Evaluation of the Impact of Low Emission Zone and Heavy Traffic Ban in Munich (Germany) on the Reduction of PM10 in Ambient Air
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Selection of the Monitoring Stations
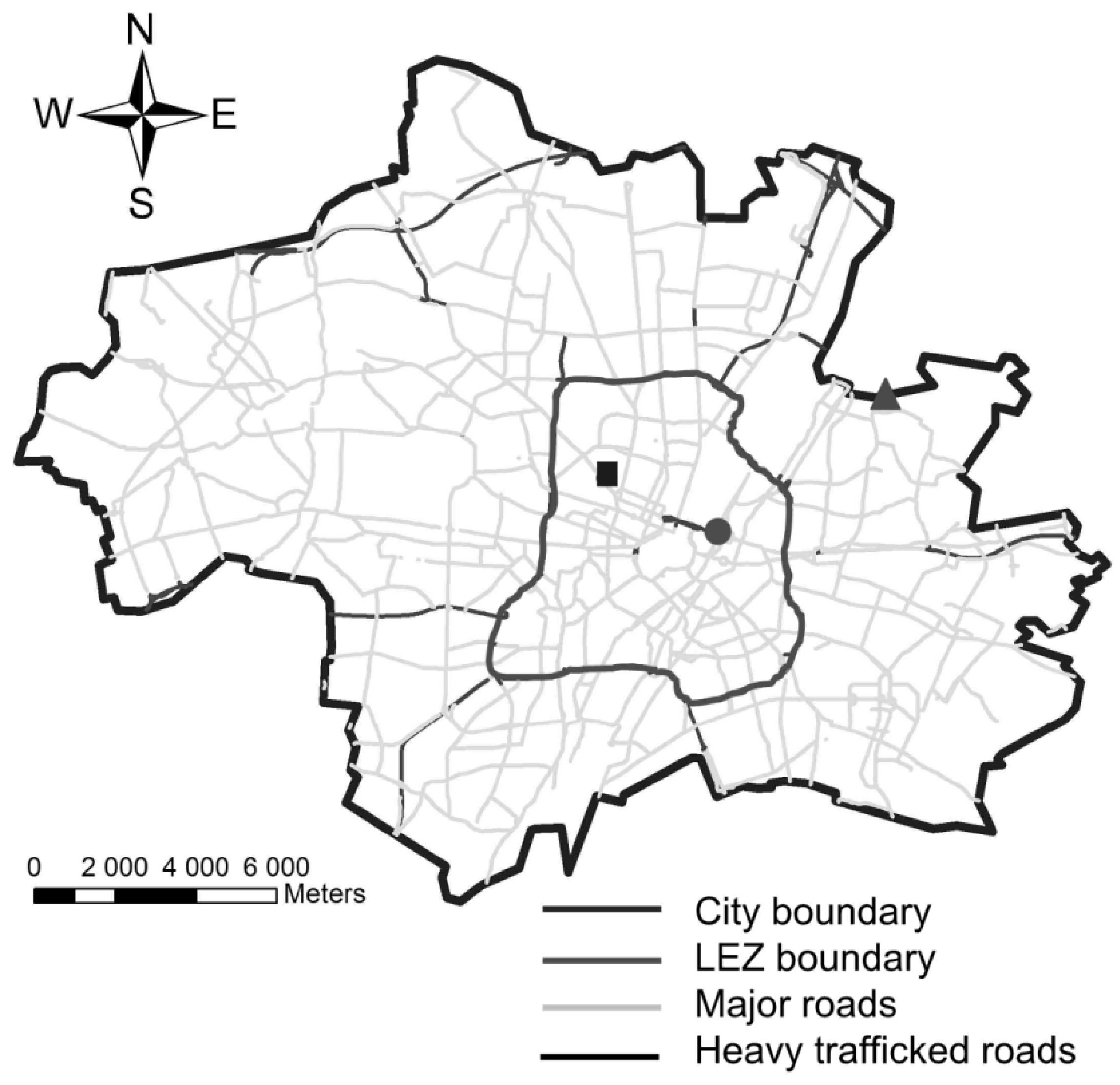
2.2. Study Period and Data
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Data Description
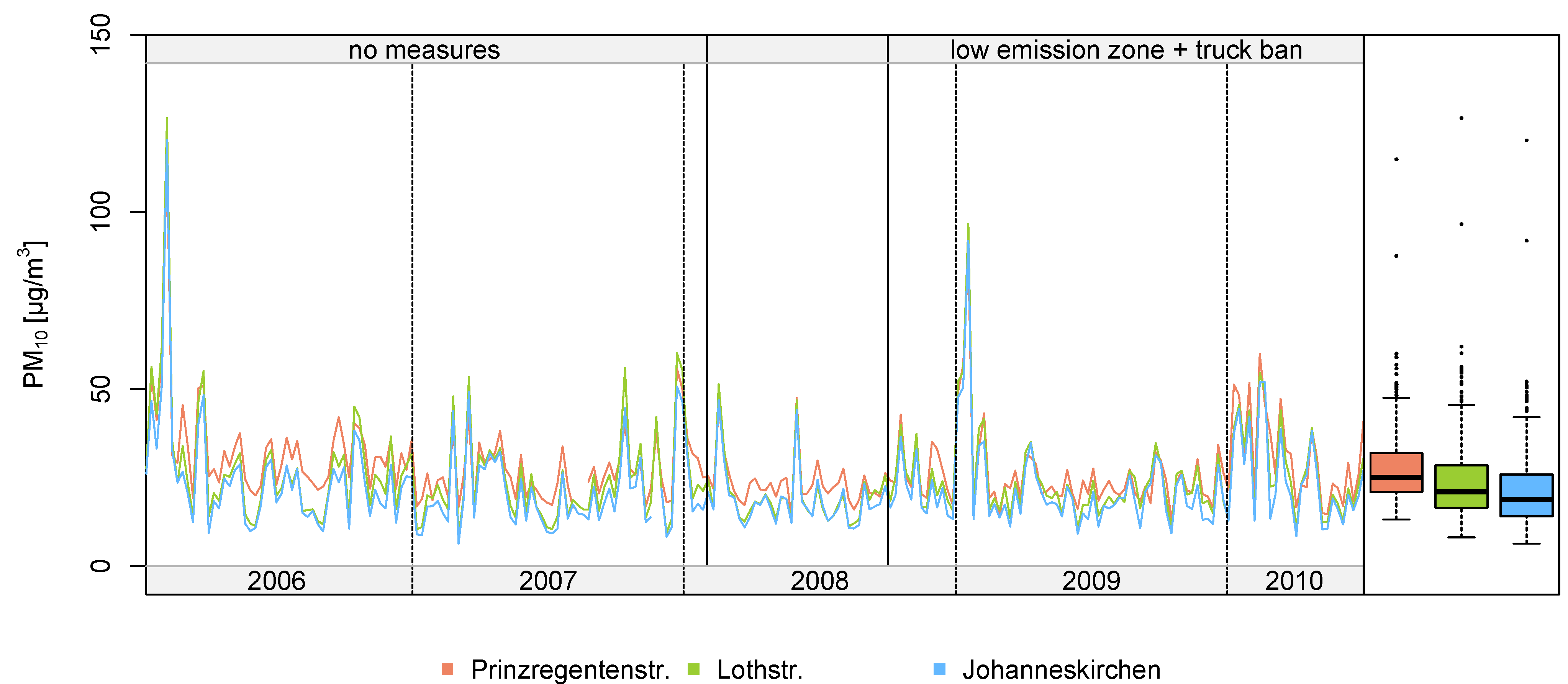
| Measurement Station | Season | Without Measures | With Measures | Percentage Difference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | PM10 mean (SD) | n | PM10 mean (SD) | |||
| Prinzregentenstr. | Summer | 8,200 | 27.2 (14.3) | 6,535 | 23.4 (14.5) | −14.0 |
| Winter | 8,562 | 30.8 (21.6) | 8,676 | 30.2 (23.6) | −1.9 | |
| Lothstr. | Summer | 8,769 | 21.3 (12.9) | 8,730 | 20.8 (15.3) | −2.3 |
| Winter | 8,520 | 28.3 (23.6) | 8,687 | 27.6 (22.0) | −2.5 | |
| Johanneskirchen | Summer | 8,765 | 19.3 (12.2) | 8,768 | 18.9 (12.3) | −2.1 |
| Winter | 8,451 | 24.3 (21.6) | 8,686 | 24.5 (20.8) | 0.8 | |
3.2. Statistical Modeling
| Measurement Station | Summer | Winter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| effect | confidence interval | p-value | effect | confidence interval | p-value | |
