Associations between Meteorological Factors and Aseptic Meningitis in Six Metropolitan Provinces of the Republic of Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
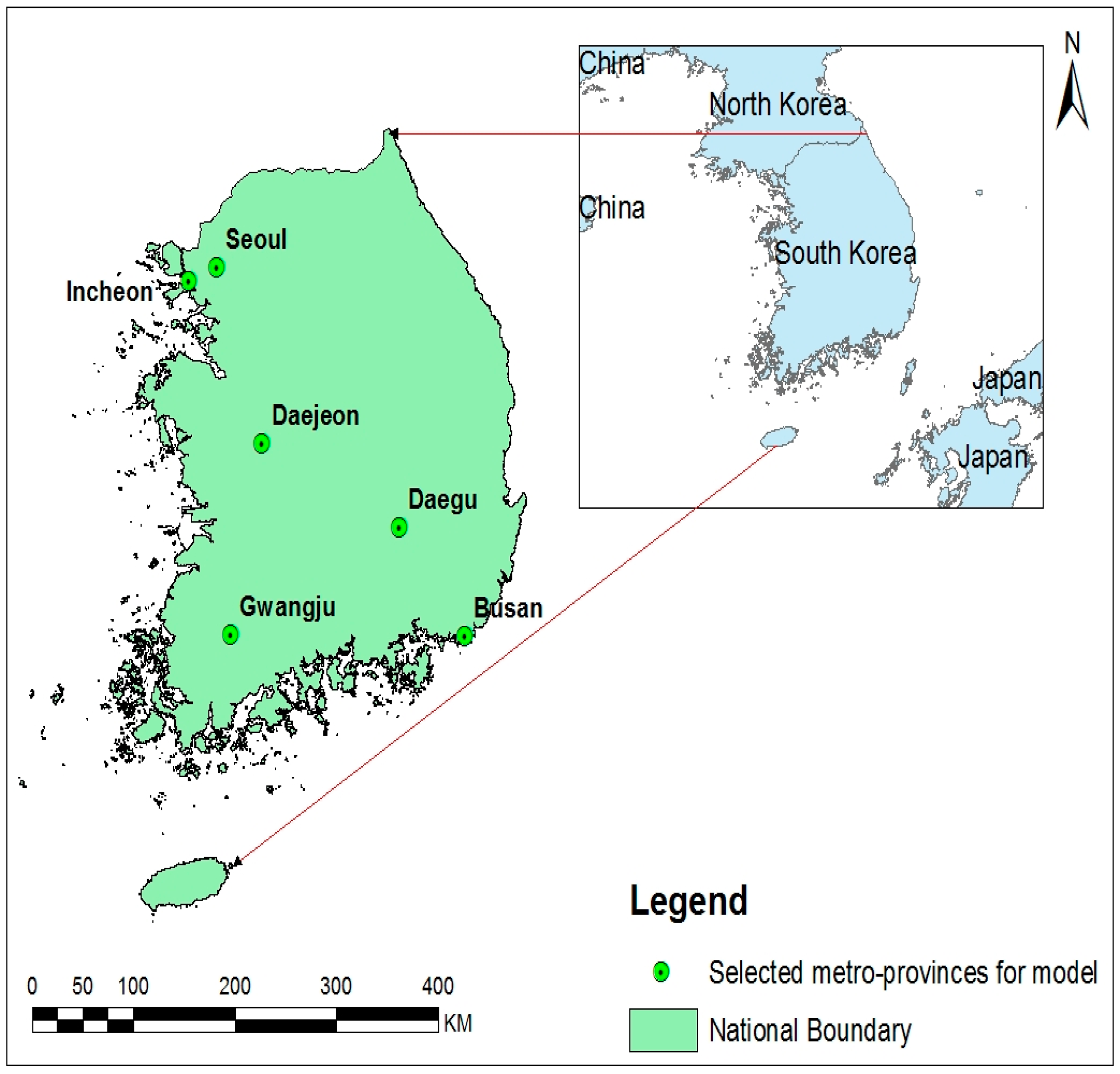
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
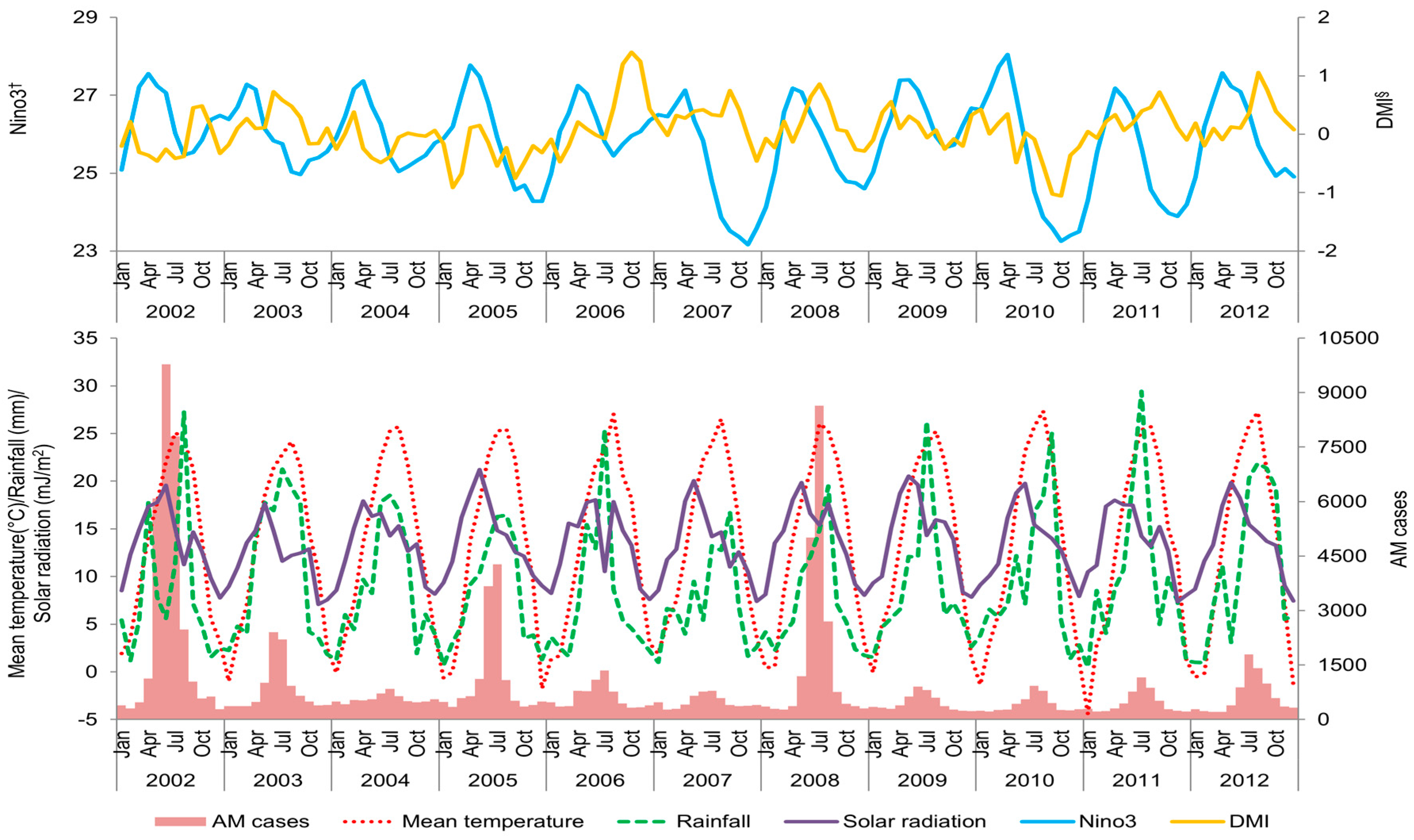
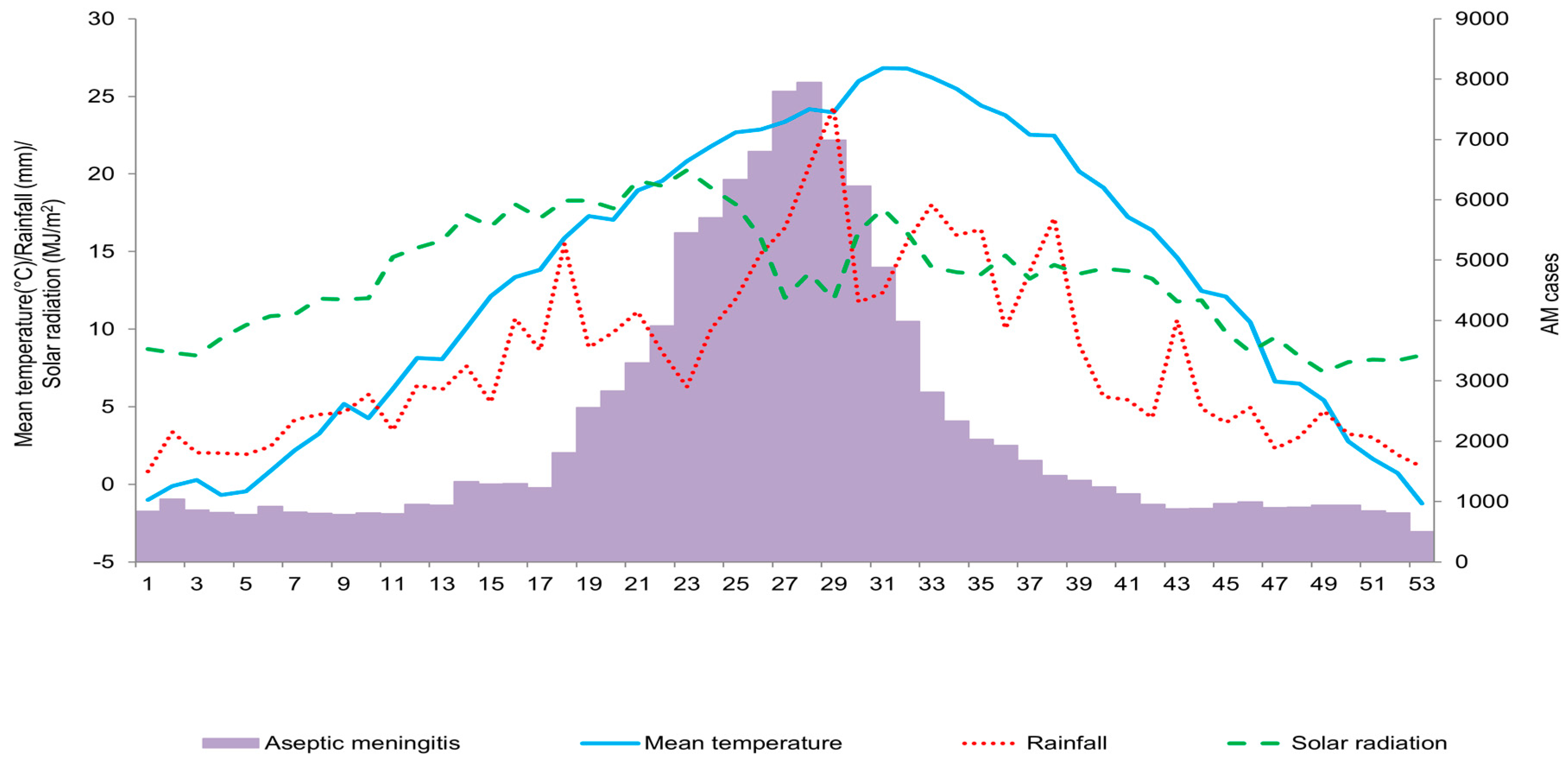
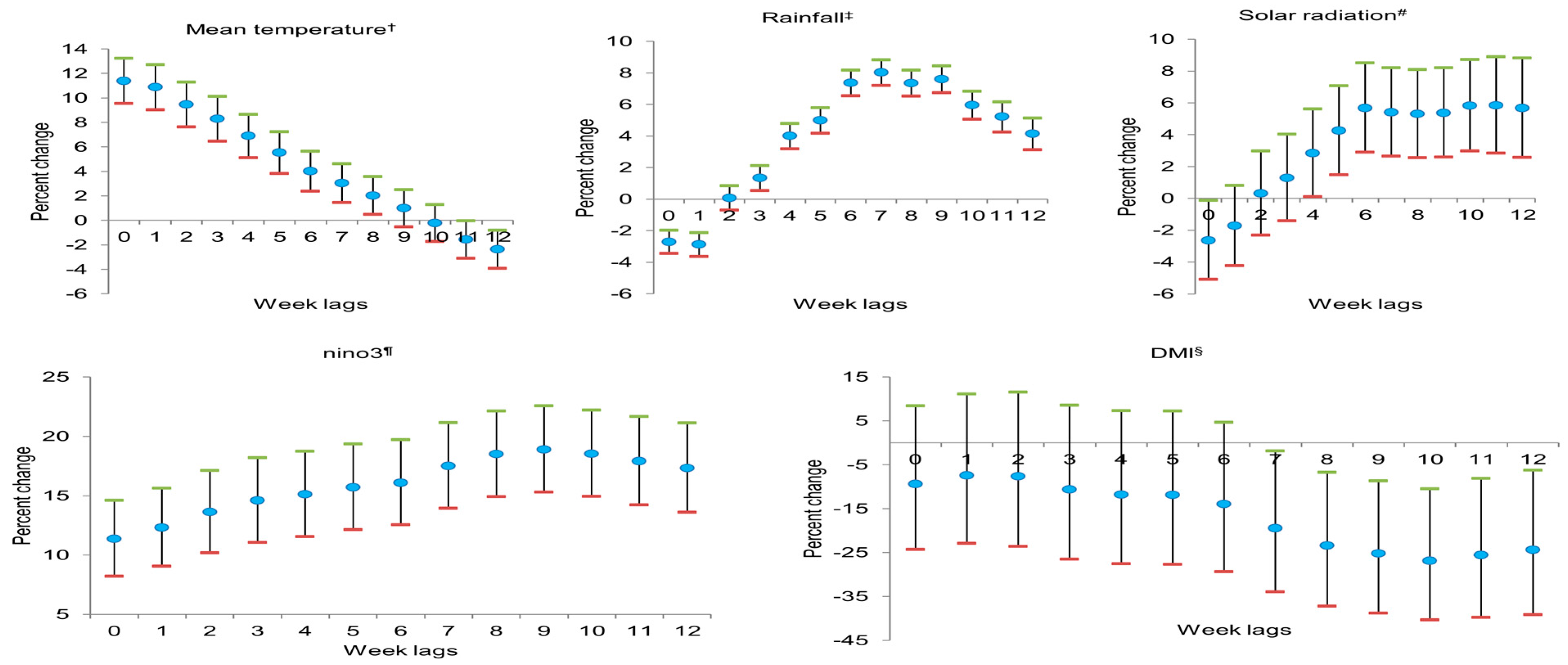
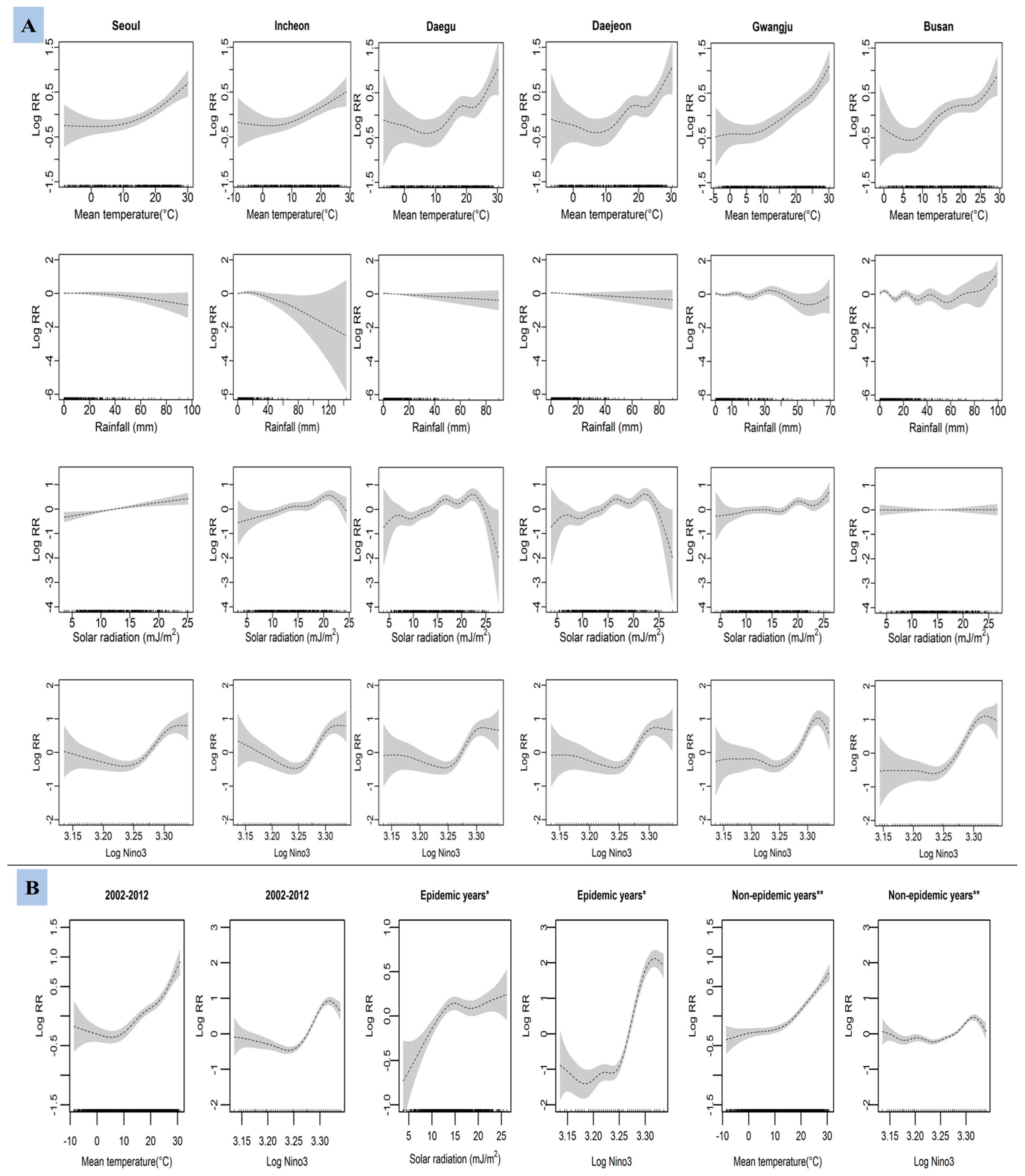
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajtar, B.; Majek, M.; Polański, Ł.; Polz-Dacewicz, M. Enteroviruses in water environment—A potential threat to public health. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2008, 15, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pöyry, T.; Kinnunen, L.; Hyypiä, T.; Brown, B.; Horsnell, C.; Hovi, T.; Stanway, G. Genetic and phylogenetic clustering of enteroviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 1699–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faustini, A.; Fano, V.; Muscillo, M.; Zaniratti, S.; Rosa, G.L.; Tribuzi, L.; Perucci, C.A. An outbreak of aseptic meningitis due to echovirus 30 associated with attending school and swimming in pools. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 10, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otatume, S.; Addy, P.A.K. Ecology of enteroviruses in tropics. Jpn. J. Microbiol. 1975, 19, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Kang, B.; Hwang, S.; Hong, J.; Kim, K.; Cheon, D.S. Epidemics of viral meningitis caused by echovirus 6 and 30 in Korea in 2008. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean, J.S.; Guo, H.R.; Chen, S.H.; Liu, C.C.; Chang, W.T.; Yang, Y.J.; Huang, M.C. The association between rainfall rate and occurrence of an enterovirus epidemic due to a contaminated well. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jee, Y.; Cheon, D.; Choi, W.; Ahn, J.; Kim, K.; Chung, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.; Noh, H.; Park, K.; et al. Updates on enterovirus surveillance in Korea. Infect. Chemother. 2004, 36, 294–303. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.H.; Lu, C.Y.; Shao, P.L.; Lee, P.I.; Kao, C.L.; Chung, M.Y.; Chang, L.Y.; Huang, L.M. Epidemiologic and clinical features of non-polio enteroviral infections in northern Taiwan in 2008. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011, 44, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Jia, L.; Yin, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, P.; Hao, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, S.; et al. An outbreak of aseptic meningitis caused by a distinct lineage of coxsackievirus B5 in China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 23, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, F.X.; Pintó, R.M.; Bosch, A. Survival of enteric viruses on environmental fomites. Appl. Environ. Microiol. 1994, 60, 3704–3710. [Google Scholar]
- Gerba, C.P.; Gramos, D.M.; Nwachuku, N. Comparative inactivation of enteroviruses and adenovirus 2 by UV light. Appl. Environ. Microiol. 2002, 68, 5167–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMichael, A.J.; Woodruff, R.E.; Hales, S. Climate change and human health: Present and future risks. Lancet 2006, 367, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsangari, H.; Paschalidou, A.K.; Kassomenos, A.P.; Vardoulakis, S.; Heaviside, C.; Georgiou, K.E.; Yamasaki, E.N. Extreme weather and air pollution effects on cardiovascular and respiratory hospital admissions in Cyprus. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 542, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J.; Samet, J.M.; Patz, J.A. Hospital admissions for heart disease: The