Association between Fetal Adipokines and Child Behavioral Problems at Preschool Age: The Hokkaido Study on Environment and Children’s Health
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
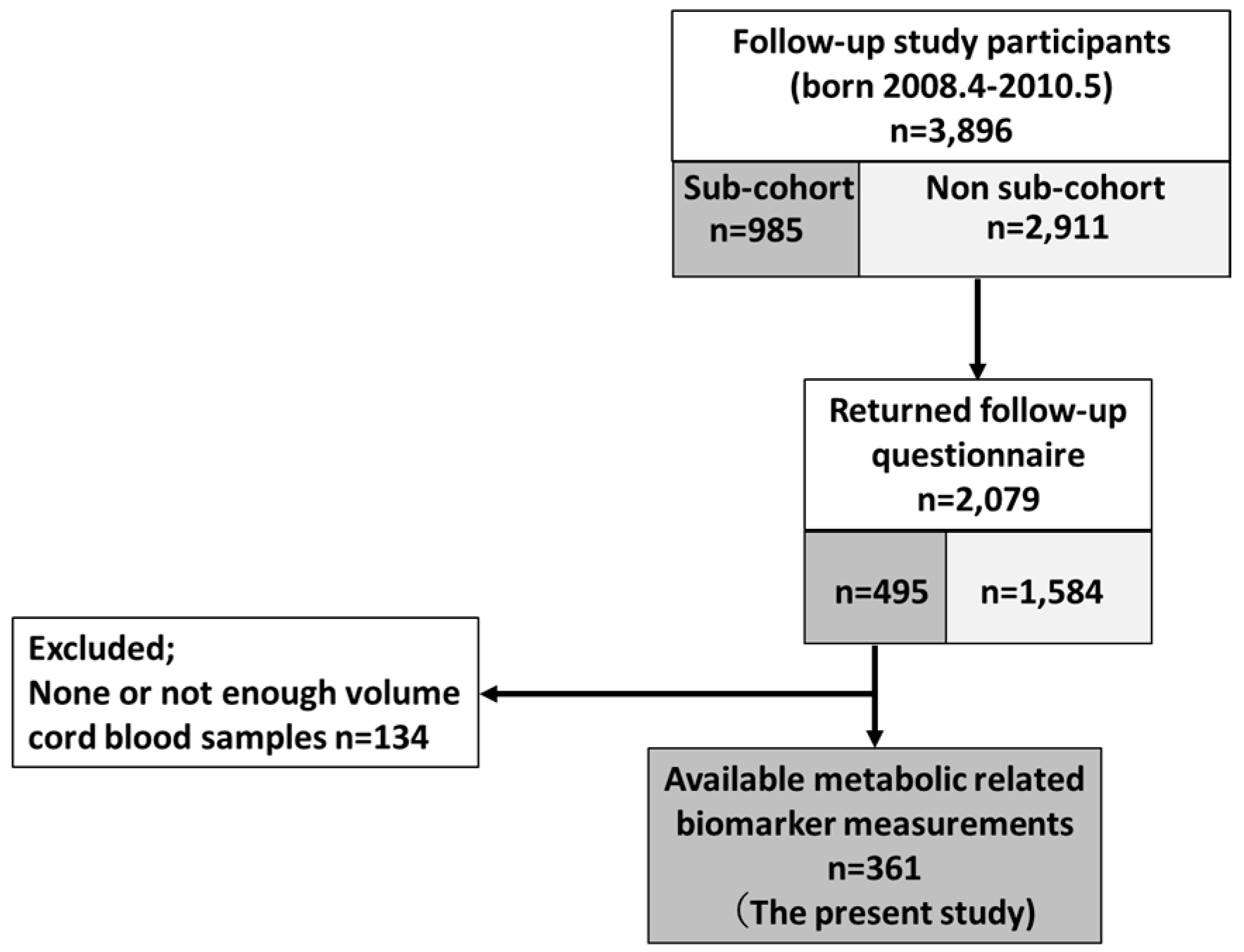
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Behavioral Problem Assessment
2.3. Adipokine Measurements
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Contu, L.; Hawkes, C.A. A Review of the Impact of Maternal Obesity on the Cognitive Function and Mental Health of the Offspring. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edlow, A.G. Maternal obesity and neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders in offspring. Prenat. Diagn. 2017, 37, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, H.M.; Christiansen, K.J.; Sullivan, E.L. The role of maternal obesity in the risk of neuropsychiatric disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mina, T.H.; Lahti, M.; Drake, A.J.; Raikkonen, K.; Minnis, H.; Denison, F.C.; Norman, J.E.; Reynolds, R.M. Prenatal exposure to very severe maternal obesity is associated with adverse neuropsychiatric outcomes in children. Psychol. Med. 2017, 47, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minatoya, M.; Itoh, S.; Araki, A.; Tamura, N.; Yamazaki, K.; Nishihara, S.; Miyashita, C.; Kishi, R. Associated factors of behavioural problems in children at preschool age: The Hokkaido study on environment and children’s health. Child Care Health Dev. 2017, 43, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, U.N. Is obesity an inflammatory condition? Nutrition 2001, 17, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.C.; Nuyt, A.M.; Delvin, E.; Fraser, W.D.; Julien, P.; Audibert, F.; Girard, I.; Shatenstein, B.; Deal, C.; Grenier, E.; et al. Maternal and fetal leptin, adiponectin levels and associations with fetal insulin sensitivity. Obesity 2013, 21, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valleau, J.C.; Sullivan, E.L. The impact of leptin on perinatal development and psychopathology. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2014, 61-62, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappas, M.; Permezel, M.; Rice, G.E. Leptin and adiponectin stimulate the release of proinflammatory cytokines and prostaglandins from human placenta and maternal adipose tissue via nuclear factor-kappaB, peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and extracellularly regulated kinase 1/2. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3334–3342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blardi, P.; de Lalla, A.; Ceccatelli, L.; Vanessa, G.; Auteri, A.; Hayek, J. Variations of plasma leptin and adiponectin levels in autistic patients. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 479, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.H.; Rocha, N.P.; Sousa, L.F.; Barbosa, I.G.; Kummer, A.; Teixeira, A.L. Changes in adipokine levels in autism spectrum disorders. Neuropsychobiology 2014, 69, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroconstanti, T.; Halmoy, A.; Haavik, J. Decreased serum levels of adiponectin in adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2014, 216, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, O.; Arslan, M.; Gungor, S.; Yuksel, T.; Selimoglu, M.A. Plasma Leptin, Adiponectin, Neuropeptide Y Levels in Drug Naive Children with ADHD. J. Atten. Disord. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, R.; Sasaki, S.; Yoshioka, E.; Yuasa, M.; Sata, F.; Saijo, Y.; Kurahashi, N.; Tamaki, J.; Endo, T.; Sengoku, K.; et al. Cohort profile: The Hokkaido study on environment and children’s health in Japan. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, R.; Kobayashi, S.; Ikeno, T.; Araki, A.; Miyashita, C.; Itoh, S.; Sasaki, S.; Okada, E.; Kobayashi, S.; Kashino, I.; et al. Ten years of progress in the Hokkaido birth cohort study on environment and children’s health: Cohort profile-updated 2013. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2013, 18, 429–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, R.; Araki, A.; Minatoya, M.; Hanaoka, T.; Miyashita, C.; Itoh, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Ait Bamai, Y.; Yamazaki, K.; Miura, R.; et al. The Hokkaido Birth Cohort Study on Environment and Children’s Health: Cohort profile-updated 2017. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2017, 22, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuishi, T.; Nagano, M.; Araki, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Iwasaki, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Nagamitsu, S.; Iizuka, C.; Ohya, T.; Shibuya, K.; et al. Scale properties of the Japanese version of the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ): A study of infant and school children in community samples. Brain Dev. 2008, 30, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, R. Psychometric properties of the strengths and difficulties questionnaire. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2001, 40, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, R. The Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire: A research note. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 1997, 38, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chittleborough, C.R.; Lawlor, D.A.; Lynch, J.W. Young maternal age and poor child development: Predictive validity from a birth cohort. Pediatrics 2011, 127, e1436–e1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.L.; Olsen, J.; Liew, Z.; Li, J.; Niclasen, J.; Obel, C. Parental Smoking during Pregnancy and ADHD in Children: The Danish National Birth Cohort. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e382–e388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delobel-Ayoub, M.; Kaminski, M.; Marret, S.; Burguet, A.; Marchand, L.; N’Guyen, S.; Matis, J.; Thiriez, G.; Fresson, J.; Arnaud, C.; et al. Behavioral Outcome at 3 Years of Age in Very Preterm Infants: The EPIPAGE Study. Pediatrics 2006, 117, 1996–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, L.M.; Byrne, S.; Thompson, A.; Ratnam, N.; Blair, E.; Bulsara, M.; Jones, T.W.; Davis, E.A. Increasing Body Mass Index z-Score Is Continuously Associated with Complications of Overweight in Children, Even in the Healthy Weight Range. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, R.H.; Houts, R.; Nader, P.R.; O’Brien, M.; Belsky, J.; Crosnoe, R. The Relationship between Body Mass Index and Behavior in Children. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, L.J.; Dezateux, C.; Hill, A. Is obesity associated with emotional and behavioural problems in children? Findings from the Millennium Cohort Study. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2011, 6, e423–e432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlboeck, G.; Romanos, M.; Tiesler, C.; Koletzko, S.; Kratzsch, J.; Thiery, J.; Bauer, C.P.; von Berg, A.; Berdel, D.; Hoffmann, B.; et al. Peer problems are associated with elevated serum leptin levels in children. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargos, A.C.; Mendonca, V.A.; Oliveira, K.S.; de Andrade, C.A.; Leite, H.R.; da Fonseca, S.F.; Vieira, E.L.; Teixeira Junior, A.L.; Lacerda, A.C. Association between obesity-related biomarkers and cognitive and motor development in infants. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 325, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley-Martin, J.; Dodds, L.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Ettinger, A.S.; Shapiro, G.D.; Fisher, M.; Morisset, A.S.; Taback, S.; Bouchard, M.F.; Monnier, P.; et al. A birth cohort study to investigate the association between prenatal phthalate and bisphenol A exposures and fetal markers of metabolic dysfunction. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, W.C.; Chen, J.L.; Lin, C.F.; Chen, Y.C.; Shih, F.C.; Chuang, C.Y. Biomonitoring of bisphenol A concentrations in maternal and umbilical cord blood in regard to birth outcomes and adipokine expression: a birth cohort study in Taiwan. Environ. Health 2011, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, J.; Wright, J.; Fairley, L.; Sattar, N.; Whincup, P.; Lawlor, D.A. Do ethnic differences in cord blood leptin levels differ by birthweight category? Findings from the Born in Bradford cohort study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, L.L.; Chan, M.H.; Lam, H.S.; Chan, P.H.; Kwok, K.M.; Chan, I.H.; Li, A.M.; Fok, T.F. Impact of fetal and childhood mercury exposure on immune status in children. Environ. Res. 2016, 144, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.F.; Wang, P.W.; Huang, L.W.; Lai, C.H.; Yang, W.; Wu, K.Y.; Lu, C.A.; Chen, H.C.; Chen, M.L. Prenatal Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A Exposures and Inflammation Are Determinants of Oxidative/Nitrative Stress: A Taiwanese Cohort Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6422–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepercq, J.; Cauzac, M.; Lahlou, N.; Timsit, J.; Girard, J.; Auwerx, J.; Hauguel-de Mouzon, S. Overexpression of placental leptin in diabetic pregnancy: A critical role for insulin. Diabetes 1998, 47, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senaris, R.; Garcia-Caballero, T.; Casabiell, X.; Gallego, R.; Castro, R.; Considine, R.V.; Dieguez, C.; Casanueva, F.F. Synthesis of leptin in human placenta. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 4501–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akerman, F.; Lei, Z.M.; Rao, C.V. Human umbilical cord and fetal membranes co-express leptin and its receptor genes. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuzaki, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Sagawa, N.; Hosoda, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Mise, H.; Nishimura, H.; Yoshimasa, Y.; Tanaka, I.; Mori, T.; et al. Nonadipose tissue production of leptin: Leptin as a novel placenta-derived hormone in humans. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassink, S.G.; de Lancey, E.; Sheslow, D.V.; Smith-Kirwin, S.M.; O’Connor, D.M.; Considine, R.V.; Opentanova, I.; Dostal, K.; Spear, M.L.; Leef, K.; et al. Placental Leptin: An Important New Growth Factor in Intrauterine and Neonatal Development? Pediatrics 1997, 100, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarandakou, A.; Protonotariou, E.; Rizos, D.; Malamitsi-Puchner, A.; Giannaki, G.; Phocas, I.; Creatsas, G. Serum leptin concentrations during the perinatal period. Am. J. Perinatol. 2000, 17, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakosta, P.; Georgiou, V.; Fthenou, E.; Papadopoulou, E.; Roumeliotaki, T.; Margioris, A.; Castanas, E.; Kampa, M.; Kogevinas, M.; Chatzi, L. Maternal Weight Status, Cord Blood Leptin and Fetal Growth: A Prospective Mother-Child Cohort Study (Rhea Study). Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2013, 27, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahima, R.S.; Bjorbaek, C.; Osei, S.; Flier, J.S. Regulation of neuronal and glial proteins by leptin: Implications for brain development. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 2755–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matochik, J.A.; London, E.D.; Yildiz, B.O.; Ozata, M.; Caglayan, S.; DePaoli, A.M.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J. Effect of leptin replacement on brain structure in genetically leptin-deficient adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 2851–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Filho, G.J.; Babikian, T.; Asarnow, R.; Delibasi, T.; Esposito, K.; Erol, H.K.