Attitudes and Learning through Practice Are Key to Delivering Brief Interventions for Heavy Drinking in Primary Health Care: Analyses from the ODHIN Five Country Cluster Randomized Factorial Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Implementation Strategies
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Randomization and Blinding
2.5. Sample Size
2.6. Statistical Methods
- TS = −1 for control, FR, eBI, FR + eBI; and + 1 for TS, TS + FR, TS + eBI, TS + FR + eBI; and
- FR = −1 for control, TS, eBI, TS + eBI; and + 1 for FR, FR +TS, FR + eBI, FR + TS + eBI
3. Results
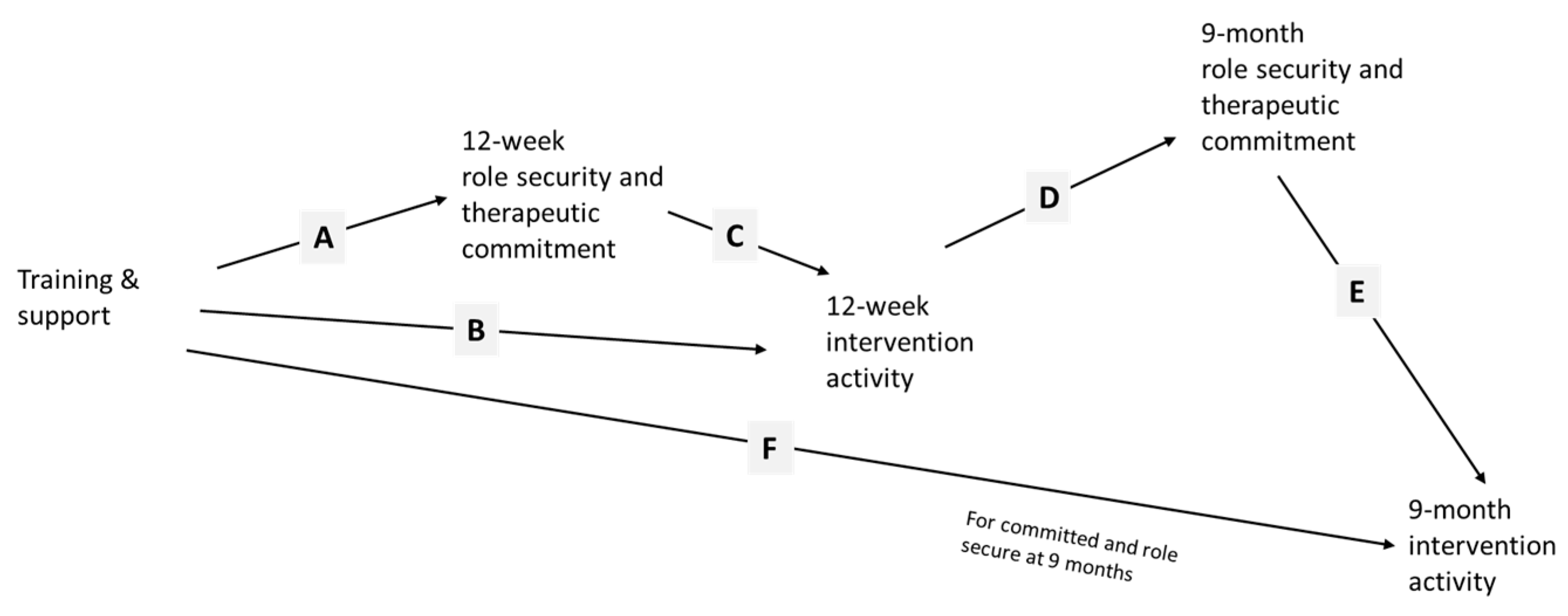
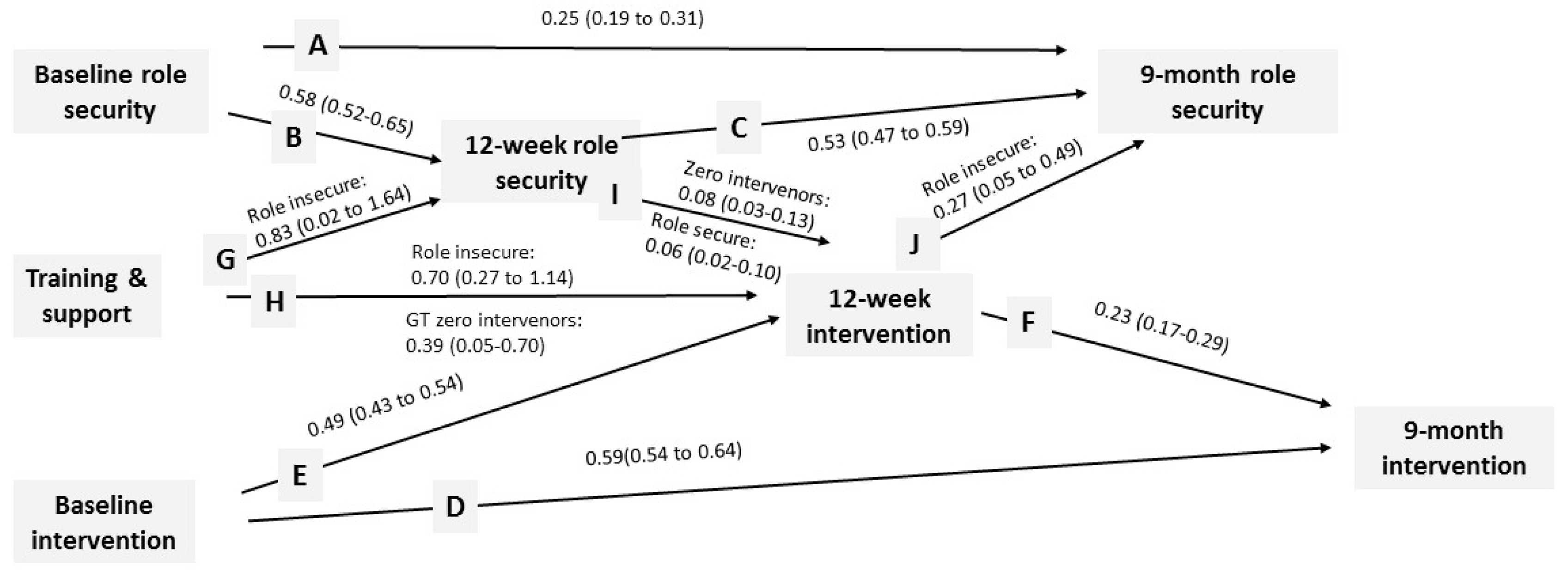
3.1. Role Security
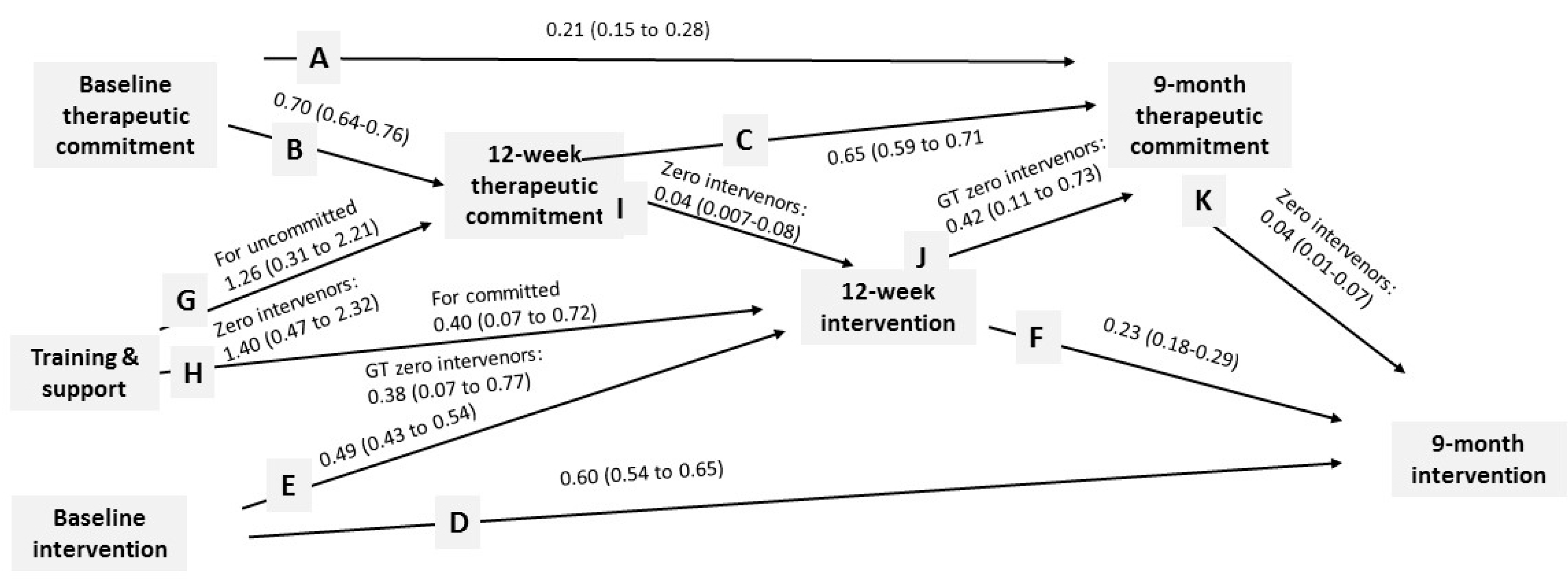
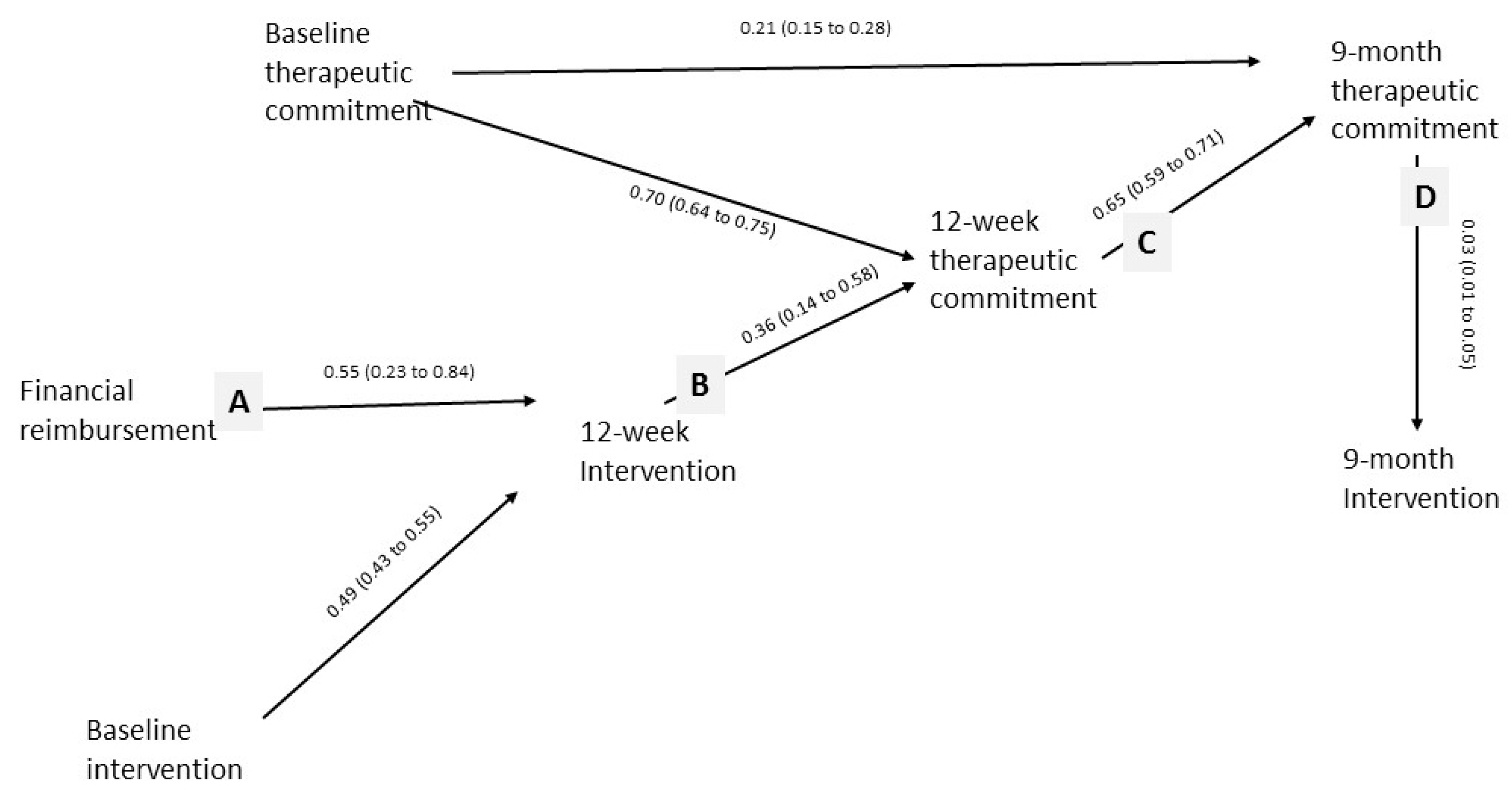
3.2. Therapeutic Commitment
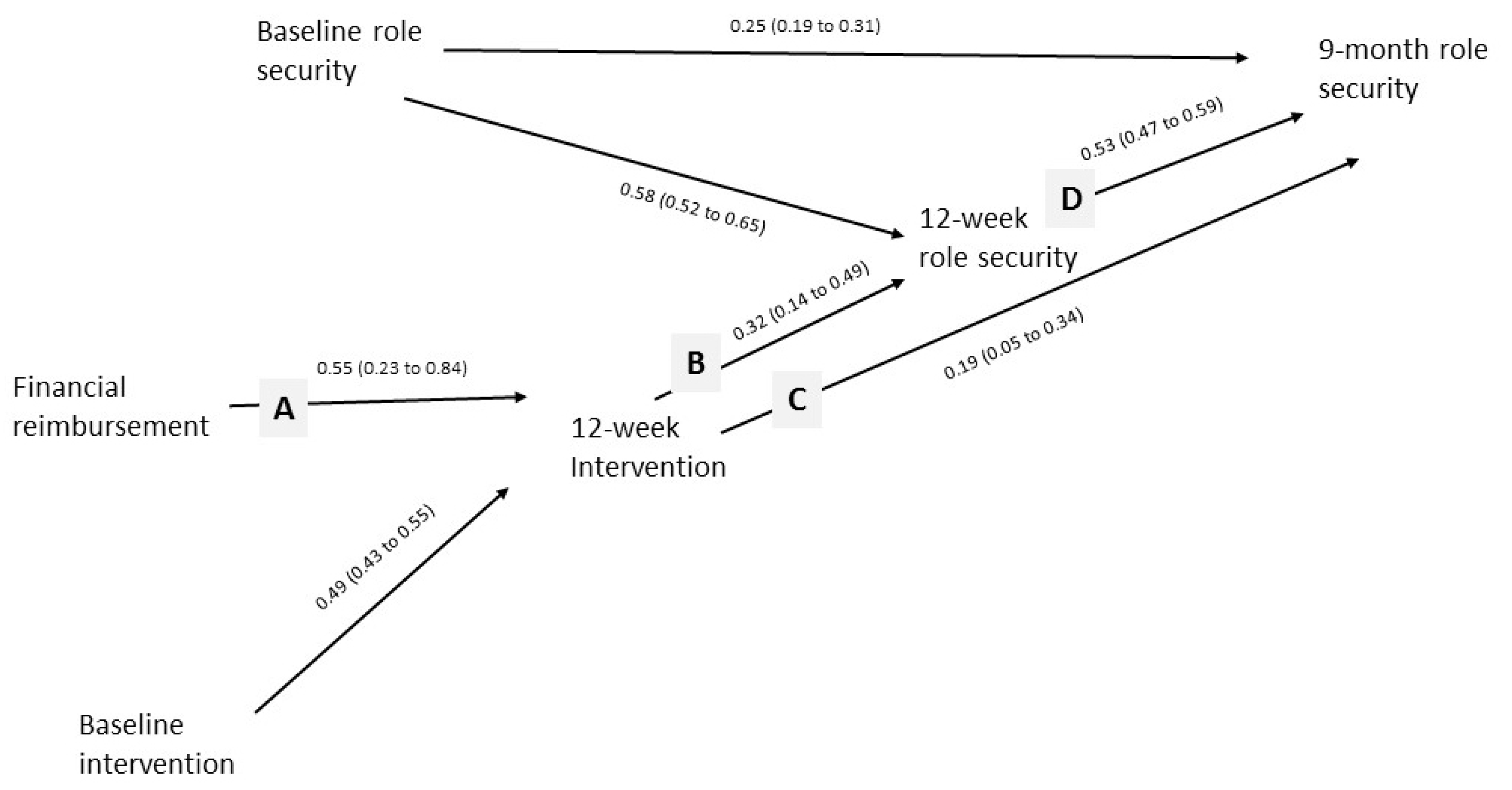
3.3. Financial Reimbursement
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thom, B.; Tellez, C. A difficult business: Detecting and managing alcohol problems in general practice. Br. J. Addict. 1986, 81, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P. Classic texts revisited: Responding to alcohol problems. Addiction 2006, 101, 750–752. [Google Scholar]