| Prinzregentenstr. | −19.63% | (−22.75%, −16.52%) | <0.001 | −6.80% | (−10.14 %, −3.47 %) | <0.001 |
| Lothstr. | −5.73% | (−7.71%, −3.74%) | <0.001 | −3.18% | (−5.24 %, −1.11 %) | 0.003 |
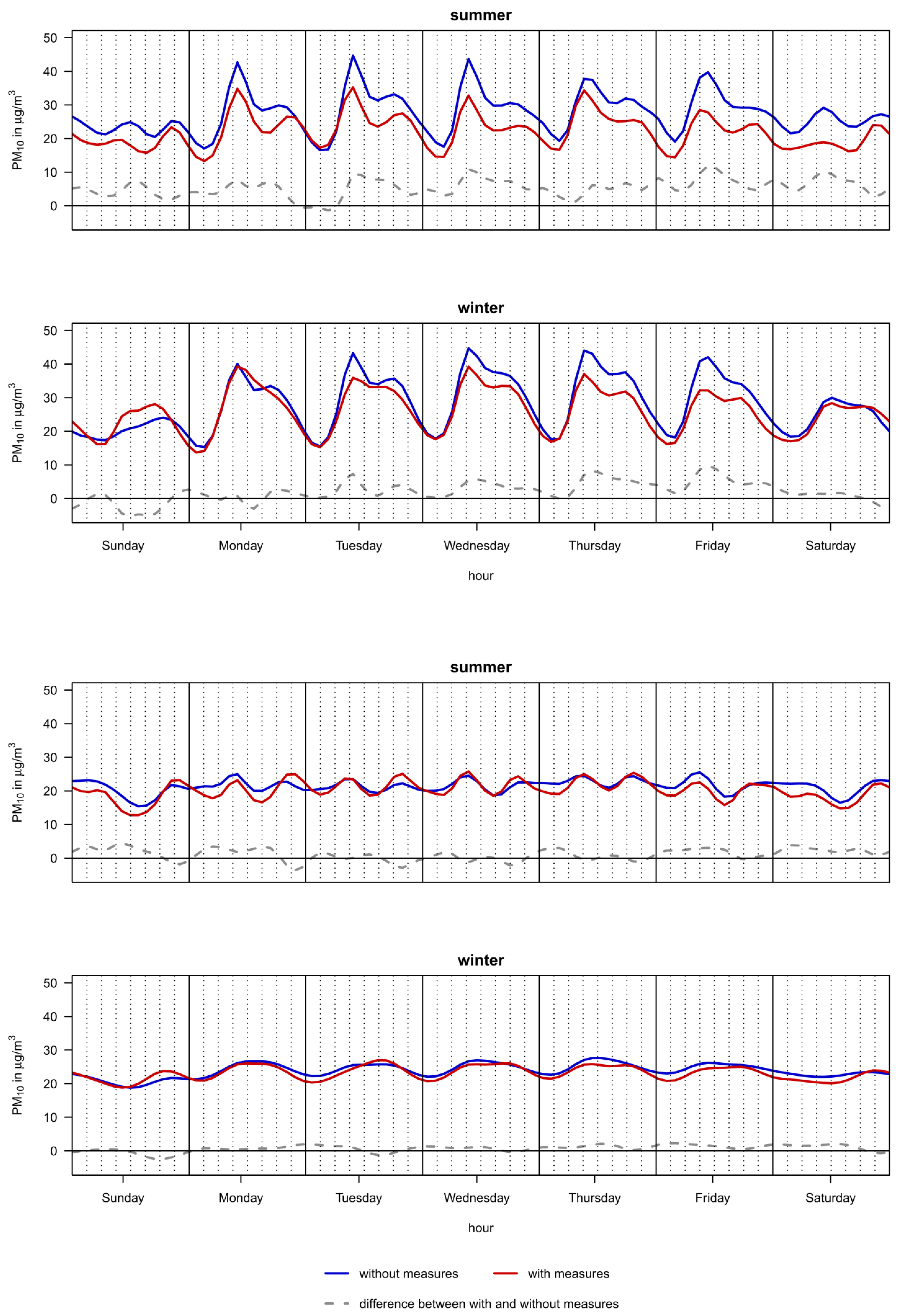

4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of the Measures on PM10 Mass Concentration
4.2. Seasonal and Diurnal Variation of the Changes in PM10 Levels
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pope, C.A., III; Dockery, D.W. Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: Lines that connect. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rückerl, R.; Schneider, A.; Breitner, S.; Cyrys, J.; Peters, A. Health effects of particulate air pollution: A review of epidemiological evidence. Inhal. Toxicol. 2011, 23, 555–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Air Quality Guidelines: Global Update 2005: Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2006.
