 1979, 27, 575–577. [Google Scholar]
- Nalewaja, J. Salt antagonism of glyphosate. Weed Sci. 1991, 39, 622–628. [Google Scholar]
- Heineke, D.; Franklin, S.J.; Raymond, K.N. Coordination chemistry of glyphosate: Structural and spectroscopic characterization of bis(glyphosate) metal(III) complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 2413–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelen, K.D.; Jackson, E.P.; Penner, D. The basis for the hardwater antagonism of glyphosate activity. Weed Sci. 1995, 42, 541–548. [Google Scholar]
- Nalewaja, J.D.; Devilliers, B.; Matysiak, R. Surfactant and salt affect glyphosate retention and absorption. Weed Res. 1996, 36, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalewaja, J. Spray carrier salts affect herbicide toxicity to Kochia (Kochia scoparia). Weed Technol. 1993, 7, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Gauvrit, C.; Gaudry, J.C. Adjuvant influence on glyphosate efficacy in the presence of Ca2+. Mededelingen 2001, 66, 705–712. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.H.; Raymond, K.N. Solid-state and solution chemistry of calcium N-(phosphonomethyl)glycinate. Inorg. Chem. 1988, 27, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, C.F.B.; Mazo, L.H. Complexos metálicos com o herbicida glifosato: Revisão. Quimica. Nova 2005, 28, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, M.; Ramalho, T.; Botrel, D.; da Cunha, E.; de Mello, W. Understanding the inactivation process of organophosphorus herbicides: A dft study of glyphosate metallic complexes with Zn2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cu2+, Co3+, Fe3+, Cr3+, and Al3+. Int. J. Quantum. Chem. 2012, 112, 2752–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, C.B.; Tobschall, H.J. The abundances of rarer trace elements in paddy (rice) soils of Sri Lanka. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrajith, R.; Seneviratna, S.; Wickramaarachchi, K.; Attanayake, T.; Aturaliya, T.; Dissanayake, C.B. Natural radionuclides and trace elements in rice field soils in relation to fertilizer application: Study of a chronic kidney disease area in Sri Lanka. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 60, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampazzo, N.; Todorovic, G.; Mentler, A.; Blum, W. Adsorption of glyphosate and amino methylphosphonic acid in soils. Int. Agrophys. 2013, 27, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, A.; Jayalath, K.; Fonseka, S.I.; Jayasumana, M.A.; Amarasinghe, M.D.; Senanayake, V.K.; Kannangara, A.; Paranagama, P.A. Determination of Arsenic Content in Synthetic and Organic Manure Based Fertilizers Available in Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Chemical Sciences, Colombo, Sri Lanka, 20–22 June 2012; pp. 129–134.
- Acquavella, J.F.; Alexander, B.H.; Mandel, J.S.; Gustin, C.; Baker, B.; Chapman, P.; Bleeke, M. Glyphosate biomonitoring for farmers and their families: results from the Farm Family Exposure Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 321–326. [Google Scholar]
- Bradberry, S.M.; Proudfoot, A.T.; Vale, J.A. Glyphosate poisoning. Toxic. Rev. 2004, 23, 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, H.B.F. The biochemical action of arsonic acids especially as phosphate analogues. Advan. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 44, 191–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, D.S.; Viola, R.E. Arsenate replacing phosphate: Alternative life chemistries and ion promiscuity. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfter Enterprises, Inc. DBA Advanced Biological Concepts. Available online: http://www.abcplus.biz/Images/Catalogs/GRP%20for%20Dogs%20Booklet%20PD1312–2.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2013).