- Rapley, T.; May, C.; Kaner, E. Still a difficult business: Negotiating alcohol-related problems in general practice consultations. Soc. Sci. Med. 2006, 63, 2418–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keurhorst, M.; van de Glind, I.; Bitarello do Amaral-Sabadini, M.; Anderson, P.; Kaner, E.; Newbury-Birch, D. Determinants of successful implementation of screening and advice for hazardous and harmful alcohol consumption in primary healthcare: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Addiction 2015, 110, 877–900. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.; Bendsten, P.; Spak, F.; Reynolds, J.; Drummond, C.; Segura, L.; Keurhorst, M.N.; Palacio-Vieira, J.; Wojnar, M.; Parkinson, K.; et al. Improving the delivery of brief interventions for heavy drinking in primary health care: Outcome results of the ODHIN five country cluster randomized factorial trial. Addiction 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, S.; Cartwright, A.; Spratley, T.; Harwin, J. Responding to Drinking Problems; London Croom Helm: London, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.; Bennison, J.; Orford, J.; Spratley, T.; Tether, P.; Tomson, P.; Wilson, D. Alcohol—A Balanced View; Royal College of General Practitioners: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright, A.K.J. The Effect of Role Insecurity on the Therapeutic Commitment of Alcoholism Counsellors. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Psychiatry, London, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright, A.K.J. The attitudes of helping agents towards the alcoholic client: The influence of experience, support, training and self-esteem. Br. J. Addict. 1980, 75, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P. Management of alcohol problems in general practice. Br. Med. J. 1985, 296, 1873–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.; Clement, S. The AAPPQ revisited: Measurement of general practitioners’ attitudes to alcohol problems. Br. J. Addict. 1987, 82, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.; Kaner, E.; Wutzke, S.; Wensing, M.; Grol, R.; Heather, N.; Saunders, J. Attitudes and management of alcohol problems in general practice: Descriptive