effects of temperature and humidity. Epidemiology 2004, 15, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovats, R.S.; Bouma, M.J.; Hajat, S.; Worrall, E.; Haines, A. El Niño and human health. Lancet 2003, 362, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, N.H.; Goswami, B.N.; Vinayachandran, P.N.; Yamagata, T. A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 1999, 401, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, E.J. EI Niño-Southern Oscillation, Indian Ocean Dipole Mode, a relationship between the two phenomena, and their impact on the climate over the Korean peninsula. J. Korean Earth Sci. Soc. 2007, 28, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, A.; Jin, Y.H.; Jinno, K.; Berndtsson, R. Impacts of ENSO on monthly precipitation in South Korea and Fukuoka, Japan. In Regional Hydrological Impacts of Climatic Change-Hydroclimatic Variability, Proceedings of the Symposium S6 Held during the Seventh IAHS Scientific Assembly, Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, 3–9 April 2005; IAHS Publication: Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, 2005; Volume 296, pp. 246–254. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Zou, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Lang, L.; Hou, X.; Li, Z. Short-term effect of El Niño-Southern Oscillation on pediatric hand, foot and mouth disease in Shenzhen, China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashizume, M.; Chaves, L.F.; Faruque, A.S.G.; Yunus, M.; Streatfield, K.; Moji, K. A differential effect of Indian Ocean Dipole and El Niño on cholera dynamics in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaraket, H.; Saito, R.; Tanabe, N.; Taniguchi, K.; Suzuki, H. Association of early annual peak influenza activity with El Niño Southern Oscillation in Japan. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2008, 2, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashizume, M.; Chaves, L.F.; Minakawa, N. Indian Ocean Dipole drives malaria resurgence in East African highlands. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banu, S.; Guo, Y.; Hu, W.; Dale, P.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Mengersen, K.; Tong, S. Impacts of El Niño Southern Oscillation and Indian Ocean Dipole on dengue incidence in Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Burgner, D.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, J.H.; Lee, M.H.