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J. Leptin Replacement Improves Cognitive Development. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghardt, P.R.; Love, T.M.; Stohler, C.S.; Hodgkinson, C.; Shen, P.H.; Enoch, M.A.; Goldman, D.; Zubieta, J.K. Leptin Regulates Dopamine Responses to Sustained Stress in Humans. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 15369–15376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulton, S.; Pissios, P.; Manchon, R.P.; Stiles, L.; Frank, L.; Pothos, E.N.; Maratos-Flier, E.; Flier, J.S. Leptin Regulation of the Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Pathway. Neuron 2006, 51, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leinninger, G.M. Lateral Thinking About Leptin: A Review of Leptin Action via the Lateral Hypothalamus. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 104, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.; Pessin, J.E. Adipokines Mediate Inflammation and Insulin Resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dexter, B.C.; Rahmouni, K.; Cushman, T.; Hermann, G.M.; Ni, C.; Nopoulos, P.C.; Thedens, D.L.; Roghair, R.D. Neonatal Leptin Deficiency Reduces Frontal Cortex Volumes and Programs Adult Hyperactivity in Mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 263, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhagen, L.A.; Luijendijk, M.C.; Adan, R.A. Leptin reduces hyperactivity in an animal model for anorexia nervosa via the ventral tegmental area. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 21, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkonen, G.E.; Hermann, G.M.; Miller, R.L.; Thedens, D.L.; Nopoulos, P.C.; Wemmie, J.A.; Roghair, R.D. Neonatal leptin administration alters regional brain volumes and blocks neonatal growth restriction-induced behavioral and cardiovascular dysfunction in male mice. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 69, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennberg, A.M.; Gustafson, D.; Hagen, C.E.; Roberts, R.O.; Knopman, D.; Jack, C.; Petersen, R.C.; Mielke, M.M. Serum Adiponectin Levels, Neuroimaging, and Cognition in the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 53, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, R.C.; Chan, K.H. Potential Neuroprotective Effects of Adiponectin in Alzheimer's Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.M.; Tofail, F.; Moonah, S.N.; Scharf, R.J.; Taniuchi, M.; Ma, J.Z.; Hamadani, J.D.; Gurley, E.S.; Houpt, E.R.; Azziz-Baumgartner, E.; et al. Febrile illness and pro-inflammatory cytokines are associated with lower neurodevelopmental scores in Bangladeshi infants living in poverty. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | All (n = 361) | Normal (n = 300) | Borderline/Clinical (n = 61) | p-Value a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD or n (%) | |||||
| Parent | |||||
| Maternal age (years) | 31.9 ± 4.4 | 32.1 ± 4.3 | 30.7 ± 4.6 | 0.022 | |
| Maternal pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | 20.8 ± 2.7 | 20.8 ± 2.7 | 21.1 ± 3.1 | 0.391 | |
| <18.5 | 60 (16.6) | 47 (15.7) | 13 (21.3) | 0.439 | |
| 18.5–24.99 | 265 (73.4) | 224 (74.7) | 41 (67.2) | ||
| ≥25 | 29 (8.0) | 23 (7.7) | 6 (9.8) | ||
| Parity | Primipara | 143 (39.6) | 115 (38.3) | 28 (45.9) | 0.174 |
| Maternal education (years) | ≤12 | 141 (39.1) | 114 (38.0) | 27 (44.3) | 0.403 |
| ≥13 | 216 (59.8) | 182 (60.7) | 34 (11.3) | ||
| Alcohol consumption during pregnancy | Yes | 40 (11.1) | 35 (11.7) | 5 (8.2) | 0.448 |
| Smoking during pregnancy | Yes | 16 (4.4) | 12 (4.0) | 4 (6.6) | 0.342 |
| Paternal age (years) | 32.8 ± 6.4 | 33.1 ± 6.7 | 31.6 ± 4.7 | 0.118 | |
| Paternal education (years) | ≤12 | 137 (38.0) | 117 (39.0) | 20 (32.8) | 0.324 |