analysis based on findings of a WHO international collaborative survey. Alcohol Alcoholism 2003, 38, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.; Kaner, E.; Wutzke, S.; Funk, M.; Heather, N.; Wensing, M.; Grol, R.; Gual, A.; Pas, L. Attitudes and managing alcohol problems in general practice: An interaction analysis based on findings from a WHO collaborative study. Alcohol Alcoholism 2004, 39, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.; Wojnar, M.; Jakubczyk, A.; Gual, A.; Reynolds, J.; Segura, L.; Sovinova, H.; Csemy, L.; Kaner, E.; Newbury-Birch, D.; et al. Managing alcohol problems in general practice in Europe: Results from the European ODHIN Survey of general practitioners. Alcohol Alcoholism 2014, 49, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendsten, P.; Anderson, P.; Wojnar, M.; Newbury-Birch, D.; Mussener, U.; Colom, J.; Karlsson, N.; Brzozka, K.; Spak, F.; Deluca, P.; et al. Professional’s attitudes do not influence screening and brief intervention rates for hazardous and harmful drinkers: Results from ODHIN study. Alcohol Alcoholism 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keurhorst, M.; Anderson, P.; Heinen, M.; Bendtsen, P.; Baena, B.; Brzozka, K.; Colom, J.; Deluca, P.L.; Drummomd, C.; Kaner, E.; et al. Impact of primary health care providers’ initial role security and therapeutic commitment in implementing brief interventions in managing risky alcohol consumption: A cluster randomised factorial trial. Implementation Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keurhorst, M.; Anderson, P.; Spak, F.; Bendtsen, P.; Segura, L.; Colom, J.; Reynolds, J.; Drummomd, C.; Deluca, P.L.; Steenkiste, B.V.; et al. Implementing training and support, financial reimbursement, and referral to an internet-based advice program to improve the early identification of hazardous and harmful alcohol consumption in primary care (ODHIN): Study protocol for a cluster randomized factorial trial. Implementation Sci. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, D.E.; Garbutt, J.C.; Brown, J.M.; Amick, H.R.; Brownley, K.A. Screening, Behavioral Counseling, and Referral in Primary Care to Reduce Alcohol Misuse. Available online: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK99199/ (accessed on 16 April 2016).
