The Variation Characteristic of Sulfides and VOSc in a Source Water Reservoir and Its Control Using a Water-Lifting Aerator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Water Sampling and Analysis
2.3. In Situ Release Experiment
2.4. Water Stability Index (RWCS)
2.5. Construction and Operation of Water-Lifting Aeration System
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Seasonal and Spatial Variation of Sulfides and VOSc in Reservoir Water
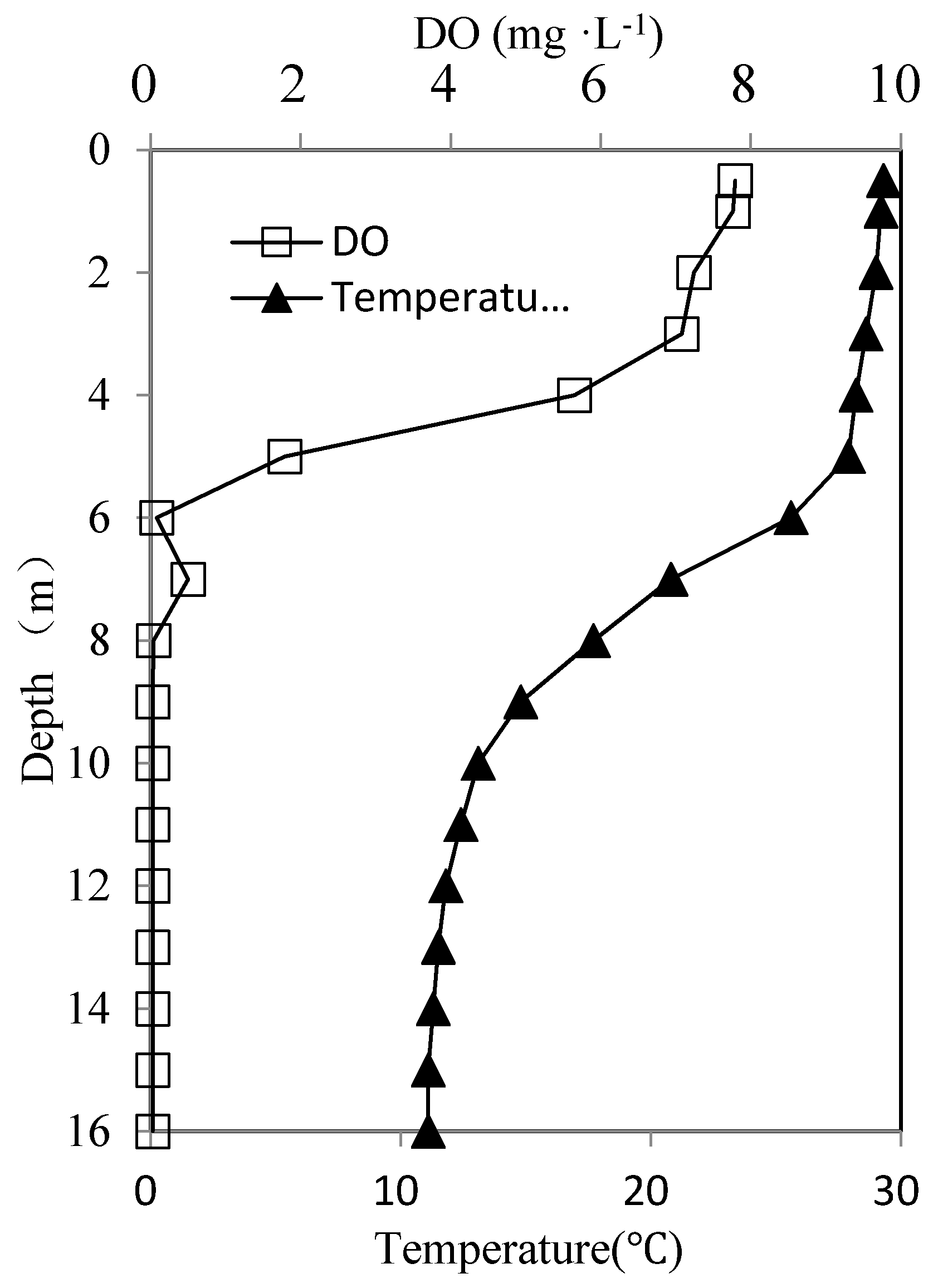
3.2. Effect of Thermal Stratification on the Concentration of Sulfides
3.3. In Situ Release of Sulfides and VOSc in Sediments
3.4. Control of Sulfides and VOSc Using Water-Lifting Aeration System
3.4.1. The Distribution of DO around WLA
3.4.2. Variation of ORP near the WLA
3.4.3. Sulfides and VOSc Distribution near the WLA
3.4.4. Principles of Water Quality Improvement Using Water-Lifting Aeration System
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VOSc | Volatile organic sulfur compounds |
| WLA | Water-lifting aerator |
| DO | Dissolved oxygen |
| ORP | Oxidation reduction potential |
| SOD | Sediments oxygen demand |
References
- Geller, W. The temperature stratification and related characteristics of chilean lakes in midsummer. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 54, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elçi, Ş. Effects of thermal stratification and mixing on reservoir water quality. Limnology 2008, 9, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.S.; Li, Z. Seasonal effects of thermal stratification on the water quality of deep reservoirs: A case study of Heihe Reservoir, Xi’an city. J. Lake Sci. 2014, 26, 698–706. [Google Scholar]
- Marc, W.B.; Theo, M.L.; Stephen, R.D.; Barry, C.M. Effects of aerobic and anaerobic conditions on P, N, Fe, Mn, and Hg accumulation in waters overlaying profundal sediments of an oligo-mesotrophic lake. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar]
- Çalışkan, A.; Elçi, Ş. Effects of selective withdrawal on hydrodynamics of a stratified reservoir. Water Res. Manag. 2008, 23, 1257–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Aramaki, T.; Hanaki, K.; Matauo, T.; Wilby, R. Lake stratification and temperature profiles simulated using downfallen cm output. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 38, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Chen, S.N.; Huang, T.L.; Ma, W.X.; Xu, J.L.; Sun, X. Vertical distribution of bacterial community diversity and water quality during the reservoir thermal stratification. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 6933–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Wu, Z.X.; Liu, M.L.; He, J.B.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Wang, M.Z.; Liu, X.H. Dissolved oxygen stratification and response to thermal structure and long-term climate change in a large and deep subtropical reservoir (Lake Qiandaohu, China). Water Res. 2015, 75, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Liu, M.L.; Shi, K.; Yu, Z.M. Seasonal-spatial distribution and long-term variation of transparency in Xin’anjiang Reservoir: Implications for reservoir management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9492–9507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, V.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Padisak, J. Cytoplast equilibrium phases during thermal stratification in a deep subtropical reservoir. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, M.; Nakano, S.; Jiao, C.; Hayakawa, K.; Tsujimura, S.; Nakajima, T.; Frenette, J.-J.; Queseda, A. Effect of cyanobacterial blooms on thermal stratification. Limnology 2000, 1, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Liu, D.; Johnson, D.M.; Yi, Z.; Huang, Y. Effects of vertical mixing on phytoplankton blooms in Xiangxi Bay of Three Gorges Reservoir: Implications for management. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marianne, H.; Storkholm, P. Sulfate reduction and sulfur cycling in lake sediments: A review. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 431–451. [Google Scholar]
