Phytoplankton Diversity Effects on Community Biomass and Stability along Nutrient Gradients in a Eutrophic Lake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
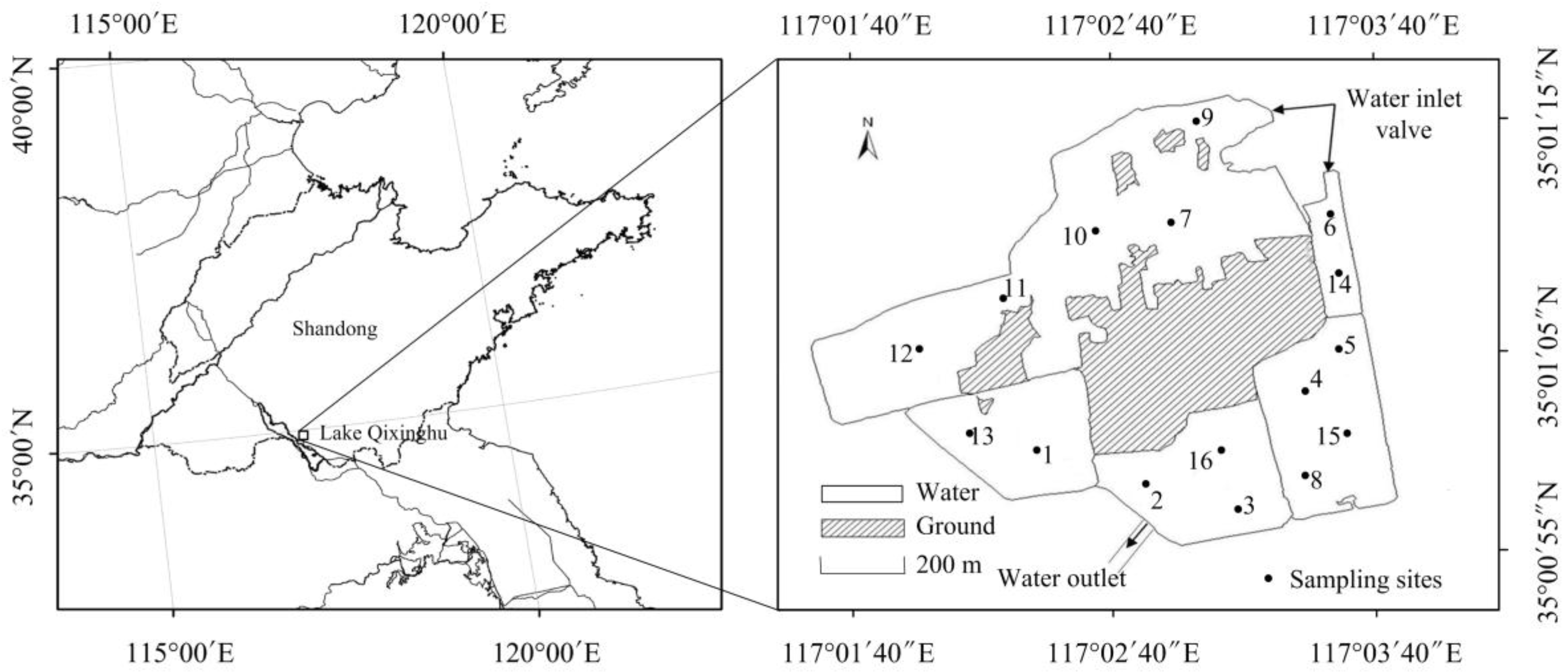
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. The Trophic States of the Lake
2.4. Sampling and Measurements
2.5. Calculation of Phytoplankton RUE and Stability
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Factors in Different Scenarios
3.2. Phytoplankton Community Compositions in Different Scenarios