- Sabath, E.; Robles-Osorio, M.L. Renal health and the environment: Heavy metal nephrotoxicity. Nefrologia. 2012, 32, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Nalewaja, J. Optimizing adjuvants to overcome glyphosate antagonistic salts. Weed Technol. 1993, 7, 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Jiraungkoorskul, W.; Upatham, E.S.; Kruatrachue, M.; Sahaphong, S.; Vichasri-Grams, S.; Pokethitiyook, P. Biochemical and histopathological effects of glyphosate herbicide on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Environ. Toxicol. 2003, 18, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoola, S.O. Histopathological effect of glyphosate on Juvenile African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Am. Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2008, 4, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Séralini, G.; Cellier, D.; de Vendomois, J. New analysis of a rat feeding study with a genetically modified maize reveals signs of hepatorenal toxicity. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 52, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizhe, E.V.; Ibrahim, N.D.; Fatihu, M.Y; Igbokwe, I.O.; George, B.D.; Ambali, S.F.; Shallangwa, J.M. Serum biochemical assessment of hepatic and renal functions of rats during oral exposure to glyphosate with zinc. Comp. Clin. Path 2013, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, K.; Najle, R.; Lifschitz, A.; Virkel, G. Effects of sub-lethal exposure of rats to the herbicide glyphosate in drinking water: Glutathione transferase enzyme activities, levels of reduced glutathione and lipid peroxidation in liver, kidneys and small intestine. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 34, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, M.; Schrödl, W.; Neuhaus, J.; Shehata, A.A. Field investigations of glyphosate in urine of Danish dairy cows. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletta, G.L.; Larriera, A.; Kleinsorge, E.; Mudry, M.D. Genotoxicity of the herbicide formulation Roundup (glyphosate) in broad-snouted caiman (Caiman latirostris) evidenced by the Comet assay and the Micronucleus test. Mutat. Res. 2009, 672, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganelli, A.; Gnazzo, V.; Acosta, H.; Lopez, S.L.; Carrasco, A.E. Glyphosate-based herbicides produce teratogenic effects on vertebrates by impairing retinoic acid signaling. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benachour, N.; Sipahutar, H.; Moslemi, S.; Gasnier, C.; Travert, C.; Seralini, G.E. Time- and dose-dependent effects of roundup on human embryonic and placental cells. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 53, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benachour, N.; Seralini, G.E. Glyphosate formulations induce apoptosis and necrosis in human umbilical, embryonic, and placental cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasnier, C.; Dumont, C.; Benachour, N.; Clair, E.; Chagnon, M.C.; Seralini, G.E. Glyphosate-based herbicides are toxic and endocrine disruptors in human cell lines. Toxicology 2009, 262, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.E.; Manitoba Environmental Management Services. Persistence of Glyphosate Residues in Northern Manitoba Ponds; Manitoba Environment and Workplace Safety and Health, Environmental Management Services: Manitoba, Canada, 1987; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Van Stempvoort, D.R.; Roy, J.W.; Brown, S.J.; Bickerton, G. Residues of the herbicide glyphosate in riparian groundwater in urban catchments. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis, J.; Kantiani, L.; Llorca, M.; Rubio, F.; Ginebreda, A.; Fraile, J.; Garrido, T.; Farre, M. Determination of glyphosate in groundwater samples using an ultrasensitive immunoassay and confirmation by on-line solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibanez, M.; Pozo, O.J.; Sancho, J.V.; Lopez, F.J.; Hernandez, F. Re-evaluation of glyphosate determination in water by liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A. 2006, 1134, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freuze, I.; Jadas-Hecart, A.; Royer, A.; Communal, P.Y. Influence of complexation phenomena with multivalent cations on the analysis of glyphosate and aminomethyl phosphonic acid in water. J. Chromatogr. A. 2007, 1175, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Community Council. Directive concerning the quality of water intended for human consumption. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 1988, 330, 32–54. [Google Scholar]
- Illing, A.C.; Shawki, A.; Cunningham, C.L.; Mackenzie, B. Substrate profile and metal-ion selectivity of human divalent metal-ion transporter-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 30485–30496. [Google Scholar]
- Cobbett, C.; Goldsbrough, P. Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: Roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002, 53, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabolić, I.; Škarica, B.M.D.; Herak-Kramberger, C.M. Role of metallothionein in cadmium traffic and toxicity in kidneys and other mammalian organs. Biometals 2010, 23, 897–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodish, H.; Berk, A.; Zipursky, S.L. Hierarchical Structure of Proteins. In The Molecular Cell Biology, 4th ed.; Freeman, H., Ed.; ASM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, Z.; Szutkowska, M.; Vernimmen, C.; Bichara, M. Recent concepts concerning the renal handling of NH3/NH4+. J. Nephrology 2006, 19, S27–S32. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.Y. Renal handling of ammonium and acid base regulation. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2009, 7, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eladari, D.; Chambrey, R. Ammonium transport in the kidney. J. Nephrology 2010, 23, S28–S34. [Google Scholar]
- Gauvrit, C. Glyphosate response to calcium, ethoxylated amine surfactant, and ammonium sulfate. Weed Technol. 2003, 17, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabolic, I. Common mechanisms in nephropathy induced by toxic metals. Nephron Physiol. 2006, 104, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, E.F.; Fowler, B.A. Mechanisms of nephrotoxicity from metal combinations: A review. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2000, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therond, P. Oxidative stress and damages to biomolecules (lipids, proteins, DNA). Ann. Pharm. Fr. 2006, 64, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnberg, D.; Lewis, M.; Moss, J.; Xu, Y.; Botto, M.; Cook, H.T. Complement activation contributes to both glomerular and tubulointerstitial damage in adriamycin nephropathy in mice. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4094–4102. [Google Scholar]
- Javaid, B.; Olson, J.L.; Meyer, T.W. Glomerular injury and tubular loss in adriamycin nephrosis. J. Amer. Soc. Nephrol. 2001, 12, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, D.V.; Gunasekar, A. Chronic kidney disease in two coastal districts of Andhra Pradesh, India: Role of drinking water. Environ. Geochem. Health 2013, 35, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Third Progress Report of the Investigation and Evaluation of CKDu in Sri Lanka. Available online: http://dh-web.org/place.names/posts/WHO-on-CKDU.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2013).