- Adams, G.; Gulliford, M.C.; Ukoumunne, O.C.; Eldridge, S.; Chinn, S.; Campbell, M.J. Patterns of intra-cluster correlation from primary care research to inform study design and analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2004, 57, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaner, E.F.S.; Lock, C.A.; McAvoy, B.R.; Heather, N.; Gilvarry, E. A RCT of three training and support strategies to encourage implementation of screening and brief alcohol intervention by general practitioners. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 1999, 49, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaner, E.F.; Dickinson, H.O.; Beyer, F.R.; Campbell, F.; Schlesinger, C.; Heather, N.; Saunders, J.B.; Burnand, B.; Pienaar, E.D. Effectiveness of brief alcohol interventions in primary care populations. Cochrane Database Sys. Rev. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, A.; Anderson, P.; Newbury-Birch, D.; Schulte, B.; Schmidt, C.; Reimer, J.; Kaner, E. The impact of brief alcohol interventions in primary healthcare: A systematic review of reviews. Alcohol Alcoholism 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, L.; Melendez-Torres, G.J.; O’Donnell, A.; Bradle, J.; Newbuey-Birch, D.; Kaner, E.; Ashton, C. How effective are brief interventions in reducing alcohol consumption: Do the setting, practitioner group and content matter? Findings from a systematic review and metaregression analysis. BMJ 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitz, R. The best evidence for alcohol screening and brief intervention in primary care supports efficacy, at best, not effectiveness: You say tomāto, I say tomăto? That’s not all it’s about. Addiction Sci. Clin. Pract. 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapid Reponses to Effectiveness of Screening and Brief Alcohol Intervention in Primary Care (SIPS Trial): Pragmatic Cluster Randomised Controlled Trial. Available online: http://www.bmj.com/content/346/bmj.e8501/rapid-responses (accessed on 17 January 2017).
- National Institute for Health Care and Excellence. Alcohol-Use Disorders: Prevention Public health Guideline. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ph24?unlid=10621021302016101483944 (accessed on 18 January 2017).
- World Health Organization. European Action Plan to Reduce the Harmful Use of Alcohol 2012–2020. Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/disease-prevention/alcohol-use/publications/2012/european-action-plan-to-reduce-the-harmful-use-of-alcohol-20122021 (accessed on 18 January 2017).
- Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development. Tackling Harmful Alcohol Use: Economics and Public Health Policy; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kaner, E. Alcohol in the European Union: Consumption, Harm and Policy Approaches; World Health Organization: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- NHS. Quality and Outcomes Framework. Available online: http://www.nhsemployers.org/your-workforce/primary-care-contacts/general-medical-services/quality-and-outcomes-framework (accessed on 24 August 2016).
- Development of Country-Wide Strategies for Implementing Early Identification and Brief Intervention in Primary Health Care. Available online: http://www.who.int/substance_abuse/publications/identification_management_alcoholproblems_phaseiv.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2017).

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anderson, P.; Kaner, E.; Keurhorst, M.; Bendtsen, P.; Steenkiste, B.V.; Reynolds, J.; Segura, L.; Wojnar, M.; Kłoda, K.; Parkinson, K.; et al. Attitudes and Learning through Practice Are Key to Delivering Brief Interventions for Heavy Drinking in Primary Health Care: Analyses from the ODHIN Five Country Cluster Randomized Factorial Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14020121
Anderson P, Kaner E, Keurhorst M, Bendtsen P, Steenkiste BV, Reynolds J, Segura L, Wojnar M, Kłoda K, Parkinson K, et al. Attitudes and Learning through Practice Are Key to Delivering Brief Interventions for Heavy Drinking in Primary Health Care: Analyses from the ODHIN Five Country Cluster Randomized Factorial Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2017; 14(2):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14020121
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnderson, Peter, Eileen Kaner, Myrna Keurhorst, Preben Bendtsen, Ben Van Steenkiste, Jillian Reynolds, Lidia Segura, Marcin Wojnar, Karolina Kłoda, Kathryn Parkinson, and et al. 2017. "Attitudes and Learning through Practice Are Key to Delivering Brief Interventions for Heavy Drinking in Primary Health Care: Analyses from the ODHIN Five Country Cluster Randomized Factorial Trial" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 14, no. 2: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14020121
APA StyleAnderson, P., Kaner, E., Keurhorst, M., Bendtsen, P., Steenkiste, B. V., Reynolds, J., Segura, L., Wojnar, M., Kłoda, K., Parkinson, K., Drummond, C., Okulicz-Kozaryn, K., Mierzecki, A., Laurant, M., Newbury-Birch, D., & Gual, A. (2017). Attitudes and Learning through Practice Are Key to Delivering Brief Interventions for Heavy Drinking in Primary Health Care: Analyses from the ODHIN Five Country Cluster Randomized Factorial Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(2), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14020121