3.3. Relationship Between Phytoplankton Diversity and Biomass
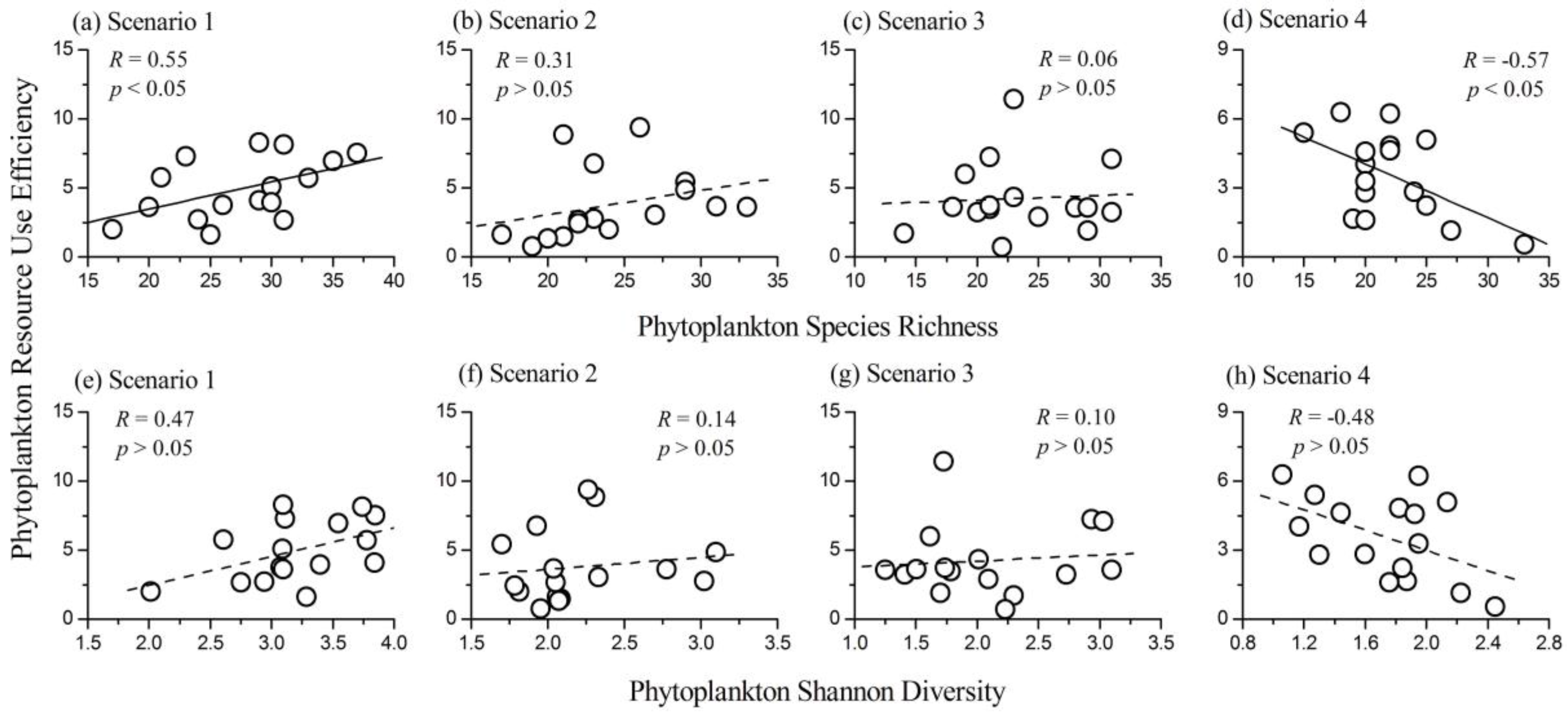
3.4. Relationship between Phytoplankton Diversity and RUE
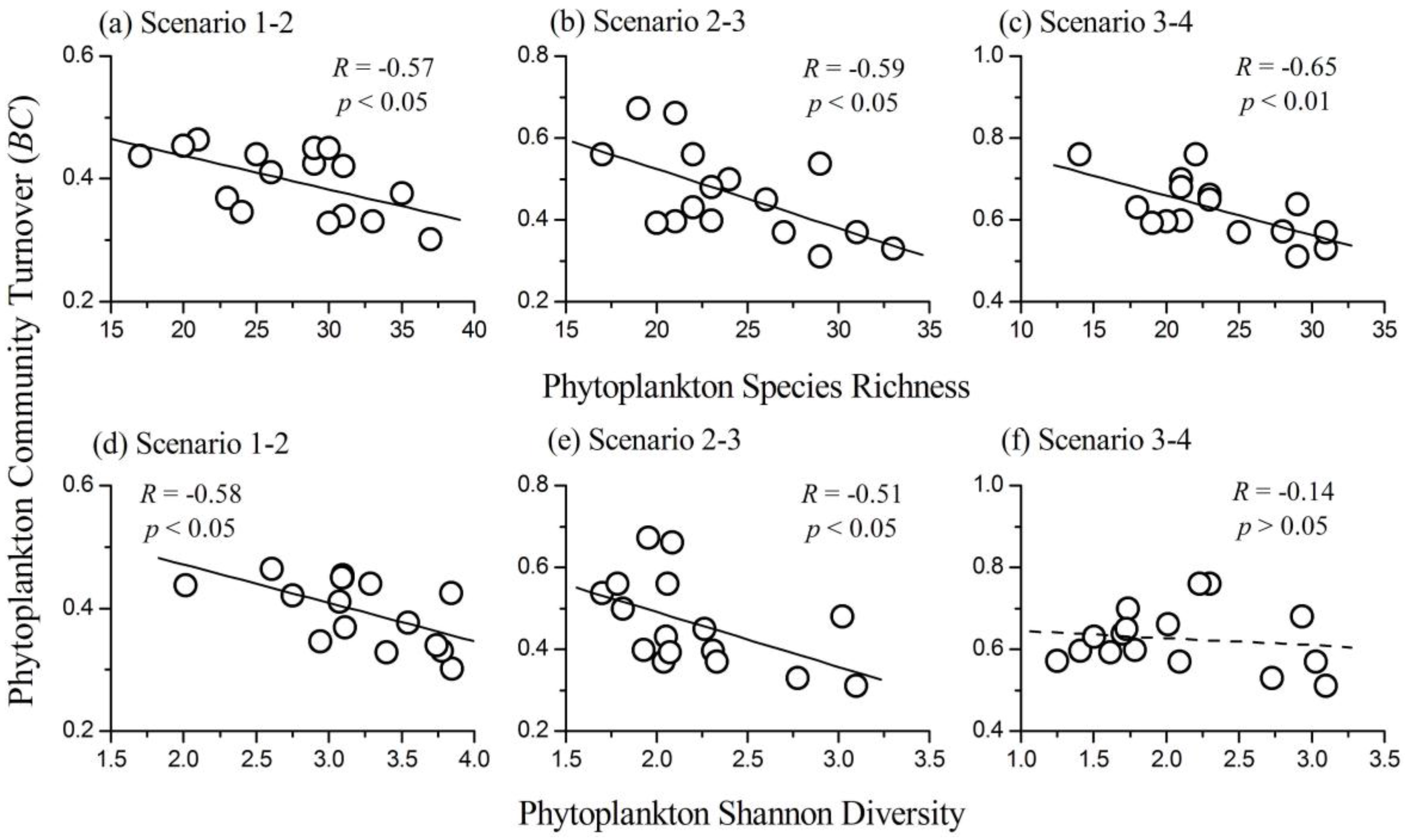
3.5. Relationship between Phytoplankton Diversity and Community Turnover
3.6. Phytoplankton Spatial Stability in Different Nutrient Gradients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
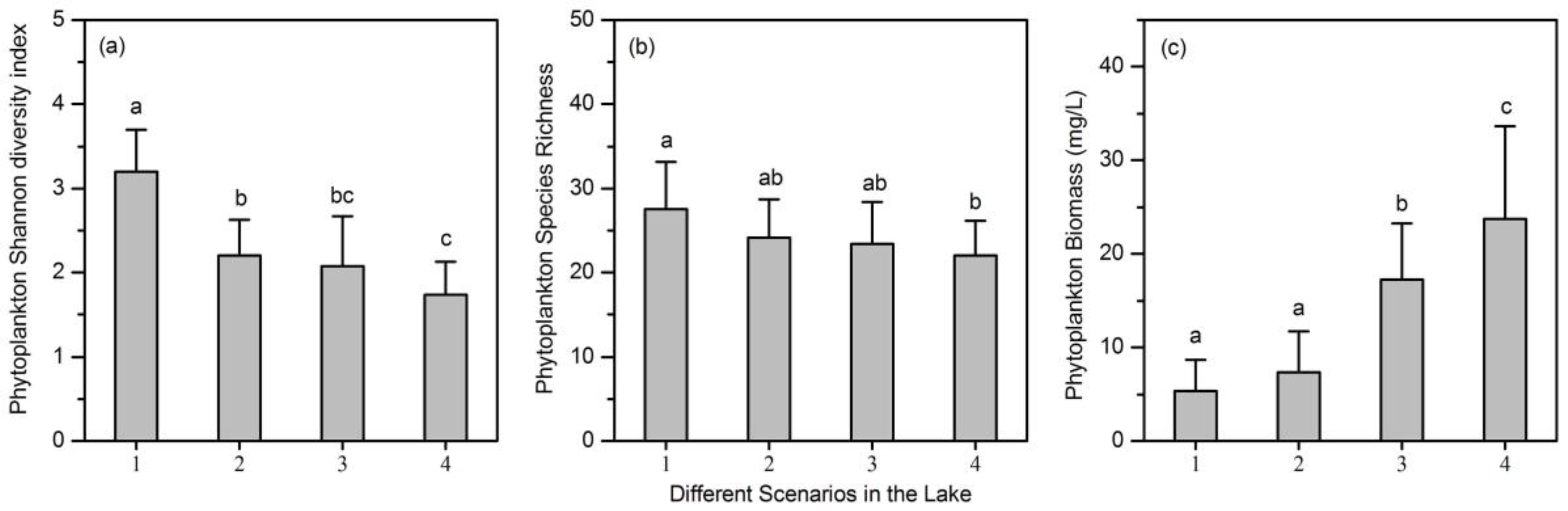
- A total of 78 phytoplankton species were identified in the lake. Phytoplankton biomass, species richness, and Shannon diversity index all showed significant differences among the nutrient gradients.
- (2)
- The relationship between phytoplankton diversity (both species richness and Shannon diversity index) and community biomass changed from positive to negative along the nutrient gradients.
- (3)
- The influence of phytoplankton species richness on RUE changed from positive to negative along the nutrient gradients. However, the influence of phytoplankton Shannon diversity index on RUE was not significant.
- (4)
- Phytoplankton diversity (both species richness and Shannon diversity index) had a negative influence on community turnover in most cases (i.e., a positive relationship between diversity and temporal stability). The underlying mechanisms changed from increasing the temporal mean to decreasing the temporal variation of biomass along the nutrient gradients.
- (5)
- The spatial stability of Cyanophyta, Chlorophyta, and total phytoplankton decreased with increasing nutrient concentrations in the lake. Eutrophication decreased the phytoplankton spatial stability mainly by increasing the temporal variance of community biomass.
