Major Natural Disasters in China, 1985–2014: Occurrence and Damages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collections
2.2. Classifications and Definitions
2.3. Statistic Analysis
2.4. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Occurrence of Natural Disasters
3.2. Temporal Trend of the Natural Disasters
3.3. Spatial Patterns of the Natural Disasters
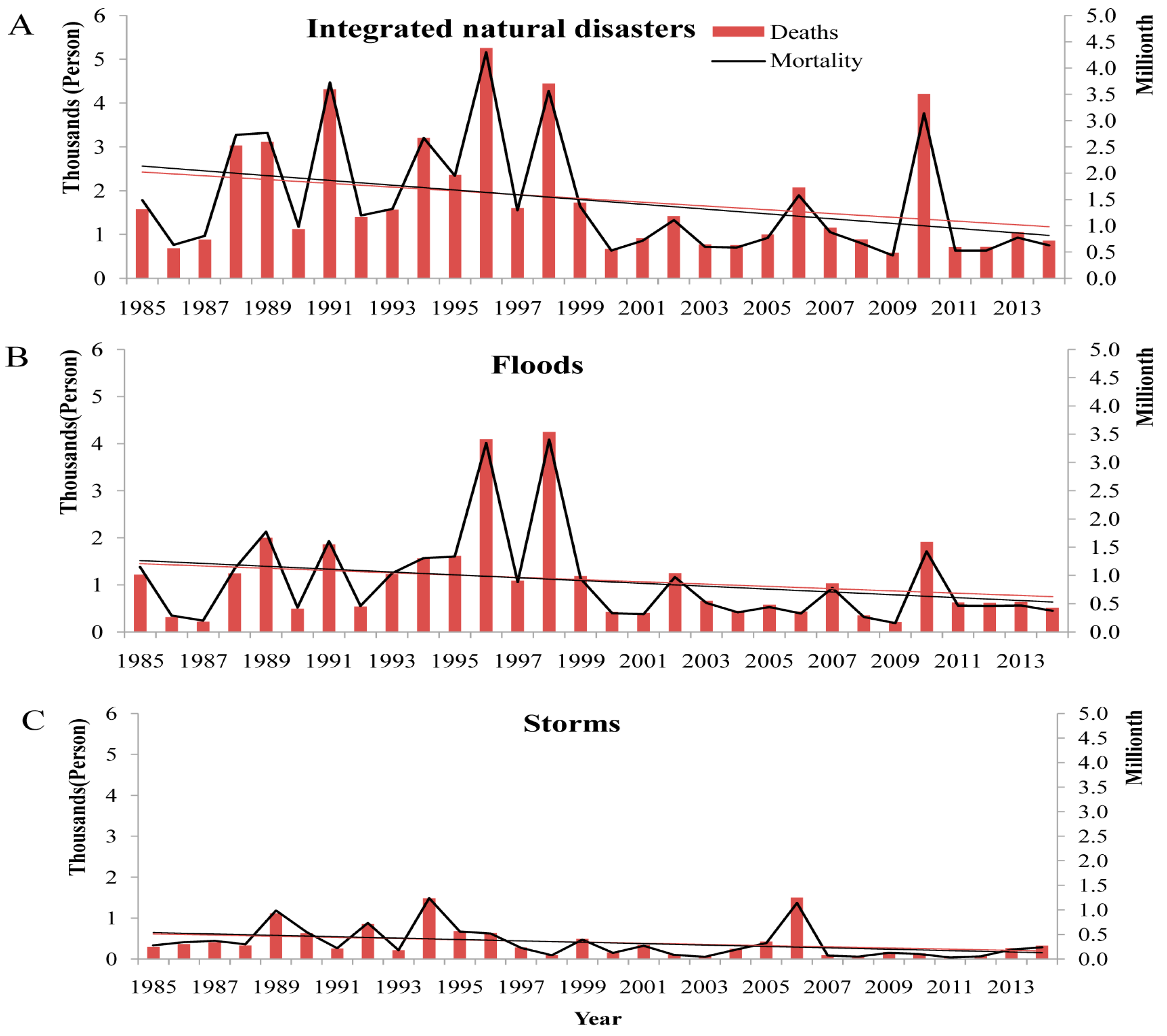
3.4. Deaths in Natural Disasters
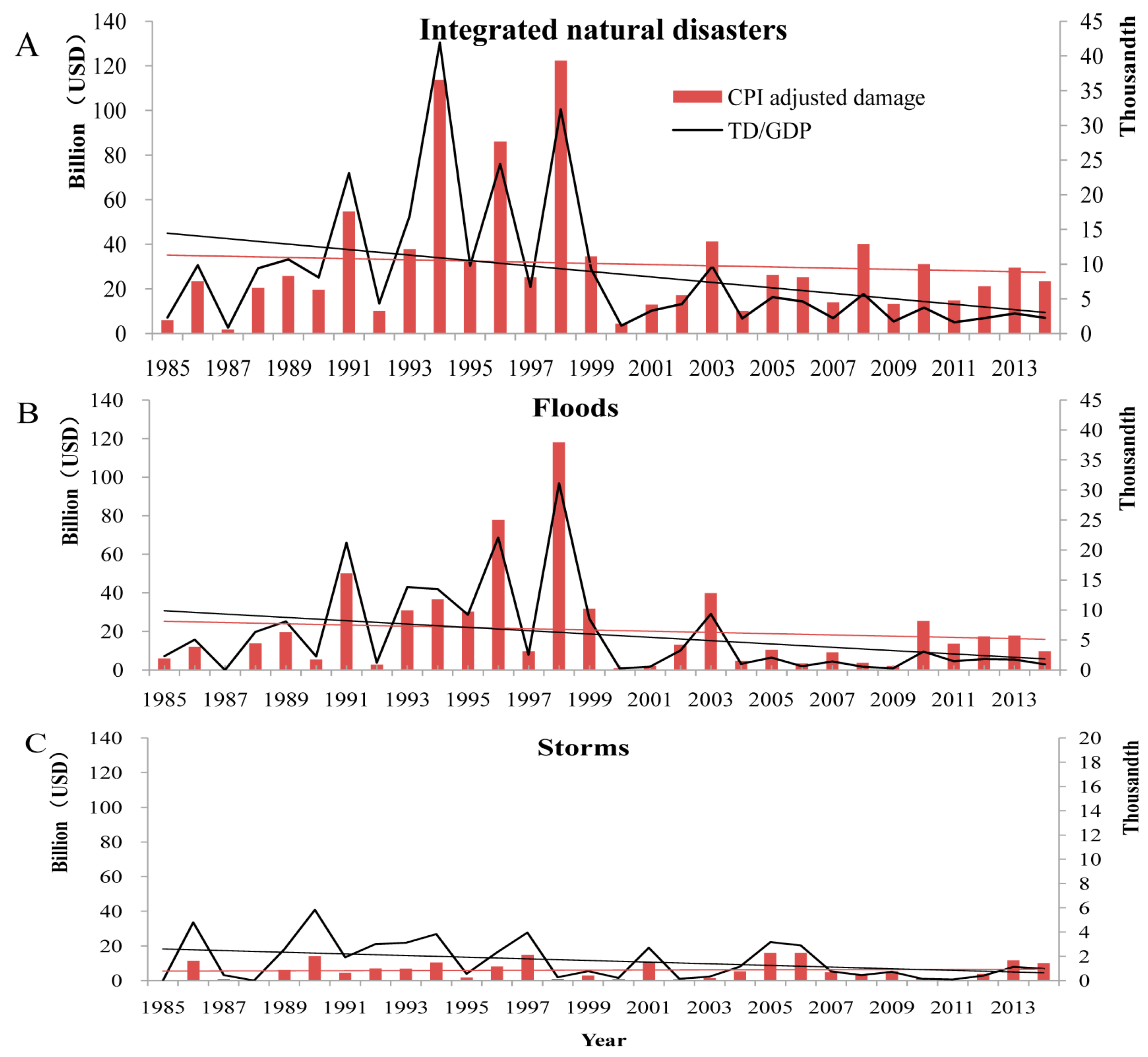
3.5. Economic Losses Caused by Natural Disasters
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ekanayake, S.; Prince, M.; Sumathipala, A.; Siribaddana, S.; Morgan, C. “We lost all we had in a second”: Coping with grief and loss after a natural disaster. World Psychiatry 2013, 12, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, Z.; Cao, G. The role of hazard vulnerability assessments in disaster preparedness and prevention in China. Mil. Med. Res. 2015, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankenberg, E.; Sikoki, B.; Sumantri, C.; Suriastini, W.; Thomas, D. Education, vulnerability, and resilience after a natural disaster. Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, R.T. Intergovernmental panel on climate change. In Proceedings of the Sixth Conference of Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, Moscow, Russian, 13–18 October 2014.