| ≥13 | 220 (60.9) | 179 (59.7) | 41 (67.2) | ||
| Annual family income at SDQ completed (million JPY) | <5 | 170 (47.1) | 137 (45.7) | 33 (54.1) | 0.154 |
| ≥5 | 175 (48.5) | 151 (50.3) | 24 (39.3) | ||
| Child | |||||
| Sex | Boys | 188 (52.1) | 149 (49.7) | 39 (63.9) | 0.042 |
| Girls | 173 (47.9) | 151 (50.3) | 22 (36.1) | ||
| Birth weight (g) | 3038 ± 358 | 3036 ± 346 | 3046 ± 402 | 0.833 | |
| Birth length (cm) | 48.9 ± 1.9 | 48.8 ± 1.8 | 49.2 ± 2.0 | 0.218 | |
| Gestational age (days) | 275 ± 8 | 275 ± 8 | 275 ± 8 | 0.528 | |
| Age at SDQ answered (months) | 66.9 ± 6.1 | 66.8 ± 6.1 | 67.3 ± 6.3 | 0.602 | |
| Adipokines | n | Median IQR (25–75th) |
|---|---|---|
| Total adiponectin (µg/mL) | 361 | 17.1 (12.8–20.8) |
| HMW adiponectin (µg/mL) | 361 | 12.8 (8.1–14.9) |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 357 | 4.9 (3.1–8.0) |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 353 | 2.45 (1.89–3.19) |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 350 | 1.06 (0.62–2.60) |
| Scales | n (%) in Borderline/Clinical | p-Value a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | Boys | Girls | ||
| TDS | 61 (16.9) | 39 (20.7) | 22 (12.7) | 0.042 |
| Conduct problems | 57 (15.8) | 36 (19.1) | 21 (12.1) | 0.068 |
| Hyperactivity/inattention | 47 (13.0) | 34 (18.1) | 13 (7.5) | 0.003 |
| Emotional symptoms | 58 (16.1) | 29 (15.4) | 29 (16.8) | 0.730 |
| Peer problems | 25 (6.9) | 12 (6.4) | 13 (7.5) | 0.672 |
| Prosocial behavior problems | 70 (19.4) | 47 (25.0) | 23 (13.3) | 0.005 |
| Adipokines | OR (95% CI) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDS | Conduct Problems | Hyperactivity/Inattention | Emotional Symptoms | Peer Problems | Prosocial Behavior Problems | |
| Total adiponectin | 0.97 (0.12–7.77) | 0.20 (0.02–1.73) | 1.11 (0.12–10.26) | 0.46 (0.06–3.75) | 2.13 (0.11–41.93) | 0.23 (0.03–1.68) |
| HMW adiponectin | 0.87 (0.19–4.05) | 0.37 (0.08–1.78) | 0.70 (0.14–3.55) | 0.49 (0.10–2.30) | 1.68 (0.19–14.77) | 0.44 (0.10–1.91) |
| Leptin | 0.44 (0.14–1.44) | 0.99 (0.30–3.24) | 0.22 (0.06–0.89) * | 0.84 (0.27–2.62) | 0.63 (0.14–2.89) | 0.40 (0.13–1.25) |
| TNF-α | 1.14 (0.26–5.03) | 0.73 (0.15–3.58) | 1.63 (0.37–7.09) | 0.53 (0.09–3.10) | 3.88 (0.83–18.13) + | 1.54 (0.41–5.82) |
| IL-6 | 0.85 (0.49–1.46) | 1.21 (0.77–1.90) | 0.91 (0.52–1.61) | 0.99 (0.60–1.64) | 1.36 (0.77–2.39) | 1.30 (0.85–1.97) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minatoya, M.; Itoh, S.; Araki, A.; Tamura, N.; Yamazaki, K.; Miyashita, C.; Kishi, R. Association between Fetal Adipokines and Child Behavioral Problems at Preschool Age: The Hokkaido Study on Environment and Children’s Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010120
Minatoya M, Itoh S, Araki A, Tamura N, Yamazaki K, Miyashita C, Kishi R. Association between Fetal Adipokines and Child Behavioral Problems at Preschool Age: The Hokkaido Study on Environment and Children’s Health. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(1):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010120
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinatoya, Machiko, Sachiko Itoh, Atsuko Araki, Naomi Tamura, Keiko Yamazaki, Chihiro Miyashita, and Reiko Kishi. 2018. "Association between Fetal Adipokines and Child Behavioral Problems at Preschool Age: The Hokkaido Study on Environment and Children’s Health" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 1: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010120
APA StyleMinatoya, M., Itoh, S., Araki, A., Tamura, N., Yamazaki, K., Miyashita, C., & Kishi, R. (2018). Association between Fetal Adipokines and Child Behavioral Problems at Preschool Age: The Hokkaido Study on Environment and Children’s Health. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(1), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010120