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, B.C. The changing epidemiology of pediatric aseptic meningitis in Daejeon, Korea from 1987 to 2003. BMC Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, H.K.; Park, S.K.; Ki, M.; Lee, K. Six year national trend of childhood aseptic meningitis incidence in Korea, 1996–2001. Korean J. Epidemiol. 2008, 30, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.; Park, K.; Jung, E.; Chung, E.; Park, J.; Choi, H.; Baek, S.; Jee, Y.; Cheon, D.; Ahn, G. Molecular and epidemiological characterization of enteroviruses isolated in Chungnam, Korea from 2005 to 2006. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Kim, J.E.; Cheon, D.S.; Chung, Y.S.; Park, J.K.; Kang, Y.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Jee, Y.M.; Yoon, J.D.; Lee, Y.J.; et al. An epidemiological study of enteroviruses as causative agents of aseptic meningitis between 1993 and 1998 in Korea. Korean J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 31, 382–389. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Meteorological Administration. Available online: http://www.data.kma.go.kr/cmmn/main.do/ (accessed on 15 July 2015).
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Climate Prediction Center. Available online: http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/ (accessed on 20 July 2015).
- Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology. Available online: http://www.jamstec.go.jp/frcgc/research/d1/iod/ (accessed on 20 July 2015).
- Statistics Korea. Available online: http://kosis.kr/eng/ (accessed on 10 May 2015).
- Jiang, F.C.; Yang, F.; Chen, L.; Jia, J.; Han, Y.L.; Hao, B.; Cao, G.W. Meteorological factors affect the hand, foot and mouth disease epidemic in Qingdao, China, 2007–2014. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 2354–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, E.; Lam, T.; Wong, C.; Chuang, S.K. Is hand, foot and mouth disease associated with meteorological parameters? Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dormann, C.F.; Elith, J.; Bacher, S.; Buchmann, C.; Carl, G.; Carré, G.; Marquéz, J.R.G.; Gruber, B.; Lafourcade, B.; Leitão, P.J.; et al. Collinearity: A review of methods to deal with it and a simulation study evaluating their performance. Ecography 2012, 36, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Generalized additive models. Stat. Sci. 1986, 1, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 May 2015).