- Heijs, S.K.; van Gemerden, H. Microbiological and environmental variables involved in the sulfide buffering capacity along metrification gradient in a coastal lagoon (basin d’arcachon, France). Hydrofoil 2000, 437, 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Luther, G.W., III; Church, J.R.; Scudlark, J.R.; Cosman, C. Inorganic and organic sulfur cycling in salt-marsh pore waters. Science 1986, 232, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfield, D.E. Reactive iron in marine sediments. Geochem. Cosmochem. Acta 1989, 53, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Environmental Protection Administration. Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 4th ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002; Volume 132–142. [Google Scholar]
- Aneja, V.P.; Overton, J.H. Emission survey of biogenic sulfur flux from terrestrial surface. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1981, 31, 256–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomans, B.P.; Smolders, A.; Intven, L.M.; Pol, A.; Op, D.; van Der Drift, D. Formation of dimethyl sulfide and methanethiol in anoxic freshwater sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 4741–4747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- State Environmental Protection Administration. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhu, X.H.; Dai, J.S.; Xu, H. Typical odorant component of Dongjiang River in China—A survey. China Environ. Sci. 2008, 28, 974–978. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, H.B.; Huang, T.L.; Chai, B.B. Research on applying a water-lifting aerator to inhibit the growth of algae in a source-water reservoir. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 43, 66–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.L.; Ma, Y.; Cong, H.B.; Tan, P. Application of the technology of water lifting and aeration on improving water quality in a deep canyon reservoir—A case study from Northern China. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 82, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.X.; Huang, T.L.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.Z.; Li, Y.; Zeng, K. The effects of storm runoff on water quality and the coping strategy of a deep canyon-shaped source water reservoir in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7839–7855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.H.; Cai, L.Y.; Lin, T.F.; Chang, C.-H.; Cai, L.-Y.; Lin, T.-F.; Chung, C.-L.; van der Linden, L.; Burch, M. Assessment of the impacts of climate change on the water quality of a small deep reservoir in a humid-subtropical climatic region. Water 2015, 7, 1687–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Wu, Z.; Liu, M.L.; He, J.B.; Shi, K.; Wang, M.Z.; Yu, Z.M. Thermal structure and response to long-term climatic changes in Lake Qiandaohu, a deep subtropical reservoir in China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liboriussen, L.; Søndergaard, M.; Jeppesen, E.; Thorsgaard, I.; Grünfeld, S.; Jakobsen, T.S.; Hansen, K. Effects of hypolimnetic oxygenation on water quality: Results from five Danish lakes. Hydrobiologia 2009, 625, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.P.; Huang, T.L.; Zeng, M.Z. Differences in phytoplankton dynamics and community structure between a wet year and dry year in the Zhoucun Reservoir. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mello, W.Z.; Hines, M. E. Application of static and dynamic enclosures for determining dimethyl sulfide and carbonyl sulfide exchange in sphagnum peatlands: Implications for the magnitude and direction of flux. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 1994, 99, 14601–14607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorgerloh, U.; Becker, R.; Nehls, I. Determination of volatile organic sulfur compounds in contaminated groundwater. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2008, 6, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardenicki, W. Determination of trace quantities of volatile sulfur-compounds in aqueous solutions by gas chromatography after purge-and-trap isolation and cryogenic focusing. J. Microcolumn Sep. 1995, 7, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.B.; Huang, T.L.; Chai, B.B.; Zhao, J.W. A new mixing—Oxygenating technology for water quality improvement of urban water source and its implication in a reservoir. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padisák, J.; Scheffler, W.; Kasprzak, P.; Koschel, R.; Krienitz, L. Interannual variability in the phytoplankton composition of Lake Stechlin (1994–2000). Ergeb. Limnol. 2003, 58, 101–133. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.J. Novel Technology for Drinking Water Safety; Architecture Industry of China Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lomans, B.P.; van der Drift, C.; Pol, A.; Op den Camp, H.J. Microbial cycling of volatile organic sulfur compounds. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zopfi, J.; Ferdelman, T.G.; Fossing, H. Distribution and fate of sulfur intermediates—Sulfite, tetrathionate, thiosulfate, and elemental sulfur—In marine sediments. In Sulfur Biogeochemistry—Past and Present; Geological Society of America Special Paper; Amend, J.P., Edwards, K., Lyons, T.W., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2004; Volume 379, pp. 97–116. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Huang, T.L.; Guo, L.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, H.H.; Zhou, S.L. Abundance and diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in the sediment of the Zhoucun drinking water reservoir in Eastern China. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 5830–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.L. Water pollution and water quality control of selected Chinese reservoir basins. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; Volume 38, pp. 279–331. [Google Scholar]







| Parameter | DO | ORP | RWCS | Sulfides |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DO | 1 | |||
| ORP | 0.66 ** | 1 | ||
| RWCS | −0.77 ** | −0.80 ** | 1 | |
| Sulfides | −0.50 * | −0.84 ** | 0.70 ** | 1 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.-C.; Huang, T.-L.; Wen, G.; Liu, F.; Qiu, X.-P.; Wang, B.-S. The Variation Characteristic of Sulfides and VOSc in a Source Water Reservoir and Its Control Using a Water-Lifting Aerator. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13040427
Shi J-C, Huang T-L, Wen G, Liu F, Qiu X-P, Wang B-S. The Variation Characteristic of Sulfides and VOSc in a Source Water Reservoir and Its Control Using a Water-Lifting Aerator. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2016; 13(4):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13040427
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Jian-Chao, Ting-Lin Huang, Gang Wen, Fei Liu, Xiao-Peng Qiu, and Bao-Shan Wang. 2016. "The Variation Characteristic of Sulfides and VOSc in a Source Water Reservoir and Its Control Using a Water-Lifting Aerator" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 13, no. 4: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13040427
APA StyleShi, J.-C., Huang, T.-L., Wen, G., Liu, F., Qiu, X.-P., & Wang, B.-S. (2016). The Variation Characteristic of Sulfides and VOSc in a Source Water Reservoir and Its Control Using a Water-Lifting Aerator. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(4), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13040427