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cardinale, B.J.; Duffy, J.E.; Gonzalez, A.; Hooper, D.U.; Perrings, C.; Venail, P.; Narwani, A.; Mace, G.M.; Tilman, D.; Wardle, D.A.; et al. Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature 2012, 486, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narwani, A.; Mazumder, A. Bottom-up effects of species diversity on the functioning and stability of food webs. J. Anim. Ecol. 2012, 81, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.U.; Adair, E.C.; Cardinale, B.J.; Byrnes, J.E.; Hungate, B.A.; Matulich, K.L.; Gonzalez, A.; Duffy, J.E.; Gamfeldt, L.; O’Connor, M.I. A global synthesis reveals biodiversity loss as a major driver of ecosystem change. Nature 2012, 486, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, I.D.; Okabe, K.; Parrotta, J.A.; Brockerhoff, E.; Jactel, H.; Forrester, D.I.; Taki, H. Biodiversity and ecosystem services: Lessons from nature to improve management of planted forests for REDD-plus. Biodivers. Conserv. 2014, 23, 2613–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Peter, H.; Willen, E. Shifts in phytoplankton species richness and biomass along a latitudinal gradient-consequences for relationships between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; O’Gorman, E.J.; Tian, W.; Ma, A.; Moore, J.C.; Borrett, S.R.; Woodward, G. Weighting and indirect effects identify keystone species in food webs. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giller, P.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Berninger, U.G.; Gessner, M.O.; Hawkins, S.; Inchausti, P.; Inglis, C.; Leslie, H.; Malmqvist, B.; Monaghan, M.T.; et al. Biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning: Emerging issues and their experimental test in aquatic environments. Oikos 2004, 104, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D. The ecological consequences of changes in biodiversity: A search for general principles. Ecology 1999, 80, 1455–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hector, A.; Schmid, B.; Beierkuhnlein, C.; Caldeira, M.C.; Diemer, M.; Dimitrakopoulos, P.G.; Finn, J.A.; Freitas, H.; Giller, P.S.; Good, J.; et al. Plant diversity and productivity experiments in European grasslands. Science 1999, 286, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downing, A.L.; Leibold, M.A. Ecosystem consequences of species richness and composition in pond food webs. Nature 2002, 416, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilman, D.; Wedin, D.; Knops, J. Productivity and sustainability influenced by biodiversity in grassland ecosystems. Nature 1996, 379, 718–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loreau, M.; Naeem, S.; Inchausti, P.; Bengtsson, J.; Grime, J.P.; Hector, A.; Hooper, D.U.; Huston, M.A.; Raffaelli, D.; Schmid, B.; et al. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: Current knowledge and future challenges. Science 2001, 294, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litchman, E.; Klausmeier, C.A. Trait-based community ecology of phytoplankton. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2008, 39, 615–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaderer, A.S.; Yoshiyama, K.; de Tezanos Pinto, P.; Swenson, N.G.; Klausmeier, C.A.; Litchman, E. Eco-evolutionary differences in light utilization traits and distributions of freshwater phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.C.; Wang, Y.S.; Wu, M.L.; Dong, J.D.; Wang, Y.T.; Sun, F.L.; Zhang, Y.Y. Seasonal variation of water quality and phytoplankton response patterns in Daya Bay, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 2951–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeem, S.; Li, S. Biodiversity enhances ecosystem reliability. Nature 1997, 390, 507–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, A.A.; Boeing, W.J. Biodiversity increases the productivity and stability of phytoplankton communities. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamfeldt, L.; Hillebrand, H.; Jonsson, P.R. Species richness changes across two trophic levels simultaneously affect prey and consumer biomass. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J.J.; Cardinale, B.J.; Forshay, K.J.; Ives, A.R. Effects of species diversity on community biomass production change over the course of succession. Ecology 2007, 88, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidtke, A.; Gaedke, U.; Weithoff, G. A mechanistic basis for under-yielding in phytoplankton communities. Ecology 2010, 91, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, E.K.; Cardinale, B.J. Is the relationship between algal diversity and biomass in North American lakes consistent with biodiversity experiments? Oikos 2014, 123, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallina, S.M.; Follows, M.J.; Dutkiewicz, S.; Montoya, J.M.; Cermeno, P.; Loreau, M. Global relationship between phytoplankton diversity and productivity in the ocean. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinale, B.J.; Wright, J.P.; Cadotte, M.W.; Carroll, I.T.; Hector, A.; Srivastava, D.S.; Loreau, M.; Weis, J.J. Impacts of plant diversity on biomass production increase through time because of species complementarity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18123–18128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steudel, B.; Hector, A.; Friedl, T.; Löfke, C.; Lorenz, M.; Wesche, M.; Kessler, M. Biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning change along environmental stress gradients. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elser, J.J.; Bracken, M.E.; Cleland, E.E.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Ngai, J.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Shurin, J.B.; Smith, J.E. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ptacnik, R.; Solimini, A.G.; Andersen, T.; Tamminen, T.; Brettum, P.; Lepistö, L.; Willén, E.; Rekolainen, S. Diversity predicts stability and resource use efficiency in natural phytoplankton communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5134–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striebel, M.; Behl, S.; Stibor, H. The coupling of biodiversity and productivity in phytoplankton communities: Consequences for biomass stoichiometry. Ecology 2009, 90, 2025–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filstrup, C.T.; Hillebrand, H.; Heathcote, A.J.; Harpole, W.S.; Downing, J.A. Cyanobacteria dominance influences resource use efficiency and community turnover in phytoplankton and zooplankton communities. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olli, K.; Ptacnik, R.; Andersen, T.; Trikk, O.; Klais, R.; Lehtinen, S.; Tamminen, T. Against the tide: Recent diversity increase enhances resource use in a coastal ecosystem. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ives, A.R.; Carpenter, S.R. Stability and diversity of ecosystems. Science 2007, 317, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donohue, I.; Petchey, O.L.; Montoya, J.M.; Jackson, A.L.; McNally, L.; Viana, M.; Healy, K.; Lurgi, M.; O’Connor, N.E.; Emmerson, M.C. On the dimensionality of ecological stability. Ecol. Let. 2013, 16, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yachi, S.; Loreau, M. Biodiversity and ecosystem productivity in a fluctuating environment: The insurance hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilman, D.; Reich, P.B.; Knops, J.M. Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade-long grassland experiment. Nature 2006, 441, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbell, F.I.; Polley, H.W.; Wilsey, B.J. Biodiversity, productivity and the temporal stability of productivity: Patterns and processes. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrady-Steed, J.; Harris, P.M.; Morin, P.J. Biodiversity regulates ecosystem predictability. Nature 1997, 390, 162–165. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, A.; Descamps-Julien, B. Population and community variability in randomly fluctuating environments. Oikos 2004, 106, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Song, B.; Jian, L. The soil seed banks of typical communities in wetlands convertedfrom farmlands by different restoration methods in Nansi Lake, China. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 60, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.H.; Zhao, B. Study on the trend of eutrophication after impounding in Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2007, 26, 863–867. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association (APHA); American Water Works Association (AWWA); Water Environment Federation (WEF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.R.; Shi, H. Discussion on the problems of total phosphor determination by Mo-Sb anti-spectrophotometry method. Pollut. Control Technol. 2009, 22, 106–108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Liu, D.Y.; Qian, S.B. Study on phytoplankton biomass I. Phytoplankton measurement biomass from cell volume or plasma volume. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 1999, 21, 75–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mittelbach, G.G.; Steiner, C.F.; Scheiner, S.M.; Gross, K.L.; Reynolds, H.L.; Waide, R.B.; Willig, M.R.; Dodson, S.I.; Gough, L. What is the observed relationship between species richness and productivity? Ecology 2001, 82, 2381–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, B.J.; Matulich, K.L.; Hooper, D.U.; Byrnes, J.E.; Duffy, E.; Gamfeldt, L.; Balvanera, P.; O’Connor, M.I.; Gonzalez, A. The functional role of producer diversity in ecosystems. Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 572–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borics, G.; Görgényi, J.; Grigorszky, I.; László-Nagy, Z.; Tóthmérész, B.; Krasznai, E.; Várbíró, G. The role of phytoplankton diversity metrics in shallow lake and river quality assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redfield, A.C. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. Am. Sci. 1958, 46, 205–221. [Google Scholar]
- Venail, P.A.; Alexandrou, M.A.; Oakley, T.H.; Cardinale, B.J. Shared ancestry influences community stability by altering competitive interactions: Evidence from a laboratory microcosm experiment using freshwater green algae. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20131548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, L.; Xu, X.; Huang, H. Plankton community stability and its relationship with phytoplankton species richness in Lake Nansihu, China. Water 2016, 8, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilliefors, H.W. On the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality with mean and variance unknown. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1967, 62, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust. J. Ecol 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, H.; Bennett, D.M.; Cadotte, M.W. Consequences of dominance: A review of evenness effects on local and regional ecosystem processes. Ecology 2008, 89, 1510–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapin, F.S.; Zavaleta, E.S.; Eviner, V.T.; Naylor, R.L.; Vitousek, P.M.; Reynolds, H.L.; Hooper, D.U.; Lavorel, S.; Sala, O.E.; Hobbie, S.E.; et al. Consequences of changing biodiversity. Nature 2000, 405, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, J.P.; Chrzanowski, T.H. Seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton in two warm temperate reservoirs: Association of taxonomic composition with temperature. J. Plankton Res. 2006, 28, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Scenario | WT (°C) | pH | DO (mg/L) | SD (cm) | TN (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1 | 23.6 ± 0.64 a (22.4, 24.7) | 7.90 ± 0.44 a (7.22, 8.50) | 8.69 ± 1.45 a (5.98, 10.51) | 73.1 ± 11.2 a (58.0, 94.0) | 1.03 ± 0.23 a (0.44, 1.91) | 0.20 ± 0.03 a (0.12, 0.28) |
| Scenario 2 | 25.8 ± 1.25 b (23.9, 29.1) | 8.45 ± 1.43 a (5.49, 10.93) | 6.41 ± 0.93 b (5.17, 8.28) | 42.2 ± 13.3 b (28.0, 70.0) | 2.17 ± 0.48 b (1.18, 3.70) | 0.30 ± 0.05 b (0.10, 0.67) |
| Scenario 3 | 24.6 ± 1.27 a (22.7, 26.2) | 7.82 ± 0.77 a (6.17, 9.34) | 5.92 ± 1.32 b (1.18, 11.3) | 45.1 ± 13.5 b (30.0, 80.0) | 4.84 ± 0.86 c (1.96, 7.46) | 0.47 ± 0.09 c (0.13, 1.19) |
| Scenario 4 | 24.2 ± 1.76 a (21.7, 28.2) | 8.39 ± 0.66 a (7.00, 9.32) | 4.58 ± 2.15 b (1.10, 9.93) | 45.2 ± 14.5 b (29.4, 76.0) | 7.17 ± 1.52 d (2.77, 10.3) | 0.87 ± 0.15 d (0.23, 2.05) |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, F.; Huang, H. Phytoplankton Diversity Effects on Community Biomass and Stability along Nutrient Gradients in a Eutrophic Lake. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010095
Tian W, Zhang H, Zhao L, Zhang F, Huang H. Phytoplankton Diversity Effects on Community Biomass and Stability along Nutrient Gradients in a Eutrophic Lake. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2017; 14(1):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010095
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Wang, Huayong Zhang, Lei Zhao, Feifan Zhang, and Hai Huang. 2017. "Phytoplankton Diversity Effects on Community Biomass and Stability along Nutrient Gradients in a Eutrophic Lake" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 14, no. 1: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010095
APA StyleTian, W., Zhang, H., Zhao, L., Zhang, F., & Huang, H. (2017). Phytoplankton Diversity Effects on Community Biomass and Stability along Nutrient Gradients in a Eutrophic Lake. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010095