- Adar, S.; Kaufman, J. Cardiovascular disease and air pollutants: Evaluating and improving epidemiological data implicating traffic exposure. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugge, D.; Durant, J.L.; Rioux, C. Near-highway pollutants in motor vehicle exhaust: A review of epidemiologic evidence of cardiac and pulmonary health risks. Environ. Health 2007, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.T.; Islam, T.; Gilliland, F.D. Recent evidence for adverse effects of residential proximity to traffic sources on asthma. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2008, 14, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samet, J.M. Traffic, air pollution, and health. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council Directive 99/30/EC of 22 April 1999 Relating to Limit Values for Sulphur Dioxide, Nitrogen Dioxide and Oxides of Nitrogen, Particulate Matter and Lead in Ambient Air. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:31999L0030 (accessed on 7 May 2014).
- Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2008 on Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2008:152:0001:0044:EN:PDF (accessed on 7 May 2014).
- Indicator: Exceedance. of Air Quality Limit Values in Urban Areas; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012.
- European Environment Agency. AirBase—The European Air Quality Database, Copenhagen, Denmark. Available online: http://acm.eionet.europa.eu/databases/airbase (accessed on 26 March 2013).
- Giannouli, M.; Kalognomou, E.A.; Mellios, G.; Moussiopoulos, N.; Samaras, Z.; Fiala, J. Impact of European emission control strategies on urban and local air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4753–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvile, R.; Hutchinson, E.; Mindell, J.; Warren, R. The transport sector as a source of air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 1537–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low Emission Zone in Europe Network (LEEZEN). Low Emission Zones in Europe—Europe-wide information on LEZs. Available online: http://www.lowemissionzones.eu (accessed on 31 March 2014).
- Umweltbundesamt. Umweltzonen in Deutschland—Ein Service des Umweltbundesamtes. Available online: http://gis.uba.de/website/umweltzonen/umweltzonen.php (accessed on 28 November 2013).