- Balica, S.F.; Douben, N.; Wright, N.G. Flood vulnerability indices at varying spatial scales. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 2571–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, C.E.; Burton, I. Adaptation options strategies for hazards and vulnerability mitigation: An international perspective. Mitig. Adapt Strat. Glob. 2005, 10, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Li, N. Integrated risk assessment of multi-hazards in China. Nat. Hazards 2015, 78, 257–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, A.; Kron, W.; Löw, P.; Steuer, M. The need for data: Natural disasters and the challenges of database management. Nat. Hazards 2014, 70, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha-Sapir, D.; Below, R.; Hoyois, P. EM-DAT: International Disaster Database—Université Catholique de Louvain, Brussels. Available online: http://www.emdat.be (accessed on 12 September 2016).
- National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. National Earth System Science Data Sharing Infrastructure. Available online: http://www.geodata.cn (accessed on 12 September 2016).
- The Word Economic Information Network. Available online: http://www.8pu.com (accessed on 12 September 2016).
- The National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn (accessed on 12 September 2016).
- Newson, R. Parameters behind “nonparametric” statistics: Kendall’s tau, Somers’ D and median differences. Stata J. 2002, 2, 45–64. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, J.K.; Getis, A. Local spatial autocorrelation statistics: Distributional issues and an application. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Clark, M.; Hou, X.Y.; Zang, Y.; FitzGerald, G. Progress and challenges of disaster health management in China: A scoping review. Glob. Health Action 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, H.; Pan, D.; Wang, J.A.; Zhang, W.C. Risk mapping of integrated natural disasters in China. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 2023–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Zhang, J.; Shan, C. China National Assessment Report on Risk Management and Adaptation of Climate Extremes and Disasters; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Wang, B.; Geng, S. Growing typhoon influence on East Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douben, K.J. Characteristics of river floods and flooding: A global overview, 1985–2003. Irrig. Drain. 2006, 55, S9–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douben, N.; Ratnayake, R.M.W. Characteristic Data on River Floods and Flooding; Facts and Figures; International Symposium on Flood Defence: Nijmegen, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Tan, X.; Zhang, N. Flood management and flood warning system in China. Irrig. Drain. 2010, 59, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Wu, R.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Ding, C.; Wang, W.; Yu, D.W. China’s transboundary waters: New paradigms for water and ecological security through applied ecology. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, W.; Wang, X. Rapid urbanization and implications for flood risk management in hinterland of the Pearl River Delta, China: The Foshan study. Sensors (Basel) 2008, 8, 2223–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H. Analysis on the weather and climate features and causes of the extraordinary flood disaster over China in 1998 and the relevant meteorological prediction services. Clim. Environ. Res. 1998, 3, 323–334. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Z.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L. A study on the flood disasters in China in 1998 and reduction measures. J. Catastrophol. 2003, 1, 56–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H. Disaster situation from January to June in 1998 in China. Nat. Disaster Reduct. China 2000, 9, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mantua, N.J.; Hare, S.R. The Pacific Decadal Oscillation. J. Oceanogr. 2002, 58, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.L.; Yamashita, T.; Mishima, T. Multi-decadal variations of ENSO, the Pacific Decadal Oscillation and tropical cyclones in the Western North Pacific. Prog. Oceanogr. 2012, 105, 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, P.J.; Holland, G.J.; Curry, J.A.; Chang, H.R. Changes in tropical cyclone number, duration, and intensity in a warming environment. Science 2006, 309, 1844–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X. Recent progress in flood management in China. Irrig. Drain. 2006, 55, S75–S82. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Tian, X. The basic system of natural disaster emergency management in China. Comp. Econ. Soc. Syst. 2006, 5, 28–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. The basic structure and challenges of China’s natural disaster management system. Adm. Reform. 2010, 10, 22–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Liao, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Ye, B.; Wang, W. Emergency response to and preparedness for extreme weather events and environmental changes in China. Asia-Pac. J. Public Health 2014, 110, 19264–19270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, R. The Natural Disaster Relief Emergency Response System Accelerates during “The Tenth Five Year Project”. Available online: http://news.xinhuanet.com/politics/2006-01/12/content_4044299.htm (accessed on 12 September 2016).