- Wesseling, C.; Crowe, J.; Hogstedt, C.; Jakobsson, K.; Lucas, R.; Wegman, D.H. The epidemic of chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in Mesoamerica: A call for interdisciplinary research and action. Amer. J. Public Health 2013, 103, 1927–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orantes, C.M.; Herrera, R.; Almaguer, M.; Brizuela, E.G.; Hernandez, C.E.; Bayarre, H.; Amaya, J.C.; Calero, D.J.; Orellana, P.; Colindres, R.M.; Velazquez, M.E.; Nunez, S.G.; Contreras, V.M.; Castro, B.E. Chronic kidney disease and associated risk factors in the Bajo Lempa region of El Salvador: Nefrolempa study, 2009. MEDICC Rev. 2011, 13, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Rubio, O.; Brooks, D.R.; Amador, J.J.; Kaufman, J.S.; Weiner, D.E.; Scammell, M.K. Chronic kidney disease in Nicaragua: A qualitative analysis of semi-structured interviews with physicians and pharmacists. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 350–359. [Google Scholar]
- Pan American Health Organization. Kidney Disease of Unknown Causes in Agricultural Communities in Central America is Declared a Serious Public Health Problem. Available online: http://www.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=9062%3Akidney-disease-of-unknown-causes-in-agricultural-communitie (accessed on 12 December 2013).
- Orantes, C.M. Clinical Characterization and Histopathology of Nephropathy in Salvadorian Agricultural Communities. In Proceedings of The International Conference on Saptial Ecotoxicology, San Salvador, El Salvador, 28–29 October 2013.
- Ribo, A.; Mejia, R.; Quinteros, E.; Lopez, A.; Orantes, C.; Jovel, R.; Valladares, E.; Lopez, D. Arsenic Pollution in the Bajo Lempa Region. In Proceedings of The International Conference on Saptial Ecotoxicology, San Salvador, El Salvador, 28–29 October 2013.
- Food and Agricultural Organization. Available online: http://www.fao.org/ag/agp/fertistat/fst_fubc_en.asp (accessed on 12 December 2013).
- Quinteros, E. DDT and Other Pesticides Pollution in the Bajo Lempa Region, El Salvador. In Proceedings of The International Conference on Saptial Ecotoxicology, San Salvador, El Salvador, 28–29 October 2013.
- Bundschuh, J.; Litter, M.I.; Parvez, F.; Roman-Ross, G.; Nicolli, H.B.; Jean, J.S.; Liu, C.W.; Lopez, D.; Armienta, M.A.; Guilherme, L.R.; Cuevas, A.G.; Cornejo, L.; Cumbal, L.; Toujaguez, R. One century of arsenic exposure in Latin America: A review of history and occurrence from 14 countries. Sci. Total Envir. 2012, 429, 2–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundschuh, J.; Nath, B.; Bhattacharya, P.; Liu, C.W.; Armienta, M.A.; Lopez, M.V.M.; Lopez, D.L.; Jean, J.S.; Cornejo, L.; Lauer Macedo, L.F.; Filho, A.T. Arsenic in the human food chain: The Latin American perspective. Sci. Total Envir. 2012, 429, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, T.R.; Chen, Y.; Bundschuh, J.; Oliver, J.T.; Navoni, J.; Olmos, V.; Lepori, E.V.; Ahsan, H.; Parvez, F. Arsenic exposure in Latin America: Biomarkers, risk assessments and related health effects. Sci. Total Envir. 2012, 429, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicaraguan Sugar, A Macro View of Today’s Economy. Available online: http://assets.coca-colacompany.com/10/58/7b94d83d4c25a4a3bb5eb919649e/NicaraguaSugarIndustry-AMacroLevelReport012309.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2013).
- Personal communication with Dr. Carlos Manuel Orantes Navarro. National coordinator of Kidney Diseases, National Institute of Health: Buenos Aires I, San Salvador, El Salvador.
- Boron, F.W.; Boulpaep, E.L. Medical Physiology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 851–862. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jayasumana, C.; Gunatilake, S.; Senanayake, P. Glyphosate, Hard Water and Nephrotoxic Metals: Are They the Culprits Behind the Epidemic of Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology in Sri Lanka? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2125-2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110202125
Jayasumana C, Gunatilake S, Senanayake P. Glyphosate, Hard Water and Nephrotoxic Metals: Are They the Culprits Behind the Epidemic of Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology in Sri Lanka? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2014; 11(2):2125-2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110202125
Chicago/Turabian StyleJayasumana, Channa, Sarath Gunatilake, and Priyantha Senanayake. 2014. "Glyphosate, Hard Water and Nephrotoxic Metals: Are They the Culprits Behind the Epidemic of Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology in Sri Lanka?" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 11, no. 2: 2125-2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110202125
APA StyleJayasumana, C., Gunatilake, S., & Senanayake, P. (2014). Glyphosate, Hard Water and Nephrotoxic Metals: Are They the Culprits Behind the Epidemic of Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology in Sri Lanka? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11(2), 2125-2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110202125