- Cyrys, J.; Peters, A.; Soentgen, J.; Wichmann, H.E. Low emission zones reduce PM10 mass concentrations and diesel soot in German cities. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 2014, 64, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.W.; Barratt, B.; Armstrong, B.; Anderson, H.R.; Beevers, S.D.; Mudway, I.S.; Green, D.; Derwent, R.G.; Wilkinson, P.; Tonne, C.; Kelly, F.J. The impact of the congestion charging scheme on ambient air pollution concentrations in London. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5493–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beevers, S.D.; Carslaw, D.C. The impact of congestion charging on vehicle emissions in London. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.S.; Ketzel, M.; Nøjgaard, J.K.; Becker, T. What are the Impacts on Air Quality of Low Emission Zones in Denmark? Annual Transport Conference at Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark, 2011. Available online: www.trafikdage.dk/papers_2011/31_SteenSolvangJensen.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2014).
- Jones, A.M.; Harrison, R.M.; Barratt, B.; Fuller, G. A large reduction in airborne particle number concentrations at the time of the introduction of the “sulphur free” diesel and the London Low Emission Zone. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, R.B.; Greaves, S.P.; Hensher, D.A. Five years of London’s low emission zone: Effects on vehicle fleet composition and air quality. Transp. Res. Pt. D-Transp. Enviro. 2013, 23, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boogaard, H.; Janssen, N.A.H.; Fischer, P.H.; Kos, G.P.A.; Weijers, E.P.; Cassee, F.R.; van der Zee, S.C.; de Hartog, J.J.; Meliefste, K.; Wang, M.; Brunekreef, B.; Hoek, G. Impact of low emission zones and local traffic policies on ambient air pollution concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 435, 132–140. [Google Scholar]
- Bruckmann, P.; Lutz, M. Verbessern Umweltzonen die Luftqualität? In Proceedings of the 12th Technischer Kongress des Verbandes der Automobilindustrie (VDA), Ludwigsburg, Germany, 24–25 March 2010; pp. 299–311.
- Bruckmann, P.; Wurzler, S.; Brandt, A.; Vogt, K. Erfahrungen mit umweltzonen in Nordrhein-Westfalen. UMID 2011, 4, 27–33. (in German). [Google Scholar]
- Cyrys, J.; Peters, A.; Wichmann, H.-E. Umweltzone München—Eine erste Bilanz. Umweltmed. Forsch. Prax. 2009, 14, 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Laberer, C.; Niedermaier, M. Wirksamkeit von Umweltzonen. ADAC-Untersuchung. Interessenvertretung Verkehr. Available online: http://www.adac.de/_mmm/pdf/umweltzonen_wirksamkeit_bericht_0609_43574.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2013).
- Lorenz, J. Feinstaub: Beim immissionsschutz sind alle in der pflicht—Erfahrungen mit der umweltzone in München. UMID 2011, 4, 19–26. (in German). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, M.; Rauterberg-Wulff, A. Ein Jahr Umweltzone Berlin: Wirkungsuntersuchungen. Available online: http://www.stadtentwicklung.berlin.de/umwelt/luftqualitaet/de/luftreinhalteplan/download/umweltzone_1jahr_stufe2_bericht.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2013).
- Rauterberg-Wulff, A.; Lutz, M. Wirkungsuntersuchungen zur umweltzone Berlin. UMID 2011, 4, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Morfeld, P.; Stern, R.; Builtjes, P.; Groneberg, D.A.; Spallek, M. Einrichtung einer umweltzone und ihre wirksamkeit auf die PM10-feinstaubkonzentration—Eine pilotanalyse am beispiel München (in German). Zentralbl. Arbeitsmed. Arbeitsschutz Ergon. 2013, 63, 105–115. (in German). [Google Scholar]
- Statistical Agency of the City of Munich. Statistisches Amt-ZIMAS—Datenbank. Available online: http://www.muenchen.de/rathaus/Stadtinfos/Statistik/CSV-Daten.html (accessed on 26 March 2014).
- Bayerisches Staatsministerium für Umwelt, Gesundheit und Verbraucherschutz: Luftreinhalte-/Aktionsplan für die Stadt München 1. Fortschreibung. Available online: http://www.regierung.oberbayern.bayern.de/imperia/md/content/regob/internet/dokumente/bereich5/technischerumweltschutz/lrp/erste_fortschreibung_lrp_muenchen.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2014).