- Zhang, J.; Norio, O.; Hirokazu, T. Integrated natural disaster risk management: Comprehensive and integrated model and Chinese strategy choice. J. Nat. Disaster 2006, 15, 31–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jonkman, S.N. Global perspectives on loss of human life caused by floods. Nat. Hazards 2005, 34, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Xiao, Z. Characteristics of tropical cyclones in China and their impacts analysis. Nat. Hazards 2010, 54, 827–837. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Zhuo, L.; Zheng, J.; Ge, Y.; Gu, Z.; Tian, Y. Assessment of the casualty risk of multiple meteorological hazards in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Li, W. Formation, distribution and risk control of landslides in China. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2011, 3, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.C.; Lee, C.F.; Ngai, Y.Y. Landslide risk assessment and management: An overview. Eng. Geol. 2002, 64, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meusburger, K.; Alewell, C. Impacts of anthropogenic and environmental factors on the occurrence of shallow landslides in an alpine catchment (Urseren Valley, Switzerland). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 8, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruschi, V.M.; Bonachea, J.; Remondo, J.; Gómez-Arozamena, J.; Rivas, V.; Barbieri, M.; Capocchi, S.; Soldati, M.; Cendrero, A. Land management versus natural factors in land instability: Some examples in Northern Spain. Environ. Manag. 2013, 52, 398–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsli, F.; Atasoy, M.; Yalcin, A.; Reis, S.; Demir, O.; Gokceoglu, C. Effects of land-use changes on landslides in a landslide-prone area (Ardesen, Rize, NE Turkey). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 156, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanacker, V.; Vanderschaeghe, M.; Govers, G.; Willems, E.; Poesen, J.; Deckers, J.; De Bievre, B. Linking hydrological, infinite slope stability and land-use change models through GIS for assessing the impact of deforestation on slope stability in high Andean watersheds. Geomorphology 2003, 52, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, V.M.; Bonachea, J.; Remondo, J.; Gómez-Arozamena, J.; Rivas, V.; Méndez, G.; Naredo, J.M.; Cendrero, A. Analysis of geomorphic systems’ response to natural and human drivers in northern Spain: Implications for global geomorphic change. Geomorphology 2013, 196, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichenbach, P.; Busca, C.; Mondini, A.C.; Rossi, M. The influence of land use change on landslide susceptibility zonation: The Briga catchment test site (Messina, Italy). Environ. Manag. 2014, 54, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T. Landslide disasters and human responses in China. Mt. Res. Dev. 1994, 14, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. Danger assessment of collapses, landslides and debris flows of geological hazards in China. J. Geomech. 2004, 10, 27–32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.; Zhao, N.; Sun, H.; Ye, L.; Zhai, J. Changes and relationships of climatic and hydrological droughts in the Jialing River Basin, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yan, D.; Wang, J.; Weng, B.; Wang, G.; Yang, M. Drought mitigation ability index and application based on balance between water supply and demand. Water 2015, 7, 1792–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maybank, J.; Bonsai, B.; Jones, K.; Lawford, R.; O’brien, E.G.; Ripley, E.A.; Wheaton, E. Drought as a natural disaster. Atmos. Ocean 1995, 33, 195–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Gimeno, L.; Nieto, R.; Morán-Tejeda, E.; Lorenzo-Lacruz, J.; Beguería, S.; Azorin-Molina, C. A multiscalar global evaluation of the impact of ENSO on droughts. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, B.; Lü, A.; Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, M. Drought hazard assessment and spatial characteristics analysis in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagman, G.; Beer, H.; Bendz, M.; Wijkman, A. Prevention Better than Cure. Report on Human and Environmental Disasters in the Third World, 2nd ed.; Swedish Red Cross: Stockholm, Sweden, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhite, D.A.; Svoboda, M.D.; Hayes, M.J. Understanding the complex impacts of drought: A key to enhancing drought mitigation and preparedness. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Disasters | Frequency | Life loss | Damages | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deaths | Mortality | CPIAD | TD/GDP | ||||||||||||
| tau | p | Sen | tau | p | Sen | tau | p | Sen * | tau | p | Sen ** | tau | p | Sen *** | |
| Integrated | 0.594 | <0.001 | 0.57 | −0.237 | 0.068 | −32.12 | −0.313 | 0.017 | 0.03 | 0.039 | 0.775 | 133.98 | −0.338 | 0.009 | −0.27 |
| Floods | 0.507 | <0.001 | 0.30 | −0.154 | 0.239 | −17.00 | −0.206 | 0.126 | −0.02 | −0.025 | 0.858 | −47.21 | −0.240 | 0.066 | −0.13 |
| Landslides | 0.365 | 0.009 | 0.06 | 0.056 | 0.681 | 0.65 | 0.035 | 0.802 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Storms | 0.289 | 0.032 | 0.14 | −0.338 | 0.009 | −11.67 | −0.406 | 0.003 | −0.01 | 0.078 | 0.556 | 43.37 | −0.160 | 0.224 | −0.05 |
| Disasters | NumberAP | 1985–1989 | 1990–1994 | 1995–1999 | 2000–2004 | 2005–2009 | 2010–2014 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Es(%) | Es(%) | Es(%) | Es(%) | Es(%) | Es(%) | Es(%) | ||
| Floods | 1 | 13(59.1) | 10(45.5) | 9(37.5) | 26(61.9) | 36(62.1) | 11(22.4) | 105(48.6) |
| 2–5 | 7(31.8) | 7(31.8) | 9(37.5) | 11(26.2) | 17(29.3) | 24(49.0) | 75(34.7) | |
| 6–9 | 1(4.5) | 3(13.6) | 3(12.5) | 2(4.8) | 3(5.2) | 8(16.3) | 20(9.3) | |
| 10~ | 0(0) | 0(0) | 2(8.3) | 2(4.8) | 1(1.7) | 2(4.1) | 7(3.2) | |
| Uncertain | 1(4.5) | 1(4.5) | 1(4.2) | 1(2.4) | 0(0) | 4(8.2) | 8(3.7) | |
| Total | 22(100) | 22(100) | 24(100) | 42(100) | 57(100) | 49(100) | 216(100) | |
| Storms | 1 | 19(70.4) | 26(66.7) | 20(60.6) | 19(50.0) | 21(44.7) | 14(28.0) | 119(50.6) |
| 2–5 | 7(25.9) | 13(33.3) | 11(33.3) | 16(42.1) | 20(42.6) | 24(48.0) | 91(38.7) | |
| 6–9 | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 3(6.4) | 3(6.0) | 6(2.6) | |
| 10~ | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | |
| Uncertain | 1(3.7) | 1(2.6) | 2(6.1) | 3(7.9) | 3(6.4) | 9(18.0) | 19(8.1) | |
| Total | 27(100) | 40(100) | 33(100) | 38(100) | 47(100) | 50(100) | 235(100) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, W.; Liang, C.; Jiang, B.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Y. Major Natural Disasters in China, 1985–2014: Occurrence and Damages. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13111118
Han W, Liang C, Jiang B, Ma W, Zhang Y. Major Natural Disasters in China, 1985–2014: Occurrence and Damages. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2016; 13(11):1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13111118
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Weixiao, Chen Liang, Baofa Jiang, Wei Ma, and Ying Zhang. 2016. "Major Natural Disasters in China, 1985–2014: Occurrence and Damages" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 13, no. 11: 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13111118
APA StyleHan, W., Liang, C., Jiang, B., Ma, W., & Zhang, Y. (2016). Major Natural Disasters in China, 1985–2014: Occurrence and Damages. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(11), 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13111118