- Chang, H.L.; Chio, C.P.; Su, H.J.; Liao, C.M.; Lin, C.Y.; Shau, W.Y.; Chi, Y.C.; Cheng, Y.T.; Chou, Y.L.; Li, C.Y.; et al. The Association between Enterovirus 71 infections and meteorological parameters in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urashima, M.; Shindo, N.; Okabe, N. Seasonal models of herpangina and hand-foot-mouth disease to simulate annual fluctuations in urban warming in Tokyo. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 56, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Goggins, W.B.; Chan, E.Y.Y. Hand, foot and mouth disease in Hong Kong: A time-series analysis on its relationship with weather. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saji, N.H.; Yamagata, T. Possible impacts of Indian Ocean dipole mode events on global climate. Clim. Res. 2003, 25, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hii, Y.L.; Rocklöv, J.; Ng, N. Short term effects of weather on hand, foot and mouth disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Provinces | Number | Incidence † | Year | Number | Incidence † |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seoul * | 50,376 | 4.6 | 2002 | 87,212 | 18.3 |
| Incheon * | 11,395 | 3.9 | 2003 | 27,564 | 5.8 |
| Daejeon * | 9722 | 5.9 | 2004 | 17,981 | 3.7 |
| Daegu * | 11,904 | 4.3 | 2005 | 37,592 | 7.8 |
| Gwangju * | 15,045 | 9.4 | 2006 | 21,125 | 4.4 |
| Ulsan | 10,562 | 8.9 | 2007 | 16,508 | 3.4 |
| Busan * | 20,939 | 5.4 | 2008 | 62,111 | 12.7 |
| Gangwon | 14,190 | 8.7 | 2009 | 18,087 | 3.7 |
| Gyeonggi | 84,805 | 7 | 2010 | 18,686 | 3.8 |
| Chungbuk | 15,373 | 9.3 | 2011 | 20,557 | 4.1 |
| Chungnam | 11,411 | 5.2 | 2012 | 23,589 | 4.7 |
| Gyeongbuk | 8925 | 3.1 | |||
| Gyeongnam | 54,686 | 15.8 | Total | 351,012 | 6.6 |
| Jeonbuk | 19,916 | 10 | |||
| Jeonnam | 10,694 | 5.3 | |||
| Jeju | 1069 | 1.8 |
| Province | Aseptic Meningitis Cases | Daily Mean Temperature (°C) | Rain Fall (mm/week) | Solar Radiation (mJ/m2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provinces | x̄ ± SD | Range | x̄ ± SD | Range | x̄ ± SD | Max | x̄ ± SD | Range |
| Seoul | 86.4 ± 139.9 | 5–1093 | 12.5 ± 10.2 | −8.5, 30.2 | 9 ± 13.3 | 97.0 | 12.2 ± 4.4 | 2.9, 25.0 |
| Incheon | 19.6 ± 34.8 | 0–262 | 11.6 ± 9.8 | −8.6, 28.8 | 8 ± 12.8 | 143.8 | 12.8 ± 4.7 | 3.2, 24.0 |
| Daegu | 20.4 ± 50.3 | 0–518 | 14.3 ± 9.4 | −3.2, 30.9 | 7.0 ± 9.6 | 80.8 | 13.6 ± 4.5 | 4.0, 25.0 |
| Daejeon | 16.7 ± 34.4 | 0–318 | 12.8 ± 9.8 | −6.8, 30.4 | 8.1 ± 10.8 | 89.9 | 13.7 ± 4.8 | 2.3, 28.0 |
| Gwangju | 25.8 ± 41.5 | 0–270 | 13.9 ± 9.3 | −4.4, 30.2 | 8.3 ± 11.2 | 69.5 | 13.8 ± 4.7 | 4.0, 26.0 |
| Busan | 35.9 ± 69.2 | 0–641 | 14.6 ± 8 | −1.7, 29.4 | 11.4 ± 15.2 | 99.5 | 14.2 ± 4.5 | 3.7, 27.0 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joshi, Y.P.; Kim, E.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Cheong, H.-K. Associations between Meteorological Factors and Aseptic Meningitis in Six Metropolitan Provinces of the Republic of Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13121193
Joshi YP, Kim E-H, Kim J-H, Kim H, Cheong H-K. Associations between Meteorological Factors and Aseptic Meningitis in Six Metropolitan Provinces of the Republic of Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2016; 13(12):1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13121193
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoshi, Yadav Prasad, Eun-Hye Kim, Jong-Hun Kim, Ho Kim, and Hae-Kwan Cheong. 2016. "Associations between Meteorological Factors and Aseptic Meningitis in Six Metropolitan Provinces of the Republic of Korea" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 13, no. 12: 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13121193
APA StyleJoshi, Y. P., Kim, E.-H., Kim, J.-H., Kim, H., & Cheong, H.-K. (2016). Associations between Meteorological Factors and Aseptic Meningitis in Six Metropolitan Provinces of the Republic of Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(12), 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13121193