- Bayerisches Landesamt für Umwelt: Anlage zur 4. Fortschreibung des Luftreinhalteplans München: Minderungswirkung von Umweltzonen auf die Luftschadstoffbelastung. Available online: http://www.regierung.oberbayern.bayern.de/imperia/md/content/regob/internet/dokumente/bereich5/technischerumweltschutz/lrp/anlage_zum_lrp___wirkungsanalyse.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2014).
- Clifford, S.; Mølgaard, B.; Choy, S.L.; Corander, J.; Hämeri, K.; Mengersen, K.; Hussein, T. Bayesian semi-parametric forecasting of ultrafine particle number concentration with penalised splines and autoregressive errors. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2012. Available online: http://arxiv.org/pdf/1207.0558.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2014).
- Barnett, A.G.; van der Pols, J.C.; Dobson, A.J. Regression to the mean: What it is and how to deal with it. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 34, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Vickers, A.J.; Altman, D.G. Statistics notes: Analysing controlled trials with baseline and follow up measurements. BMJ 2001, 323, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.H.; Le, N.D.; Sun, L.; Zidek, J.V. Spatial-Temporal models for ambient hourly PM10 in Vancouver. Environmetrics 1999, 10, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 6 March 2014).
- Wood, S.N. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction wit R; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bayerisches Landesamt für Umwelt. Minderungswirkung von Umweltzonen auf die Luftschadstoffbelastung—Umweltzone München. Anlage zur 4. Fortschreibung des Luftreinhalteplans München. Available online: http://www.regierung.oberbayern.bayern.de/imperia/md/content/regob/internet/dokumente/bereich5/technischerumweltschutz/lrp/anlage_zum_lrp___wirkungsanalyse.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2013).
- Regierung von Oberbayern. Luftreinhalteplan für die Stadt München 4. Fortschreibung. Available online: http://www.regierung.oberbayern.bayern.de/imperia/md/content/regob/internet/dokumente/bereich5/technischerumweltschutz/lrp/lrp_m_4__fortschr_stmug_endfassung___05_09_2010.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2014).
- Tonne, C.; Beevers, S.; Armstrong, B.; Kelly, F.; Wilkinson, P. Air pollution and mortality benefits of the London congestion charge: Spatial and socioeconomic inequalities. Occup. Environ. Medicine 2008, 65, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.; Burman, L.; Forsberg, B. The effects of congestions tax on air quality and health. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4843–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichmann, H.-E. Feinstaub: Lufthygienisches Problem Nr. 1—Eine aktuelle Übersicht. Umweltmed. Forsch. Prax. 2005, 10, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Quadir, R.M.; Abbaszade, G.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Chow, J.C.; Zimmermann, R. Concentrations and source contributions of particulate organic matter before and after implementation of low emission zone in Munich, Germany. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 175, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Supplementary Files
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Fensterer, V.; Küchenhoff, H.; Maier, V.; Wichmann, H.-E.; Breitner, S.; Peters, A.; Gu, J.; Cyrys, J. Evaluation of the Impact of Low Emission Zone and Heavy Traffic Ban in Munich (Germany) on the Reduction of PM10 in Ambient Air. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 5094-5112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110505094
Fensterer V, Küchenhoff H, Maier V, Wichmann H-E, Breitner S, Peters A, Gu J, Cyrys J. Evaluation of the Impact of Low Emission Zone and Heavy Traffic Ban in Munich (Germany) on the Reduction of PM10 in Ambient Air. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2014; 11(5):5094-5112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110505094
Chicago/Turabian StyleFensterer, Veronika, Helmut Küchenhoff, Verena Maier, Heinz-Erich Wichmann, Susanne Breitner, Annette Peters, Jianwei Gu, and Josef Cyrys. 2014. "Evaluation of the Impact of Low Emission Zone and Heavy Traffic Ban in Munich (Germany) on the Reduction of PM10 in Ambient Air" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 11, no. 5: 5094-5112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110505094




